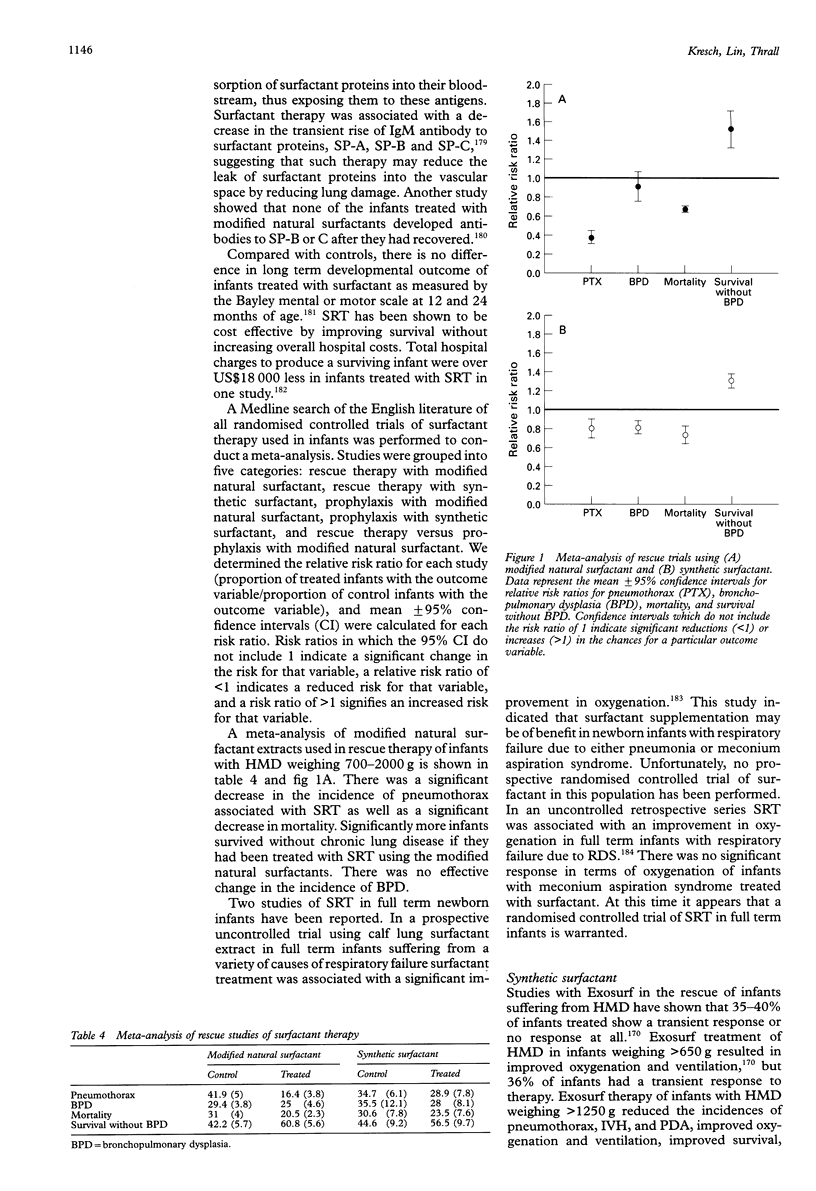
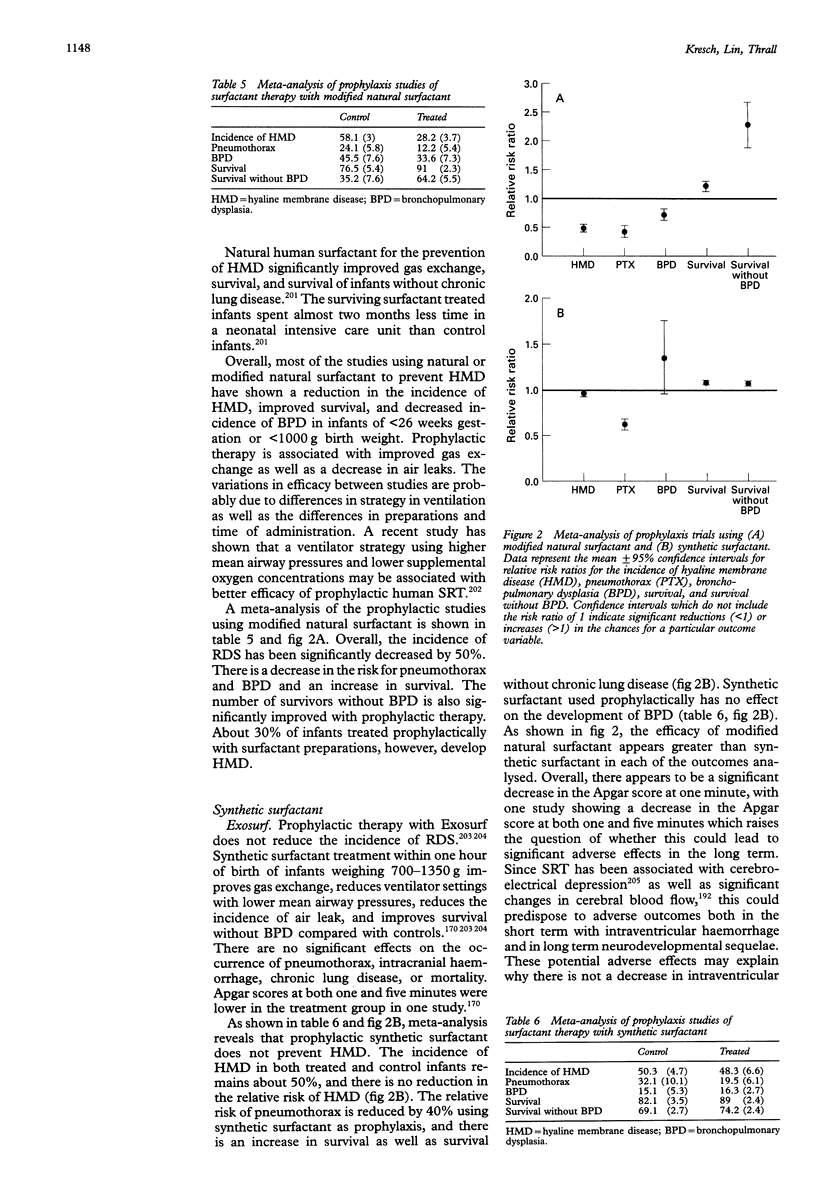
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVERY M. E., MEAD J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):517–523. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi S., Bhutani V. K., Gerdes J. S. Long-term pulmonary consequences of respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants treated with exogenous surfactant. J Pediatr. 1993 Mar;122(3):446–452. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams F. H., Towers B., Osher A. B., Ikegami M., Fujiwara T., Nozaki M. Effects of tracheal instillation of natural surfactant in premature lambs. I. Clinical and autopsy findings. Pediatr Res. 1978 Aug;12(8):841–848. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197808000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams F. H., Towers B., Osher A. B., Ikegami M., Fujiwara T., Nozaki M. Effects of tracheal instillation of natural surfactant in premature lambs. I. Clinical and autopsy findings. Pediatr Res. 1978 Aug;12(8):841–848. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197808000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon S., Grigg J., Silverman M. Pulmonary inflammatory cells in ventilated preterm infants: effect of surfactant treatment. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Jul;69(1 Spec No):44–48. doi: 10.1136/adc.69.1_spec_no.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auten R. L., Notter R. H., Kendig J. W., Davis J. M., Shapiro D. L. Surfactant treatment of full-term newborns with respiratory failure. Pediatrics. 1991 Jan;87(1):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auten R. L., Watkins R. H., Shapiro D. L., Horowitz S. Surfactant apoprotein A (SP-A) is synthesized in airway cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Nov;3(5):491–496. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.5.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Ertsey R., Gonzales L. K., Liley H. G., Williams M. C. Isolation and characterization of differentiated alveolar type II cells from fetal human lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 4;883(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers M. F., Wali A., Eckenhoff M. F., Feinstein S. I., Fisher J. H., Fisher A. B. An antibody with specificity for surfactant protein C precursors: identification of pro-SP-C in rat lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Oct;7(4):368–378. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.4.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggren P., Lachmann B., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Robertson B. Gas exchange and lung morphology after surfactant replacement in experimental adult respiratory distress syndrome induced by repeated lung lavage. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1986 May;30(4):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1986.tb02423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermel M. S., McBride J. T., Notter R. H. Lavaged excised rat lungs as a model of surfactant deficiency. Lung. 1984;162(2):99–113. doi: 10.1007/BF02715636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D., Ikegami M., Jobe A. Respiratory distress and surfactant inhibition following vagotomy in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Nov;61(5):1741–1748. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.5.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose C., Corbet A., Bose G., Garcia-Prats J., Lombardy L., Wold D., Donlon D., Long W. Improved outcome at 28 days of age for very low birth weight infants treated with a single dose of a synthetic surfactant. J Pediatr. 1990 Dec;117(6):947–953. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander A., Claypool W. D., Jr, Strauss J. F., 3rd, Fisher A. B. Uptake of liposomal phosphatidylcholine by granular pneumocytes in primary culture. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):C397–C404. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.5.C397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander A., Reicherter J., Fisher A. B. Degradation of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine by isolated rat granular pneumocytes and reutilization for surfactant synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1133–1138. doi: 10.1172/JCI112929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon A., Taeusch W., Fitzgibbon C., Smith G. B., Treves S. T., Phelps D. S. Factors associated with surfactant treatment response in infants with severe respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1989 Mar;83(3):348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida S., Phelps D. S., Soll R. F., Taeusch H. W. Surfactant proteins and anti-surfactant antibodies in sera from infants with respiratory distress syndrome with and without surfactant treatment. Pediatrics. 1991 Jul;88(1):84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J., Clements J. A., Cotton E. K., Klaus M. H., Sweet A. Y., Tooley W. H., Bradley B. L., Brandorff L. C. Neonatal pulmonary ischemia. I. Clinical and physiological studies. Pediatrics. 1967 Oct;40(4 Suppl):709–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Yu S. H., Whitsett J. A., Harding P. G., Possmayer F. Effect of surfactant-associated protein-A (SP-A) on the activity of lipid extract surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 26;1002(3):348–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyman R. I., Jobe A., Heymann M., Ikegami M., Roman C., Payne B., Mauray F. Increased shunt through the patent ductus arteriosus after surfactant replacement therapy. J Pediatr. 1982 Jan;100(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. J., Kuehl T. J., Escobedo M. B., Hilliard J. L., Smith F., Meredith K., Null D. M., Jr, Walsh W., Johnson D., Robotham J. L. A baboon model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. II. Pathologic features. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Dec;37(3):335–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D. Pulmonary surfactant protein B (SP-B): structure-function relationships. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):566–568. doi: 10.1126/science.1948032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Rust K., Marienchek W., Parghi D., Chang D., Persson A. Developmental expression of pulmonary surfactant protein D (SP-D). Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):13–18. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. J., Holm B. A., Hudak M. L., Hudak B. B., Ferguson W. H., Egan E. A. A controlled clinical comparison of four different surfactant preparations in surfactant-deficient preterm lambs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):999–1004. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Jörnvall H., Robertson B., Bergman T., Berggren P. Two hydrophobic low-molecular-mass protein fractions of pulmonary surfactant. Characterization and biophysical activity. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M., Russ G. A., Metlay L., Dickerson B., Greenspan B. S. Short-term distribution kinetics of intratracheally administered exogenous lung surfactant. Pediatr Res. 1992 May;31(5):445–450. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199205000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. S., Shennan A. T., Possmayer F. Single- versus multiple-dose surfactant replacement therapy in neonates of 30 to 36 weeks' gestation with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1990 Oct;86(4):564–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. S., Shennan A. T., Zayack D., Possmayer F. Bovine surfactant replacement therapy in neonates of less than 30 weeks' gestation: a randomized controlled trial of prophylaxis versus treatment. Pediatrics. 1991 Mar;87(3):377–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. J., Clyman R. I., Heymann M. A., Clements J. A., Mauray F., Kitterman J., Ballard P. Effects of a protein-free, synthetic surfactant on survival and pulmonary function in preterm lambs. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):775–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan E. A., Notter R. H., Kwong M. S., Shapiro D. L. Natural and artificial lung surfactant replacement therapy in premature lambs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):875–883. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan E. A., Notter R. H., Kwong M. S., Shapiro D. L. Natural and artificial lung surfactant replacement therapy in premature lambs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):875–883. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eijking E. P., van Daal G. J., Tenbrinck R., Luijendijk A., Sluiters J. F., Hannappel E., Lachmann B. Effect of surfactant replacement on Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. Intensive Care Med. 1991;17(8):475–478. doi: 10.1007/BF01690770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eijking E. P., van Daal G. J., Tenbrinck R., Sluiters J. F., Hannappel E., Erdmann W., Lachmann B. Improvement of pulmonary gas exchange after surfactant replacement in rats with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;316:293–298. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3404-4_34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom P. C., Holm B. A., Matalon S. Surfactant replacement attenuates the increase in alveolar permeability in hyperoxia. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Aug;67(2):688–693. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.2.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhorning G., Robertson B., Milne E., Wagner R. Radiologic evaluation of the premature newborn rabbit after pharyngeal deposition of surfactant. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Feb 15;121(4):475–480. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhorning G., Shennan A., Possmayer F., Dunn M., Chen C. P., Milligan J. Prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome by tracheal instillation of surfactant: a randomized clinical trial. Pediatrics. 1985 Aug;76(2):145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhorning G., Shumel B., Keicher L., Sokolowski J., Holm B. A. Phospholipases introduced into the hypophase affect the surfactant film outlining a bubble. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Sep;73(3):941–945. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.3.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennema J. J., Kobayashi T., Robertson B., Curstedt T. Inactivation of exogenous surfactant in experimental respiratory failure induced by hyperoxia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1988 Nov;32(8):665–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1988.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo M. B., Hilliard J. L., Smith F., Meredith K., Walsh W., Johnson D., Coalson J. J., Kuehl T. J., Null D. M., Jr, Robotham J. L. A baboon model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. I. Clinical features. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Dec;37(3):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. B., Chander A., Reicherter J. Uptake and degradation of natural surfactant by isolated rat granular pneumocytes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C792–C796. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Phelps D. S., Taeusch H. W. Biosynthesis and in vitro translation of the major surfactant-associated protein from human lung. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Steinbrink R., Jacobs K., Phelps D., Kriz R., Recny M., Sultzman L., Jones S., Taeusch H. W., Frank H. A. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for the 35-kDa pulmonary surfactant-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9029–9033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Konishi M., Chida S., Okuyama K., Ogawa Y., Takeuchi Y., Nishida H., Kito H., Fujimura M., Nakamura H. Surfactant replacement therapy with a single postventilatory dose of a reconstituted bovine surfactant in preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome: final analysis of a multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial and comparison with similar trials. The Surfactant-TA Study Group. Pediatrics. 1990 Nov;86(5):753–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Maeta H., Chida S., Morita T., Watabe Y., Abe T. Artificial surfactant therapy in hyaline-membrane disease. Lancet. 1980 Jan 12;1(8159):55–59. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90489-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan A. M., Rooney S. A. Arachidonic acid metabolites stimulate phosphatidylcholine secretion in primary cultures of type II pneumocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 8;833(2):336–341. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan A. M., Rooney S. A. Purinoceptor agonists stimulate phosphatidylcholine secretion in primary cultures of adult rat type II pneumocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 13;917(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin J. D., Soll R. F., Parad R. B., Horbar J. D., Feldman H. A., Lucey J. F., Taeusch H. W. Randomized controlled trial of exogenous surfactant for the treatment of hyaline membrane disease. Pediatrics. 