Abstract
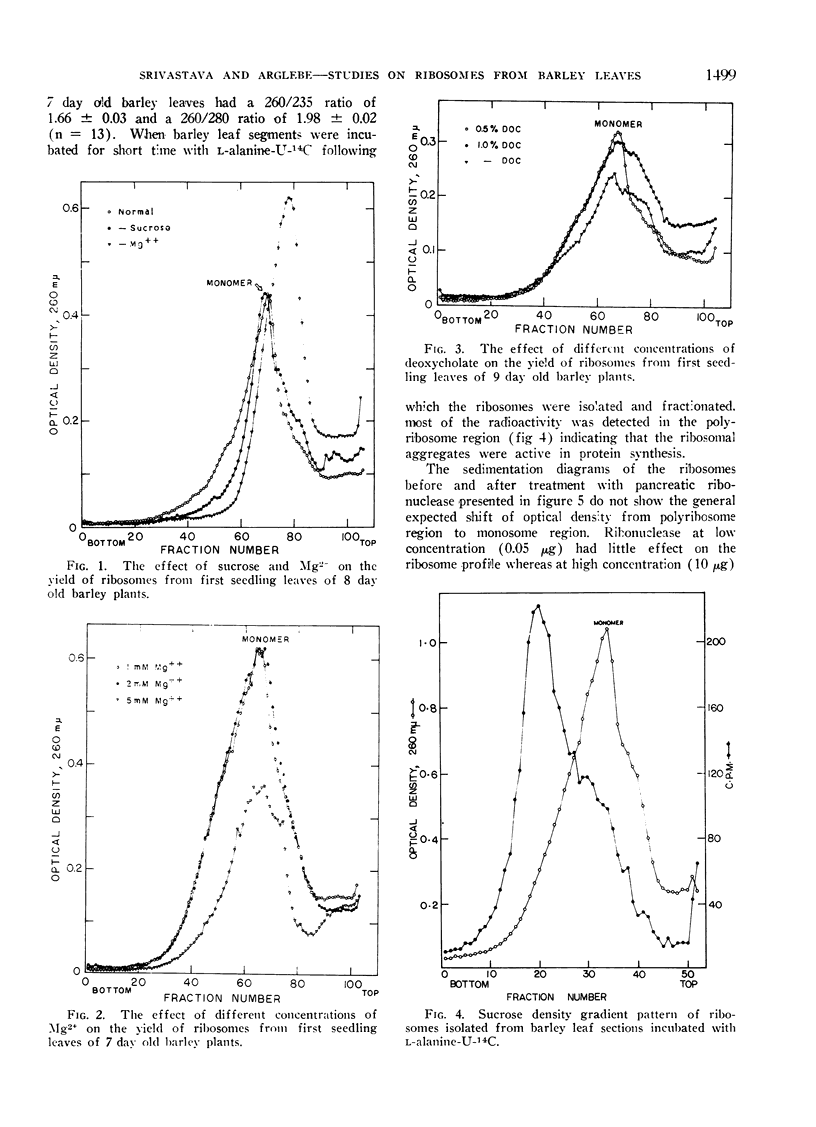
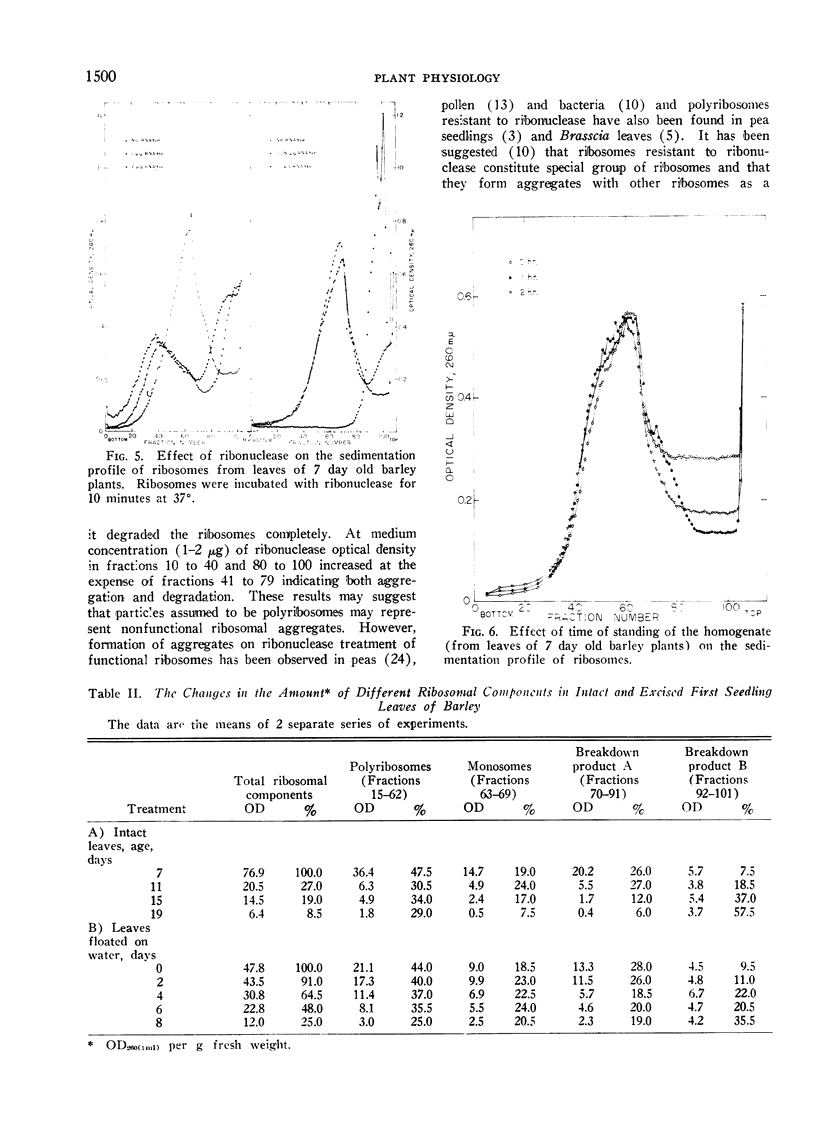
The effect of sucrose, Mg2+ and deoxycholate on the yield of ribosomes from barley leaves was determined and the changes in the amount and the composition of ribosomes during senescence of intact and excised first seedling leaves were examined.
