Abstract
Vascular brain injury results in loss of structural and functional connectivity and leads to cognitive impairment. Its various manifestations, including microinfarcts, microhaemorrhages and white matter hyperintensities, result in microstructural tissue integrity loss and secondary neurodegeneration. Among these, tissue microstructural alteration is a relatively early event compared with atrophy along the aging and neurodegeneration continuum. Understanding its association with cognition may provide the opportunity to further elucidate the relationship between vascular health and clinical outcomes. Magnetic resonance elastography offers a non-invasive approach to evaluate tissue mechanical properties, providing a window into the microstructural integrity of the brain. This retrospective study evaluated brain stiffness as a potential biomarker for vascular brain injury and its role in mediating the impact of vascular dysfunction on cognitive impairment. Seventy-five participants from the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging underwent brain imaging using a 3T MR imager with a spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence for magnetic resonance elastography and T1- and T2-weighted pulse sequences. This study evaluated the effects of vascular biomarkers (white matter hyperintensities and cardiometabolic condition score) on brain stiffness using voxelwise analysis. Partial correlation analysis explored associations between brain stiffness, white matter hyperintensities, cardiometabolic condition and global cognition. Mediation analysis determined the role of stiffness in mediating the relationship between vascular biomarkers and cognitive performance. Statistical significance was set at P-values < 0.05. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance elastography stiffness for white matter hyperintensities and cardiometabolic condition was evaluated using receiver operator characteristic curves. Voxelwise linear regression analysis indicated white matter hyperintensities negatively correlate with brain stiffness, specifically in periventricular regions with high white matter hyperintensity levels. A negative association between cardiovascular risk factors and stiffness was also observed across the brain. No significant patterns of stiffness changes were associated with amyloid load. Global stiffness (µ) negatively correlated with both white matter hyperintensities and cardiometabolic condition when all other covariables including amyloid load were controlled. The positive correlation between white matter hyperintensities and cardiometabolic condition weakened and became statistically insignificant when controlling for other covariables. Brain stiffness and global cognition were positively correlated, maintaining statistical significance after adjusting for all covariables. These findings suggest mechanical alterations are associated with cognitive dysfunction and vascular brain injury. Brain stiffness significantly mediated the indirect effects of white matter hyperintensities and cardiometabolic condition on global cognition. Local cerebrovascular diseases (assessed by white matter hyperintensities) and systemic vascular risk factors (assessed by cardiometabolic condition) impact brain stiffness with spatially and statistically distinct effects. Global brain stiffness is a significant mediator between vascular disease measures and cognitive function, highlighting the value of magnetic resonance elastography-based mechanical assessments in understanding this relationship.
Keywords: vascular brain injury, cognitive impairment, magnetic resonance elastography, brain stiffness, dementia
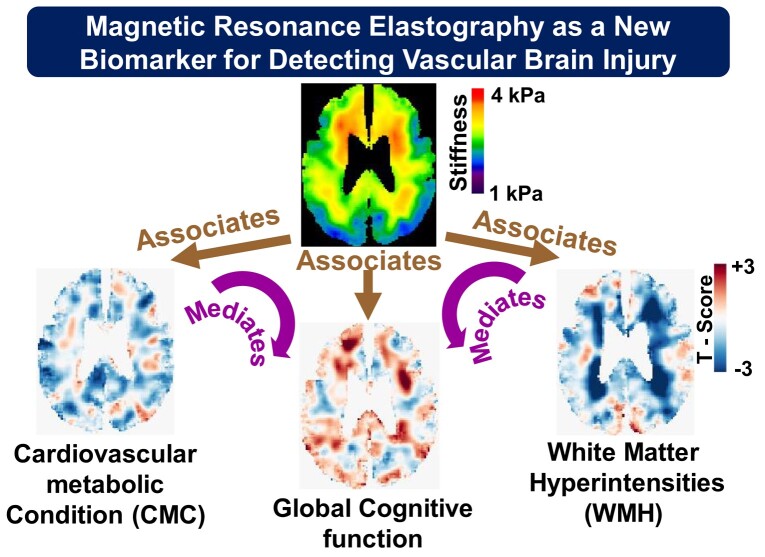
Pavuluri et al. investigated brain stiffness as a potential new biomarker for vascular brain injury, using magnetic resonance elastography. They found brain stiffness relates to vascular health and cognitive function, mediating the impact of white matter hyperintensities and cardiovascular conditions on cognition, suggesting its diagnostic potential for vascular cognitive impairments.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract.
Introduction
Vascular brain injury encompasses a wide range of disease processes related to structural alterations and dysfunction of the cerebral vasculature, ultimately impacting the cognitive function. These processes include clinically asymptomatic cerebral infarctions, white matter (WM) hyperintensities (WMH), microinfarctions and microbleeds, as well as more general changes in the brain such as blood–brain barrier dysfunction, impaired interstitial fluid drainage, altered cerebral blood flow and microstructural myelin injury.1 In epidemiological clinical–pathological studies of aging, cerebrovascular pathologies such as gross infarcts and moderate-to-severe atherosclerosis, arteriolosclerosis and cerebral amyloid angiopathy have been observed in 20–30% of brains examined.2,3 These pathologies are found to be independently associated with cognitive decline in late life.2 Irrespective of the underlying mechanism, the terms ‘vascular brain injury’ and ‘vascular cognitive impairment’ are commonly used to describe cerebrovascular diseases.4,5,6-10 Neurovascular dysfunction has been increasingly recognized to impact cognitive outcomes when coexistent with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathologies .11,12 Several studies have shown that vascular abnormality may be an early event in AD that promotes the cognitive decline and lowers the threshold of Aβ burden to cause clinically overt dementia.13,14 The heterogeneity of cerebrovascular disease and coexistence of proteinopathy, especially with AD, makes it challenging to elucidate the neuropathological substrates and mechanisms of vascular degeneration.14-16 Recent advances in neuroimaging, neuropathology, epidemiology and genetics have expedited the understanding of the relationship between vascular injury and cognitive function.
