Summary
BCR::ABL1-independent pathways contribute to primary resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and play a role in leukemic stem cell persistence. Here, we perform ex vivo drug screening of CML CD34+ leukemic stem/progenitor cells using 100 single drugs and TKI-drug combinations and identify sensitivities to Wee1, MDM2, and BCL2 inhibitors. These agents effectively inhibit primitive CD34+CD38− CML cells and demonstrate potent synergies when combined with TKIs. Flow-cytometry-based drug screening identifies mepacrine to induce differentiation of CD34+CD38− cells. We employ genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening for six drugs, and mediator complex, apoptosis, and erythroid-lineage-related genes are identified as key resistance hits for TKIs, whereas the Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 and mepacrine exhibit distinct resistance profiles. KCTD5, a consistent TKI-resistance-conferring gene, is found to mediate TKI-induced BCR::ABL1 ubiquitination. In summary, we delineate potential mechanisms for primary TKI resistance and non-BCR::ABL1-targeting drugs, offering insights for optimizing CML treatment.
Keywords: CML, TKI, BCR::ABL1-independent resistance, progenitor, stem cell, drug screening, CRISPR-Cas9 screening, drug repurposing, KCTD5, drug combination
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Ex vivo drug screening finds sensitivities to Wee1, MDM2, and BCL2 inhibitors in CML
-
•
Mepacrine induces differentiation of primitive CD34+CD38− CML cells
-
•
CRISPR screen identifies common BCR::ABL1-independent TKI-resistance mechanisms
-
•
Downregulation of the ubiquitination regulator KCTD5 mediates TKI resistance
Adnan Awad et al. investigate the BCR::ABL1-independent resistance mechanisms in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) with integrated ex vivo drug screening and genome-wide CRISPR screening. Discovered drugs targeting leukemia stem and progenitor cells, along with resistance mechanisms to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, offer therapeutic options for CML patients.
Introduction
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the reciprocal translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11) that generates the hallmark hybrid gene BCR::ABL1.1 Targeting BCR::ABL1 fusion protein using tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has revolutionized CML management and enabled almost normal life expectancy for most CML patients.2 Hence, a new goal of CML management has emerged: the achievement of durable treatment-free remission (TFR) after TKI discontinuation.3 However, a subset of TKI-treated CML patients who lack mutations in BCR::ABL1 develop primary resistance to treatment attributed to BCR::ABL1-independent mechanisms.4,5 In addition, CML leukemic stem cells (CML-LSCs) can intrinsically activate several BCR::ABL1-independent pathways and thus resist BCR::ABL1 inhibition by TKIs.4 Even potent TKIs are unable to eradicate CML-LSCs,6,7 which are the main culprit of disease relapse upon TKI discontinuation. TKI treatment has also been shown to induce a stemness signature in CML-LSCs.8,9 Therefore, targeted therapies tackling BCR::ABL1-independent survival mechanisms are needed to overcome CML cell persistence and enable curative approaches.
High-throughput ex vivo drug screening is a powerful tool to identify effective compounds and drug repurposing candidates,10,11 but characterization of the drug sensitivity profile of CML-LSCs is challenging.12 In contrast to acute leukemia, patients with chronic-phase (CP)-CML have low numbers of blasts in peripheral blood and bone marrow samples even at diagnosis. Screening of drug sensitivities from bulk unsorted samples does not reflect the in vivo responses, because the differentiation status of cells affects the drug sensitivity profile.13,14 Sorted CD34+ cells, including leukemia stem and progenitor cells (LSPCs), from CML samples could better reflect the in vivo treatment responses.13 The paucity of primitive CD34+CD38− cells in CML patients’ samples also hinders the direct application of flow-cytometry-based drug sensitivity screening, which has been successfully applied in other leukemias.14,15 Considering these limitations, previous studies have focused on profiling sensitivities of CML-LSCs to individual candidate drugs rather than running high-throughput drug screening.
Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening is an efficient technology for discovering cancer cell vulnerabilities and prioritizing therapeutic targets.16 In addition, this functional genomics tool can be applied to decipher the potential mechanisms of resistance and sensitization to candidate targeted drugs and immunotherapies.17,18 To the best of our knowledge, only a single previous study has applied genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening in CML to identify imatinib-specific resistance genes,19 yet comprehensive characterization of the pan-TKI resistance and sensitivity mechanisms is still lacking.
In this study, we implemented ex vivo drug sensitivity and resistance testing (DSRT), using a library of 82 single drugs in addition to 18 TKI-drug combinations to evaluate the drug sensitivities of primary CML-LSPCs. In addition, we performed flow-cytometry-based DSRT (FC-DSRT) of CML samples to delineate the effect of the drug candidates on different cell populations. We identified promising candidate drugs and drug combinations that effectively target CD34+CD38− CML cells. We further applied genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 gene-perturbation screens to CML cells to identify potential BCR::ABL1-independent resistance-inducing pathways to six selected drugs, including TKIs and DSRT-based top candidate drugs, and further validated the results in individual gene-knockout (KO) models. Our study provides insights into the mechanisms underlying primary TKI resistance and also identifies potential effective therapeutic approaches.
Results
Drug sensitivity profiling reveals vulnerabilities of CML-LSPCs to VEGFR, Wee1, and MDM2 inhibitors
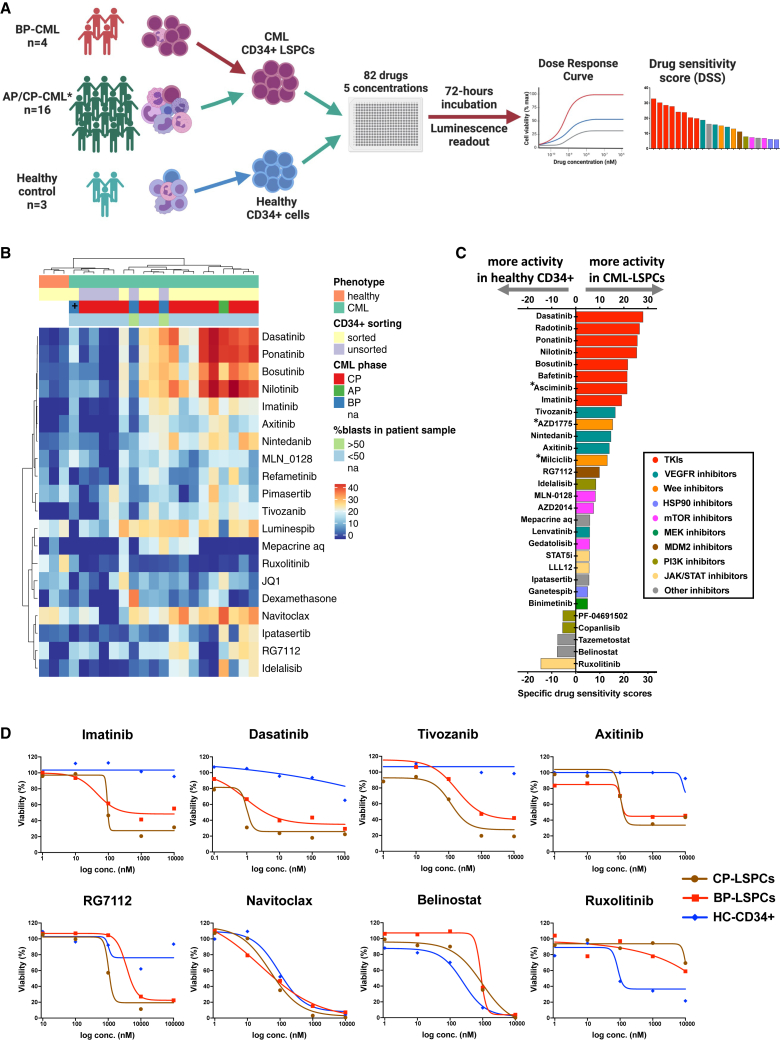
To assess the drug sensitivity profile of CML-LSPCs, we performed ex vivo DSRT for samples from 20 CML patients (Table S1), including 4 accelerated phase/blast phase (AP/BP)- and 16 CP-CML patients, in addition to 3 healthy controls (Figure 1A). Samples from 1 AP-CML and 12 CP-CML patients as well as from healthy donors were sorted to enrich for the CD34+ fraction. Demographic characteristics of the patients subjected to DSRT profiling are summarized in Table 1. We used a library of 82 approved or investigational drugs targeting several functional pathways (Table S2). The culture medium conditions were first optimized to support the viability of CML-LSPCs and to minimize cell differentiation (Figure S1). StemSpan medium was selected, preserving best the cell viability and original CD34 phenotype.
Figure 1.
High-throughput screening identifies VEGFR, Wee1, and MDM2 inhibitors as specific effective drugs against CML-LSPCs
(A) Schematic of the high-throughput drug sensitivity and resistance testing experiments. Sixteen primary CML samples (12 CP, 1 AP, and 3 BP) and 3 healthy donor samples were screened using a library of 82 drugs in five different concentrations. In 12 CP and 1 AP-CML samples in which the blast population represented <20%, as well as in healthy donor samples, CD34+ cells were sorted using magnetic sorting to enrich for the stem and progenitor cell (SPC) population. ∗In addition to the indicated 16 sorted samples, unsorted samples from 4 CP-CML patients were also tested. Further information about disease phase and sorting status of samples assigned to DSRT can be found in Table S1.
(B) Heatmap of the drug sensitivity of CP-LSPC (n = 11), AP/BP (n = 4), unsorted CP-CML (n = 4), and healthy CD34+ (n = 3) samples. Drug sensitivity scores (DSSs) of the most variable 20 drugs are shown. Explanatory tracks from top to bottom show disease status (CML, healthy), sorting status, phase of CML (CP, AP, or BP), and blast percentage in the initial sample prior to sorting. (+) indicates a BP patient with ABL T315I pan-TKI resistance mutation. Ward’s hierarchical clustering method was used for production of the heatmap.
(C) Bar plot of the selective drug sensitivity of CML-LSPCs (n = 16) compared to healthy CD34+ (n = 3). Drugs are colored by their targeted functional classes. Bar height represents the specific DSS (sDSS) as calculated by the average of DSS responses in CML samples after subtraction of the average of DSS responses in healthy samples. (∗) indicates drugs that were tested only in a subset of samples.
(D) Dose-response curves of TKIs (imatinib, dasatinib), VEGFR inhibitors (tivozanib, axitinib), the MDM2 inhibitor RG-7112, the BCL2 inhibitor navitoclax, the HDAC inhibitor belinostat, and the JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib in CP-LSPCs (n = 11), BP (n = 5), and healthy CD34+ (n = 3) samples. Dots represent the median values for each group. Plots showing the individual sample’s dose-response curves for the drugs shown here are shown in Figure S2C. See also Figures S1–S3 and Tables S1, S2, and S3.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of patients subjected to DSRT profiling
| All | CP | BP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 25 | 16 | 9 |
| Age, median (range) years | 55 (24–81) | 58 (25–81) | 53 (24–74) |
| Gender, male/female/N/A (%) | 10/10/5 (40/40/20) | 5/6/5 (31/38/31) | 5/4/0 (56/44/0) |
| Disease stage at diagnosis, CP/AP/BP (%) | 21/1/3 (84/4/12) | 16/0/0 (100/0/0) | 5/1/3 (56/11/33) |
| WBC count, median (range), ×109/L | 107 (0.9–317) | 140.8 (15.6–261) | 54.6 (0.9–317) |
| PB blast (%) | 3 (0–70) | 0.5 (0–5) | 46 (6–70) |
| BM blast (%) | 6 (1–90) | 1 (1–5) | 48 (6–90) |
| Sokal score, low/intermediate/high/N/A | 4/5/1/15 | 4/5/1/6 | N/A |
| Frontline treatment, imatinib/2G TKI/chemotherapy/N/A | 13/4/3/5 | 8/3/0/5 | 5/1/3/0 |
| Clinical response, poor/suboptimal/optimal/N/A | 0/0/9/16 | 0/0/9/7 | N/A |
CP, chronic phase; BP, blast phase; AP, accelerated phase; WBC, white blood cell; PB, peripheral blood; BM, bone marrow; 2G, second generation; clinical response, patients who achieved major molecular response (MMR) either by 12 months (optimal) or after 12 months (suboptimal), patients who never achieved MMR or progressed to BP (poor); N/A, not available (clinical data not available).
