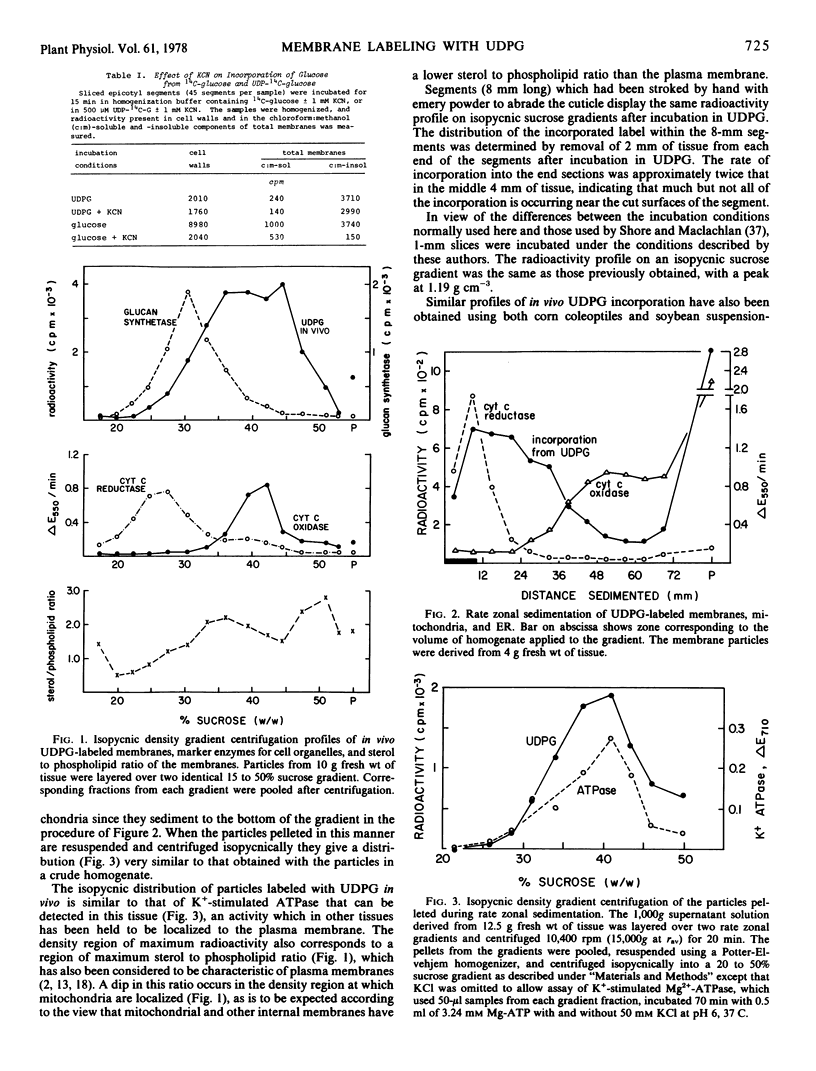
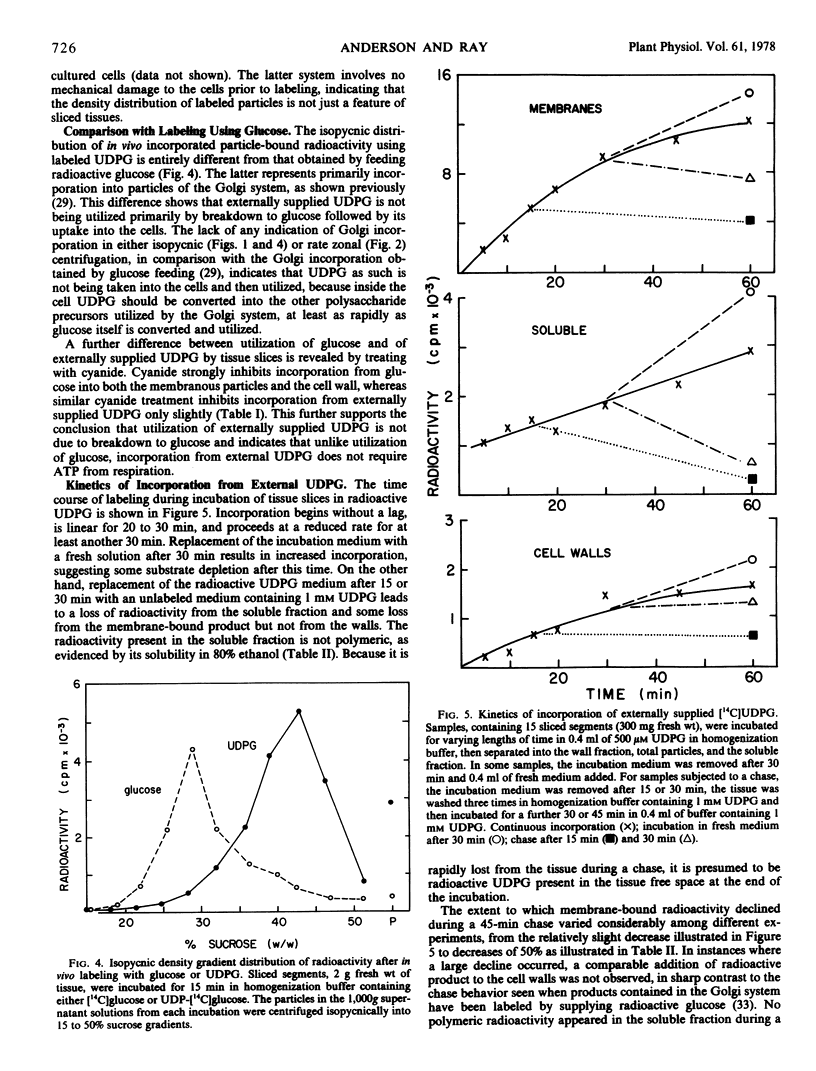
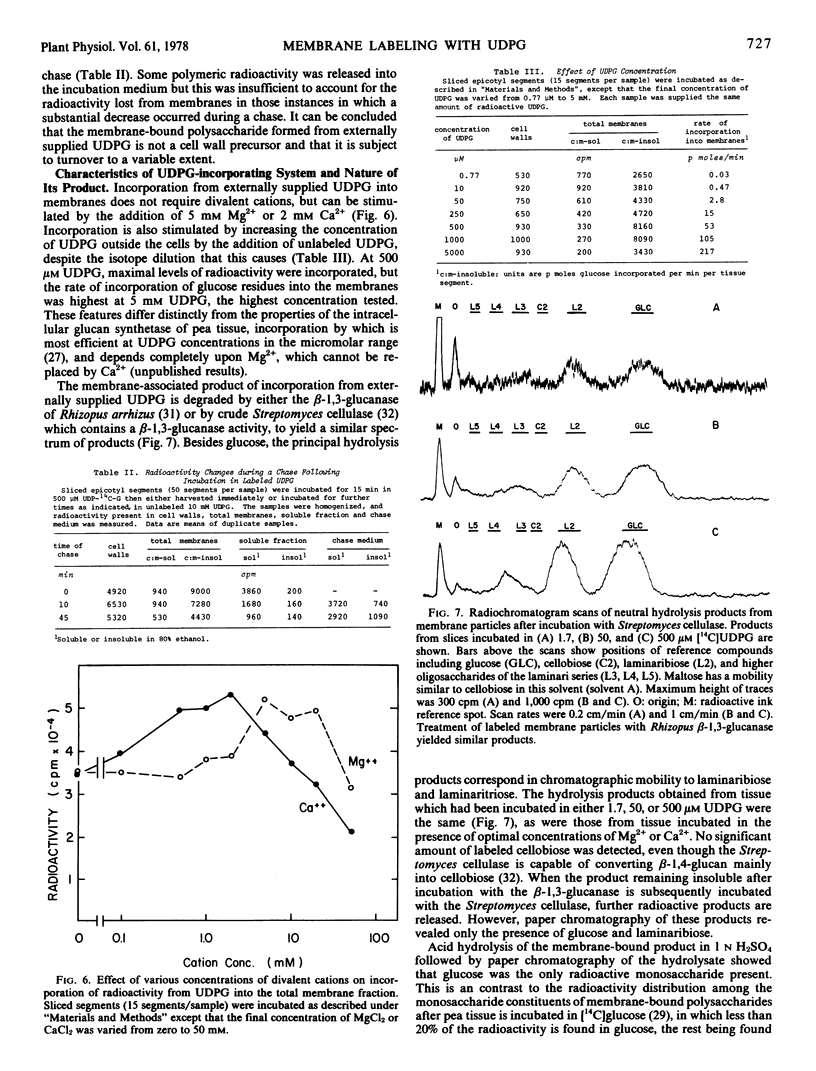
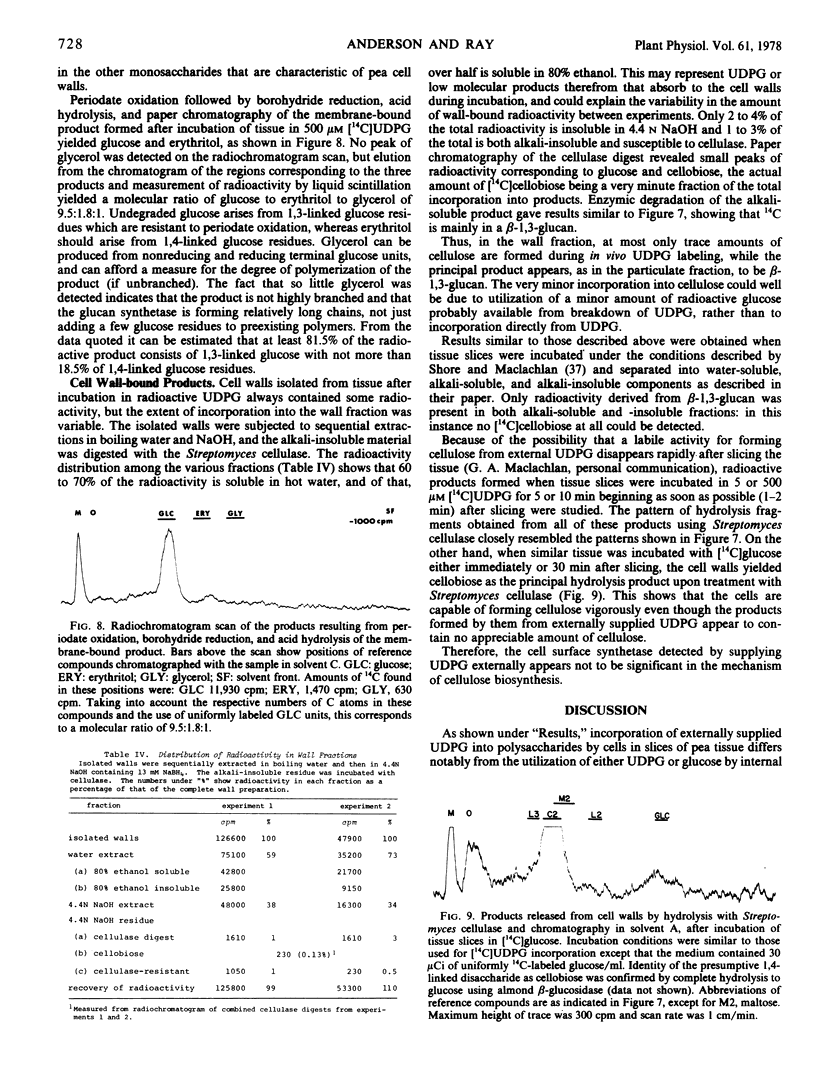
Abstract
When radioactive UDP-glucose is supplied to 1-millimeter-thick slices of pea (Pisum sativum) stem tissue, radioactive glucose becomes incorporated into membrane-bound polysaccharides. Evidence is given that this incorporation does not result from breakdown of UDP-glucose and utilization of the resultant free glucose, and that the incorporation most likely takes place at the cell surface, leading to a specific labeling of the plasma membrane. The properties of the plasma membrane that are indicated by this method of recognition, including the association of K+-stimulated ATPase activity with the plasma membrane, resemble properties inferred using other approaches. The membrane-associated polysaccharide product formed from UDP-glucose is largely 1,3-linked glucan, presumably callose, and does not behave as a precursor of cell wall polymers. No substantial amount of cellulose is formed from UDP-glucose in this procedure, even though these cells incorporate free glucose rapidly into cellulose. This synthetase system that uses external UDP-glucose may serve for formation of wound callose.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colbeau A., Nachbaur J., Vignais P. M. Enzymic characterization and lipid composition of rat liver subcellular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):462–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowler M. J., Rayle D. L. Auxin Does Not Alter the Permeability of Pea Segments to Tritium-labeled Water. Plant Physiol. 