WMH, microbleeds, microinfarcts, cortical superficial siderosis, widened perivascular spaces and large infarcts are commonly used imaging markers to identify vascular brain injury.1 Of these, WMH are the most widely utilized17,18 markers of vascular changes in the brain, although these changes are reported to occur even before WMH become detectable.19 WMH may represent only the extreme end of a continuous spectrum of WM injury, creating a need for imaging approaches that can detect more subtle changes.17 Advanced and conventional MRI methods have been investigated for this application including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), arterial spin labelling, T2-weighted MRI and volumetric measurements and provide quantitative measures of WM microstructural integrity, cerebral blood flow and dilated perivascular spaces.1 Effective early diagnosis of vascular dysfunction is necessary in order to implement lifestyle modifications that delay the onset and the progression of various age-related dementia and stroke.20 Moreover, the relationship between current measures of vascular health and clinical outcomes remains probabilistic, reflecting an incomplete understanding of the mechanisms that link the two and suggesting that additional biomarkers may be beneficial in bridging the gap.
Over the last decade, magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) has proved to be a reliable non-invasive imaging technique to measure brain viscoelastic properties. Viscoelastic properties provide insights into microstructural integrity of brain tissue and reflect the rigidity and organization of neurons, axons and extracellular matrix (ECM).21-23 MRE has been applied to assess the viscoelastic changes in aging brain and several neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, multiple sclerosis and dementia with Lewy bodies.24-31 Most of these studies reported mechanical property differences in the whole brain and hippocampal, lobar and cortical grey matter regions.32-34 Recent advances in high-resolution MRE techniques have demonstrated that mechanical biomarkers are related to cognitive function,35-37 motivating further study on the use of MRE as a clinical biomarker in assessing aging and neurodegeneration. Viscoelastic properties, specifically damping ratio of hippocampal subfields, were shown to associate with aspects of memory in young adults.29,34 In later studies by the same group, brain stiffness and cognition were shown to relate in paediatric cerebral palsy and adolescent risk-taking tasks.38,39 Furthermore, a detailed assessment of the relation between hippocampal subfield stiffness and specific aspects of memory was reported.37 However, less is known about the relationship between mechanical properties and cognitive function in older adults and how this relationship is related to specific pathologies that can be measured by other modalities.
Therefore, the hypothesis of this study is that MRE-based biomarkers can provide a global indication of brain vascular health. To this end, we evaluated the association between brain stiffness with cerebrovascular disease, systemic vascular health, amyloid load and cognition. In addition, we assessed the mediatory role of stiffness as a marker of vascular disease and its impact on cognition.
Methods and materials
Study participants
After obtaining approval from the Mayo Clinic Institute Review Board and written informed consent, data were acquired in 75 participants including fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI, MRE examinations, PET, vascular health clinical record summary and cognitive assessments. Participants were enrolled from the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging (MCSA) and Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, including 44 cognitively unimpaired participants free of significant amyloid load and 31 along the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum with significant amyloid burden. MRE data of all the participants were acquired as a part of previous aging and AD studies.26,32
Data acquisition
Anatomic MRI
For assessing cerebrovascular disease, MRI data were obtained for each participant on a 3T GE MRI scanner using T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid gradient echo (MPRAGE) and FLAIR sequences to segment the WMH.40 Three-dimensional T1-weighted images were acquired with 1.05 mm in-plane resolution and 1.2 mm interslice spacing. Imaging parameters were repetition time (TR)/echo time (TE), 7.0/2.8 ms; 11° flip angle; inversion time, 400 ms; field of view (FOV), 27 cm; imaging matrix, 256 × 256; bandwidth, ±31.25 kHz; 1.75× array spatial sensitivity encoding technique acceleration; and 200 slice locations in sagittal orientation and superior–inferior frequency-encoding direction. Acquisition parameters for FLAIR MRI scans were TR = 11 s, TE = 147 ms, inversion time = 2250 ms, 256 × 192 matrix, 24 cm FOV and 3 mm slice thickness.
MRE imaging
MRE acquisitions were performed on the same 3T MR scanner (SIGNA Excite, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI) with an 8-channel receive-only head coil using a modified flow-compensated, spin-echo echo-planar imaging pulse sequence.41,42 Displacement images with 3 mm isotropic resolution were collected at 60 Hz vibration frequency for eight evenly spaced phase offsets in <7 min for each participant. MRE imaging parameters including TR = 3.6 s; TE = 62 ms; FOV = 24 cm; BW = ±250 kHz; 72 × 72 imaging matrix reconstructed to 80 × 80; frequency encoding in the right-to-left direction; 3× parallel imaging acceleration; 48 contiguous 3-mm-thick axial slices; ±x, ±y and ±z motion encoding gradients with amplitude of 4 G/cm; and duration of 18.2 ms were used on each side of the refocusing radio frequency pulse.
Amyloid PET imaging
Amyloid levels were assessed using PET imaging with Pittsburgh compound B (PiB), as described in detail previously.43 A global PET standardized uptake value ratio (SUVr) was calculated by averaging the median uptake in prefrontal, orbitofrontal, parietal, temporal, anterior and posterior cingulate and precuneus regions of interest (ROIs) weighted by voxel number. This value was then normalized to the cerebellar crus grey median using an in-house pipeline built with Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM12). To meet the model assumptions, amyloid deposition was initially log-transformed and subsequently standardized, such that a unit increase corresponds to 1 standard deviation (SD).