In contrast to unsorted bulk CML and healthy CD34+ samples, CML-LSPCs showed high sensitivity to TKIs driven by the sensitivity of the dominant CD34+ progenitor population (Figures 1B and S1K; Table S4). Interestingly, also drugs targeting other functional classes showed activity against CML-LSPCs, including HSP90 inhibitors, VEGFR inhibitors, and the BCL2 inhibitor navitoclax. Other drugs, such as the MDM2 inhibitor (RG7112) and mepacrine, were effective in a subset of samples (Figures 1B and S2A–S2C). In contrast to CP-LSPCs, we observed a functional diversity of active drugs in BP-LSCs (Figures S2D and S2E), including sensitivity to STAT3/STAT5 inhibitors and dexamethasone, underscoring the activation of additional signaling pathways during CML progression.
Using the drug sensitivity score (DSS) responses of healthy CD34+ samples as reference, we calculated the specific DSS (sDSS), which represents the ability to selectively inhibit CML-LSPCs, sparing normal hematopoietic cells. TKIs exhibited the highest sDSS responses on CML-LSPCs, followed by VEGFR, Wee1, and MDM2 inhibitors. On the other hand, the JAK inhibitor (ruxolitinib) and HDAC inhibitors showed higher activity in healthy CD34+ samples (Figures 1C, 1D, S2, and S3A). We were able to collect enough CD34+ cells from an individual CP patient to run the 82-drug library for sorted CD34+/CD38− stem (LSCs) and CD38+ progenitor (LPCs) populations (Figures S3B–S3D). As expected, LPCs showed higher sensitivity to TKIs and other drug families, whereas some other drugs, such as RG7112, were more effective in LSCs. In addition, LSCs shared DSS response profile similarities with healthy CD34+, such as increased sensitivity to ruxolitinib and belinostat.
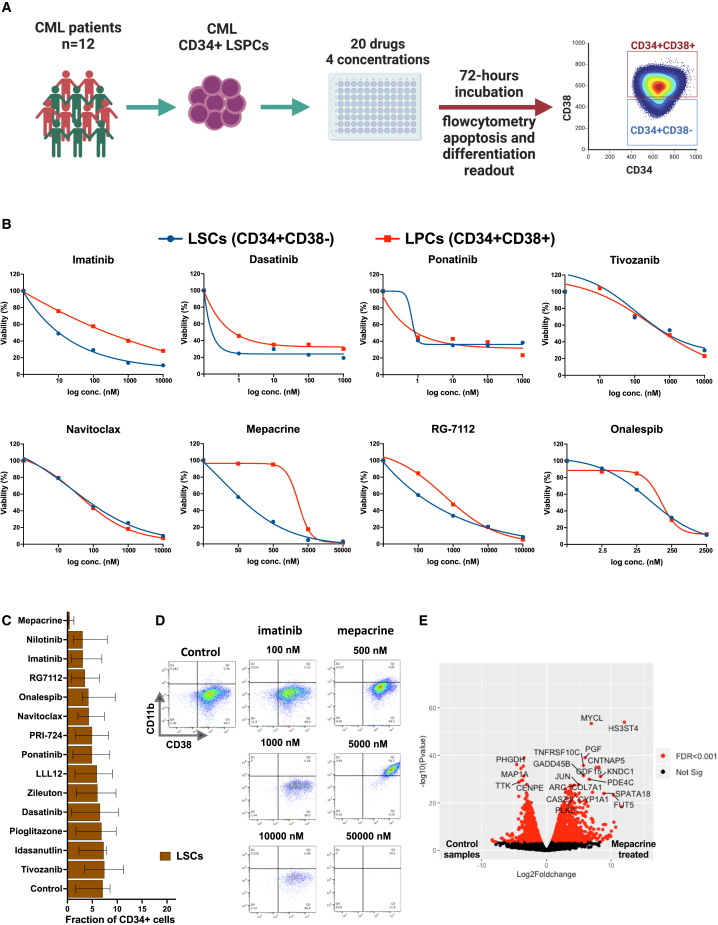
Flow-cytometry-based drug sensitivity profiling reveals enhanced sensitivities of CD34+CD38− CML cells to mepacrine and MDM2 and BCL2 inhibitors
Since the drug sensitivity profiling of the CD34+ LSPCs may potentially be driven by the dominant LPC rather than the less frequent CD34+CD38− putative leukemia-initiating LSC population,20,21,22 we next aimed to delineate population-specific drug sensitivity profiles of CML-LSPCs by implementing FC-DSRT in samples from 12 CML patients, including 6 CP-LSPC and 6 BP-bone marrow mononuclear cell (BMNC) samples. Apoptosis and differentiation readouts were measured for 20 drugs over four log concentrations (Figure 2A; Tables S1 and S2). TKIs showed comparable sensitivities in both CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ populations but were still unable to completely eradicate CD34+CD38− cells even at the highest tested concentrations, more prominently in BP samples (Figures 2B and S4). Interestingly, we identified additional drugs, such as mepacrine and RG7112, which exhibited selective activity against the CD34+CD38− population. Other drugs, such as navitoclax, onalespib, and tivozanib, inhibited both populations at comparably high activities (Figure 2B). In contrast, drugs of other functional classes, including drugs suggested as adjuvants to TKIs (PPARγ inhibitors and leukotriene modifiers), exhibited mild to moderate sensitivity profiles, with no remarkable activity against CD34+CD38− cells (Figure S4A). In general, both CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ populations in BP samples were less sensitive to most of the tested drugs compared to CP counterpart populations (Figure S4B).
Figure 2.
Flow-cytometry-based drug sensitivity profiling revealed selective activities of mepacrine and MDM2 and BCL2 inhibitors against CD34+CD38− CML cells
(A) Schematic of the flow-cytometry-based drug sensitivity and resistance testing experiments (FC-DSRT). Twelve primary CML samples (6 CP, 6 AP/BP) were screened for sensitivity of 20 drugs in four different concentrations. A flow cytometry antibody panel, including stem cell and myeloid differentiation markers, as well as viability stains, was used to estimate the drug-induced differentiation and killing activity. Further information about disease phase and sorting status of samples assigned to FC-DSRT is in Table S1.
(B) Dose-response curves of selected drugs, including TKIs (imatinib, dasatinib, ponatinib), the VEGFR inhibitor tivozanib, the BCL2 inhibitor navitoclax, mepacrine, the MDM2 inhibitor RG-7112, and the HSP90 inhibitor onalespib in putative CML-LSCs (CD34+CD38−) and LPCs (CD34+CD38+). Dots represent the mean values from 12 CML patient samples. Plots showing the individual samples’ dose-response curves for the drugs shown here are shown in Figure S3D.
(C) Bar plot of the efficiency of the tested drugs in targeting the CD34+CD38− cell fraction of total CD34+ cells in the studied cohort (n = 12). Control represents the values from DMSO-treated samples. Bar length represents median value with error bars representing the interquartile range.
(D) Flow cytometry showing the expression of myeloid differentiation markers CD38 (x axis) and CD11b (y axis) on CD34+-gated cells from control and imatinib- and mepacrine-treated CML cells over three log concentrations.
(E) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in mepacrine-treated primary CML-LSPCs (n = 4) compared to matched DMSO-treated samples. Genes with false discovery rate (FDR) values <0.001 (Bayesian statistical test) are colored in red. In addition, DEGs with >3-fold-change differences and −log10 (p value) > 20 are labeled with gene names. See also Figures S3–S5 and Tables S1, S2, S3, and S4.
Analysis of FC-DSRT data revealed a distinct mechanism of mepacrine inducing eradication of CML CD34+CD38− cells compared to the other tested drugs (Figure 2C). Mepacrine induced a significant differentiation of CD34+CD38− cells as evident by induced surface expression of CD11b and CD38, in contrast to the other drugs (Figures 2D and S5A–S5D). In addition, mepacrine demonstrated significant inhibition of the colony-forming capacity of CML-LSPCs alone and in combination with imatinib, but only a minimal effect on the long-term-colony-initiating cell (LTC-IC) capacity of CML-LSPCs was observed (Figures S5E–S5H). Using RNA sequencing of mepacrine-treated and untreated LSPCs from four CML patients, we identified mepacrine-activated pathways in CML-LSPCs. We identified 6,919 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between mepacrine-treated and control samples (Figure 2E; Table S4). Pathway enrichment analysis of the top DEGs (>3-fold changes) revealed upregulation of TP53, TNF-α, and WNT signaling pathways in mepacrine-treated samples. On the other hand, genes controlling the G2M checkpoint of the cell cycle, as well as targets of E2F and MYC transcription factors, were significantly downregulated (Figures S5I and S5J).
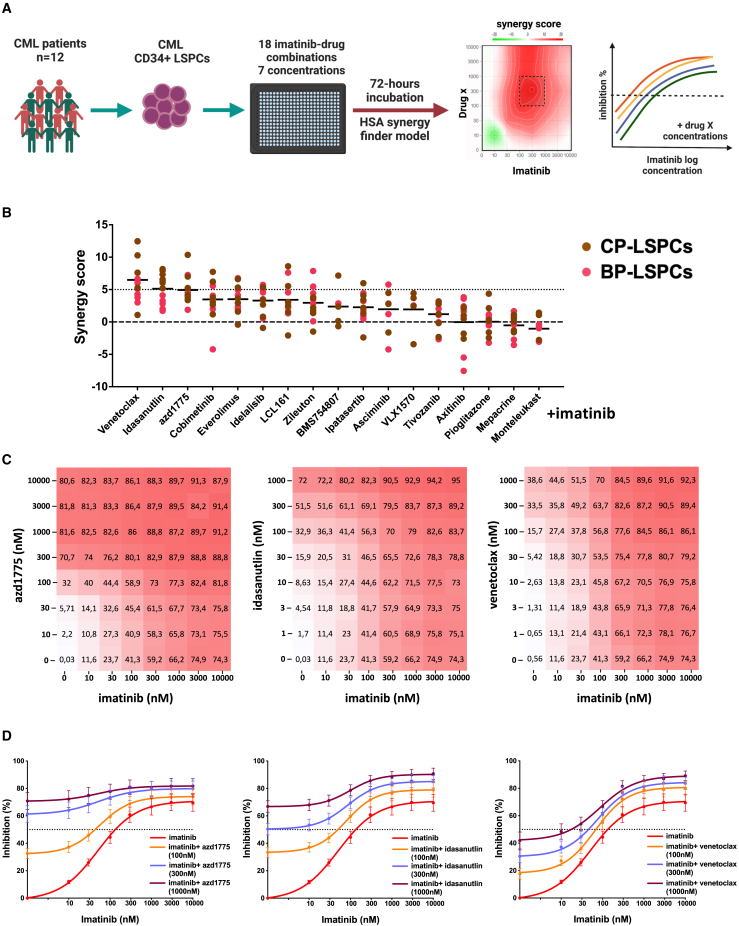
Synergistic effects of idasanutlin, venetoclax, and AZD1775 combinations with imatinib in co-inhibiting CML CD34+CD38− cells
To identify synergistic TKI-drug combinations that effectively co-inhibit CML CD34+CD38− cells, we screened 12 CML-LSPC samples (6 CP and 6 AP/BP) using a library of 18 imatinib-drug combinations that were selected based on DSRT screening of CML-LSPCs (Figure 3A; Table S2). The most promising imatinib drug combinations included combinations with idasanutlin, venetoclax, and AZD1775, which showed potent synergy (HSA synergy score >5) in most of the samples (Figures 3B–3D, S6A, and S6B; Table S3). We also tested these drug candidates with Ba/f3 cells carrying a T315I BCR::ABL1 kinase domain mutation and noticed that AZD1775 especially retained its activity against the T315I BCR::ABL1 mutant form, whereas imatinib, dasatinib, and idasanutlin lost their activity (Figure S6C). Similarly, one patient sample with the T315I BCR::ABL1 mutant was rather resistant to idasanutlin, whereas a sample carrying the E255K mutant was more sensitive (Figures S5D and S5E). Other imatinib combinations showing potent synergy in a subset of samples (in at least 25% of samples) were with cobimetinib, idelalisib, everolimus, and LCL161 (Figure 3B), which also showed moderate activity as single agents. In addition, imatinib combinations with ipatasertib, zileuton, and asciminib showed mild synergy or rather an additive effect (HSA synergy score >3) in individual samples. Despite showing high activity as single agents, VEGFR inhibitors tivozanib and axitinib, as well as drugs with a narrow activity window, such as mepacrine, demonstrated a mild additive effect when combined with imatinib (Figures 3B and S6B). We also tested the most effective imatinib combinations (idasanutlin, venetoclax, and AZD1775) with either second- (dasatinib) or third- (asciminib) line TKIs. Interestingly, both TKIs showed significant synergy with venetoclax but to a lesser degree with idasanutlin and AZD1775 (Figure S6F).
