Abstract
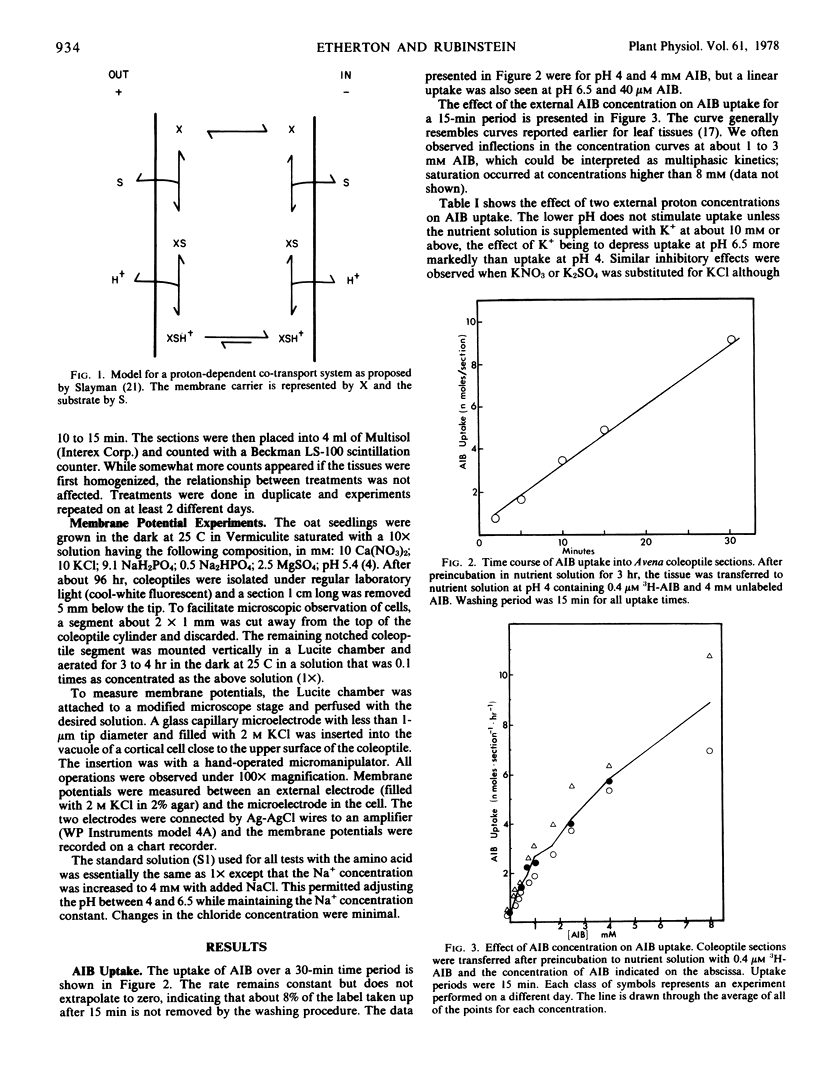
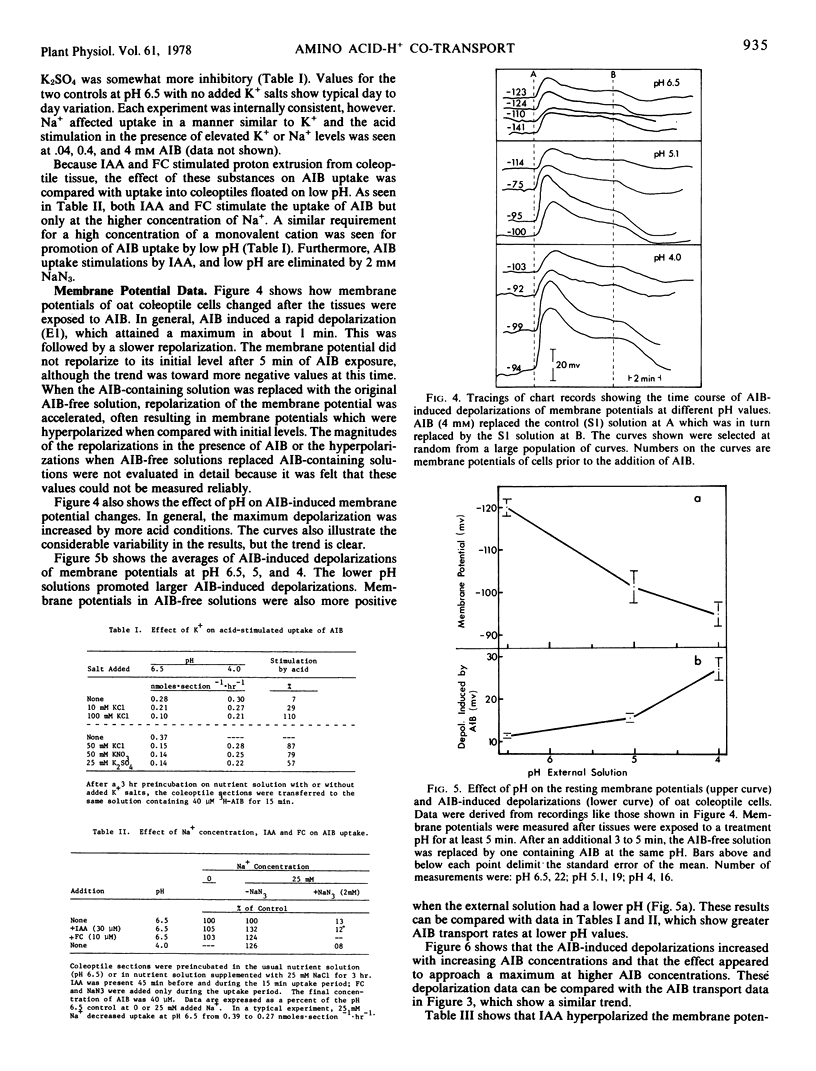
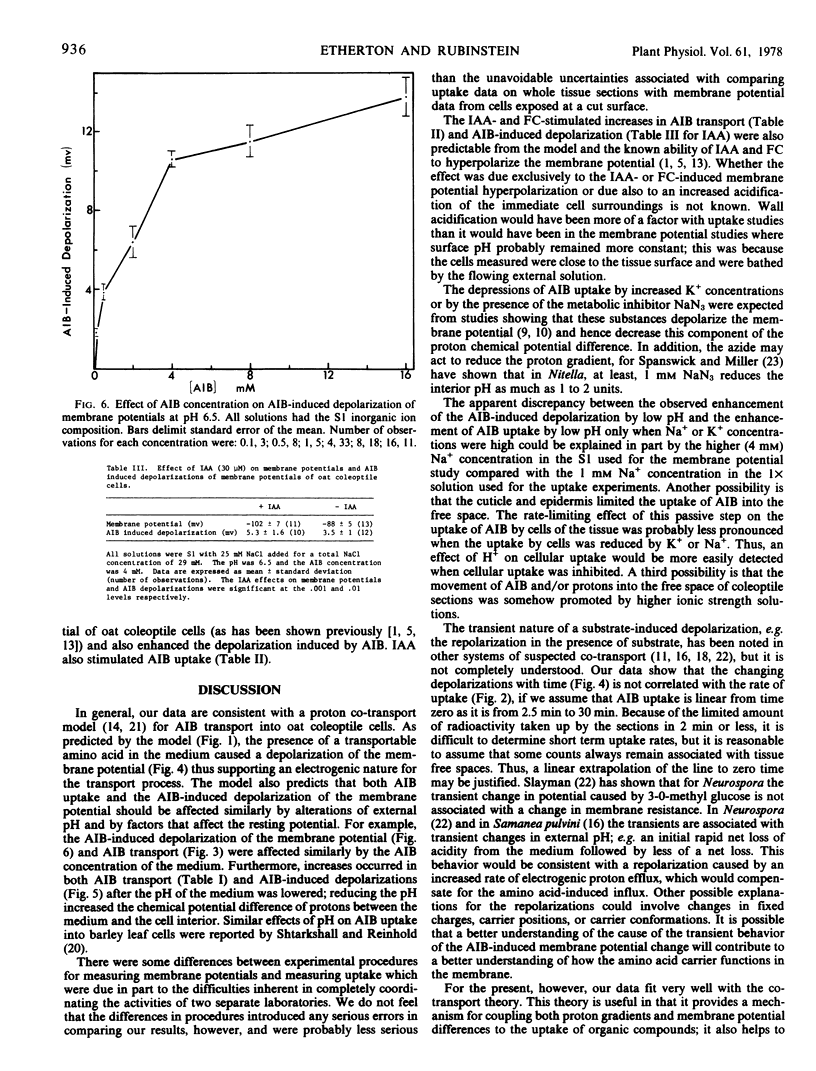
Microelectrode and tracer techniques were used to test for possible amino acid-H+ co-transport in coleoptiles of Avena sativa L. cv. “Garry.” The amino acid analogue α-aminoisobutyric acid (AIB) caused transient depolarization of the membrane potential. The absolute magnitude of the maximum depolarization was affected by the same factors that affected AIB transport. Both increased with higher concentrations of AIB, increased with higher acidities in the medium, and were enhanced by indoleacetic acid (which hyperpolarized the membrane potential). AIB transport was reduced as K+ concentrations in the medium were increased and by the metabolic inhibitor NaN3, both of which reduce membrane potentials. Our data fit an amino acid-H+ co-transport model in which transport is controlled by both the membrane potential and proton concentration components of the chemical potential difference of protons across the coleoptile cell membrane.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleland R. E., Prins H. B., Harper J. R., Higinbotham N. Rapid Hormone-induced Hyperpolarization of the Oat Coleoptile Transmembrane Potential. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):395–397. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombini M., Johnstone R. M. Na+-gradient-stimulated AIB transport in membrane vesicles from Ehrlich ascites cells. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(3-4):315–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01870120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Effect of Indole-3-acetic Acid on Membrane Potentials of Oat Coleoptile Cells. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):527–528. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Relationship of Cell Transmembrane Electropotential to Potassium and Sodium Accumulation Ratios in Oat and Pea Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1963 Sep;38(5):581–585. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.5.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaquinta R. Phloem Loading of Sucrose: pH Dependence and Selectivity. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):750–755. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higinbotham N., Etherton B., Foster R. J. Effect of External K, NH(4), Na, Ca, Mg, and H Ions on the Cell Transmembrane Electropotential of Avena Coleoptile. Plant Physiol. 1964 Mar;39(2):196–203. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.2.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. The determination of the membrane ptoential of Chlorella vulgaris. Evidence for electrogenic sugar transport. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E. Regulation of active alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport expressed in membrane vesicles from mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2614–2618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Translocations through natural membranes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:33–87. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayman C. L., Slayman C. W. Depolarization of the plasma membrane of Neurospora during active transport of glucose: evidence for a proton-dependent cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1935–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanswick R. M., Miller A. G. Measurement of the Cytoplasmic pH in Nitella translucens: Comparison of Values Obtained by Microelectrode and Weak Acid Methods. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):664–666. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