Cardiometabolic condition score
Systemic cardiovascular health was assessed from the clinical record as the summation of seven cardiovascular and metabolic conditions proposed by the US Department of Health and Human Services in 2010: hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, diabetes mellitus and stroke.44-47
Cognitive performance tests
All participants underwent a neuropsychological battery consisting of nine tests covering four cognitive domains: executive (Trail Making Test Part B and Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Revised Digit Symbol), language (Boston Naming Test and category fluency), memory [Wechsler Memory Scale—Revised Logical Memory II (delayed recall), Wechsler Memory Scale—Revised Visual Reproduction II (delayed recall) and Auditory Learning Verbal Test delayed recall] and visuospatial performance (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Revised Picture Completion and Block Design).48,49 Individual global Z-score was estimated from the z-transformation of the four-domain average Z-score including memory, language, attention and visuospatial performance. Analyses involving cognitive function were performed in a subset of 66 participants who completed all tests within 1 year of the MRE exam.
Image processing
T2-weighted FLAIR WMH were segmented with a previously described semiautomated in-house algorithm.40 In brief, the FLAIR and MPRAGE scans of all study participants were registered and aligned to a common template using a unified segmentation algorithm in SPM12.50 The FLAIR images were then masked using the WM mask from the MPRAGE image to remove non-brain tissue and voxels other than WMH. A semiautomated clustering technique was used to segment the WMH voxels on the FLAIR images, as described in a previous study.40 These custom masks were further reviewed and edited by trained analysts to remove any artefacts from the WMH volume. The final WMH measure used in this study was the log transform of the fraction of WMH volume relative to the total intracranial volume.
Stiffness maps were computed using neural network inversion (NNI),51 trained using data generated by a finite difference model of harmonic motion in a linear viscoelastic, inhomogeneous and isotropic material. We generated a set of 4500 displacement fields for training, each consisting of 64 × 64 × 64 cubes at 1.5 mm isotropic resolution, which were then downsampled to 3 mm resolution to match the acquired MRE resolution. Training patches of size 11 × 11 × 11 were then randomly selected from different locations within each field, and a randomly selected mask patch drawn from the in vivo brain masks was applied to each patch. Gaussian noise was then added to these data. Subsequently, the curl of the synthetic displacement patch was computed. All components of the computed curl were the inputs of the neural network, while the true stiffness value at the centre of the patch was the target. For in vivo data, phase unwrapping was performed on the MRE wave images using graph cuts.52 For use during inversion, tissue probability maps were computed in MRE space using a unified segmentation algorithm in SPM1250 with an in-house template.53,54 T1-weighted images of each participant were coregistered and resliced to the MRE magnitude image. During segmentation, both MRE and T1 spaces were used to reduce misregistration errors between the MRE data and the computed segmentations. A brain mask was generated indicating voxels with combined grey and white matter probabilities greater than that of CSF.51,52 A 22-region lobar atlas was utilized to divide the phase unwrapped brain into 6 distinct processing regions including cerebellum, brainstem, the union of the frontal lobes + deep grey matter and WM + parietal lobe + occipital lobe + corpus callosum (left and right hemispheres) and the union of the occipital parietal + temporal lobes + parietal lobes (left and right hemispheres). These regions were chosen to avoid inversion across the major dural folds (the cerebral falx, tentorium, that act as wave sources) and lateral sulcus (where CSF separates anatomically distinct regions and expands due to atrophy) as described previously.42 In each region, the region mask was applied, and we used previously described edge-aware methods of curl computation to remove longitudinal waves.55 Voxels with curl estimates that fell outside the mean plus or minus 3 times the SD in a 11 × 11 × 11 voxel sliding window were removed (∼4.6% voxels). The curl images were then scaled such that the maximum amplitude of the first harmonic in the entire volume was equal to 1 (to fall within the amplitude range of the NNI training data) and sent through the neural network inversion. Stiffness was estimated separately in the 6 subregions (specified above), and final maps were computed by union of these subregion estimates. For voxels present in two regions (such as the corpus callosum), the final stiffness map was assigned the mean value of the two estimates.
Statistical analysis
Five different statistical analyses were performed using in-house MATLAB (R2023a, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) and Python (version 3.10, Python Software Foundation) scripts. First, voxelwise linear modelling was performed to interrogate the topography of stiffness changes associated with each measure of vascular health. To this end, following spatial normalization of each participant’s stiffness map to template space,53 a linear model was fit to the data at each voxel with predictors including age, sex, WMH, cardiometabolic condition (CMC) and PiB. Voxels which are present in at least half of the participants were used for the voxel analysis. T-score maps of WMH, CMC and PiB effects on brain stiffness were computed.
For the remaining analyses, stiffness was summarized as the mean value in the cerebrum. To assess whether partial volume effects impact this summary measure, we used a previously published simulation data set to determine the correlations between estimated stiffness with both true stiffness and brain volume.51 A partial correlation analysis was then performed to assess the relationship between global brain stiffness (µ), WMH and CMC in the participants. In addition, the partial correlation between stiffness and global cognition was assessed in the subset of participants with neuropsychological assessments. Pairwise correlation between the residuals resulting from the linear regression between global brain stiffness (µ), WMH, CMC and cognition was calculated without controlling other variables, partial control for age and sex and full control of all covariables including amyloid load, respectively.
After finding statistically significant partial correlations between stiffness, vascular health measures and global cognition, we sought to determine if the vascular biomarkers played a mediating role in these correlations. Specifically, we conducted mediation analysis56,57 to investigate whether brain stiffness captured the influence of vascular disease on cognitive outcomes. Results were considered significant if the P-value was <0.05.
The diagnostic performance of brain stiffness for discriminating participants with WMH and CMC was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Area under the curve (AUC) was computed at various cut-off values for each WMH and CMC. At each cut-off, a logistic regression model was fit incorporating age, sex, stiffness, CMC and amyloid load as predictors. AUC was then computed using the estimated probabilities.