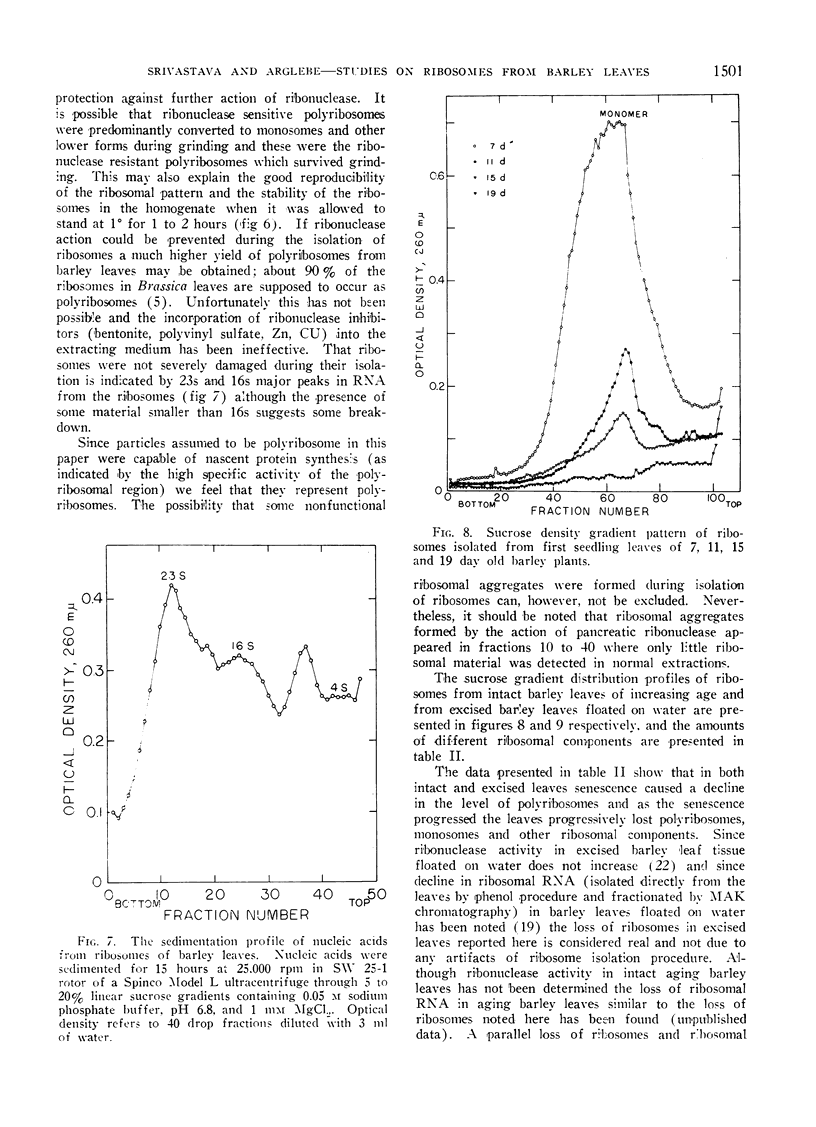
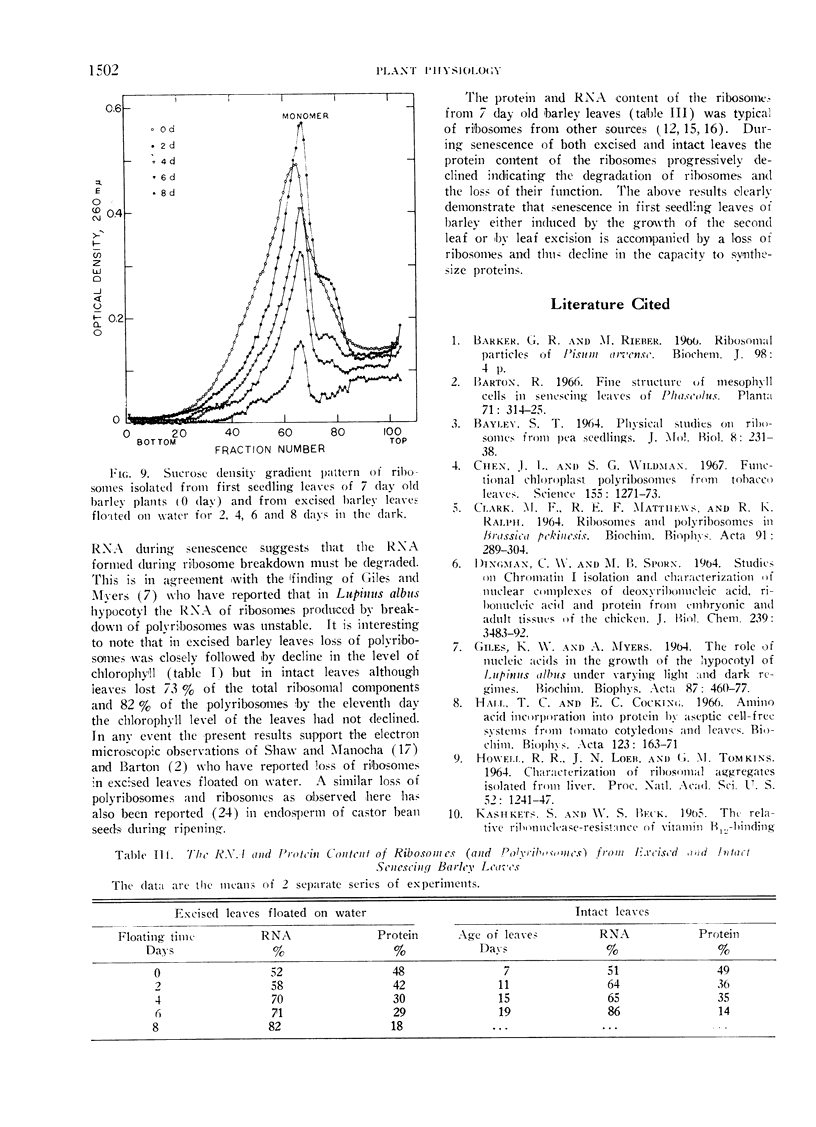
The extraction medium containing 20 mm tris-HCl, 0.25 m sucrose, 1 mm MgCl2 and 0.5% deoxycholate (pH 7.8) gave the maximum yield of polyribosomes and ribosomes. That polyribosomes were not non-specific aggregates was suggested by their capacity to synthesize nascent protein. During senescence of both intact and excised leaves polyribosomes and ribosomes were lost and the ribosomes-polyribosomes which originally contained 48% protein and 52% RNA showed substantial decline in the protein content during senescence indicating the degradation of ribosomes and the loss of their function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAYLEY S. T. PHYSICAL STUDIES ON RIBOSOMES FROM PEA SEEDLINGS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:231–238. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONNER J., TS'O P. O., VINOGRAD J. Microsomal nucleoprotein particles from pea seedlings. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4):451–466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEROBERTIS E., PELLEGRINODEIRALDI A., RODRIGUEZDELORES G., ZIEHER L. M. SYNAPTIC VESICLES FROM THE RAT HYPOTHALMUS. ISOLATION AND NOREPINEPHRINE CONTENT. Life Sci. 1965 Jan;4:193–201. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES K. W., MYERS A. THE ROLE OF NUCLEIC ACIDS IN THE GROWTH OF THE HYPOCOTYL OF LUPINUS ALBUS UNDER VARYING LIGHT AND DARK REGIMES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 22;87:460–477. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL R. R., LOEB J. N., TOMKINS G. M. CHARACTERIZATION OF RIBOSOMAL AGGREGATES ISOLATED FROM LIVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1241–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Cocking E. C. Amino acid incorporation into protein by aseptic cell-free systems from tomato cotyledons and leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 20;123(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku L. L., Romani R. J. Ribosomes from pear fruit. Science. 1966 Oct 21;154(3747):408–410. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3747.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Y., Key J. L., Bracker C. E. Association of D-RNA with Polyribosomes in the Soybean Root. Plant Physiol. 1966 Jun;41(6):976–982. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.6.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRIVASTAVA B. I. EFFECT OF KINETIN ON THE ECTEOLA CELLULOSE ELUTION PROFILE AND OTHER PROPERTIES OF RNA FROM THE EXCISED FIRST SEEDLING LEAVES OF BARLEY. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Apr;110:97–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava B. I., Ware G. The effect of kinetin on nucleic acids and nucleases of excised barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jan;40(1):62–64. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