1974 Feb;53(2):229–232. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith D. W., Northcote D. H. The isolation of plasma membrane from protoplasts of soybean suspension cultures. J Cell Sci. 1977 Apr;24:295–310. doi: 10.1242/jcs.24.1.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. W., Cherry J. H., Morré D. J., Lembi C. A. Enhancement of RNA polymerase activity by a factor released by auxin from plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3146–3150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiniger U., Delmer D. P. UDP-glucose: Glucan Synthetase in Developing Cotton Fibers: II. Structure of the Reaction Product. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):719–723. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T., Bracker C. E., Keenan T. W. Purification of an ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots: association with plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labavitch J. M., Ray P. M. Turnover of cell wall polysaccharides in elongating pea stem segments. Plant Physiol. 1974 May;53(5):669–673. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hansen D., Hodges T. K. Membrane-bound Adenosine Triphosphatase Activities of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):749–754. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Vanderwoude W. J. Isolation of plasma membranes from corn roots by sucrose density gradient centrifugation: an anomalous effect of ficoll. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):105–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Wagner G. J., Siegelman H. W., Hind G. Membrane-bound ATPase of intact vacuoles and tonoplasts isolated from mature plant tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 14;465(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN G. V. A method for measurement of cholesterol in blood serum. Clin Chem. 1961 Jun;7:275–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H., Browning A. Failure of lactoperoxidase to iodinate specifically the plasma membrane of cucurbita tissue segments. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):759–766. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., MANDELS M. Beta-D-1, 3 Glucanases in fungi. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Apr;5(2):173–185. doi: 10.1139/m59-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., SMAKULA E., PERLIN A. S. Enzymic production of cellotriose from cellulose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Nov;85:171–175. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M. Auxin-binding Sites of Maize Coleoptiles Are Localized on Membranes of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):594–599. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M. Regulation of beta-Glucan Synthetase Activity by Auxin in Pea Stem Tissue: I. Kinetic Aspects. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):601–608. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M., Shininger T. L., Ray M. M. ISOLATION OF beta-GLUCAN SYNTHETASE PARTICLES FROM PLANT CELLS AND IDENTIFICATION WITH GOLGI MEMBRANES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):605–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland J. C., Lembi C. A., Morré D. J. Phosphotungstic acid-chromic acid as a selective electron-dense stain for plasma membranes of plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):195–200. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungie J. M., Wiskich J. T. Salt-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase from Smooth Microsomes of Turnip. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):1064–1068. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore G., Maclachlan G. A. The site of cellulose synthesis. Hormone treatment alters the intracellular location of alkali-insoluble beta-1,4-glucan (cellulose) synthetase activities. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):557–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore G., Raymond Y., Maclachlan G. A. The Site of Cellulose Synthesis: Cell Surface and Intracellular beta-1, 4-Glucan (Cellulose) Synthetase Activities in Relation to the Stage and Direction of Cell Growth. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):34–38. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Hassid W. Z. Substrate Activation of beta-(1 --> 3) Glucan Synthetase and Its Effect on the Structure of beta-Glucan Obtained from UDP-d-glucose and Particulate Enzyme of Oat Coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):998–1001. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Woude W. J., Lembi C. A., Morré D. J. beta-Glucan Synthetases of Plasma Membrane and Golgi Apparatus from Onion Stem. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):333–340. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