Results
Participant characteristics:
The demographics and characteristics of all the participants are presented in Table 1 including age at the time of MRE, brain stiffness, WMH, CMC and all the cognitive measures. Pearson correlations between the pairs of variables are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1.
Table 1.
Characteristics table of participants with mean (SD) listed for the continuous variables and count (%) for the categorical variables
| Number of participants = 75 | |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age (y) | 76.25 (8.7) |
| Males, no (%) | 53.3 |
| Cognitive measures | |
| MMSE | 27.31 (2.79) |
| Global cognition Z-score | −0.42 (1.41) |
| Memory | −0.45 (1.5) |
| Language | −0.51 (1.42) |
| Attention | −0.44 (1.46) |
| Visuospatial performance | −0.04 (1.10) |
| Amyloid load | |
| PiB-SUvr | 1.61 (0.46) |
| Vascular degeneration measures | |
| CMC | 2.25 (1.52) |
| WMH | 0.82 (0.99) |
| Global brain stiffness (k Pa) | 2.51 (0.16) |
Voxelwise analysis
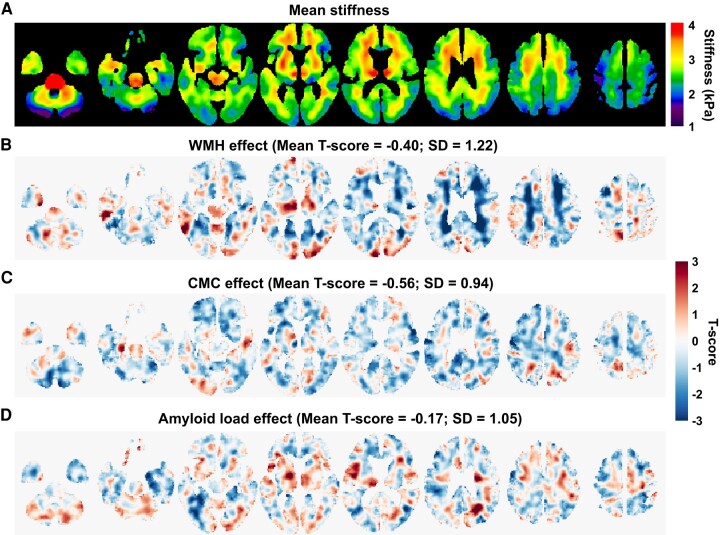
Estimated mean stiffness maps from the voxelwise modelling are presented in Fig. 1A. T-score maps of the WMH, CMC and PiB effects on stiffness are shown in Fig. 1B–D, respectively. From the T-score maps of WMH, a negative association of WMH-stiffness is observed, primarily in the periventricular voxels. Mean and SD of T-score over the entire brain are −0.40 and 1.22. On the other hand, the CMC effect (mean T-score = −0.56; SD = 0.94) is associated with widespread decreased stiffness with smaller amplitude effects. No clear patterns were observed between stiffness and amyloid load. The amyloid effect on stiffness across the entire brain exhibits a relatively smaller mean T-score of −0.17, with an SD of 1.05. We used amyloid load as a covariable in our further statistical analysis.
Figure 1.
Mean stiffness maps and voxelwise effects on stiffness. (A) Mean stiffness maps at different slice locations. (B), (C) and (D) are T-score maps of estimated voxelwise effects of WMH, CMC score and amyloid load (PiB-SUVr) on stiffness, respectively. Mean and SD of T-score distribution over the entire brain are indicated.
Evaluation of global stiffness estimates in simulation
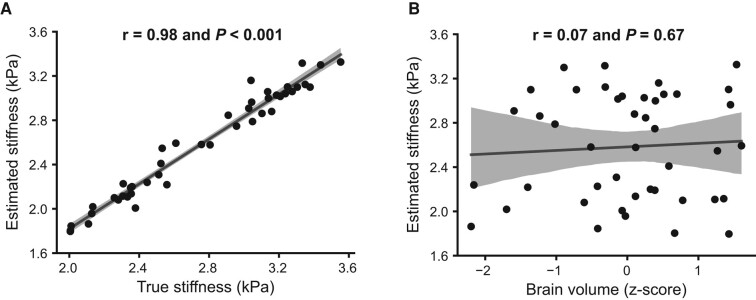
Correlations of estimated global stiffness with true stiffness and brain volume for the simulated data are given in Fig. 2A and B. Global stiffness estimates are highly correlated with the ground truth (r = 0.98, P < 0.001) but not significantly associated with total brain volume (r = 0.067, P = 0.67).
Figure 2.
Correlations of estimated stiffness with true stiffness and global brain volume. (A) The correlation between estimated global stiffness and true stiffness. (B) The correlation between estimated global stiffness and global brain volume.
Associations between brain stiffness and measures of vascular disease
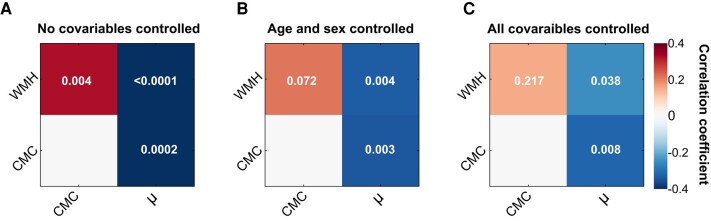
The results of the partial correlation analysis to assess the degree of association between the vascular biomarkers of interest are presented in Fig. 3. The degree of associations (ρ) between all possible pair of variables (µ, WMH, CMC) along with their statistical significance for three different scenarios, (i) without controlling for covariables, (ii) with control for age and sex and (iii) with control of all covariables, are shown in Fig. 3A–C, respectively. Stiffness is strongly correlated with WMH (ρ = −0.63; P < 0.0001), CMC (ρ = −0.41; P = 0.0002) and global cognition (ρ = 0.52; P < 0.0001) with no covariables controlled. The µ–WMH association is slightly reduced (ρ = −0.33; P = 0.004; ρ = −0.25; P = 0.038), and the statistical significance is preserved after controlling for age and sex and all covariables, respectively. When controlling for age and sex or for all covariables, we observed a slight reduction in the degree of association between stiffness and CMC (ρ = −0.34; P = 0.003; ρ = −0.31; P = 0.008, but the statistical significance is preserved. The degree of positive association between the stiffness and global cognition is reduced by half (ρ = 0.27; P = 0.036; ρ = 0.26; P = 0.046), but the statistical significance is preserved even after controlling for age, sex or all covariables. CMC and WMH are positively associated (ρ = 0.33; P = 0.004) without controlling for any covariables, and the statistical significance of this correlation is not preserved after controlling for the covariables.
