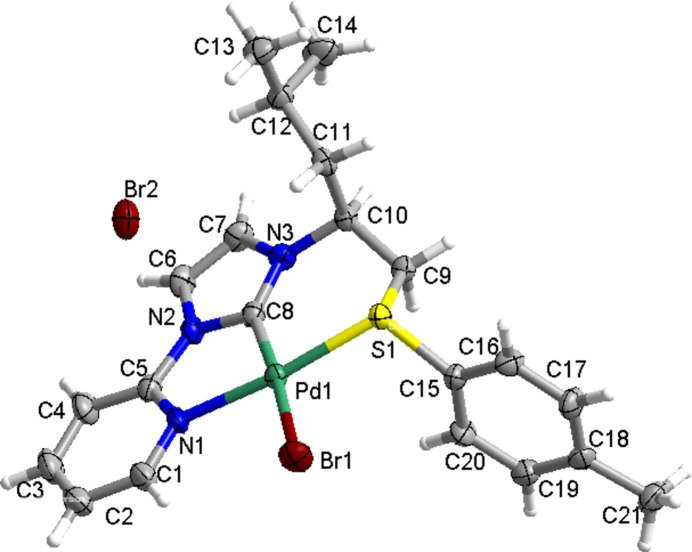
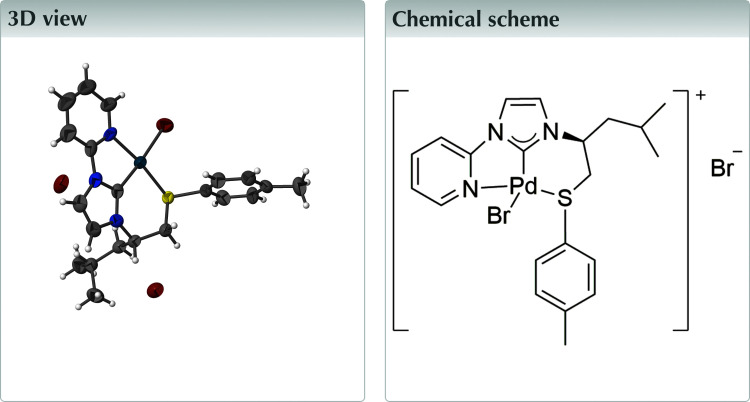
The molecule of the title NCNHCS pincer N-heterocyclic carbene palladium(II) complex, [PdBr(C21H25N3S)]Br, exhibits a slightly distorted square-planar coordination at the palladium(II) atom, with the five-membered chelate ring nearly planar. The six-membered chelate ring adopts an envelope conformation. Upon chelation, the sulfur atom becomes a stereogenic centre with an RS configuration induced by the chiral carbon of the precursor imidazolium salt.
Keywords: crystal structure, N-heterocyclic carbene, palladium(II), hydrogen bonds
Abstract
The molecule of the title NCNHCS pincer N-heterocyclic carbene palladium(II) complex, [PdBr(C21H25N3S)]Br, exhibits a slightly distorted square-planar coordination at the palladium(II) atom, with the five-membered chelate ring nearly planar. The six-membered chelate ring adopts an envelope conformation. Upon chelation, the sulfur atom becomes a stereogenic centre with an RS
configuration induced by the chiral carbon of the precursor imidazolium salt. There are intramolecular C—H⋯Br—Pd hydrogen bonds in the structure. The two interstitial Br atoms, as the counter-anion of the structure, are both located on crystallographic twofold axes and are connected to the complex cations via C—H⋯·Br hydrogen bonds.