Figure 3.
Drug combination screening identified potential synergistic combinations of imatinib with idasanutlin, venetoclax, and AZD1775 in CML-LSPC samples
(A) Schematic of the drug combination testing experiments. Twelve primary CML samples (6 CP, 6 AP/BP) were screened with 18 imatinib-drug combinations in seven different concentrations. HSA synergy scores and most synergistic area scores were calculated using the SynergyFinder web application.23 Further information about disease phase and sorting status of samples assigned to combination DSRT is in Table S1.
(B) Dot plot of the synergy scores of imatinib-drug combinations in the studied CML cohort (n = 12). Dots are colored brown or red according to CML phase CP or BP. HSA synergy score >5 is indicated by a dotted line.
(C) Heatmaps of dose-combination responses in CML-LSPC samples (n = 12) showing the combinations of imatinib with the Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775, MDM2 inhibitor idasanutlin, and BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax across the tested concentration matrices. Average percentage inhibition values are indicated in the heatmaps. Drug combination heatmap matrices for individual samples are provided in Figure S6A.
(D) Dose-response curves for combinations of imatinib with AZD1775, idasanutlin, and venetoclax (each partner drug in three different indicated concentrations) in CML-LSPC samples (n = 12). Dots represent the mean values with error bar representing standard error of the mean (SEM). Plots showing the dose-combination responses of individual samples for the combinations shown here are shown in Figure S6C. See also Figure S6 and Tables S1, S2, and S3.
Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 loss-of-function screens identify BCR::ABL1-independent TKI-resistance pathways and potential candidate drug targets
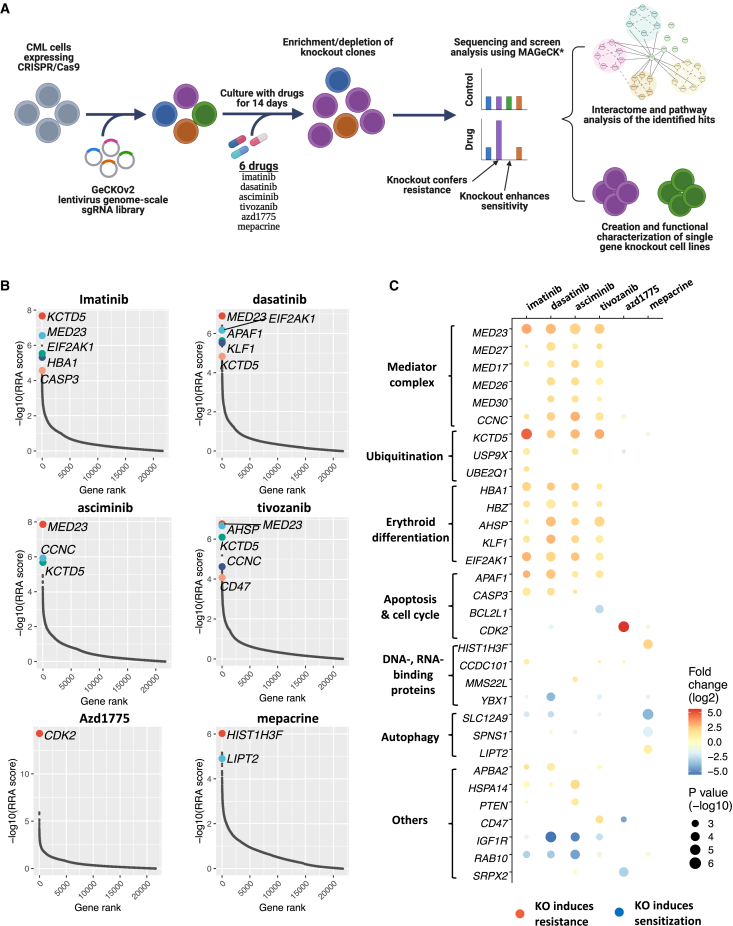
To investigate BCR::ABL1-independent resistance pathways in CML, we applied a functional genomic approach employing genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 gene perturbation screens to K562 cells using the Genome-Scale CRISPR Knockout version 2 (GeCKO v.2) lentiviral single guide RNA (sgRNA) library targeting ∼19,000 genes in the presence of six selected drugs (Figure 4A). In addition to exploring BCR::ABL1-independent resistance mechanisms by screening different TKIs (imatinib, dasatinib, and asciminib), we screened three DSRT-based candidate drugs (tivozanib, AZD1775, and mepacrine) to identify potential targetable pathways and resistance mechanisms. By comparing sgRNA barcode sequencing data between the drug-treated and the control conditions using MAGeCK analysis, we determined the relative enrichment or depletion of sgRNAs, which indicates potential resistance or sensitizing roles of the targeted genes to the drug treatment.
Figure 4.
Genome-wide CRISPR screens identified resistance and sensitization gene-perturbation signatures for TKIs and other drugs in CML cells
(A) Schematic of the CRISPR-Cas9 loss-of-function screening approach.
(B) Positively selected hits of CRISPR-Cas9 screens in K562 cells treated with selected drugs (imatinib, dasatinib, asciminib, tivozanib, AZD1775, and mepacrine) compared with control K562 cells. Genes are ranked by −log10 of the MAGeCK RRA score for positive selection.
(C) Bubble plot of the significant resistance and sensitization hits (FDR < 0.15, MAGeCK analysis) for the six tested drugs and their functional annotations. The size of the bubble represents the significance level (−log(p value)); the color indicates the selection direction being positive (resistance) or negative (sensitization) as red or blue, respectively; and the color intensity represents the log fold change of the level of the gene-targeting gRNAs. See also Figure S7 and Table S5.
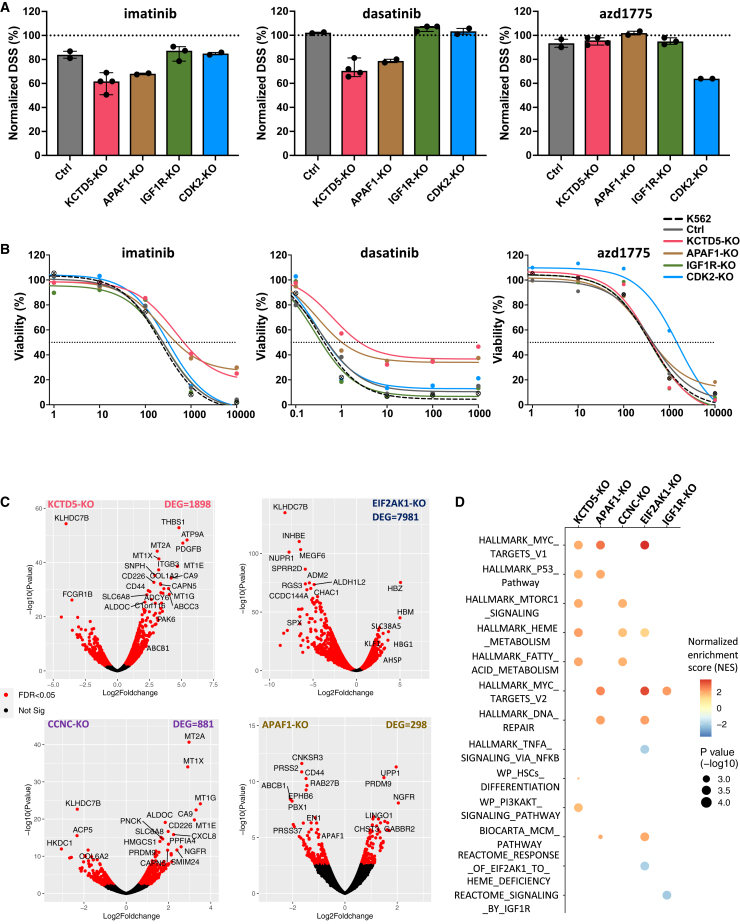
Exploration of gene perturbation-induced resistance/sensitivity profiles revealed that TKIs shared many resistance hits, suggesting a common BCR::ABL1-independent TKI-resistance machinery (Figures 4B, 4C, and S7A). The top resistance hits included genes encoding components of the mediator complex (MED23, MED17, CCNC), erythroid markers (KLF1, HBA1), and apoptosis (APAF1, CASP3), as well as unrelated genes such as KCTD5 and EIF2AK1. In addition, some gene perturbations induced resistance to individual TKIs, such as CCDC101-KO with imatinib and PTEN-KO with asciminib. On the other hand, RAB10-KO was among the top sensitization hits in TKI screens. Other potential sensitizing hits to specific TKIs included YBX1-KO with dasatinib and IGF1R-KO with both asciminib and dasatinib. The resistance/sensitivity profile of the VEGFR inhibitor tivozanib shared many similarities with BCR::ABL1-inhibiting TKIs, suggesting that tivozanib mainly targets the same TKI-actionable pathways in CML cells. Tivozanib’s profile exhibited some specific hits, such as BCL2L1-KO as a sensitizing and CD47-KO as a resistance hit (Figures 4B and 4C). Unlike tivozanib, AZD1775 and mepacrine showed distinct resistance/sensitivity profiles compared to TKIs. The only significant resistance hit for the Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 was CDK2-KO. For mepacrine, HIST1H3F-KO was the top resistance hit, while KO of autophagy regulator genes, SLC12A9 and SPNS1, sensitized cells to mepacrine effects (Figures 4B and 4C).
Transcriptional profiling of individual-gene-KO cells to identify the mechanisms underlying the perturbation-induced phenotype
To validate the resistance and sensitization hits identified by the genome-scale screens, we next targeted selected top-ranking genes using CRISPR-Cas9 in K562 cells. The selected genes represent different pathways and drug specificities, including KCTD5 and APAF1 as examples of consistent resistance hits for multiple TKIs and IGF1R as a multi-TKI sensitization hit, in addition to CDK2 as a non-TKI-specific resistance hit. KO efficiencies of the targeted genes ranged between 60% and 94% (Table S5). While KCTD5-KO and APAF1-KO showed reduced sensitivity to all TKIs but not to AZD1775, CDK2-KO cells showed specific reduction of sensitivity to AZD1775 in 3-day DSRT screens (Figures 5A, 5B, and S7B–S7E). In concordance with the K562 results, KCTD5-KO and APAF1-KO demonstrated reduced sensitivity to imatinib and dasatinib in the LAMA84 CML cell line (Figures S7F–S7I). Furthermore, analysis of previously published RNA-sequencing data24 from TKI-resistant K562 cells revealed significant downregulation of KCTD5, EIF2AK1, and APAF1 and upregulation of IGF1R genes in resistant cells (Figure S8A).
Figure 5.