Figure 3.
Partial correlation analysis. Pairwise associations between brain stiffness (µ), WMH load and CMC score. Associations are tested without controlling any covariables (A), controlling only age and sex (B) and controlling for all covariables (C). Statistical significance (P-values) of pairwise association is indicated in each box.
Partial correlation between age and stiffness is much stronger (ρ = −0.6004; P < 10–7), indicating a more substantial association. The correlation between sex and stiffness is negligible (ρ = −0.0007; P = 0.9956), indicating no significant association between sex and brain stiffness in this study.
Effect of vascular disease on cognition is explained by stiffness
The mediatory roles of stiffness, WMH and CMC in six paths with global cognition as an outcome are presented in Table 2. Each of the direct and indirect effects of the paths is assessed by controlling for age, sex, amyloid levels and the rest of the vascular biomarker covariables. Stiffness strongly mediates the effects of WMH on global cognition (T-score = −3.36; P = 0.0009) and CMC on global cognition (T-score = −2.10; P = 0.021). WMH mediates the effects of µ on global cognition (T-score = 2.44; P = 0.001). No statistically significant mediation role of WMH is observed for the relation between CMC and global cognition. There is no statistically significant mediating effect of CMC on the relationships between global cognition and µ and WMH.
Table 2.
Mediating roles of vascular biomarkers with global cognition as outcome
| Mediator | Path | T-score | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stiffness | WMH → global cognition | −3.36 | 0.0009 |
| CMC → global cognition | −2.10 | 0.021 | |
| WMH | µ → global cognition | 2.44 | 0.001 |
| CMC → global cognition | −0.53 | 0.879 | |
| CMC | µ → global cognition | 0.43 | 0.491 |
| WMH → global cognition | 0.11 | 0.410 |
Both direct and indirect effects are assessed by controlling for age, sex and the rest of the covariables.
Diagnostic accuracy of MRE stiffness for WMH and CMC
The ROC curves, as depicted in Supplementary Fig. 2, delineate the trade-off between sensitivity and specificity across a spectrum of thresholds for both WMH and CMC. For WMH, an AUC of 0.8 or above across the explored threshold range underscores a good diagnostic accuracy of MRE stiffness. On the other hand, an AUC of 0.7 or above for CMC denotes an acceptable level of diagnostic accuracy.
Discussion
Our findings demonstrate that brain stiffness exhibits non-overlapping sensitivity to cerebrovascular disease and systemic vascular health and provides a measure of the impact of vascular health on cognitive outcomes. Voxelwise modelling illustrates that the whole brain softens with the systemic cardiovascular risk factors, and brain stiffness is negatively associated with WMH where these lesions are most often present. Partial correlation analysis between the vascular biomarkers suggests that the negative association between stiffness and vascular disease measures (both WMH and CMC) is detected with or without controlling for all the covariables (age, sex, PiB, WMH and CMC). The positive association between CMC score and WMH is statistically significant only when no covariables are controlled. Partial correlation between stiffness and WMH is statistically significant with a reduced degree of association after including age, sex, PiB and CMC. Partial correlations of stiffness with WMH and CMC are relatively moderate compared with that with age. Softening of the brain with age26 can confound the relationship between stiffness and WMH. Also, the association of age58 and vascular risk factors13 with WMH can weaken the correlation between stiffness and WMH. Stiffness associations with the vascular markers are significant even after controlling for amyloid load. Taken together, the findings of mediation analysis indicate that stiffness strongly mediates the effects of vascular measures on cognitive outcomes. WMH mediates the µ versus global cognition relationship, whereas CMC did not demonstrate a significant mediatory role between these biomarkers. These findings along with the ROC analysis suggest MRE brain stiffness as a promising biomarker in the evaluation of cerebrovascular disease.
