Abstract
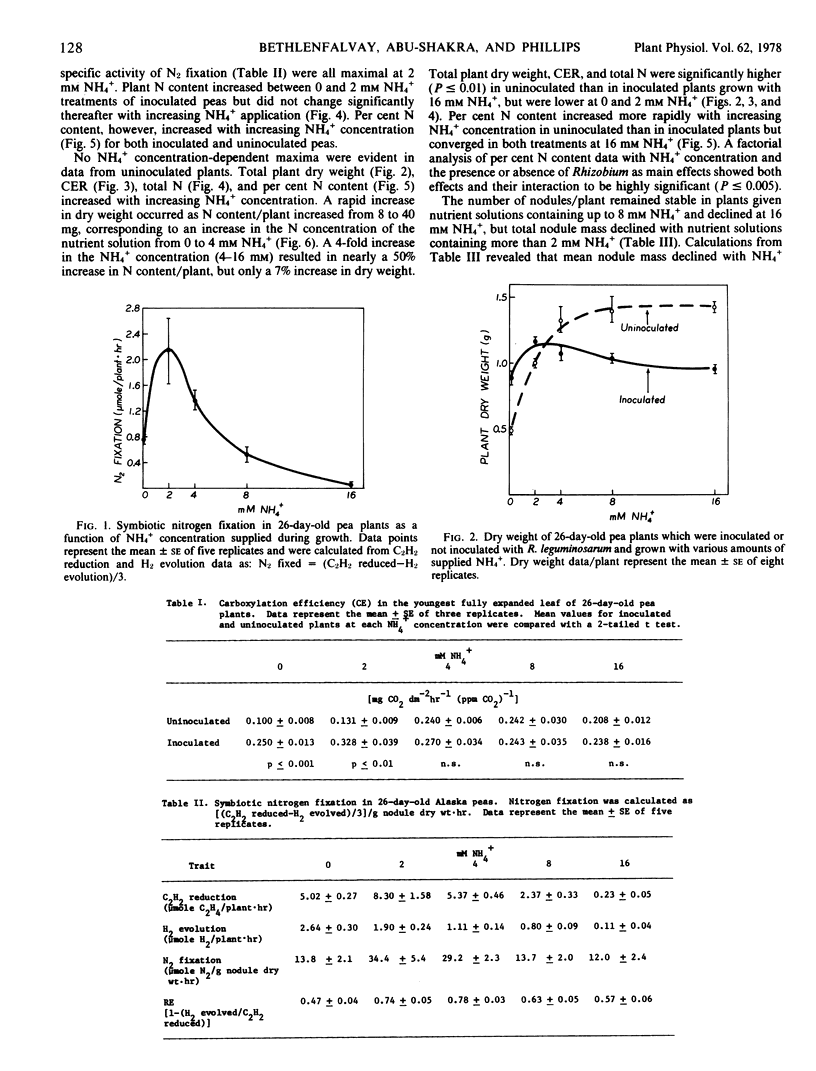
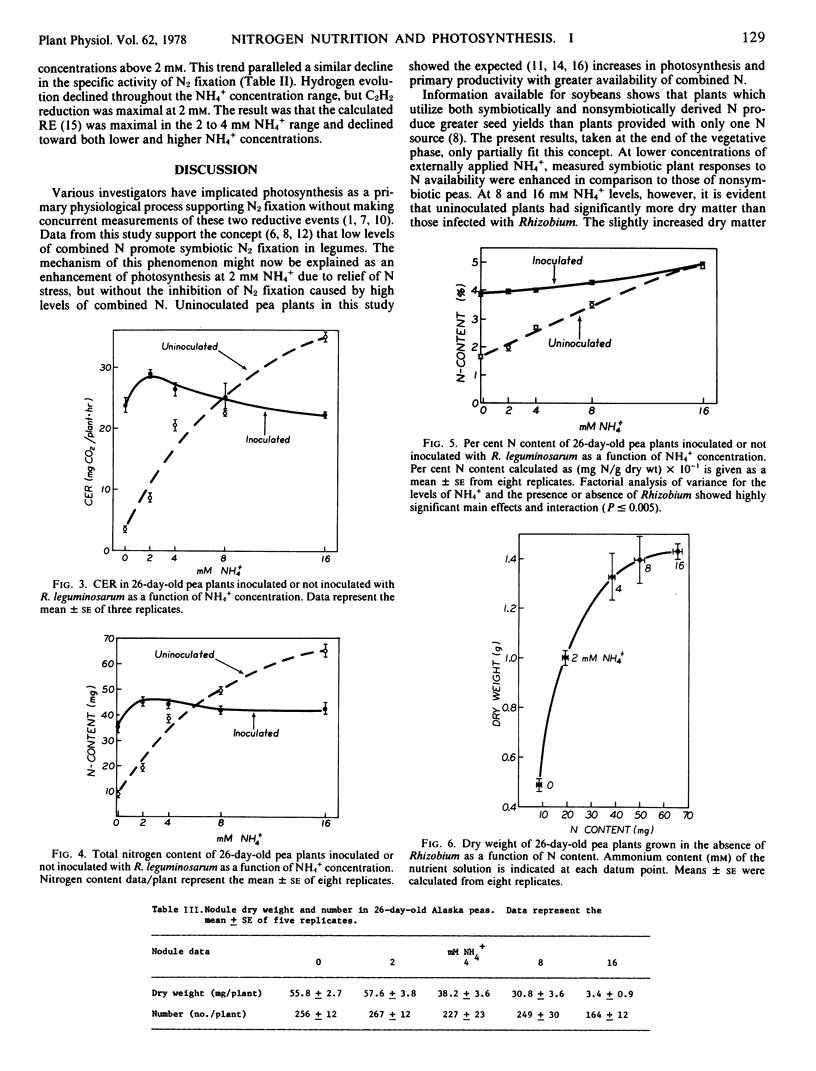
Photosynthesis, primary productivity, N content, and N2 fixation were determined as a function of applied NH4+ in peas (Pisum sativum L. cv. Alaska) which were inoculated or not inoculated with Rhizobium leguminosarum. Cabon dioxide exchange rate (CER) increased 10-fold, total N content 7-fold, and total dry weight 3-fold in 26-day-old uninoculated plants as applied NH4+ was increased from 0 to 16 millimolar. In inoculated plants of the same age CER and dry weight were maximal at 2 millimolar NH4+, and total N content increased between 0 and 2 millimolar NH4+ but did not change significantly with higher NH4+ applications. Per cent N content of uninoculated plants was significantly lower than that of inoculated plants except at the highest NH4+ concentration (16 millimolar). Symbiotic N2 fixation by inoculated plants was maximal in peas grown with 2 millimolar NH4+; and apparent relative efficiency of N2 fixation, calculated from C2H2 reduction and H2 evolution, was maximal in the 2 to 4 millimolar NH4+ concentration range. The capacity to fix N2 through the Rhizobium-legume symbiosis significantly enhanced the rate and efficiency of photosynthesis and plant N content when NH4+ concentration in the nutrient solution was below 8 millimolar. Above 8 millimolar NH4+ concentration uninoculated plants had greater CER, N content, and dry weight.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Abu-Shakra S. S., Phillips D. A. Interdependence of Nitrogen Nutrition and Photosynthesis in Pisum sativum L: II. Host Plant Response to Nitrogen Fixation by Rhizobium Strains. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):131–133. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Phillips D. A. Effect of Light Intensity on Efficiency of Carbon Dioxide and Nitrogen Reduction in Pisum sativum L. Plant Physiol. 1977 Dec;60(6):868–871. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.6.868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Phillips D. A. Ontogenetic Interactions between Photosynthesis and Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Legumes. Plant Physiol. 1977 Sep;60(3):419–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Havelka U. D. Nitrogen fixation research: a key to world food? Science. 1975 May 9;188(4188):633–643. doi: 10.1126/science.188.4188.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puritch G. S., Barker A. V. Structure and function of tomato leaf chloroplasts during ammonium toxicity. Plant Physiol. 1967 Sep;42(9):1229–1238. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.9.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