Drug sensitivity and transcriptional profiling of individual gene-KO cells
(A) Bar plots of the drug sensitivity scores (DSSs) of imatinib, dasatinib, and AZD1775 in different individual gene-KO K562 cells. DSSs were obtained from the 72-h DSRT experiments (see STAR Methods) and were normalized and expressed as percentage of the drug-specific DSSs in the parental K562 cells (indicated by dotted line). CRISPR-Cas9-expressing K562 cells transduced with nontargeting gRNA was used as a control (Ctrl). Dots represent the number of biological replicates used for each gene-KO condition. Bar height represents the median value, with error bars representing 95% confidence interval (CI).
(B) Dose-response curves of imatinib, dasatinib, and AZD1775 in individual gene-KO K562 cells. Dose-response curves of the drugs in parental K562 cells are represented by dashed curves. Viability of the cells at different concentrations is presented as a percentage of the viability compared to DMSO-treated wells. A dotted line indicates 50% viability of cells. Dots represent the median value for each condition. Number of replicates for each condition is as indicated by dot number in (A).
(C) Volcano plots of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in different individual gene-KO K562 cells compared to control K562 cells (transduced with nontargeting gRNA). Experiments were performed using biological triplicates of each condition. Significant genes (FDR < 0.05, Bayesian statistical test) are colored in red. The number of DEGs is indicated for each condition.
(D) Dot plot of pathway analysis of DEGs in individual gene KOs using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). Dot size indicates the significance level and dot color indicates up- (red) or downregulation (blue). The color intensity represents the normalized enrichment score (NES) of the identified pathway. Pathways with adjusted p = 0 in GSEA output were replaced by p = 0.0001 for data presentation. See also Figures S7 and S8 and Tables S4 and S5.
We next investigated the mechanisms underlying gene perturbation-associated phenotypes using transcriptional profiling of individual gene-KO cells. In addition to the above-described genes, we performed RNA sequencing of additional resistance hits, including EIF2AK1-KO and CCNC-KO K562 cells. Expression levels of the targeted genes were significantly reduced in the edited cells. The number of DEGs varied widely between the gene KOs, ranging from 298 genes in APAF1-KO cells to 7,981 genes in EIF2AK1-KO cells (Figure 5C; Table S4). Pathway analysis revealed activation of various signaling pathways in association with individual gene KOs. For example, EIF2AK1-KO cells showed significant downregulation of heme-deficiency-responsive genes and upregulation of erythroid transcription factor KLF1 and many hemoglobin genes. APAF1 KO was associated with upregulation of TP53 and MCM signaling pathways. CCNC KO showed upregulation of fatty acid metabolism and MTORC1 signaling. Interestingly, KCTD5 KO was associated with a relatively large number of DEGs (n = 1,898), showing upregulation of multi-drug-resistance genes, hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) differentiation, and TP53 and PI3K/AKT pathways (Figure 5D). Taken together, modulation of hematopoietic cell differentiation and the TP53 apoptosis related pathways as well as activation of additional signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR represent shared resistance mechanisms by different resistance-conferring gene KOs.
Regulation of KCTD5-mediated ubiquitination as a primary resistance mechanism to TKIs in CML
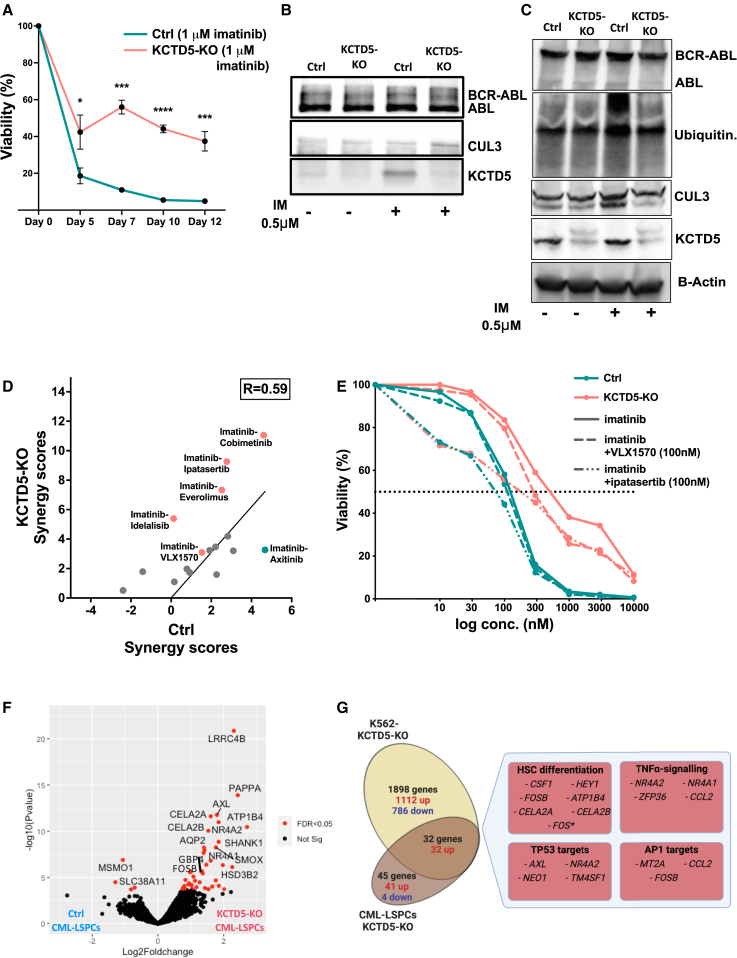
Given the consistency of KCTD5 as a top resistance hit in TKI screens, we further investigated the role of KCTD5 in mediating TKI resistance in CML. We analyzed RNA-sequencing data from CML patients,25 which revealed concordant downregulation of the KCTD5 gene in diagnostic BP- and CP-LSPCs compared to HSCs (Figure S8B). Similar KCTD5 downregulation was noted in a CP-LSPC sample with a low imatinib response (DSS < 15) compared to CP-LSPC samples showing a high imatinib response (DSS > 15) (Figure S8C). KCTD5-KO K562 cells showed significant resistance to TKIs in long-term cultures (Figure 6A). A similar but less prominent effect was observed in LAMA84 cells (Figures S8D–S8G). Because KCTD5 is reported to function as a substrate adapter for E3 ubiquitin ligase, we first investigated whether BCR::ABL1 is interacting with KCTD5/CUL3 complex. Immunoprecipitation using ABL antibody confirmed the presence of both CUL3 and KCTD5 proteins in the precipitated complexes (Figure 6B). Interestingly, imatinib treatment (0.5 μmol) was associated with increased KCTD5 and, to a minor extent, CUL3 in parental K562 cells (Figures 6C and S8H). However, only CUL3 levels increased in ABL complexes from KCTD5-KO cells upon imatinib treatment (Figure 6B). Immunoblotting showed enhanced ubiquitination of BCR::ABL1 in K562 cells upon imatinib treatment, but not in imatinib-treated KCTD5-KO cells (Figure 6C).
Figure 6.
KCTD5 KO induces TKI resistance in CML cells through impairment of KCTD5-mediated BCR::ABL1 ubiquitination
(A) Viability of KCTD5-KO and control K562 cells treated with imatinib (1 μmol) in long-term culture. Experiments were performed using biological triplicates of each condition. Dots represent median value and error bars indicate 95% CI. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (adjusted p value, multiple unpaired t test corrected for multiple comparisons).
(B) Protein levels of KCTD5 and CUL3 proteins in complexes immunoprecipitated by ABL antibody from untreated and imatinib-treated (0.5 μmol) control and KCTD5-KO K562 cell lysates. Densitometric analysis revealed an imatinib-induced increase in the CUL3 levels, with treated to untreated CUL3 level ratios of 1.71 in control and 1.57 in KCTD5-KO cells. KCTD5 levels showed an 8.2-fold increase in imatinib-treated compared to untreated control samples. Data from a replicate experiment are shown in Figure S8I.
(C) Protein levels of BCR-ABL, KCTD5, and CUL3 proteins as well as ubiquitination levels in untreated and imatinib-treated (0.5 μmol) control and KCTD5-KO K562 cell lysates. The levels of CUL3, KCTD5, and ubiquitination demonstrated 1.52-, 1.39-, and 3.12-fold increases in the imatinib-treated control sample compared to untreated control sample by densitometry analysis. Negligible changes in the quantified protein levels were found in KCTD5-KO samples with imatinib treatment.
(D) Association of HSA synergy scores between controls and KCTD5-KO K562 cells from drug combination screening experiments (R = 0.593, Pearson correlation, p = 0.016). Combinations with enhanced synergistic activity in KCTD5-KO K562 cells are colored in red and those with enhanced synergistic activity in control cells are colored in blue.
(E) Dose-response curves of combinations of imatinib with the deubiquitinase inhibitor VLX1570 (100 nmol) and the AKT inhibitor ipatasertib (100 nmol) in control (solid curves) and KCTD5-KO (dashed curves) K562 cells. Viability of the cells at different concentrations is presented as a percentage of the viability compared to DMSO-treated wells. A dotted line indicates 50% viability of cells.
(F) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in KCTD5-KO CML-LSPCs (n = 2) compared to matched control LSPC samples. KCTD5 targeting CRISPR sgRNA was transduced to primary CD34+ cells with lentivirus and RNA sequencing was performed on KO and control cells. FDR < 0.05 (Bayesian statistical test) is colored in red.
(G) Venn diagram showing the overlap of DEGs from RNA-sequencing experiments between KCTD5-KO and control LSPCs (n = 2) or K562 cells (n = 3, biological replicates). Boxes show the main molecular pathways significantly enriched in the overlapping DEGs by pathway enrichment analysis. Genes listed are significantly differentially expressed between KCTD5-KO and control LSPCs or K562 (FDR < 0.05, Bayesian statistical test), except for the FOS gene (marked with ∗), which showed borderline significance (FDR = 0.056) in LSPC samples. See also Figure S8 and Tables S4 and S5.
Next, we investigated the potential downstream effects of impaired ubiquitination of proteins other than BCR::ABL1 in KCTD5-KO cells, by investigating their sensitivity to targeted drugs using single-agent and drug-combination DSRT. Interestingly, we identified potential TKI-drug synergies in KCTD5-KO cells, including imatinib combinations with the AKT inhibitor ipatasertib, MEK inhibitor cobimetinib, and mTOR inhibitor everolimus, in addition to an additive effect of the deubiquitinase (DUB) inhibitor, VLX1570 (Figures 6D and S8J–S8M). On the other hand, the single-drug DSS responses of these drugs were comparable between KCTD5-KO and control cells (Figure S8N). This synergy of AKT/mTOR and DUB inhibitors with imatinib in KCTD5-KO cells suggests a potential contribution of these pathways to TKI resistance (Figure 6E), which was supported by elevation of p-AKT levels in imatinib-treated KCTD5-KO cells (Figure S8I). We also tested imatinib combinations with MEK/mTOR inhibitors utilizing primary CML-LSPCs and noticed effective inhibition of the clonogenicity in short-term cultures, whereas no similar effects were seen in the LTC-IC assays (Figures S8O–S8P). However, it should be noted that the tested patient samples were from diagnostic CML-CP patients with presumably normal KCTD5 levels.
Finally, we investigated the effect of KCTD5 gene KO in primary CML-LSPC CD34+ cells from two CP patients with CRISPR editing and RNA sequencing. We identified 45 protein-coding DEGs in KCTD5-KO CML-LSPCs, including 41 upregulated and 4 downregulated genes (Figure 6F; Table S4). Interestingly, the majority of the significantly upregulated genes in KCTD5-KO LSPCs were similarly upregulated in KCTD5-KO K562 cells (32/41 genes), such as FOSB, GBP4, SHANK1, AXL, NR4A1, and NR4A2. Upregulated genes in KCTD5-KO LSPC samples showed enrichment of genes involved in HSC differentiation, TNF-α, and TP53 pathways (Figure 6G).