Structure description
N-Heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) have been widely used as ancillary ligands in coordination chemistry and organic catalysis due to their characteristic electronic properties and easy structural modification (Hopkinson et al., 2014 ▸; Gardiner et al., 2018 ▸). Introduction of a coordinating heteroatom functional group to the N-atom substituents of the NHCs leads to the formation of a potentially chelating ligand, and facilitates the formation of stable pincer NHC–metal complexes that can possess catalytic activities. Metal complexes containing heteroatom donors, such as P, N, O and S, have been synthesized, characterized and employed extensively as catalysts for a variety of organic transformations (Ahrens et al., 2006 ▸; Bierenstiel & Cross, 2011 ▸; Meyer et al., 2012 ▸; Peris & Crabtree, 2004 ▸). Our group has investigated the synthesis and catalytic performance of a series of chelating NHC–palladium complexes derived from natural amino alcohols (Yang et al., 2015 ▸, 2023 ▸; Yang, Zhang, Xiao & Mao, 2016 ▸; Yang, Zhang, Yuan et al., 2016 ▸; Meng et al., 2022 ▸). As part of our work on the study of NHC–metal complexes containing heteroatom-functionalized N-atom substituents, we present here the crystal structure of the title NCNHCS pincer NHC palladium(II) complex (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title complex, shown with 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
In the title complex, the palladium(II) atom is coordinated to C8, N1, Br1, and S1, resulting in a slightly distorted square-planar coordination. The Pd1—C8, Pd1—N1, Pd1—Br1 and Pd1—S1 bond lengths are 1.946 (8), 2.093 (6), 2.4663 (10), and 2.2603 (17) Å, respectively. The five-membered chelate ring (C8/Pd1/N1/C5/N2) is almost planar, with Pd1—N1—C5—N2 and C5—N2—C8—Pd1 torsion angles of −0.3 (8) and 2.0 (8)°, respectively. The six-membered chelate ring (C8/Pd1/S1/C9/C10/N3) adopts an envelope conformation with puckering parameters of θ = 51.6 (6)° and φ= 125.4 (8)°, which are close to the expected values for this conformation (Boeyens, 1978 ▸).
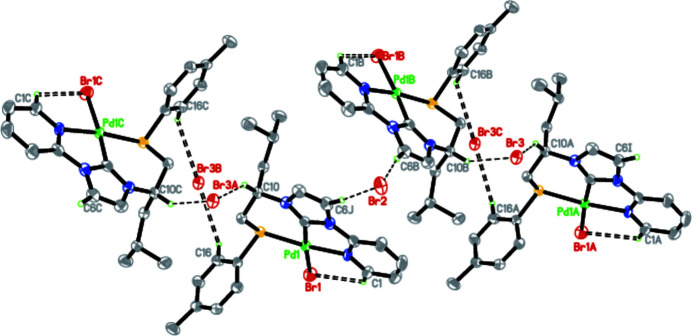
Upon chelation, the sulfur atom becomes a stereogenic centre, resulting in the formation of molecules with an RS configuration. This can be attributed to the chiral induction of the chiral carbon C(5), which retains the same S configuration as in the precursor imidazolium salt. The environment of the sulfur atoms of the molecule is approximately triangular pyramidal. This is indicated by the bond angles C9—S1—Pd1, C15—S1—Pd1 and C9—S1–15, which were found to be 106.2 (2), 111.0 (2), and 97.2 (3)°, respectively, with an average of 105.0°. In the crystal, intra- and intermolecular C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds occur (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1⋯Br1 | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.510 (10) | 124 |
| C6—H6⋯Br2i | 0.93 | 2.74 | 3.661 (9) | 173 |
| C10—H10⋯Br3 | 0.98 | 2.78 | 3.624 (7) | 144 |
| C16—H16⋯Br3ii | 0.93 | 3.11 | 3.742 (7) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
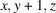 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 .
.
Figure 2.
The C—H⋯Br interactions in the structure.