The observed negative association of stiffness with vascular disease burden may indicate myelin loss, inflammation or hypoperfusion.18,59,60 In WMH, previous studies indicate that altered perfusion occurs due to the compromise of blood flow in cerebral vasculature and of the neurovascular unit (NVU).61 This alteration in perfusion is notably associated with changes in cerebral blood flow, especially in individuals with cerebrovascular risk factors.62 Recent arterial spin labelling (ASL) studies have shown that perivascular perfusion alterations are associated with cerebral blood flow in the aging population.63 Such alterations in blood flow and perfusion can have profound effects on tissue health and integrity. Hetzer et al.64 reported the significant correlation between perfusion and MRE brain stiffness. Hetzer et al.64 provided evidence for this, reporting a significant correlation between perfusion and MRE brain stiffness. Consequently, the observed negative correlation between WMH and stiffness could be indicative of these perfusion disturbances influencing tissue microstructure. Areas with a higher burden of WMH might undergo altered perfusion, leading to tissue changes that manifest as reduced stiffness. It is worth mentioning that some studies have indicated that chronic cerebral hypoperfusion occurs even prior to the formation of WMH.65-67 Softer WMH brain regions may also simply represent inflammation. Studies have demonstrated that MRE can potentially uncover the mechanistic intricacies of neuroinflammation, making it a viable alternative to gadolinium-based contrast MRI.68 In the context of multiple sclerosis with WM lesions, recent studies involving both mouse models and human patients indicated that brain tissue softens as neuroinflammatory processes progress, revealing insights into acute inflammatory activity and the severity of the disease.30,69 Enhancement of perivascular spaces and detachment of astrocyte endfeet may be potential mechanisms that contribute to weaker neuronal–vascular network connections and, consequently, result in reduced tissue stiffness.68,70 Hypoperfusion induces the activation and degeneration of astrocytes, which ultimately leads to fibrosis of the ECM.71 Sweeney et al.11 described that cerebral hypoperfusion may disrupt the NVU and the integrity of the blood–brain barrier (BBB). This in turn contributes to demyelination, decreased synaptic plasticity and impaired brain function even before structural damage occurs.72-74 Eventually, the uncoupling of the NVU is accompanied by mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, neuronal death, changes in cerebral glucose metabolism and brain tissue atrophy.75,76 In this study, we also report the associations of brain stiffness with global cognitive performance, supporting the potential of mechanical biomarkers to help correlate with the cognitive outcomes during normal aging and in age-related disorders. Previous studies from Johnson et al. reported a significant negative correlation of memory performance with damping ratio of hippocampus and subfields in young adults.36,77,78 In a healthy aging population, they observed left hippocampal damping ratio is negatively associated with episodic memory performance.79 Our current study assesses the relation between brain stiffness and global cognition in an older cohort with a relatively wide range of stiffness. Our findings are in line with the recent studies by the same group37 where the relation between hippocampal subfield stiffness and cognitive function is reported in the healthy aging population.
Various cross-sectional and longitudinal studies have reported that global cognition change is strongly associated with brain grey matter volume change, with independent effects of global grey matter change and specific temporal lobe grey matter change.80,81 Depending on the processing methods used, partial volume effects can bias MRE-based stiffness measurements, especially in an older age population as shown in this study.55 This study utilized a neural network inversion designed to mitigate these partial volume effects by segmenting out displacement measurements from outside the brain prior to inversion and training the algorithm to estimate stiffness despite these missing measurements.51 Using the simulated data set previously published,51 we measured that global stiffness estimates were highly correlated with the ground truth but not significantly associated with total brain volume. On this basis, we expect that the findings reported here reflect primarily alterations in the brain parenchyma and not atrophy-related bias.
This study is a preliminary investigation to understand the association between vascular health, cognition and brain stiffness. The statistical analyses here are limited by the sample size. With additional data, a more sensitive region of interest for brain stiffness could be developed in an independent data set to improve sensitivity to the vascular measures. Although multiple markers of vascular health were explored, the impact of microinfarcts and microbleeds were not considered and will be the subject of future investigation. The coexistence of vascular and amyloid pathologies and the mechanisms linking these to cognitive decline needs further investigation.
Conclusions
Strong associations of vascular markers and global cognitive function with stiffness establish the potential value of viscoelastic properties in understanding the vascular cognitive impairment. A statistically significant mediating role of stiffness on the indirect effects of WMH and CMC on cognition indicates the possible utilization of tissue mechanical alterations in probing microstructural damage and cognition decline. These results motivate a future longitudinal study exploring the mechanisms linking stiffness to cognitive decline in aging and dementia.
Supplementary Material
Contributor Information
KowsalyaDevi Pavuluri, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
John Huston, III, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Richard L Ehman, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Armando Manduca, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA; Department of Physiology and Biomedical Engineering, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Clifford R Jack, Jr, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Matthew L Senjem, Department of Information Technology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Prashanthi Vemuri, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Matthew C Murphy, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
Supplementary material
Supplementary material is available at Brain Communications online.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH): EB 027064, EB 001981, U01 NS100620, P30 AG062677, U01 AG006786, U19 AG63911, U01 AG045390, U54 NS092089 and R01 AG076636.
Competing interests
This research has been reviewed by the Mayo Clinic Conflict of Interest Review Board and is being conducted in compliance with Mayo Clinic Conflict of Interest policies. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests. Mayo Clinic, J.H., R.L.E., A.M. and M.C.M. have a financial interest in MRE technology.
Data availability
Clinical imaging data used in this study has not been made available to protect patient confidentiality in accordance with the Mayo Clinic institutional review board policies. In-house data processing and analysis scripts are available upon reasonable request after the completion of data sharing agreement.