Discussion
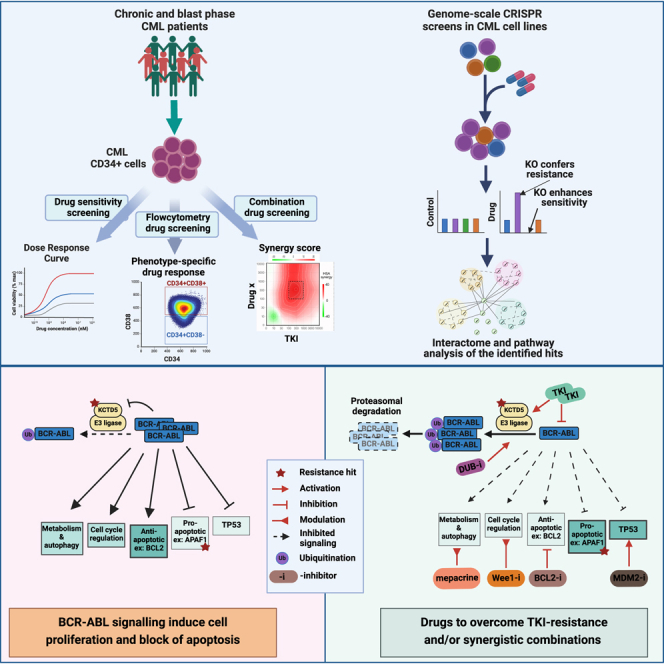
Novel drugs and drug combinations targeting BCR::ABL1-independent pathways are needed to provide therapeutic options to overcome primary TKI resistance and enable efficient eradication of CML-LSCs. The application of ex vivo drug profiling and flow-cytometry-based drug screening of primary CML-LSPCs in our study enabled identification of potentially effective drugs, including mepacrine and MDM2, BCL2, and Wee1 inhibitors, which represent promising candidates for TKI-drug combination strategies in CML management. Using FC-DSRT, we further discovered drugs that specifically target the primitive CD34+CD38− CML population. In addition, we employed genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screens to explore primary resistance mechanisms in CML and to identify targets for the identified drug candidates. We identified resistance pathways common to different TKIs, such as ubiquitination, apoptosis, and cell-cycle regulation, which can be targeted to overcome primary TKI resistance. Finally, we identified KCTD5 in mediating primary TKI resistance through regulation of BCR::ABL1 ubiquitination, which represents a promising targetable hub in CML.
Using FC-DSRT, we identified drugs specifically targeting the TKI-persistent CD34+CD38− CML cells, including mepacrine, navitoclax, and MDM2 inhibitors. Our results highlighted the efficiency of mepacrine in ablating these cells through the induction of cell differentiation. Mepacrine is an anti-malarial drug recently suggested to be repurposed as a cancer treatment.26 Mepacrine exerts inhibitory effects through targeting several pathways, including autophagy, TP53-dependent apoptosis, and DNA damage repair.27 Transcriptional profiling of mepacrine-treated CML-LSPCs revealed a dual effect significantly upregulating TP53 and downregulating MYC pathways, a strategy reported to be efficient in eradicating CML-LPSCs.28 Our CRISPR-Cas9 screens suggested autophagy to partially mediate mepacrine effects in CML cells, as supported by the enrichment of lysosomal genes, such as SLC12A929 and SPSN1,30 as sensitization hits to mepacrine. This finding was further substantiated by a strong positive correlation observed between the DSSs of mepacrine and another autophagy inhibitor, hydroxychloroquine, in our CML-LSPC DSRT screens (Spearman’s correlation coefficient r = 0.92, p = 0.0005). Surprisingly, in the LTC-IC assay, mepacrine showed only a minimal effect, but this could be due to the challenges in the assay conditions, as mepacrine has a very narrow active concentration window, and suboptimal dosage/drug incubation times needed to be used to avoid wiping out all colonies in the short-term assays. Thus, further optimization of mepacrine dosage and combination regimes is needed to prove its potential benefit in eradicating LSCs.31,32 Our results also highlighted the efficiency of apoptotic modulators, including BCL2 and MDM2 inhibitors, against CD34+CD38− CML cells and their synergy with TKIs, emphasizing apoptosis targeting as a promising approach to eradicate CML-LSCs.33,34 Congruently, genes of the apoptosis pathway, such as APAF1 and BCL2L1, were among the top-ranking genes modifying TKI sensitivity. Results agree with previous CRISPR-Cas9 screens, underscoring the role of apoptotic regulatory genes in modifying sensitivity to cancer therapy.35
DSRT profiles of CML-LSPCs demonstrated specific sensitivities to additional functional drug classes, which represent potential combination candidates to synergize with TKIs. The Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 showed high efficacy against CML-LSPCs both as a single agent and in combination with imatinib. AZD1775 exerts anti-tumor effects through controlling the cell-cycle regulators and modulating DNA damage response.36,37 Notably, CDK2-KO was the top resistance hit to AZD1775 in CRISPR-Cas9 screens, suggesting that AZD1775 exerts its inhibitory effect in CML cells through the previously reported inhibition of CDK2-dependent response to DNA damage.38 Interestingly, a recent study highlighted the AZD1775-TKI combination as efficiently targeting CML-LSCs.39 In addition, a VEGFR inhibitor, tivozanib, showed specific activity against CML-LSPCs. We previously identified tivozanib to inhibit BP-CML cells.40 We also reported that another VEGFR inhibitor, axitinib, exhibits a potent BCR::ABL1-inhibitory activity with clinical translation potentials especially in T315I-mutated cases.41 Notably, VEGFR inhibitors showed a mild additive effect when combined with imatinib, which can be attributed to their potential reliance on BCR::ABL1 inhibition as the main mechanism of action in CML cells.
CRISPR-Cas9 screens have been increasingly used to identify druggable hits to overcome therapy resistance in cancer,42 including hematological malignancies.43 They have, however, seldom been applied to study BCR::ABL1-independent TKI resistance in CML. One previous study employed the genome-scale GeCKO v.2 library to investigate mechanisms of imatinib resistance in K562 cells.19 Interestingly, many of the reported imatinib-resistance genes, such as KLF1, EIF2AK1, APAF1, and MED23, were similarly identified in our study, representing an important cross-validation and highlighting the reproducibility of CRISPR-Cas9 screens to study drug resistance mechanisms. The results demonstrated some differences between the two studies, which can be attributed to technical differences such as the targeted depth coverage of the gRNA (250× vs. 700×) and incubation period (4 days followed by 3 days drug-free culture vs. 14 days) between the Lewis et al.19 study and our study, respectively. The longer drug incubation with optimized selection pressure in our design allows better identification of imatinib-specific resistance hits. In addition, we used both pre- and post-treatment controls for filtering nonspecific essential and tumor-suppressor genes.
Results from CRISPR-Cas9 screens revealed a gene-perturbation signature associated with primary BCR::ABL1-independent resistance to TKIs, including imatinib, dasatinib, the allosteric inhibitor asciminib, and tivozanib. Enriched in the TKI-resistance signature were many genes encoding components of the mediator complex, a multi-unit transcriptional co-activator complex. Many of the identified mediator complex components were concordantly associated with resistance to other targeted cancer therapies,44,45 but were also controversially identified as essential genes in CML cells.46 The mechanisms by which specific mediator complex components mediate resistance to targeted therapy remain to be explored. Enrichment of erythroid genes as TKI-resistance hits can be presumably attributed to the erythroleukemia phenotype of K562 cells. However, a recent study suggested that erythroid transcription factors are a marker of good response to TKI treatment in CML patients, further supporting the role of this pathway in modifying TKI sensitivity.47 In addition, other TKI-resistance hits, such as EIF2AK1 and CCDC101, are key regulatory factors of erythroid differentiation of HSCs.48,49 On the other hand, potential TKI-sensitization hits included RAB10, IGF1R, and YBX1 genes. RAB10 is one of the small GTPases, implicated in regulating cellular processes such as vesicular trafficking and lysosomal functions.50 RAB10 KO was associated with tumor suppression in solid tumors.51 Confirming the TKI-sensitization effect of IGF1R KO, IGF1R inhibitors were reported to overcome TKI resistance in CML.52 YBX1 is an oncogenic pro-survival factor in leukemia,53,54 and therefore, YBX1 depletion is expected to enhance dasatinib killing through impairment of the DNA damage response in CML cells.55 Furthermore, dasatinib-induced SRC inhibition has been reported to inhibit YBX-1 phosphorylation and activation, which may explain the specific enrichment of YBX1 KO as a sensitization hit to dasatinib.56
Interestingly, our results highlighted KCTD5 as a consistent resistance hit to all tested TKIs. KCTD5 functions as a substrate adaptor for cullin3-based ubiquitin E3 ligases.57 Ubiquitination of BCR::ABL1 can destine it to aggresomal sequestration or proteasomal degradation with further block of downstream signaling.58 Our results confirmed the direct interaction between KCTD5, CUL3, and BCR::ABL1 proteins, with impairment of TKI-induced BCR::ABL1 ubiquitination upon KCTD5 KO. In addition, KCTD5 KO was reported as a negative regulator of AKT signaling,59 which can play a role in mediating TKI resistance.60 Interestingly, KCTD5 KO was reported to induce resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancers,61 underscoring the importance of this pathway in mediating multi-drug resistance. The ubiquitination pathway appears to play a pivotal role in CML TKI resistance, as evidenced by the frequent mutations affecting genes related to ubiquitin during CML progression.62 In addition, the enrichment of ubiquitination-related genes among TKI-resistance hits in CRISPR screens further underscores the potential significance of targeting the ubiquitination pathway in the context of high-risk CML.63
In conclusion, we consider our data utilizing primary CML patient cells to be a valuable resource for understanding BCR::ABL1-independent TKI resistance in CML-LSPCs and believe they serve as a foundation for future translational research aiming to identify clinically efficient treatment strategies dually targeting BCR::ABL1-dependent and -independent pathways, which may enable eradication of CML-LSCs and achievement of a CML cure.