1987 Jan;79(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone I. M., Ray A. O., Salafia C. M., Pérez-Fontán J., Mercurio M. R., Jacobs H. C. Effect of artificial surfactant on pulmonary function in preterm and full-term lambs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Aug;69(2):465–472. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.2.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Weaver T. E., Clark J. C., Pilot-Matias T., Meuth J., Fox J. L., Whitsett J. A. cDNA, deduced polypeptide structure and chromosomal assignment of human pulmonary surfactant proteolipid, SPL(pVal). J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gortner L., Bernsau U., Hellwege H. H., Hieronimi G., Jorch G., Reiter H. L. A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial of bovine surfactant for prevention of respiratory distress syndrome. Lung. 1990;168 (Suppl):864–869. doi: 10.1007/BF02718221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann G., Larsson I., Nilsson R., Robertson B., Rydhag L., Stenius P. Lung expansion in premature newborn rabbits treated with emulsified synthetic surfactant; principles for experimental evaluation of synthetic substitutes for pulmonary surfactant. Respiration. 1984;45(4):327–338. doi: 10.1159/000194639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagsman H. P., van Golde L. M. Synthesis and assembly of lung surfactant. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:441–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday H. L., McCord F. B., McClure B. G., Reid M. M. Acute effects of instillation of surfactant in severe respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Jan;64(1 Spec No):13–16. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.1_spec_no.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Merritt T. A., Bry K., Berry C. Association between neonatal care practices and efficacy of exogenous human surfactant: results of a bicenter randomized trial. Pediatrics. 1993 Mar;91(3):552–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Merritt T. A., Jarvenpaa A. L., Boynton B., Mannino F., Gluck L., Moore T., Edwards D. Exogenous human surfactant for treatment of severe respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized prospective clinical trial. J Pediatr. 1985 Jun;106(6):963–969. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Shiffer K. Structures and properties of the surfactant-associated proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:375–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström-Westas L., Bell A. H., Skov L., Greisen G., Svenningsen N. W. Cerebroelectrical depression following surfactant treatment in preterm neonates. Pediatrics. 1992 Apr;89(4 Pt 1):643–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra R. E., Jackson J. C., Myers T. F., Frantz I. D., 3rd, Stern M. E., Powers W. F., Maurer M., Raye J. R., Carrier S. T., Gunkel J. H. Improved neonatal survival following multiple doses of bovine surfactant in very premature neonates at risk for respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1991 Jul;88(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm B. A., Keicher L., Liu M. Y., Sokolowski J., Enhorning G. Inhibition of pulmonary surfactant function by phospholipases. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Jul;71(1):317–321. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.71.1.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm B. A., Notter R. H. Effects of hemoglobin and cell membrane lipids on pulmonary surfactant activity. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1434–1442. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horbar J. D., Soll R. F., Schachinger H., Kewitz G., Versmold H. T., Lindner W., Duc G., Mieth D., Linderkamp O., Zilow E. P. A European multicenter randomized controlled trial of single dose surfactant therapy for idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1990 Mar;149(6):416–423. doi: 10.1007/BF02009663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horbar J. D., Soll R. F., Sutherland J. M., Kotagal U., Philip A. G., Kessler D. L., Little G. A., Edwards W. H., Vidyasagar D., Raju T. N. A multicenter randomized, placebo-controlled trial of surfactant therapy for respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 13;320(15):959–965. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904133201502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horbar J. D., Wright L. L., Soll R. F., Wright E. C., Fanaroff A. A., Korones S. B., Shankaran S., Oh W., Fletcher B. D., Bauer C. R. A multicenter randomized trial comparing two surfactants for the treatment of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J Pediatr. 1993 Nov;123(5):757–766. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Adams F. H., Towers B., Osher A. B. The quantity of natural surfactant necessary to prevent the respiratory distress syndrome in premature lambs. Pediatr Res. 1980 Sep;14(9):1082–1085. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198009000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Agata Y., Elkady T., Hallman M., Berry D., Jobe A. Comparison of four surfactants: in vitro surface properties and responses of preterm lambs to treatment at birth. Pediatrics. 1987 Jan;79(1):38–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A. H., Tabor B. L., Rider E. D., Lewis J. F. Lung albumin recovery in surfactant-treated preterm ventilated lambs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):1005–1008. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Glatz T. Surface activity following natural surfactant treatment in premature lambs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Aug;51(2):306–312. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Glatz T. Surface activity following natural surfactant treatment in premature lambs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Aug;51(2):306–312. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Jacobs H., Jones S. J. Sequential treatments of premature lambs with an artificial surfactant and natural surfactant. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):491–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI110280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Jacobs H., Jones S. J. Sequential treatments of premature lambs with an artificial surfactant and natural surfactant. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):491–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI110280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Silverman J., Adams F. H. Restoration of lung pressure-volume characteristics with various phospholipids. Pediatr Res. 1979 Jun;13(6):777–780. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197906000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Silverman J., Adams F. H. Restoration of lung pressure-volume characteristics with various phospholipids. Pediatr Res. 1979 Jun;13(6):777–780. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197906000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Ueda T., Absolom D., Baxter C., Rider E., Jobe A. H. Changes in exogenous surfactant in ventilated preterm lamb lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Oct;148(4 Pt 1):837–844. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.4_Pt_1.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H. C., Berry D. D., Duane G., Ikegami M., Jobe A. H., Jones S. Normalization of arterial blood gases after treatment of surfactant-deficient lambs with Tween 20. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Dec;132(6):1313–1318. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.6.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H., Jobe A., Ikegami M., Glatz T., Jones S. J., Barajas L. Premature lambs rescued from respiratory failure with natural surfactant: clinical and biophysical correlates. Pediatr Res. 1982 Jun;16(6):424–429. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198206000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs K. A., Phelps D. S., Steinbrink R., Fisch J., Kriz R., Mitsock L., Dougherty J. P., Taeusch H. W., Floros J. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a high molecular weight precursor to a 6-kDa pulmonary surfactant-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9808–9811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Ikegami M., Glatz T., Yoshida Y., Diakomanolis E., Padbury J. Duration and characteristics of treatment of premature lambs with natural surfactant. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):370–375. doi: 10.1172/JCI110044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Ikegami M., Glatz T., Yoshida Y., Diakomanolis E., Padbury J. Saturated phosphatidylcholine secretion and the effect of natural surfactant on premature and term lambs ventilated for 2 days. Exp Lung Res. 1983 May;4(4):259–267. doi: 10.3109/01902148309055013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Ikegami M., Jacobs H., Jones S. Surfactant and pulmonary blood flow distributions following treatment of premature lambs with natural surfactant. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):848–856. doi: 10.1172/JCI111280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Ikegami M. Surfactant for the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1256–1275. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattwinkel J., Bloom B. T., Delmore P., Davis C. L., Farrell E., Friss H., Jung A. L., King K., Mueller D. Prophylactic administration of calf lung surfactant extract is more effective than early treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in neonates of 29 through 32 weeks' gestation. Pediatrics. 1993 Jul;92(1):90–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendig J. W., Notter R. H., Cox C., Reubens L. J., Davis J. M., Maniscalco W. M., Sinkin R. A., Bartoletti A., Dweck H. S., Horgan M. J. A comparison of surfactant as immediate prophylaxis and as rescue therapy in newborns of less than 30 weeks' gestation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 28;324(13):865–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103283241301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khammash H., Perlman M., Wojtulewicz J., Dunn M. Surfactant therapy in full-term neonates with severe respiratory failure. Pediatrics. 1993 Jul;92(1):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Kataoka H., Ueda T., Murakami S., Takada Y., Kokubo M. Effects of surfactant supplement and end-expiratory pressure in lung-lavaged rabbits. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Oct;57(4):995–1001. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolobow T., Solca M., Presenti A., Buckhold D., Pierce J. D. The prevention of hyaline membrane disease (HMD) in the preterm fetal lamb through the static inflation of the lungs: the conditioning of the fetal lungs. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1980;26:567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresch M. J., Dynia D. W., Gross I. Culture of differentiated and undifferentiated type II cells from fetal rat lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 19;930(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresch M. J., Gross I. The biochemistry of fetal lung development. Clin Perinatol. 1987 Sep;14(3):481–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Akino T. Roles of collagenous domain and oligosaccharide moiety of pulmonary surfactant protein A in interactions with phospholipids. Biochem Int. 1991 May;24(2):225–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Chemical modification of surfactant protein A alters high affinity binding to rat alveolar type II cells and regulation of phospholipid secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17596–17602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Pulmonary surfactant apoprotein A structure and modulation of surfactant secretion by rat alveolar type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3388–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Shiratori M., Murata Y., Akino T. Surfactant protein D (SP-D) counteracts the inhibitory effect of surfactant protein A (SP-A) on phospholipid secretion by alveolar type II cells. Interaction of native SP-D with SP-A. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):115–119. doi: 10.1042/bj2790115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong M. S., Egan E. A., Notter R. H., Shapiro D. L. Double-blind clinical trial of calf lung surfactant extract for the prevention of hyaline membrane disease in extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 1985 Oct;76(4):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käpä P., Kero P., Saraste M. Synthetic surfactant replacement therapy decreases estimated pulmonary artery pressure in respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1992 Aug;146(8):961–964. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160200083033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käpä P., Seppänen M., Kero P., Saraste M. Pulmonary hemodynamics after synthetic surfactant replacement in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1993 Jul;123(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann B. Animal studies of surfactant replacement therapy. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1989;13(2-4):164–172. doi: 10.1159/000457600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann B., Armbruster S., Erdmann W. Oxygen uptake and surfactant replacement. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;222:511–517. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9510-6_61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann B., Robertson B., Vogel J. In vivo lung lavage as an experimental model of the respiratory distress syndrome. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1980 Jun;24(3):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1980.tb01541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm W. J., Albert R. K. Surfactant replacement improves lung recoil in rabbit lungs after acid aspiration. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1279–1283. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang M. J., Hall R. T., Reddy N. S., Kurth C. G., Merritt T. A. A controlled trial of human surfactant replacement therapy for severe respiratory distress syndrome in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 1990 Feb;116(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82897-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liechty E. A., Donovan E., Purohit D., Gilhooly J., Feldman B., Noguchi A., Denson S. E., Sehgal S. S., Gross I., Stevens D. Reduction of neonatal mortality after multiple doses of bovine surfactant in low birth weight neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1991 Jul;88(1):19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., White R. T., Warr R. G., Benson B. J., Hawgood S., Ballard P. L. Regulation of messenger RNAs for the hydrophobic surfactant proteins in human lung. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1191–1197. doi: 10.1172/JCI114000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo M. L., Bisagno A. M., Zasadzinski J. A., Bruni R., Waring A. J. A function of lung surfactant protein SP-B. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.8332910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeta H., Raju T. N., Vidyasagar D., Bhat R., Esterly J., Matsuda H., Shimada S., Krukenkamp I. B., Shanklin D. R. Effect of exogenous surfactant on the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a baboon hyaline membrane disease model. Crit Care Med. 1990 Apr;18(4):403–409. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199004000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeta H., Vidyasagar D., Raju T. N., Bhat R., Matsuda H. Early and late surfactant treatments in baboon model of hyaline membrane disease. Pediatrics. 1988 Feb;81(2):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeta H., Vidyasagar D., Raju T., Bhat R., Matsuda H. Response to bovine surfactant (surfactant TA) in two different HMD models (lambs and baboons). Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Feb;147(2):162–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00442215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniscalco W. M., Kendig J. W., Shapiro D. L. Surfactant replacement therapy: impact on hospital charges for premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1989 Jan;83(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Dobbs L. G., Greenleaf R. D., Williams M. C. Alveolar type II cells. Fed Proc. 1977 Dec;36(13):2697–2702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean L. R., Krstenansky J. L., Jackson R. L., Hagaman K. A., Olsen K. A., Lewis J. E. Mixtures of synthetic peptides and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine as lung surfactants. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):L292–L300. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.3.L292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean L. R., Lewis J. E., Hagaman K. A., Owen T. J., Jackson R. L. Amphipathic alpha-helical peptides based on surfactant apoprotein SP-A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Feb 10;1166(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90280-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean L. R., Lewis J. E., Krstenansky J. L., Hagaman K. A., Cope A. S., Olsen K. F., Matthews E. R., Uhrhammer D. C., Owen T. J., Payne M. H. An amphipathic alpha-helical decapeptide in phosphatidylcholine is an effective synthetic lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Feb;147(2):462–465. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.2.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Berry C., Pohjavuori M., Edwards D. K., 3rd, Jaaskelainen J., Grafe M. R., Vaucher Y., Wozniak P., Heldt G. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of human surfactant given at birth versus rescue administration in very low birth weight infants with lung immaturity. J Pediatr. 1991 Apr;118(4 Pt 1):581–594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Bloom B. T., Berry C., Benirschke K., Sahn D., Key T., Edwards D., Jarvenpaa A. L., Pohjavuori M. Prophylactic treatment of very premature infants with human surfactant. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 25;315(13):785–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609253151301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Holcomb K., Strayer D., Bloom B., Revak S., Cochrane C. G. Human surfactant treatment of severe respiratory distress syndrome: pulmonary effluent indicators of lung inflammation. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 1):741–748. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)81058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. D., Vyas H., Hopkin I. E. Effects of artificial surfactant on lung function and blood gases in idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Jun;58(6):458–460. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.6.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. J., Banhham A. D., Johnson P., Thorburn G. D., Jenkin G. Physical and physiological properties of dry lung surfactant. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):162–163. doi: 10.1038/271162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. J., Greenough A., Miller N. G., Bangham A. D., Pool J., Wood S., South M., Davis J. A., Vyas H. Randomized trial of artificial surfactant (ALEC) given at birth to babies from 23 to 34 weeks gestation. Early Hum Dev. 1988 May;17(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/s0378-3782(88)80056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C., Robertson B., Lachmann B., Nilsson R., Bangham A., Grossmann G., Miller N. Artificial surfactant and natural surfactant. Comparative study of the effects on premature rabbit lungs. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Oct;55(10):758–765. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.10.