References
- 1. Vemuri P, Decarli C, Duering M. Imaging markers of vascular brain health: Quantification, clinical implications, and future directions. Stroke. 2022;53:416–426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Boyle PA, Yu L, Wilson RS, Leurgans SE, Schneider JA, Bennett DA. Person-specific contribution of neuropathologies to cognitive loss in old age. Ann Neurol. 2018;83:74–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Greenberg SM. Vascular contributions to brain health: Cross-cutting themes. Stroke. 2022;53:391–393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Dichgans M, Leys D. Vascular cognitive impairment. Circ Res. 2017;120:573–591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Biesbroek JM, Biessels GJ. Diagnosing vascular cognitive impairment: Current challenges and future perspectives. Int JStroke. 2023;18:36–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wolters FJ, Ikram MA. Epidemiology of vascular dementia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39:1542–1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cipollini V, Troili F, Giubilei F. Emerging biomarkers in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia: From pathophysiological pathways to clinical application. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kalaria RN, Maestre GE, Arizaga R, et al. Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in developing countries: Prevalence, management, and risk factors. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:812–826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. van der Flier WM, Skoog I, Schneider JA, et al. Vascular cognitive impairment. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Farooqui AA. Chapter 5—Neurochemical aspects of vascular dementia. In: Farooqui AA, eds. Molecular mechanisms of dementia. Academic Press; 2019:151–181. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Sweeney MD, Kisler K, Montagne A, Toga AW, Zlokovic BV. The role of brain vasculature in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1318–1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Raghavan S, Przybelski SA, Reid RI, et al. White matter damage due to vascular, tau, and TDP-43 pathologies and its relevance to cognition. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022;10:16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. O'Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): A case-control study. Lancet (London, England). 2010;376:112–123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Attems J, Jellinger KA. The overlap between vascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease–Lessons from pathology. BMC Med. 2014;12:206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Chui HC, Ramirez-Gomez L. Clinical and imaging features of mixed Alzheimer and vascular pathologies. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015;7:21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Gold G, Giannakopoulos P, Herrmann FR, Bouras C, Kövari E. Identification of Alzheimer and vascular lesion thresholds for mixed dementia. Brain. 2007;130:2830–2836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Prins ND, Scheltens P. White matter hyperintensities, cognitive impairment and dementia: An update. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11:157–165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Vemuri P, Graff-Radford J, Lesnick TG, et al. White matter abnormalities are key components of cerebrovascular disease impacting cognitive decline. Brain Commun. 2021;3:fcab076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Nasel C, Boubela R, Kalcher K, Moser E. Normalised time-to-peak-distribution curves correlate with cerebral white matter hyperintensities—Could this improve early diagnosis? J Cerebral Blood Flow Metabol. 2017;37:444–455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Kalaria RN. Vascular basis for brain degeneration: Faltering controls and risk factors for dementia. Nutr Rev. 2010;68(Suppl 2):S74–S87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Tyler WJ. The mechanobiology of brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:867–878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Schregel K, EWn T, Garteiser P, et al. Demyelination reduces brain parenchymal stiffness quantified in vivo by magnetic resonance elastography. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2012;109:6650–6655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Hall CM, Moeendarbary E, Sheridan GK. Mechanobiology of the brain in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;53:3851–3878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Sack I, Beierbach B, Wuerfel J, et al. The impact of aging and gender on brain viscoelasticity. NeuroImage. 2009;46:652–657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Hiscox LV, Schwarb H, McGarry MDJ, Johnson CL. Aging brain mechanics: Progress and promise of magnetic resonance elastography. NeuroImage. 2021;232:117889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Arani A, Murphy MC, Glaser KJ, et al. Measuring the effects of aging and sex on regional brain stiffness with MR elastography in healthy older adults. NeuroImage. 2015;111:59–64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Murphy MC, Huston J III, Jack CR Jr, et al. Decreased brain stiffness in Alzheimer’s disease determined by magnetic resonance elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:494–498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Huston J III, Murphy MC, Boeve BF, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of frontotemporal dementia. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;43:474–478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Sandroff BM, Johnson CL, Motl RW. Exercise training effects on memory and hippocampal viscoelasticity in multiple sclerosis: A novel application of magnetic resonance elastography. Neuroradiology. 2017;59:61–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Wuerfel J, Paul F, Beierbach B, et al. MR-elastography reveals degradation of tissue integrity in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage. 2010;49:2520–2525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Pavuluri K, Huston J III, Ehman RL, et al. Regional brain stiffness analysis of dementia with Lewy bodies. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022;55:1907–1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Murphy MC, Jones DT, Jack CR, et al. Regional brain stiffness changes across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. NeuroImage Clin. 2016;10:283–290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Hiscox LV, Johnson CL, McGarry MDJ, et al. Mechanical property alterations across the cerebral cortex due to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun. 2020;2(1):fcz049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Delgorio PL, Hiscox LV, Daugherty AM, et al. Effect of aging on the viscoelastic properties of hippocampal subfields assessed with high-resolution MR elastography. Cerebral Cortex (New York, NY: 1991). 2021;31:2799–2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Johnson CL, Schwarb H, DJM M, et al. Viscoelasticity of subcortical gray matter structures. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016;37:4221–4233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Johnson CL, Schwarb H, Horecka KM, et al. Double dissociation of structure-function relationships in memory and fluid intelligence observed with magnetic resonance elastography. NeuroImage. 2018;171:99–106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Delgorio PL, Hiscox LV, Daugherty AM, et al. Structure–function dissociations of human hippocampal subfield stiffness and memory performance. J Neurosci. 2022;42:7957–7968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. McIlvain G, Tracy JB, Chaze CA, et al. Brain stiffness relates to dynamic balance reactions in children with cerebral palsy. J Child Neurol. 2020;35:463–471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. McIlvain G, Clements RG, Magoon EM, Spielberg JM, Telzer EH, Johnson CL. Viscoelasticity of reward and control systems in adolescent risk taking. NeuroImage. 2020;215:116850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Graff-Radford J, Arenaza-Urquijo EM, Knopman DS, et al. White matter hyperintensities: Relationship to amyloid and tau burden. Brain. 2019;142:2483–2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Muthupillai R, Lomas DJ, Rossman PJ, Greenleaf JF, Manduca A, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science (New York, NY). 1995;269:1854–1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Murphy MC, Cogswell PM, Trzasko JD, et al. Identification of normal pressure hydrocephalus by disease-specific patterns of brain stiffness and damping ratio. Invest Radiol. 