Limitations of the study
Our approaches do have certain limitations, such as the inability to evaluate the effects of candidate drugs or gene KOs in an in vivo setting, which would offer more conclusive clinical insights. In addition, it would be optimal to test drug combinations in samples from patients with primary BCR::ABL1-independent TKI resistance in addition to BP-CML and CP-CML samples used in this study. In addition, further functional studies are required to explore and validate the role of the KCTD5 gene in primary TKI resistance in CML.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| CD11b-BV605 | BD Biosciences | Cat#562721; RRID:AB_2737745 |
| CD26-APC | Biolegend | Cat#302709; RRID:AB_10916120 |
| CD33-BV421 | BD Biosciences | Cat#565949; AB_2737405 |
| CD34-PE | BD Biosciences | Cat#550761; AB_393871 |
| CD34-FITC | BD Biosciences | Cat#345801; RRID:AB_2868825 |
| CD38-FITC | BD Biosciences | Cat#340909; RRID:AB_2868744 |
| CD38-PE | BD Biosciences | Cat#345806; RRID:AB_2868828 |
| CD117-PE-Cy7 | Biolegend | Cat#313212; RRID:AB_893222 |
| 7-AAd | BD Biosciences | Cat#559925; RRID:AB_2869266 |
| c-Abl (Rabbit) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2862S; RRID:AB_2257757 |
| Kctd5 (Rabbit) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#94396; RRID:AB_2800228 |
| Cul3 (E4G3M, Rabbit) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#10450; RRID:AB_2943632 |
| Ubiquitin (P4D1, Mouse) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#3936; RRID:AB_331292 |
| β-Actin (8H10D10, Mouse) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#3700S; RRID:AB_2242334 |
| anti-rabbit | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#7074S; RRID:AB_2099233 |
| anti-mouse | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#7076S; RRID:AB_330924 |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| RQ1 RNase-Free DNase | Promega | Cat#M6101 |
| StemRegenin1 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#72342 |
| UM729 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#72332 |
| StemSpan™ CD34+ Expansion Supplement | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#02691 |
| RPMI-1640 medium | Lonza | Cat#12-702F |
| StemSpan™ SFEMII | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat# 09655 |
| CellTiter-Glo 2.0 reagent | Promega | Cat#G9243 |
| MethoCult™ H4434 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#04434 |
| MyeloCult™ H5100 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#05100 |
| MethoCult™ H4435 | STEMCELL Technologies | Cat#04435 |
| Lipofectamine™ 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#10696153 |
| PLUS™ Reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#11514-015 |
| protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#87786 |
| Laemmli buffer | Bio-Rad | Cat#161-0747 |
| Odyssey blocking buffer | LI-COR Biosciences | Cat#927-70001 |
| Pierce™ IP lysis buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#87788 |
| RIPA Lysis and Extraction Buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#89900 |
| DMSO | Sigma | Cat#D2650 |
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| CRISPR Knock-Out version 2 (GeCKOv2) sgRNA library in lentiGuide-Puro plasmid | Addgene | Cat#1000000049 |
| lentiCas9-EGFP plasmid | Addgene | Cat#63592; RRID:Addgene_63592 |
| lentiCRISPRv2-GFP plasmid | Addgene | Cat#52961; RRID:Addgene_52961 |
| pCMV-VSV-G plasmid | Addgene | Cat#8454; RRID:Addgene_8454 |
| psPAX2 plasmid | Addgene | Cat#12260; RRID:Addgene_12260 |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| CD34 MicroBead Kit | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat#130-046-702/703; RRID:AB_2848167 |
| NucleoBond MidiEF kit | Macherey-Nagel | Cat#740420.5 |
| QIAamp DNA Blood Maxi Kit | Qiagen | Cat#51192 |
| miRNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | Cat#217004 |
| Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#23225 |
| Trans-Blot® Turbo™ Mini Nitrocellulose Transfer Packs | Bio-Rad | Cat# 1704158 |
| PureProteome™ Protein A/G Mix Magnetic Beads | Merck | Cat#LSKMAGAG02 |
| Qubit® dsDNA BR assay kit | Life Technologies | Cat#Q32850 |
| Biological samples | ||
| Primary bone marrow and/or peripheral blood samples | This paper | N/A |
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
| K562 | DSMZ | ACC10 |
| LAMA84 | DSMZ | ACC168 |
| 293FT (HEK) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#R70007 |
| Deposited data | ||
| FASTQ files of RNA seq from individual gene KO in K562 | This paper | Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8065111; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8063669; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8064683; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8065099; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8065103; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8065107; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8065115; https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.8065370 |
| FASTQ files of DNA deep sequencing for genome scale CRISPR screens with drugs | This paper | Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8064009 |
| Oligonucleotides: Guide RNA (sg) and PCR primers (forward [-F] and reverse [-R]) | ||
| Sequences of oligonucleotides used in this paper are available from Table S5 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | N/A |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| Breeze | Potdar et al. and Yadav et al.64,65 | https://breeze.fimm.fi |
| SynergyFinder 3.0 web-tool | Ianevski et al.23 | N/A |
| FlowJo V10 | TreeStar Inc. | N/A |
| MAGeCK v0.5.6. 5 | Li et al.66 | N/A |
| TIDE | Brinkman et al.67 | N/A |
| STAR aligner | Dobin et al.68 | N/A |
| SubRead | Liao et al.69 | N/A |
| edgeR | Robinson et al.70 | N/A |
| GSEA | Subramanian et al.71 Broad Institute | N/A |
| Enrichr | Kuleshov et al. and Chen et al.72,73 | N/A |
| ImageJ | Schneider et al.74 | N/A |
| GraphPad Prism 10 | GraphPad Software Inc. | N/A |
| R 3.5.0 | N/A | |
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact, Satu Mustjoki (satu.mustjoki@helsinki.fi).
Materials availability
Viral constructs and cell lines generated in this study will be made available on request with the Materials Transfer Agreement.
Data and code availability
-
•
The amplicon sequencing data from CRISPR-Cas9 screens as well as RNA-sequencing data from individual gene-KO cell lines are deposited to Zenodo (zenodo.org). De-identified individual participants’ gene expression data are deposited to Zenodo (zenodo.org) under restricted access due to GDPR, and access request for research use can be sent to the corresponding authors. DOIs are listed in the key resources table. This paper does not generate original code.
-
•
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this work paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
Experimental model and study participant details
Cell lines and cell culture
K562 and LAMA84 CML cell lines were obtained from DSMZ (German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures). Both cell lines were cultured in RPMI-1640 (Lonza) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine (Lonza), and 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco). The 293HEK-FT cell line used for lentivirus production was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific and cultured in DMEM (Lonza) with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco) (D10).
Patient samples
Primary bone marrow and/or peripheral blood samples were collected from 25 CML patients at diagnosis and subsequently used in different drug screening experiments as indicated in Table S1. Samples from 3 healthy donors and from CML patients, where blasts constitute <20% of bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMNCs), were sorted for CD34+ fraction using magnetic cell sorting (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany). For CML patients, disease diagnosis and progression were defined according to the 2016 edition of World Health Organization criteria.75 In line with the analysis of drug sensitivity profiles of CD34+ samples from CML patients described in the main manuscript, we have also analyzed DSRT data of unsorted samples from our previously published patient’ cohort including 34 CML and 4 atypical CML patients.13 All subjects gave their written informed consent in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki and study was approved by the Helsinki University Hospital ethics committee.
Method details
Processing and culture of patient samples
BM or peripheral blood (PB) samples were enriched for mononuclear cells (MNCs) using Ficoll gradient centrifugation. For samples from CML patients, where blasts constitute <20% of bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMNCs), as well as from 3 healthy donors, CD34+ fraction was enriched using magnetic cell sorting (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany), according to the manufacturer recommendations, and purity were checked using antiCD34-FITC (BDbioscience, Cat# 345801). Thawed samples were resuspended in StemSpan™ SFEMII (STEMCELL Technologies), supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin. After thawing, samples were treated with 50 μl of RQ1 RNase-Free DNase (Promega, #M6101) for 30 min in 1 ml of media, if cell clumps were if needed. Samples were recovered for 2-4 h in appropriate amount of StemSpan (at a concentration of 1 million/ml) before plating on drug plates. For media optimization, StemSpan™ CD34+ Expansion Supplement (STEMCELL Technologies), StemRegenin1 (STEMCELL Technologies, Cat#72342) and UM729 (STEMCELL Technologies, Cat#72332) were tested.
Drug sensitivity and resistance testing (DSRT)
The drug library for patient sample screening consisted of 82 approved drugs and investigational oncological compounds. For the individual gene-KO cell lines, a broader library of 134 compounds were used. An extensive library of 528 compounds (156 approved, 372 investigational) was specifically used for the KCTD5-KO K562 cells. The drugs included in different libraries that were used in this study can be found from Table S2. All drugs were purchased from commercial vendors and dissolved in either 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or water. DSRT was performed as previously described.76 In short, each compound was tested in five different concentrations, covering a 10 000-fold concentration range, that were pre-printed on 384-microwell plates (Corning) using an acoustic liquid handling device (Echo 550, Labcyte Inc.). Five μl culture medium per well was first added to dissolve the pre-plated drugs and plates were shaken for 10 min. Cells were thawed and or processed into a single-cell suspension (10000 cells for CML-LSPCs and 5000 cells for cell lines, in 20 μl per well), that was dispensed using Multi-Drop Combi peristaltic dispenser (Thermo Scientific) and MultiFlo FX Liquids dosing dispenser (BioTek). Patient samples were suspended in StemSpan™ SFEMII (STEMCELL Technologies), supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin, while cell lines were suspended in RPMI media (Lonza Bioscience), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% L-glutamine and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Plates were then incubated for 72 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. CellTiter-Glo 2.0 reagent (Promega) was used to measure cell viability according to the manufacturer’s instructions using a Pherastar FS plate reader. Luminescence measurements of cell viability were normalized to 100 mM benzethonium chloride-containing wells (positive control) and DMSO-only wells (negative control). DSRT data was analyzed using Breeze,64 a web-based DSRT data analysis platform (https://breeze.fimm.fi). Drug responses were quantified using the drug sensitivity score (DSS) model.65
Drug combination testing
For the combination drug screening, 18 imatinib-drug combinations were tested using dose-response matrices comprising of seven different concentrations for each drug (Table S2). Combination drug testing was performed as previously described.77 Sample processing for combination drug screening was carried out as above-described for single agent drug testing. Drug combinations were pre-plated on 384-well plates with dose-response matrices comprising 7 different concentrations for each drug as well as DMSO controls. SynergyFinder 3.0 web-tool23 was utilized to quantify drug combination synergy with the highest single agent (hsa) synergy score. cNMF algorithm78 implemented in SynergyFinder was utilized for the outlier detection and replacement. A combinatorial synergistic activity was reported if the corresponding summary hsa synergy score was above 5, and antagonistic if less than -5, otherwise combination effect was considered as additive.
Flowcytometry-based drug sensitivity profiling (FC-DSRT)
For the FC-DSRT, 20 compounds were tested in four different concentrations (Table S2). FC-DSRT were performed as previously described.79 Compounds were dissolved in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide or water, and dispensed on a 96-well polypropylene plate (Corning) in a four doses log concentration series using an Echo 550 acoustic liquid handling device (Labcyte). CML-LSPCs were dispensed with MultiFlow FX.RAD (BioTek) to compound plates, 20,000 live cells in 100 μl StemSpan™ SFEMII in each well and incubated for 72 h at 37°C and 5% CO2. Monoclonal antibodies were added on cells and stained for 30 min at room temperature using optimized no-wash protocol. Dead cell exclusion dye 7-AAd (BD Biosciences, #559925) were added for 2 minutes before acquisition of samples by iQue Screener Plus flow cytometer (Intellicyt).
Colony forming (CFA) and long-term colony initiating cell (LTC-IC) assays
For CFA, 1.5x104 BM CD34+ sorted cells from a CP-CML patient were re-suspended in 0.4 ml StemSpan™ SFEMII (STEMCELL Technologies) and the samples were mixed with 4 ml of methylcellulose (MethoCult™ H4434, STEMCELL Technologies). Drugs (imatinib, mepacrine, navitoclax) were added in the indicated concentrations. 1.1 ml were plated on 35–mm-dishes in triplicate according to instructions of the manufacturer (STEMCELL Technologies). Colonies were counted after 14 days using an inverted microscope. LTC-IC assay was performed following the instructions from STEMCELL Technologies. 1.5x104 BM CD34+ sorted cells from a CP-CML patient were cultured in human long-term culture medium (MyeloCult™ H5100, STEMCELL Technologies) on irradiated M2-10B4 cells (STEMCELL Technologies) monolayer in duplicates on a 6-well plate for five weeks with half-weekly change of the media. Cells were then collected and 5x104 transferred to 4 ml of methylcellulose (MethoCult™ H4435, STEMCELL Technologies) and were then processed similar to CFA to determine the drug effects on the colonogenic capacity of long-term culture cells.
Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screens
CRISPR-Cas9 gene-perturbation screens were performed as previously described.18 The Genome-Scale CRISPR Knock-Out version 2 (GeCKOv2) sgRNA library in the lentiGuide-Puro plasmid 44(Addgene #1000000049) was amplified in Endura competent cells (Lucigen) according to instructions provided by the Zhang lab and Lucigen. Plasmid DNA was extracted using NucleoBond-MidiEF kit (Macherey-Nagel), with maximum 0.5g bacterial pellet per column. Sufficient sgRNA representation from half libraries was confirmed by deep sequencing of the resulting plasmid pool. The ratio between the 10th and 90th percentile of sgRNA read counts was less than 6-folds. For lentivirus production, 10 μg of both libraries’ plasmids were transfected into 293FT cells, seeded one day before at 11.4 million cells per T-225 flask, together with 10 μg of pCMV-VSV-G and 15 μg of psPAX2 using 100 μl Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 200 μl of Plus Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After 6 hours incubation, the culture medium was replaced with 30 ml of D10 containing 1% BSA. Viral supernatant was harvested after 60 hours, filtered using a 0.45 μm filter, and stored in -70°C.
