Abstract
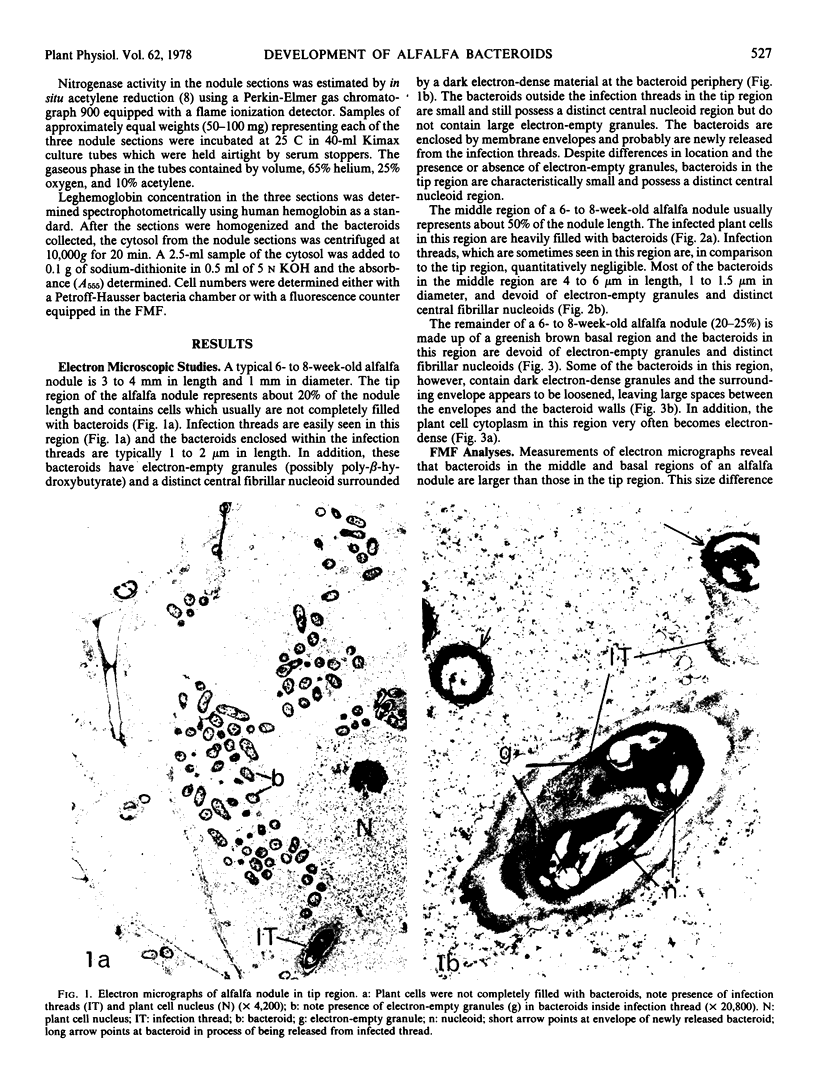
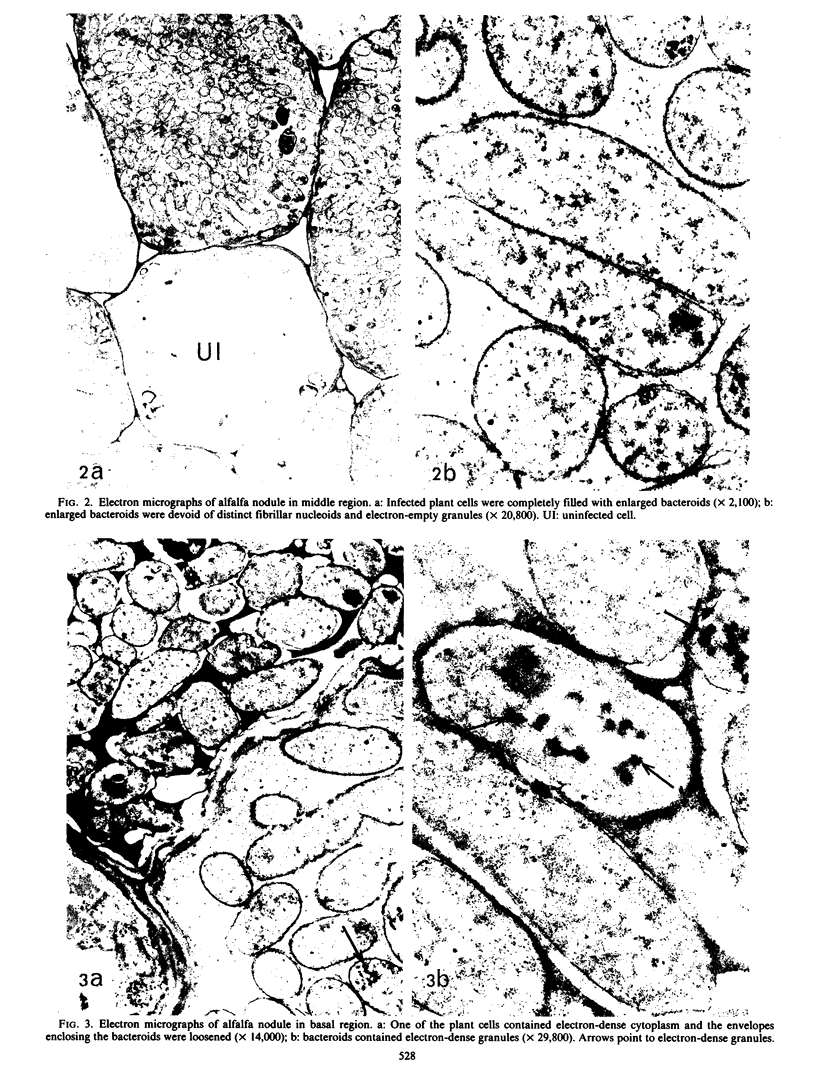
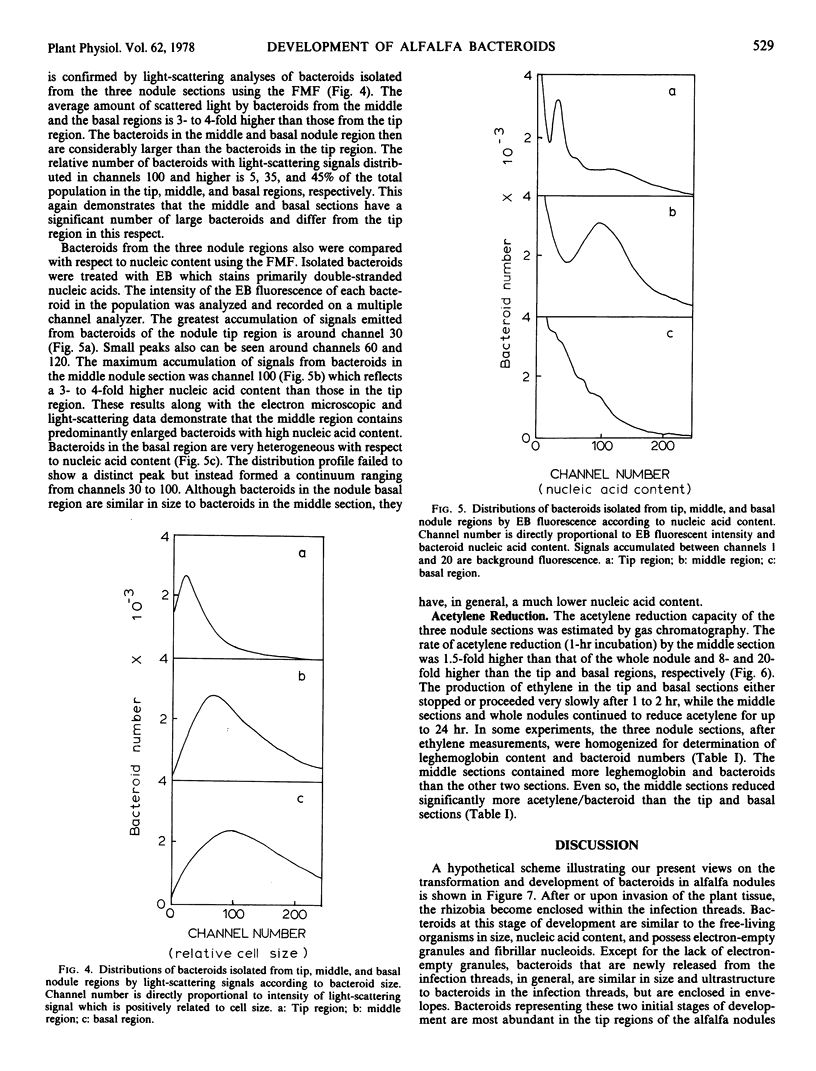
The morphology, acetylene reduction capability, and nucleic acid content of bacteroids in different regions of alfalfa (Medicago sativa var. Buffalo) nodules were studied by electron microscopy, gas chromatography, and laser flow microfluorometry, respectively. Bacteroids in the nodule tips were small (1 to 2.5 micrometers in length), had low nucleic acid content, and contained distinct central nucleoids. These bacteroids were comparatively inactive in acetylene reduction in situ. Bacteroids in the middle regions of alfalfa nodules were greatly enlarged (5 to 7 micrometers in length), had relatively high nucleic acid content, and did not possess central nucleoids. The bacteroids were very active in acetylene reduction. Bacteroids in the basal nodule region also were enlarged and without distinct nucleoid regions, but had relatively low nucleic acid content and low in situ acetylene-reducing activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ching T. M., Hedtke S. Isolation of bacteria, transforming bacteria, and bacteroids from soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 1977 Nov;60(5):771–774. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.5.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowles J. R., Evans H. J., Russell S. A. B12 coenzyme-dependent ribonucleotide reductase in Rhizobium species and the effects of cobalt deficiency on the activity of the enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1460–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1460-1465.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowles J. R., Evans H. J. Some properties of the ribonucleotide reductase from Rhizobium meliloti. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):770–778. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourret J. P., Fernandez-Arias H. Etude ultrastructurale et cytochimique de la différenciation des bactéroïdes de Rhizobium trifolii Dangeard dans les nodules de Trifolium repens L. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1169–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Cowles J. R., Oro J. Flow-microfluorometric analysis of Escherichia coli, Rhizobium meliloti, and Rhizobium japonicum at different stages of the growth cycle. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1165–1169. doi: 10.1139/m77-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Lee D., Cowles J. R. Comparison of nucleic acid content in populations of free-living and symbiotic Rhizobium meliloti by flow microfluorometry. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1156–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1156-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijnders L., Visser L., Aalbers A. M., Van Kammen A., Houwers A. A comparison of DNA from free living and endosymbiotic Rhizobium leguminosarum (strain PRE). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 4;414(2):206–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp J. A., Fulwyler M. J., Coulter J. R., Hiebert R. D., Horney J. L., Mullancy P. F. A new multiparameter separator for microscopic particles and biological cells. Rev Sci Instrum. 1973 Sep;44(9):1301–1310. doi: 10.1063/1.1686375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., Mahoney P. Preparation and Fractionation of Rhizobium Bacteroids by Zone Sedimentation through Sucrose Gradients. Plant Physiol. 1977 Nov;60(5):800–802. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.5.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]