2020;55:200–208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Jack CR Jr, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, et al. Defining imaging biomarker cut points for brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13:205–216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Vemuri P, Lesnick TG, Przybelski SA, et al. Age, vascular health, and Alzheimer disease biomarkers in an elderly sample. Ann Neurol. 2017;82:706–718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Rocca WA, Boyd CM, Grossardt BR, et al. Prevalence of multimorbidity in a geographically defined American population: Patterns by age, sex, and race/ethnicity. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:1336–1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Rocca WA, Gazzuola Rocca L, Smith CY, et al. Bilateral oophorectomy and accelerated aging: Cause or effect?. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72:1213–1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Vassilaki M, Aakre JA, Cha RH, et al. Multimorbidity and risk of mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:1783–1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Roberts RO, Geda YE, Knopman DS, et al. The Mayo Clinic Study of Aging: Design and sampling, participation, baseline measures and sample characteristics. Neuroepidemiology. 2008;30:58–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Petersen RC, Roberts RO, Knopman DS, et al. Prevalence of mild cognitive impairment is higher in men. The Mayo Clinic Study of Aging. Neurology. 2010;75:889–897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Unified segmentation. NeuroImage. 2005;26:839–851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Vemuri P, Lesnick TG, Przybelski SA, et al. Association of lifetime intellectual enrichment with cognitive decline in the older population. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:1017–1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Bioucas-Dias JM, Valadao G. Phase unwrapping via graph cuts. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2007;16:698–709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Schwarz CG, Gunter JL, Ward CP, et al. [P2–415]: The mayo clinic adult lifespan template: Better quantification across the lifespan. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13:P792–P792. [Google Scholar]
- 54. Schwarz CG, Gunter JL, Wiste HJ, et al. A large-scale comparison of cortical thickness and volume methods for measuring Alzheimer’s disease severity. NeuroImage Clin. 2016;11:802–812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Murphy MC, Huston J III, Jack CR Jr, et al. Measuring the characteristic topography of brain stiffness with magnetic resonance elastography. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Wager TD, Davidson ML, Hughes BL, Lindquist MA, Ochsner KN. Prefrontal-subcortical pathways mediating successful emotion regulation. Neuron. 2008;59:1037–1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Wager TD, Waugh CE, Lindquist M, Noll DC, Fredrickson BL, Taylor SF. Brain mediators of cardiovascular responses to social threat: Part I: Reciprocal dorsal and ventral sub-regions of the medial prefrontal cortex and heart-rate reactivity. NeuroImage. 2009;47:821–835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM. Incidence and prevalence of dementia associated with transient ischaemic attack and stroke: Analysis of the population-based Oxford Vascular Study. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:248–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Hase Y, Horsburgh K, Ihara M, Kalaria RN. White matter degeneration in vascular and other ageing-related dementias. J Neurochem. 2018;144:617–633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Ihara M, Polvikoski TM, Hall R, et al. Quantification of myelin loss in frontal lobe white matter in vascular dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119:579–589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Rundek T, Tolea M, Ariko T, Fagerli EA, Camargo CJ. Vascular cognitive impairment (VCI). Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19:68–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Bahrani AA, Powell DK, Yu G, Johnson ES, Jicha GA, Smith CD. White matter hyperintensity associations with cerebral blood flow in elderly subjects stratified by cerebrovascular risk. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26:779–786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Liu S, Hou B, You H, et al. The association between perivascular spaces and cerebral blood flow, brain volume, and cardiovascular risk. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:599724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Hetzer S, Birr P, Fehlner A, et al. Perfusion alters stiffness of deep gray matter. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;38:116–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Poh L, Sim WL, Jo D-G, et al. The role of inflammasomes in vascular cognitive impairment. Mol Neurodegener. 2022;17:4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Kawamura J, Meyer JS, Terayama Y, Weathers S. Leukoaraiosis correlates with cerebral hypoperfusion in vascular dementia. Stroke. 1991;22:609–614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Appelman AP, van der Graaf Y, Vincken KL, Mali WP, Geerlings MI. Combined effect of cerebral hypoperfusion and white matter lesions on executive functioning—The SMART-MR study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2010;29:240–247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Wang S, Millward JM, Hanke-Vela L, et al. MR elastography-based assessment of matrix remodeling at lesion sites associated with clinical severity in a model of multiple sclerosis. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Silva RV, Morr AS, Mueller S, et al. Contribution of tissue inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption to brain softening in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:701308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Fehlner A, Behrens JR, Streitberger KJ, et al. Higher-resolution MR elastography reveals early mechanical signatures of neuroinflammation in patients with clinically isolated syndrome. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;44:51–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Rosenberg Gary A. Extracellular matrix inflammation in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Clin Sci. 2017;131:425–437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Ruitenberg A, den Heijer T, Bakker SL, et al. Cerebral hypoperfusion and clinical onset of dementia: The Rotterdam Study. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:789–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Bell RD, Winkler EA, Sagare AP, et al. Pericytes control key neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain and during brain aging. Neuron. 2010;68:409–427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:347–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Chen B, Friedman B, Cheng Q, et al. Severe blood-brain barrier disruption and surrounding tissue injury. Stroke. 2009;40:e666–e674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Marlatt MW, Lucassen PJ, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X. Alzheimer’s disease: Cerebrovascular dysfunction, oxidative stress, and advanced clinical therapies. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;15:199–210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Schwarb H, Johnson CL, McGarry MDJ, Cohen NJ. Medial temporal lobe viscoelasticity and relational memory performance. NeuroImage. 2016;132:534–541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Schwarb H, Johnson CL, Daugherty AM, et al. Aerobic fitness, hippocampal viscoelasticity, and relational memory performance. NeuroImage. 2017;153:179–188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Hiscox LV, Johnson CL, McGarry MDJ, et al. Hippocampal viscoelasticity and episodic memory performance in healthy older adults examined with magnetic resonance elastography. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020;14:175–185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Fletcher E, Gavett B, Harvey D, et al. Brain volume change and cognitive trajectories in aging. Neuropsychology. 2018;32:436–449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Armstrong NM, An Y, Shin JJ, et al. Associations between cognitive and brain volume changes in cognitively normal older adults. NeuroImage. 2020;223:117289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Clinical imaging data used in this study has not been made available to protect patient confidentiality in accordance with the Mayo Clinic institutional review board policies. In-house data processing and analysis scripts are available upon reasonable request after the completion of data sharing agreement.