To generate K562-Cas9 cells, K562 were transduced with virus produced using the lentiCas9-EGFP plasmid (Addgene, #63592), single-cell sorted using a Sony SH800 cell sorter, and a clone with high and uniform EGFP expression was selected for the subsequent steps. The amount of lentivirus to be used for screen was first titrated to select the concentration achieving 10-20% transduction efficiency to ensure that majority of the cells receive only one sgRNA. For the GW screen, K562-Cas9 transduced with the genome-wide library, 429 million cells were transduced in 12x12-well plates, where in each well 3 million cells were suspended in the titrated virus volume (16 μl of GeCKO v2 library virus + 64 μl R10) and 80 μl Polybrene, centrifuged at 37°C at 800 g for 2 h, after which virus was washed away. Transduced cells were then distributed to T-225 flasks (0.5 million/ml) and selected with 0.9 μg/ml puromycin for 6 days starting 48h post-transduction.
On day 8 post-transduction, cells were divided into the following conditions with 90 million cells each in 2xT-225 flask with 90 ml R10: 1) K562 only (DMSO), 2) K562+imatinib (900nM), 3) K562+dasatinib (1nM), 4) K562+asciminib (100nM), 5) K562+tivozanib (800nM), 6) K562+azd1775 (1000nM). For Mepacrine (5000nM), biological triplicate was kept along with triplicate control conditions. The selection of the three tested drugs (tivozanib, AZD1775, and mepacrine) among other DSRT-based drug candidates was made according to their activity in K562 cells (inactive drugs in K562 cells were excluded). For example, the TP53-mutated K562 cells are resistant to idasanutlin and RG-7112 drugs. A pre-treatment 90 million cell pellet was frozen in -70. The drug concentrations were selected to achieve sufficient selection pressure, where the number of cells remains almost constant throughout the screen, and cells were passaged every 3 days, for 2 weeks. At day 14 of drug incubation, cells were pelleted, frozen in -70 °C, and later thawed for genomic DNA extraction using Blood Maxi Kit (Qiagen).
Sequencing and data analysis
Sequencing and data analysis were performed as previously described.18 A two-step PCR protocol were used to amplify amplicons containing sgRNA sequences using primers flanking the sgRNA cassette. Following overhangs were added to locus-specific primers to make them compatible with the index primers. Oligo primer sequences were adapted from Illumina adapter sequences document #1000000002694. In the first PCR, the reaction mix (50 μl) included containing 1200 ng of sample DNA, 25 μl of 2× Phusion High-Fidelity PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 0.5 μM of each locus specific primer. Each sample was amplified for 96 separate times, then the 96 reactions were pooled together, used as a template in the second PCR reaction (index PCR). The second PCR was done using 1 μl of the first step pooled product, 10 μl of 2× Phusion High-Fidelity PCR Master Mix, 0.375 μM of index primer 1, and 0.375 μM of index primer 2, in a final volume of 20 μl. Seven identical reactions were performed, using a unique combination of dual indexes for each sample pool each. DNA Engine Tetrad 2 (Bio-Rad Laboratories) or G-Storm GS4 (Somerton) thermal cyclers were used to cycle the PCR reactions using the recommended programs. The seven amplified and indexed reactions from each sample were pooled, then purified using Agencourt AMPure XP beads twice by adding 0.8x volume of beads compared to the sample volume. Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Genomics) was used to quantify the yield of the purified sample pools. Sample pools were sequenced with Illumina HiSeq 2000 System (Illumina). Read length used in the run was PE100. Screen data were analyzed using MAGeCK v0.5.6. 5 Forward direction reads were aligned to the GeCKO v2 library sgRNA sequences using the ‘mageck count’ command with default parameters. Comparisons across conditions were performed on the resulting sgRNA read count matrix using the ‘mageck test’ command with default parameters.
CRISPR-Cas9 screen hit validation using cells expressing individual sgRNAs
For validation of hits from genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen, sgRNA-expressing cells were generated expressing either single-guide RNAs targeting screen hits and control sgRNAs non-targeting sgRNAs (2 different sgRNA were used for each gene). sgRNAs were cloned into lentiCRISPRv2-GFP backbone plasmid (Addgene, #52961), including KCTD5, APAF1, EIF2AK1, IGF1R, CCNC and CDK2 genes (sgRNAs sequences are listed in Table S5). After lentivirus production, K562 and LAMA84 cells were transduced for stable expression of sgRNAs. Cells were GFP-selected, sorted using single-cell sorting (Sony SH800 cell sorter), and further grown prior to experiments. For creating KCTD5-KO in CML-LSPCs samples (n=2), KCTD5 targeting sgRNA was cloned into lentiCRISPRv2-GFP backbone plasmid (Addgene, #52961) and transduced into CML-LSPCs, where the transduction efficiency ranged between 12-20% of LSPCs. Transduction efficiencies were measured by assessing GFP positivity from fixed transduced samples. Analysis of editing efficiency was performed using Sanger sequencing and TIDE analysis.67 A list of primers used for Sanger sequencing in addition to the detected targeting efficiencies can be found from Table S5.
RNA sequencing
RNA sequencing and gene expression analysis were performed as previously described.80 Total RNA was isolated from drug-treated and control LSPCs as well as from individual gene-KO cell lines using miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). Qubit RNA kit (Life Technologies) was used to quantitate RNA in samples. We used 1.5 μg of Truseq standard total RNA preparation kit (illumina) to perform ribodepletion of rRNA and further for RNA-seq library preparation for all samples. RNA-sequencing libraries were purified using SPRI beads (Agencourt AMPure XP, Beckman Coulter). High Sensitivity chips by Agilent Bioanalyzer (Agilent) was used to evaluate the library quality. Paired-end sequencing of sequencing libraries was performed using Novaseq S2 XP NS2-200 (Illumina). For analysis of RNA-sequencing data were pre-processed and filtered paired-end reads were aligned using STAR68 guided with EnsEMBL v82 gene models to human reference genome build 38 (EnsEMBLv82). Feature counts were generated using SubRead.69 Conversion of feature counts expression estimates was done using Trimmed Mean of M-values (TMM) normalization.81 Genomic features with a CPM value ≤1.00 in less than half of samples were removed. Differential expression testing was then performed using the edgeR70 software. In the statistical testing, P-values were adjusted with Storey’s Q-value for multiple comparisons.82 Differentially expressed genomic features were determined with Q ≤0.05 cutoff value.
Pathway enrichment analysis
Pathway enrichment analysis was done using GSEA71 software (Broad Institute) and Enrichr72,73. In the GSEA analysis, a pre-ranked analysis was done using gene list prepared by ordering genes by their log-fold change between individual gene-KO and control groups using CPM data. GSEA analysis was performed using default values. False discovery rate (FDR) q <0.05 was used as a threshold to filter analysis output. When nominal P-values in GSEA analysis equals 0, it was replaced by the lowest identified P-value in the analysis for visualization. The Enrichr was applied to the protein coding genes significantly differentially expressed between different conditions and control groups.
Western blot analysis and immunoprecipitation
Western blot was performed mainly as previously described.83 Cells were washed twice with cold PBS and further lysed in ice-cold RIPA buffer supplemented with 1× protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific, #87786). For removal of cell debris, samples were centrifuged for 10 min at 4 °C, 12,000×g. Total protein concentration was measured with Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, #23225) and samples were prepared using Laemmli buffer (Bio-Rad Laboratories). After SDS-PAGE, Trans-Blot® Turbo™ Transfer System (Bio-rad) was used to transfer the proteins into a nitrocellulose membrane (0.2 μm pore-size nitrocellulose, Bio-rad). Primary antibodies (1:1000 dilution) were incubated overnight at 4 °C in the Odyssey blocking buffer (LI-COR Biosciences, #927-70001) containing 0.2% Tween 20. Secondary antibodies (1:15,000 dilution) in the blocking buffer containing 0.2% Tween 20 were then incubated for 2 h at room temperature. Proteins bands were visualized using Odyssey Imaging Systems (LI-COR Biosciences). For co-immunoprecipitation, K562 cells were lysed using PierceTM IP lysis buffer (ThermoFisher, Cat#87788). One milligram of cell lysates was pre-cleared with PureProteome™ Protein A/G Mix Magnetic Beads (Merck, Cat#LSKMAGAG02) for 1 hour at 4 °C. Pre-cleared supernatants were incubated with anti-Abl antibody overnight at 4 °C with gentle rocking. Magnetic beads were added to the immune complexes, and then incubated at room temperature for 15 min with gentle rocking. The immune complexes were washed three times in PBST, resuspended in the elution buffer and heated at 70 °C for 10 min. Bands were quantified using ImageJ.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Information of the statistical tests used is reported in the figure legends. Patient samples used for the individual experiments are reported the Table S1. Mann-Whitney U-test (for non-parametric test comparisons), Two-tailed Student t-test (for parametric test comparisons), Fisher Exact test (for categorical data), Pearson’ correlation and Spearman correlation coefficients were used where indicated and computed using GraphPad Prism 8 software or R 3.5.0. False discovery rate approach to correct for multiple comparisons was used where indicated.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the Hematology Research Unit Helsinki (Hanna Lähteenmäki, Tiina Kasanen, Minna Pajuportti, Saara Vaalas), Finnish Institute of Molecular Medicine High Throughput Biomedicine (FIMM-HTB) Unit (Laura Turunen, Katja Suomi, Maria Nurmi, Tanja Ruokoranta), and Sequencing Laboratory Unit (Pekka Ellonen, Sari Hannula, Tiina Hannunen, Pirkko Mattila, Anu Suoranta) at the Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM) for their excellent technical assistance. CSC (IT Center for Science Ltd.) is acknowledged for their expert help and computing resources.
This work was supported by the Academy of Finland (grant nos. 292605, 287224, 310507, 313267, and 326238); a Finnish special governmental subsidy for health sciences, research, and training; the Signe and Ane Gyllenberg Foundation; the Finnish Cancer Institute; the Nordic Cancer Union; the Helsinki Institute of Life Science; Cancer Foundation Finland; the Relander Foundation; the EUTOS project for CML 2022; a Pfizer investigator initiated research grant; the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research & Innovation Programme (REMEDi4ALL project, grant agreement no. 101057442); the Cancer Society of Finland; and the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation. The FIMM-HTB unit is supported by the University of Helsinki, HiLIFE, and Biocenter Finland.
Author contributions
S.A.A. designed the study, performed experiments, and analyzed the data from flow cytometry, genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screens, RNA sequencing, and drug sensitivity experiments. O.D. and J.K. contributed to CRISPR-Cas9 screens. E.K. and M.W. contributed to designing and performing flow cytometry drug screening. A.I. and T.A. contributed to plate design and analysis of combination drug testing data. P.P., S.P., and K.W. contributed to library design, media optimization, and analysis of drug sensitivity data. K.L. and K.P. contributed to preparation and collection of biological samples and clinical data. S.M. conceived and designed the study and directed and supervised the research. S.A.A. wrote the manuscript with the help of S.M. All authors contributed to writing the paper and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of interests
S.A.A. has received research funding from Incyte. S.M. has received honoraria and research funding from Novartis, Pfizer, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and honoraria from DrenBio (all not related to this study).
Published: April 22, 2024
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101521.
Contributor Information
Shady Adnan Awad, Email: shady.awad@helsinki.fi.
Satu Mustjoki, Email: satu.mustjoki@helsinki.fi.