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson R. The artificially ventilated preterm rabbit neonate as experimental model of hyaline membrane disease. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1982 Apr;26(2):89–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1982.tb01733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noack G., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Nilsson R., Robertson B. Passive expiratory flow-volume recordings in immature newborn rabbits. Effect of surfactant replacement on the time constant of the respiratory system. Respiration. 1990;57(1):1–5. doi: 10.1159/000195811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohara K., Berggren P., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Nilsson R., Robertson B. Correlations between physical and physiological properties of various preparations of lung surfactant. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;69(5):321–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter R. H., Egan E. A., Kwong M. S., Holm B. A., Shapiro D. L. Lung surfactant replacement in premature lambs with extracted lipids from bovine lung lavage: effects of dose, dispersion technique, and gestational age. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jun;19(6):569–577. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198506000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter R. H., Shapiro D. L., Ohning B., Whitsett J. A. Biophysical activity of synthetic phospholipids combined with purified lung surfactant 6000 dalton apoprotein. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987 Jun;44(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(87)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obladen M., Popp D., Schöll C., Schwarz H., Jähnig F. Studies on lung surfactant replacement in respiratory distress syndrome. Rapid film formation from binary mixed liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 9;735(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oetomo S. B., Reijngoud D. J., Ennema J. J., Okken A., Wildevuur C. R. Surfactant replacement therapy in surfactant-deficient rabbits: early effects on lung function and biochemical aspects. Lung. 1988;166(2):65–73. doi: 10.1007/BF02714030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Crouch E. Surfactant protein D is a divalent cation-dependent carbohydrate-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5755–5760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Rust K., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. Purification and biochemical characterization of CP4 (SP-D), a collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6361–6367. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Rust K., Chang D., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. CP4: a pneumocyte-derived collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Evidence for heterogeneity of collagenous surfactant proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8576–8584. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Floros J. Localization of surfactant protein synthesis in human lung by in situ hybridization. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):939–942. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Smith L. M., Taeusch H. W. Characterization and partial amino acid sequence of a low molecular weight surfactant protein. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1112–1117. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs R. H., Ballard R. A., Clements J. A., Heilbron D. C., Phibbs C. S., Schlueter M. A., Sniderman S. H., Tooley W. H., Wakeley A. Initial clinical trial of EXOSURF, a protein-free synthetic surfactant, for the prophylaxis and early treatment of hyaline membrane disease. Pediatrics. 1991 Jul;88(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possmayer F. A proposed nomenclature for pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):990–998. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBILLARD E., ALARIE Y., DAGENAIS-PERUSSE P., BARIL E., GUILBEAULT A. MICROAEROSOL ADMINISTRATION OF SYNTHETIC BETA-GAMMA-DIPALMITOYL-L-ALPHA-LECITHIN IN THE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDOME: A PRELIMINARY REPORT. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 11;90:55–57. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju T. N., Vidyasagar D., Bhat R., Sobel D., McCulloch K. M., Anderson M., Maeta H., Levy P. S., Furner S. Double-blind controlled trial of single-dose treatment with bovine surfactant in severe hyaline membrane disease. Lancet. 1987 Mar 21;1(8534):651–656. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90414-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Cochrane C. G. Reconstitution of surfactant activity using purified human apoprotein and phospholipids measured in vitro and in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1258–1265. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Ross G. F., Singleton F. M., Dingle S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):692–698. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider E. D., Ikegami M., Whitsett J. A., Hull W., Absolom D., Jobe A. H. Treatment responses to surfactants containing natural surfactant proteins in preterm rabbits. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Mar;147(3):669–676. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B., Berry D., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Ikegami M., Jacobs H., Jobe A., Jones S. Leakage of protein in the immature rabbit lung; effect of surfactant replacement. Respir Physiol. 1985 Sep;61(3):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(85)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Kobayashi T., Kokubo M., Suzuki Y. Prolonged ventilation of the premature newborn rabbit after treatment with natural or apoprotein-based artificial surfactant. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Feb;147(2):168–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00442216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. European multicenter trials of curosurf for treatment of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Lung. 1990;168 (Suppl):860–863. doi: 10.1007/BF02718220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. Surfactant inactivation and surfactant replacement in experimental models of ARDS. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1991;95:22–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1991.tb03396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. C., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Isolation and culture of human alveolar type II epithelial cells. Characterization of their phospholipid secretion. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Dec;130(6):1156–1160. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.6.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A., Gobran L. I. Adenosine and leukotrienes have a regulatory role in lung surfactant secretion in the newborn rabbit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 2;960(1):98–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A. Lung surfactant. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Apr;55:205–226. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8455205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A. The surfactant system and lung phospholipid biochemistry. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):439–460. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. K., Ramirez O., King M. Mucus rheology and transport in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome and the effect of surfactant therapy. Chest. 1992 Apr;101(4):1080–1085. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.4.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhar B. K., Niblett D. J., Argiras E. P., Dunnill M. S., Sykes M. K. Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on hyaline membrane formation in a rabbit model of the neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 1988;14(5):538–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00263527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Involvement of protein kinase C in pulmonary surfactant secretion from alveolar type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12725–12729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. A., Hallman M., Benirschke K., Gluck L. Human surfactant: a therapeutic trial in premature rabbits. J Pediatr. 1982 Apr;100(4):619–622. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80769-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch S., Bachofen H., Goerke J., Possmayer F. A captive bubble method reproduces the in situ behavior of lung surfactant monolayers. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Dec;67(6):2389–2396. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.6.2389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch S., Possmayer F., Cheng S., Cockshutt A. M. Pulmonary SP-A enhances adsorption and appears to induce surface sorting of lipid extract surfactant. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):L210–L218. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.2.L210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. L., Notter R. H., Morin F. C., 3rd, Deluga K. S., Golub L. M., Sinkin R. A., Weiss K. I., Cox C. Double-blind, randomized trial of a calf lung surfactant extract administered at birth to very premature infants for prevention of respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1985 Oct;76(4):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Raju T. N., Vidyasagar D., Maeta H., Bhat R. Chest radiographic course after exogenous surfactant therapy in baboons with respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1990 Sep;18(9):969–973. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199009000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solca M., Kolobow T., Huang H., Pesenti A., Buckhold D., Pierce J. E. Management of the antenatal preterm fetal lung in the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in lambs. Biol Neonate. 1983;44(2):93–101. doi: 10.1159/000241701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll R. F., Hoekstra R. E., Fangman J. J., Corbet A. J., Adams J. M., James L. S., Schulze K., Oh W., Roberts J. D., Jr, Dorst J. P. Multicenter trial of single-dose modified bovine surfactant extract (Survanta) for prevention of respiratory distress syndrome. Ross Collaborative Surfactant Prevention Study Group. Pediatrics. 1990 Jun;85(6):1092–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer C. P., Harms K., Herting E., Neumann N., Curstedt T., Robertson B. Early versus late surfactant replacement therapy in severe respiratory distress syndrome. Lung. 1990;168 (Suppl):870–876. doi: 10.1007/BF02718222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer C. P., Robertson B., Curstedt T., Halliday H. L., Compagnone D., Gefeller O., Harms K., Herting E., McClure G., Reid M. Randomized European multicenter trial of surfactant replacement therapy for severe neonatal respiratory distress syndrome: single versus multiple doses of Curosurf. Pediatrics. 1992 Jan;89(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spissinger T., Schäfer K. P., Voss T. Assembly of the surfactant protein SP-A. Deletions in the globular domain interfere with the correct folding of the molecule. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 1;199(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark A. R., Frantz I. D., 3rd Respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Jun;33(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)36041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun B., Kobayashi T., Cursted T., Grossmann G., Robertson B. Application of a new ventilator-multi-plethysmograph system for testing efficacy of surfactant replacement in newborn rabbits. Eur Respir J. 1991 Mar;4(3):364–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Kobayashi T., Nilsson R., Nohara K., Robertson B. The role of the low-molecular weight (less than or equal to 15,000 daltons) apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;69(5):336–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Takei T., Aiba T., Masuda K., Kiuchi A., Fujiwara T. Development of synthetic lung surfactants. J Lipid Res. 1986 May;27(5):475–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Takei T., Kanazawa Y. Lung surfactants. II. Effects of fatty acids, triacylglycerols and protein on the activity of lung surfactant. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1983 Nov;31(11):4100–4109. doi: 10.1248/cpb.31.4100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Takei T., Masuda K. Lung surfactants. III. Correlations among activities in vitro, in situ and in vivo, and chemical composition. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1983 Nov;31(11):4110–4115. doi: 10.1248/cpb.31.4110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Robinson S. L., Borchelt J., Wright J. R. Human pulmonary surfactant protein (SP-A), a protein structurally homologous to C1q, can enhance FcR- and CR1-mediated phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13923–13928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte J. G., Lin W. H., Motola N. C., Pivarnik P. E., Bhongle N. N., Heyman H. R., Shirali S. S., Lu Z., Notter R. H. Chemical synthesis and surface activity of lung surfactant phospholipid analogs. III. Chiral N-substituted ether-amide phosphonolipids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 May-Jun;58(1-2):81–95. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90114-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte J. G., Lin W. H., Pivarnik P. E., Sacco A. M., Shirali S. S., Bermel M. M., Lu Z., Notter R. H. Chemical synthesis and surface activity of lung surfactant phospholipid analogs. II. Racemic N-substituted diether phosphonolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 19;1084(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90048-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte J. G., Sacco A. M., Steim J. M., Tabak S. A., Notter R. H. Chemical synthesis and surface properties of an analog of the pulmonary surfactant dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 24;488(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaucher Y. E., Harker L., Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Gist K., Bejar R., Heldt G. P., Edwards D., Pohjavuori M. Outcome at twelve months of adjusted age in very low birth weight infants with lung immaturity: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of human surfactant. J Pediatr. 1993 Jan;122(1):126–132. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83505-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman A. R., Hall S. B., Whitsett J. A., Notter R. H. Enhancement of biophysical activity of lung surfactant extracts and phospholipid-apoprotein mixtures by surfactant protein A. Chem Phys Lipids. 1990 Dec;56(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90101-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilstrup C., Gommers D., Bos J. A., Lachmann B., Werner O., Larsson A. Natural surfactant instilled in premature lambs increases lung volume and improves ventilation homogeneity within five minutes. Pediatr Res. 1992 Nov;32(5):595–599. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199211000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Eistetter H., Schäfer K. P., Engel J. Macromolecular organization of natural and recombinant lung surfactant protein SP 28-36. Structural homology with the complement factor C1q. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90448-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther F. J., Blanco C. E., Houdijk M., Bevers E. M. Single versus repetitive doses of natural surfactant as treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in premature lambs. Pediatr Res. 1985 Feb;19(2):224–227. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198502000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Taeusch H. W., Soll R. F., McCormick M. C. Health and developmental outcomes of a surfactant controlled trial: follow-up at 2 years. Pediatrics. 1990 Jun;85(6):1103–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E., Ross G., Daugherty C., Whitsett J. A. Synthesis of surfactant-associated protein, 35,000 daltons, in fetal lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Aug;61(2):694–700. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.2.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegman M. E. Annual summary of vital statistics--1991. Pediatrics. 1992 Dec;90(6):835–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Hull W. M., Luse S. Failure to detect surfactant protein-specific antibodies in sera of premature infants treated with survanta, a modified bovine surfactant. Pediatrics. 1991 Apr;87(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Hull W. M., Ohning B., Ross G., Weaver T. E. Immunologic identification of a pulmonary surfactant-associated protein of molecular weight = 6000 daltons. Pediatr Res. 1986 Aug;20(8):744–749. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198608000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Ohning B. L., Ross G., Meuth J., Weaver T., Holm B. A., Shapiro D. L., Notter R. H. Hydrophobic surfactant-associated protein in whole lung surfactant and its importance for biophysical activity in lung surfactant extracts used for replacement therapy. Pediatr Res. 1986 May;20(5):460–467. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198605000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Ross G., Weaver T., Rice W., Dion C., Hull W. Glycosylation and secretion of surfactant-associated glycoprotein A. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15273–15279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T., Hull W., Ross G., Dion C. Synthesis of surfactant-associated glycoprotein A by rat type II epithelial cells. Primary translation products and post-translational modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 5;828(2):162–171. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Hawgood S., Hamilton R. L. Changes in lipid structure produced by surfactant proteins SP-A, SP-B, and SP-C. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):41–50. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):426–444. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Wager R. E., Hamilton R. L., Huang M., Clements J. A. Uptake of lung surfactant subfractions into lamellar bodies of adult rabbit lungs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Mar;60(3):817–825. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.3.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Wager R. E., Hawgood S., Dobbs L., Clements J. A. Surfactant apoprotein Mr = 26,000-36,000 enhances uptake of liposomes by type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2888–2894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Cellular uptake and processing of surfactant lipids and apoprotein SP-A by rat lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1336–1342. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola E. M., Gunkel J. H., Chan R. K., Lim M. O., Knox I., Feldman B. H., Denson S. E., Stonestreet B. S., Mitchell B. R., Wyza M. M. Comparison of three dosing procedures for administration of bovine surfactant to neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1993 Mar;122(3):453–459. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van 't Veen A., So K. L., Lachmann B. Surfactant replacement therapy in animal models of respiratory failure due to viral infection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994;345:83–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2468-7_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Bor M., Ma E. J., Walther F. J. Cerebral blood flow velocity after surfactant instillation in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1991 Feb;118(2):285–287. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