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of (S)-N-(4-methyl-1-(p-tolylthio)pentan-2-yl)-N′-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-imidazolium bromide (1.0 mmol, 0.43 g), PdCl2 (1.0 mmol, 0.18 g), NaOAc (1.0 mmol, 0.10 g), and NaBr (4 mmol, 0.41 g) in CH3CN (10 ml) was heated at 80°C for 24 h, and then the volatiles were evaporated. Purification of the residue by column chromatography (silica gel, CH2Cl2/MeOH 15/1 ∼1:1, v/v) produced the title complex as a yellow solid (0.32 g, 60%). Crystallization of the solid from CH3CN afforded the title complex as yellow crystals, m.p. 269–277°C. HR—MS (ESI) m/z calculated for C21H25BrN3PdS+ (M – Br)+ 535.9987, found 535.9998. F T–IR (ATR mode): ν = 3388, 3012, 2910, 1681, 1496, 1376, 1316, 1144, 1014, 914, 806, 780, 738, 666, 448 cm−1. [α]15 589: 8.3 (1.00, CH2Cl2).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [PdBr(C21H25N3S)]Br |
| M r | 617.72 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2 |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 25.8993 (7), 6.6206 (2), 13.4938 (3) |
| β (°) | 96.425 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 2299.23 (12) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 11.52 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.14 × 0.1 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Xcalibur, Eos, Gemini |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2023 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.419, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 20069, 3950, 3693 |
| R int | 0.050 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.611 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.030, 0.072, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3950 |
| No. of parameters | 258 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.36, −0.38 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 1371 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.030 (7) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003602/zl4070sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003602/zl4070Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 2312031
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms Y. Zhu for technical assistance.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| [PdBr(C21H25N3S)]Br | F(000) = 1216 |
| Mr = 617.72 | Dx = 1.785 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 25.8993 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 8595 reflections |
| b = 6.6206 (2) Å | θ = 4.5–70.1° |
| c = 13.4938 (3) Å | µ = 11.52 mm−1 |
| β = 96.425 (2)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 2299.23 (12) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.14 × 0.1 × 0.03 mm |
Data collection
| Xcalibur, Eos, Gemini diffractometer | 3950 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube, Enhance (Cu) X-ray Source | 3693 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.050 |
| Detector resolution: 16.2312 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 70.5°, θmin = 3.4° |
| ω scans | h = −31→31 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2023) | k = −8→6 |
| Tmin = 0.419, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −16→16 |
| 20069 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Least-squares matrix: full | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.033P)2 + 2.7656P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| wR(F2) = 0.072 | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| S = 1.04 | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 3950 reflections | Extinction correction: SHELXL-2014/7 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 258 parameters | Extinction coefficient: 0.00034 (4) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1371 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: −0.030 (7) |
| Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. The H atoms on the carbons were positioned geometrically and constrained to ride on their parent atoms. C—H bond distances were constrained to 0.93 Å for aromatic and alkene C—H moieties, and to 0.98, 0.91 and 0.96 Å for aliphatic C—H, CH2 and CH3 moieties, respectively. Methyl CH3 H atoms were allowed to rotate but not to tip to best fit the experimental electron density. Uiso(H) values were set to a multiple of Ueq(C) with 1.5 for CH3, and 1.2 for C—H and CH2 units, respectively. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pd1 | 0.37598 (2) | 0.06095 (8) | 0.28758 (3) | 0.03701 (15) | |
| S1 | 0.40637 (6) | −0.0902 (3) | 0.15555 (12) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.3574 (2) | 0.2356 (11) | 0.4079 (4) | 0.0443 (16) | |
| N2 | 0.4255 (2) | 0.4165 (10) | 0.3607 (4) | 0.0413 (14) | |
| N3 | 0.4680 (2) | 0.3203 (10) | 0.2419 (4) | 0.0381 (13) | |
| C1 | 0.3187 (3) | 0.2026 (16) | 0.4635 (6) | 0.057 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.2972 | 0.0912 | 0.4501 | 0.069* | |
| C2 | 0.3100 (4) | 0.3329 (18) | 0.5414 (7) | 0.069 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.2832 | 0.3085 | 0.5804 | 0.083* | |
| C3 | 0.3414 (4) | 0.4954 (18) | 0.5587 (7) | 0.074 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.3359 | 0.5840 | 0.6099 | 0.089* | |
| C4 | 0.3813 (3) | 0.5318 (18) | 0.5021 (6) | 0.061 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.4033 | 0.6422 | 0.5144 | 0.073* | |
| C5 | 0.3873 (3) | 0.3975 (13) | 0.4263 (5) | 0.0450 (18) | |
| C6 | 0.4650 (3) | 0.5562 (15) | 0.3556 (5) | 0.0478 (16) | |
| H6 | 0.4719 | 0.6686 | 0.3963 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.4911 (3) | 0.4978 (13) | 0.2812 (6) | 0.049 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.5195 | 0.5632 | 0.2593 | 0.059* | |
| C8 | 0.4280 (2) | 0.2737 (13) | 0.2911 (5) | 0.0393 (16) | |
| C9 | 0.4434 (2) | 0.1033 (12) | 0.0964 (5) | 0.0415 (18) | |
| H9A | 0.4574 | 0.0439 | 0.0394 | 0.050* | |
| H9B | 0.4199 | 0.2108 | 0.0720 | 0.050* | |
| C10 | 0.4877 (3) | 0.1938 (11) | 0.1649 (5) | 0.0366 (15) | |
| H10 | 0.5072 | 0.2821 | 0.1242 | 0.044* | |
| C11 | 0.5255 (2) | 0.0360 (13) | 0.2122 (5) | 0.0397 (16) | |
| H11A | 0.5325 | −0.0599 | 0.1610 | 0.048* | |
| H11B | 0.5085 | −0.0373 | 0.2617 | 0.048* | |
| C12 | 0.5777 (3) | 0.1161 (12) | 0.2623 (5) | 0.0441 (19) | |
| H12 | 0.5707 | 0.2109 | 0.3150 | 0.053* | |
| C13 | 0.6081 (3) | −0.0612 (16) | 0.3099 (7) | 0.065 (3) | |
| H13A | 0.5892 | −0.1208 | 0.3598 | 0.097* | |
| H13B | 0.6413 | −0.0150 | 0.3404 | 0.097* | |
| H13C | 0.6132 | −0.1599 | 0.2598 | 0.097* | |
| C14 | 0.6090 (3) | 0.2258 (18) | 0.1894 (7) | 0.072 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.6092 | 0.1467 | 0.1298 | 0.108* | |
| H14B | 0.6440 | 0.2448 | 0.2196 | 0.108* | |
| H14C | 0.5935 | 0.3549 | 0.1729 | 0.108* | |
| C15 | 0.3558 (3) | −0.1214 (13) | 0.0549 (5) | 0.0428 (18) | |
| C16 | 0.3572 (3) | −0.2944 (13) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0494 (19) | |
| H16 | 0.3814 | −0.3949 | 0.0174 | 0.059* | |
| C17 | 0.3221 (3) | −0.3171 (14) | −0.0853 (6) | 0.054 (2) | |
| H17 | 0.3225 | −0.4353 | −0.1224 | 0.064* | |
| C18 | 0.2862 (3) | −0.1665 (14) | −0.1157 (5) | 0.048 (2) | |
| C19 | 0.2848 (3) | 0.0021 (14) | −0.0560 (5) | 0.051 (2) | |
| H19 | 0.2601 | 0.1015 | −0.0734 | 0.061* | |
| C20 | 0.3190 (3) | 0.0263 (14) | 0.0282 (5) | 0.049 (2) | |
| H20 | 0.3176 | 0.1415 | 0.0672 | 0.059* | |
| C21 | 0.2512 (3) | −0.1845 (17) | −0.2126 (6) | 0.067 (3) | |
| H21A | 0.2684 | −0.1290 | −0.2659 | 0.101* | |
| H21B | 0.2195 | −0.1116 | −0.2075 | 0.101* | |
| H21C | 0.2433 | −0.3242 | −0.2261 | 0.101* | |
| Br1 | 0.30979 (4) | −0.20451 (15) | 0.29589 (7) | 0.0603 (3) | |
| Br2 | 0.5000 | 0.0140 (2) | 0.5000 | 0.0609 (4) | |
| Br3 | 0.5000 | 0.61892 (17) | 0.0000 | 0.0480 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pd1 | 0.0397 (2) | 0.0390 (3) | 0.0327 (2) | −0.0004 (2) | 0.00594 (15) | −0.0005 (2) |
| S1 | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0388 (11) | 0.0362 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | −0.0042 (8) |
| N1 | 0.050 (3) | 0.054 (5) | 0.030 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.009 (2) | −0.007 (3) |
| N2 | 0.050 (3) | 0.036 (4) | 0.038 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.007 (3) |
| N3 | 0.042 (3) | 0.031 (4) | 0.042 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.002 (3) |
| C1 | 0.054 (4) | 0.073 (7) | 0.047 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.015 (3) | −0.002 (4) |
| C2 | 0.063 (5) | 0.091 (9) | 0.055 (5) | 0.018 (5) | 0.019 (4) | 0.003 (5) |
| C3 | 0.089 (7) | 0.087 (9) | 0.050 (4) | 0.020 (6) | 0.019 (4) | −0.017 (5) |
| C4 | 0.071 (5) | 0.058 (7) | 0.054 (4) | 0.012 (5) | 0.010 (3) | −0.019 (5) |
| C5 | 0.051 (4) | 0.043 (5) | 0.038 (4) | 0.010 (4) | −0.006 (3) | −0.007 (4) |
| C6 | 0.061 (4) | 0.030 (4) | 0.050 (4) | −0.001 (4) | −0.001 (3) | −0.008 (4) |
| C7 | 0.052 (4) | 0.038 (5) | 0.055 (4) | −0.011 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.000 (4) |
| C8 | 0.042 (3) | 0.037 (5) | 0.036 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C9 | 0.042 (3) | 0.047 (6) | 0.035 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.001 (3) |
| C10 | 0.045 (3) | 0.031 (4) | 0.034 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.008 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C11 | 0.049 (3) | 0.032 (4) | 0.039 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.000 (4) |
| C12 | 0.043 (3) | 0.048 (6) | 0.041 (3) | −0.005 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C13 | 0.051 (4) | 0.073 (7) | 0.068 (5) | 0.007 (4) | −0.005 (4) | 0.010 (5) |
| C14 | 0.051 (5) | 0.096 (9) | 0.069 (6) | −0.019 (5) | 0.006 (4) | 0.022 (6) |
| C15 | 0.038 (3) | 0.051 (5) | 0.039 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.009 (4) |
| C16 | 0.047 (4) | 0.038 (5) | 0.062 (5) | 0.003 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.009 (4) |
| C17 | 0.056 (4) | 0.051 (6) | 0.051 (4) | −0.001 (4) | −0.006 (3) | −0.020 (4) |
| C18 | 0.036 (3) | 0.058 (6) | 0.048 (4) | −0.011 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.006 (4) |
| C19 | 0.042 (4) | 0.060 (7) | 0.050 (4) | 0.007 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.000 (4) |
| C20 | 0.051 (4) | 0.046 (6) | 0.051 (4) | 0.014 (4) | 0.004 (3) | −0.011 (4) |
| C21 | 0.058 (5) | 0.079 (8) | 0.061 (5) | −0.003 (5) | −0.014 (4) | −0.006 (5) |
| Br1 | 0.0612 (5) | 0.0547 (7) | 0.0674 (5) | −0.0142 (4) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0042 (5) |
| Br2 | 0.0953 (9) | 0.0421 (9) | 0.0444 (5) | 0.000 | 0.0037 (5) | 0.000 |
| Br3 | 0.0607 (6) | 0.0392 (8) | 0.0460 (5) | 0.000 | 0.0141 (4) | 0.000 |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Pd1—S1 | 2.2603 (17) | C10—H10 | 0.9800 |
| Pd1—N1 | 2.093 (6) | C10—C11 | 1.522 (10) |
| Pd1—C8 | 1.946 (8) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| Pd1—Br1 | 2.4663 (10) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| S1—C9 | 1.836 (7) | C11—C12 | 1.537 (9) |
| S1—C15 | 1.789 (7) | C12—H12 | 0.9800 |
| N1—C1 | 1.335 (9) | C12—C13 | 1.517 (11) |
| N1—C5 | 1.330 (10) | C12—C14 | 1.527 (10) |
| N2—C5 | 1.405 (9) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C6 | 1.387 (10) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C8 | 1.340 (9) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| N3—C7 | 1.396 (10) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N3—C8 | 1.328 (9) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N3—C10 | 1.470 (9) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.376 (11) |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (13) | C15—C20 | 1.384 (11) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.354 (15) | C16—C17 | 1.380 (11) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (12) | C17—C18 | 1.393 (12) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.379 (11) |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (11) | C18—C21 | 1.511 (10) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.329 (10) | C19—C20 | 1.370 (10) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | C21—H21A | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9700 | C21—H21B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.513 (9) | C21—H21C | 0.9600 |
| S1—Pd1—Br1 | 91.46 (5) | C9—C10—H10 | 107.3 |
| N1—Pd1—S1 | 170.64 (19) | C9—C10—C11 | 113.1 (6) |
| N1—Pd1—Br1 | 97.90 (19) | C11—C10—H10 | 107.3 |
| C8—Pd1—S1 | 92.2 (2) | C10—C11—H11A | 108.3 |
| C8—Pd1—N1 | 78.4 (3) | C10—C11—H11B | 108.3 |
| C8—Pd1—Br1 | 175.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 116.1 (7) |
| C9—S1—Pd1 | 106.2 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.4 |
| C15—S1—Pd1 | 111.0 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 108.3 |
| C15—S1—C9 | 97.2 (3) | C12—C11—H11B | 108.3 |
| C1—N1—Pd1 | 126.7 (6) | C11—C12—H12 | 108.5 |
| C5—N1—Pd1 | 114.3 (5) | C13—C12—C11 | 108.0 (7) |
| C5—N1—C1 | 119.0 (7) | C13—C12—H12 | 108.5 |
| C6—N2—C5 | 131.8 (6) | C13—C12—C14 | 110.6 (7) |
| C8—N2—C5 | 118.1 (7) | C14—C12—C11 | 112.7 (6) |
| C8—N2—C6 | 110.0 (6) | C14—C12—H12 | 108.5 |
| C7—N3—C10 | 125.5 (6) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C8—N3—C7 | 109.3 (6) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C8—N3—C10 | 124.9 (6) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 119.5 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.1 (9) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.5 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.8 | C12—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.4 (8) | C12—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.8 | C12—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.3 (9) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 121.5 | C16—C15—S1 | 116.9 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.0 (10) | C16—C15—C20 | 120.2 (7) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.5 | C20—C15—S1 | 122.7 (6) |
| N1—C5—N2 | 113.0 (6) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.4 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 123.2 (8) | C15—C16—C17 | 119.2 (8) |
| C4—C5—N2 | 123.8 (8) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.4 |
| N2—C6—H6 | 126.8 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.3 |
| C7—C6—N2 | 106.5 (7) | C16—C17—C18 | 121.4 (8) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 126.8 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.3 |
| N3—C7—H7 | 126.3 | C17—C18—C21 | 121.0 (8) |
| C6—C7—N3 | 107.4 (7) | C19—C18—C17 | 117.9 (7) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 126.3 | C19—C18—C21 | 121.1 (8) |
| N2—C8—Pd1 | 116.1 (5) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.3 |
| N3—C8—Pd1 | 137.2 (6) | C20—C19—C18 | 121.5 (8) |
| N3—C8—N2 | 106.7 (7) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.3 |
| S1—C9—H9A | 108.7 | C15—C20—H20 | 120.1 |
| S1—C9—H9B | 108.7 | C19—C20—C15 | 119.7 (8) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 107.6 | C19—C20—H20 | 120.1 |
| C10—C9—S1 | 114.1 (5) | C18—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 108.7 | C18—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9B | 108.7 | C18—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| N3—C10—C9 | 111.0 (5) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| N3—C10—H10 | 107.3 | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| N3—C10—C11 | 110.6 (5) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| Pd1—S1—C9—C10 | 58.1 (5) | C7—N3—C8—Pd1 | −179.7 (6) |
| Pd1—S1—C15—C16 | −143.9 (5) | C7—N3—C8—N2 | −0.4 (8) |
| Pd1—S1—C15—C20 | 41.2 (7) | C7—N3—C10—C9 | −144.6 (7) |
| Pd1—N1—C1—C2 | −179.1 (6) | C7—N3—C10—C11 | 89.0 (8) |
| Pd1—N1—C5—N2 | −0.3 (8) | C8—N2—C5—N1 | −1.1 (9) |
| Pd1—N1—C5—C4 | 179.8 (6) | C8—N2—C5—C4 | 178.8 (8) |
| S1—C9—C10—N3 | −69.7 (7) | C8—N2—C6—C7 | 0.8 (9) |
| S1—C9—C10—C11 | 55.2 (7) | C8—N3—C7—C6 | 0.9 (9) |
| S1—C15—C16—C17 | −173.9 (6) | C8—N3—C10—C9 | 41.5 (9) |
| S1—C15—C20—C19 | 173.0 (6) | C8—N3—C10—C11 | −84.8 (8) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.7 (14) | C9—S1—C15—C16 | 105.7 (6) |
| N2—C6—C7—N3 | −1.0 (9) | C9—S1—C15—C20 | −69.3 (7) |
| N3—C10—C11—C12 | −68.7 (7) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 166.1 (5) |
| C1—N1—C5—N2 | −178.3 (7) | C10—N3—C7—C6 | −173.7 (7) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 1.8 (12) | C10—N3—C8—Pd1 | −5.0 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (15) | C10—N3—C8—N2 | 174.3 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (15) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 176.6 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −1.6 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C14 | −60.9 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—N2 | 178.6 (8) | C15—S1—C9—C10 | 172.5 (5) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | −1.3 (12) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 1.5 (13) |
| C5—N2—C6—C7 | 177.4 (7) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | −1.8 (12) |
| C5—N2—C8—Pd1 | 2.0 (8) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −3.5 (12) |
| C5—N2—C8—N3 | −177.4 (6) | C16—C17—C18—C21 | 174.6 (8) |
| C6—N2—C5—N1 | −177.5 (7) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 2.9 (12) |
| C6—N2—C5—C4 | 2.4 (13) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | −0.3 (12) |
| C6—N2—C8—Pd1 | 179.2 (5) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | 1.2 (12) |
| C6—N2—C8—N3 | −0.2 (8) | C21—C18—C19—C20 | −175.2 (8) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1···Br1 | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.510 (10) | 124 |
| C6—H6···Br2i | 0.93 | 2.74 | 3.661 (9) | 173 |
| C10—H10···Br3 | 0.98 | 2.78 | 3.624 (7) | 144 |
| C16—H16···Br3ii | 0.93 | 3.11 | 3.742 (7) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) x, y−1, z.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (grant No. 242300420186).
References
- Ahrens, S., Zeller, A., Taige, M. & Strassner, T. (2006). Organometallics, 25, 5409–5415.
- Bierenstiel, M. & Cross, E. D. (2011). Coord. Chem. Rev. 255, 574–590.
- Boeyens, J. C. A. (1978). J. Cryst. Mol. Struct. 8, 317–320.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Gardiner, M. G. & Ho, C. C. (2018). Coord. Chem. Rev. 375, 373–388.
- Hopkinson, M. N., Richter, C., Schedler, M. & Glorius, F. (2014). Nature, 510, 485–496. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Meng, X., Yang, L., Liu, Q., Dong, Z., Yuan, J., Xiao, Y. & Mao, P. (2022). Chin. J. Org. Chem. 42, 3747–3756.
- Meyer, D., Zeller, A. & Strassner, T. (2012). J. Organomet. Chem. 701, 56–61.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Peris, E. & Crabtree, R. H. (2004). Coord. Chem. Rev. 248, 2239–2246.
- Rigaku OD (2023). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Yang, L., Guo, M., Yuan, J., Wangx, J., Xia, Y., Xiao, Y. & Mao, P. (2023). Chin. J. Org. Chem. 43, 2002–2025.
- Yang, L., Yuan, J., Mao, P. & Guo, Q. (2015). RSC Adv. 5, 107601–107607.
- Yang, L., Zhang, W., Xiao, Y. & Mao, P. (2016). ChemistrySelect, 4, 680–684.
- Yang, L., Zhang, X., Yuan, J., Xiao, Y. & Mao, P. (2016). J. Organomet. Chem. 818, 179–184.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003602/zl4070sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314624003602/zl4070Isup3.hkl
CCDC reference: 2312031
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report