Supplemental information
References
- 1.Chereda B., Melo J.V. In: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Hematologic Malignancies. Hehlmann R., editor. Springer International Publishing; 2016. The Biology and Pathogenesis of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia; pp. 17–39. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bower H., Björkholm M., Dickman P.W., Höglund M., Lambert P.C., Andersson T.M.-L. Life Expectancy of Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Approaches the Life Expectancy of the General Population. J. Clin. Orthod. 2016;34:2851–2857. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.66.2866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Saußele S., Richter J., Hochhaus A., Mahon F.-X. The concept of treatment-free remission in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:1638–1647. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Loscocco F., Visani G., Galimberti S., Curti A., Isidori A. BCR-ABL Independent Mechanisms of Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2019;9:939. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jabbour E., Parikh S.A., Kantarjian H., Cortes J. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia – Mechanisms of Resistance and Treatment. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2011;25:981–v. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2011.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Copland M., Hamilton A., Elrick L.J., Baird J.W., Allan E.K., Jordanides N., Barow M., Mountford J.C., Holyoake T.L. Dasatinib (BMS-354825) targets an earlier progenitor population than imatinib in primary CML but does not eliminate the quiescent fraction. Blood. 2006;107:4532–4539. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-07-2947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Corbin A.S., Agarwal A., Loriaux M., Cortes J., Deininger M.W., Druker B.J. Human chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are insensitive to imatinib despite inhibition of BCR-ABL activity. J. Clin. Invest. 2011;121:396–409. doi: 10.1172/JCI35721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Charaf L., Mahon F.-X., Lamrissi-Garcia I., Moranvillier I., Beliveau F., Cardinaud B., Dabernat S., de Verneuil H., Moreau-Gaudry F., Bedel A. Effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on stemness in normal and chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2017;31:65–74. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Warfvinge R., Geironson L., Sommarin M.N.E., Lang S., Karlsson C., Roschupkina T., Stenke L., Stentoft J., Olsson-Strömberg U., Hjorth-Hansen H., et al. Single-cell molecular analysis defines therapy response and immunophenotype of stem cell subpopulations in CML. Blood. 2017;129:2384–2394. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-07-728873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Malani D., Kumar A., Brück O., Kontro M., Yadav B., Hellesøy M., Kuusanmäki H., Dufva O., Kankainen M., Eldfors S., et al. Implementing a Functional Precision Medicine Tumor Board for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:388–401. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kornauth C., Pemovska T., Vladimer G.I., Bayer G., Bergmann M., Eder S., Eichner R., Erl M., Esterbauer H., Exner R., et al. Functional Precision Medicine Provides Clinical Benefit in Advanced Aggressive Hematologic Cancers and Identifies Exceptional Responders. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:372–387. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patel S.B., Kuznetsova V., Matkins V.R., Franceski A.M., Bassal M.A., Welner R.S. Ex Vivo Expansion of Phenotypic and Transcriptomic Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Exp. Hematol. 2022;115:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2022.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pietarinen P.O., Eide C.A., Ayuda-Durán P., Potdar S., Kuusanmäki H., Andersson E.I., Mpindi J.P., Pemovska T., Kontro M., Heckman C.A., et al. Differentiation status of primary chronic myeloid leukemia cells affects sensitivity to BCR-ABL1 inhibitors. Oncotarget. 2017;8:22606–22615. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuusanmäki H., Leppä A.M., Pölönen P., Kontro M., Dufva O., Deb D., Yadav B., Brück O., Kumar A., Everaus H., et al. Phenotype-based drug screening reveals association between venetoclax response and differentiation stage in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2020;105:708–720. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.214882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Spinner M.A., Aleshin A., Santaguida M.T., Schaffert S.A., Zehnder J.L., Patterson A.S., Gekas C., Heiser D., Greenberg P.L. Ex vivo drug screening defines novel drug sensitivity patterns for informing personalized therapy in myeloid neoplasms. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2768–2778. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Behan F.M., Iorio F., Picco G., Gonçalves E., Beaver C.M., Migliardi G., Santos R., Rao Y., Sassi F., Pinnelli M., et al. Prioritization of cancer therapeutic targets using CRISPR–Cas9 screens. Nature. 2019;568:511–516. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee D.-H., Kang S.-H., Choi D.-S., Ko M., Choi E., Ahn H., Min H., Oh S.J., Lee M.S., Park Y., Jin H.S. Genome wide CRISPR screening reveals a role for sialylation in the tumorigenesis and chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2021;510:37–47. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dufva O., Koski J., Maliniemi P., Ianevski A., Klievink J., Leitner J., Pölönen P., Hohtari H., Saeed K., Hannunen T., et al. Integrated drug profiling and CRISPR screening identify essential pathways for CAR T-cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 2020;135:597–609. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lewis M., Prouzet-Mauléon V., Lichou F., Richard E., Iggo R., Turcq B., Mahon F.-X. A genome-scale CRISPR knock-out screen in chronic myeloid leukemia identifies novel drug resistance mechanisms along with intrinsic apoptosis and MAPK signaling. Cancer Med. 2020;9:6739–6751. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chu S., McDonald T., Lin A., Chakraborty S., Huang Q., Snyder D.S., Bhatia R. Persistence of leukemia stem cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in prolonged remission with imatinib treatment. Blood. 2011;118:5565–5572. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-327437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Herrmann H., Sadovnik I., Cerny-Reiterer S., Rülicke T., Stefanzl G., Willmann M., Hoermann G., Bilban M., Blatt K., Herndlhofer S., et al. Dipeptidylpeptidase IV (CD26) defines leukemic stem cells (LSC) in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2014;123:3951–3962. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-536078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kinstrie R., Horne G.A., Morrison H., Irvine D., Munje C., Castañeda E.G., Moka H.A., Dunn K., Cassels J.E., Parry N., et al. CD93 is expressed on chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells and identifies a quiescent population which persists after tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Leukemia. 2020;34:1613–1625. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0684-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ianevski A., Giri A.K., Aittokallio T. SynergyFinder 3.0: an interactive analysis and consensus interpretation of multi-drug synergies across multiple samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:W739–W743. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Noel B.M., Ouellette S.B., Marholz L., Dickey D., Navis C., Yang T.-Y., Nguyen V., Parker S.J., Bernlohr D., Sachs Z., Parker L.L. Multiomic Profiling of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant K562 Cells Suggests Metabolic Reprogramming To Promote Cell Survival. J. Proteome Res. 2019;18:1842–1856. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Adnan Awad S., Kankainen M., Ojala T., Koskenvesa P., Eldfors S., Ghimire B., Kumar A., Kytölä S., Kamel M.M., Heckman C.A., et al. Mutation accumulation in cancer genes relates to nonoptimal outcome in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2020;4:546–559. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Oien D.B., Pathoulas C.L., Ray U., Thirusangu P., Kalogera E., Shridhar V. Repurposing quinacrine for treatment-refractory cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021;68:21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zheng X., Zhang J., Li S., Gao X., Zhang Y., Wang M., Dong L., Sun L., Zhao N., Ma Z., et al. Low doses of niclosamide and quinacrine combination yields synergistic effect in melanoma via activating autophagy-mediated p53-dependent apoptosis. Transl. Oncol. 2022;21 doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abraham S.A., Hopcroft L.E.M., Carrick E., Drotar M.E., Dunn K., Williamson A.J.K., Korfi K., Baquero P., Park L.E., Scott M.T., et al. Dual targeting of p53 and c-Myc selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells. Nature. 2016;534:341–346. doi: 10.1038/nature18288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Akter F., Ponnaiyan S., Kögler-Mohrbacher B., Bleibaum F., Damme M., Renard B.Y., Winter D. Multi cell line analysis of lysosomal proteomes reveals unique features and novel lysosomal proteins. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.12.21.423747. Preprint at. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sasaki T., Lian S., Khan A., Llop J.R., Samuelson A.V., Chen W., Klionsky D.J., Kishi S. Autolysosome biogenesis and developmental senescence are regulated by both Spns1 and v-ATPase. Autophagy. 2017;13:386–403. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1256934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Eriksson A., Chantzi E., Fryknäs M., Gullbo J., Nygren P., Gustafsson M., Höglund M., Larsson R. Towards repositioning of quinacrine for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia - Promising synergies and in vivo effects. Leuk. Res. 2017;63:41–46. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu L., Chatla S., Lin Q., Chowdhury F.A., Geldenhuys W., Du W. Quinacrine-CASIN combination overcomes chemoresistance in human acute lymphoid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:6936. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27300-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Carter B.Z., Mak P.Y., Mu H., Zhou H., Mak D.H., Schober W., Leverson J.D., Zhang B., Bhatia R., Huang X., et al. Combined targeting of BCL-2 and BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase eradicates chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016;8 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aag1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Carter B.Z., Mak P.Y., Mu H., Wang X., Tao W., Mak D.H., Dettman E.J., Cardone M., Zernovak O., Seki T., Andreeff M. Combined inhibition of MDM2 and BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase targets chronic myeloid leukemia stem/progenitor cells in a murine model. Haematologica. 2020;105:1274–1284. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.219261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stover E.H., Baco M.B., Cohen O., Li Y.Y., Christie E.L., Bagul M., Goodale A., Lee Y., Pantel S., Rees M.G., et al. Pooled Genomic Screens Identify Anti-apoptotic Genes as Targetable Mediators of Chemotherapy Resistance in Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019;17:2281–2293. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Elbæk C.R., Petrosius V., Benada J., Erichsen L., Damgaard R.B., Sørensen C.S. WEE1 kinase protects the stability of stalled DNA replication forks by limiting CDK2 activity. Cell Rep. 2022;38 doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ha D.-H., Min A., Kim S., Jang H., Kim S.H., Kim H.-J., Ryu H.S., Ku J.-L., Lee K.-H., Im S.-A. Antitumor effect of a WEE1 inhibitor and potentiation of olaparib sensitivity by DNA damage response modulation in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:9930. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66018-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Garcia T.B., Fosmire S.P., Porter C.C. Increased activity of both CDK1 and CDK2 is necessary for the combinatorial activity of WEE1 inhibition and cytarabine. Leuk. Res. 2018;64:30–33. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2017.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mancini M., De Santis S., Monaldi C., Castagnetti F., Lonetti A., Bruno S., Dan E., Sinigaglia B., Rosti G., Cavo M., et al. Polo-like kinase-1, Aurora kinase A and WEE1 kinase are promising druggable targets in CML cells displaying BCR::ABL1-independent resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2022;12 doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.901132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pietarinen P.O., Pemovska T., Kontro M., Yadav B., Mpindi J.P., Andersson E.I., Majumder M.M., Kuusanmäki H., Koskenvesa P., Kallioniemi O., et al. Novel drug candidates for blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia from high-throughput drug sensitivity and resistance testing. Blood Cancer J. 2015;5:e309. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2015.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pemovska T., Johnson E., Kontro M., Repasky G.A., Chen J., Wells P., Cronin C.N., McTigue M., Kallioniemi O., Porkka K., et al. Axitinib effectively inhibits BCR-ABL1(T315I) with a distinct binding conformation. Nature. 2015;519:102–105. doi: 10.1038/nature14119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vazquez F., Sellers W.R. Are CRISPR Screens Providing the Next Generation of Therapeutic Targets? Cancer Res. 2021;81:5806–5809. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ancos-Pintado R., Bragado-García I., Morales M.L., García-Vicente R., Arroyo-Barea A., Rodríguez-García A., Martínez-López J., Linares M., Hernández-Sánchez M. High-Throughput CRISPR Screening in Hematological Neoplasms. Cancers. 2022;14:3612. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shalem O., Sanjana N.E., Hartenian E., Shi X., Scott D.A., Mikkelson T., Heckl D., Ebert B.L., Root D.E., Doench J.G., Zhang F. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science. 2014;343:84–87. doi: 10.1126/science.1247005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Goh C.J.H., Wong J.H., El Farran C., Tan B.X., Coffill C.R., Loh Y.-H., Lane D., Arumugam P. Identification of pathways modulating vemurafenib resistance in melanoma cells via a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screen. G3 (Bethesda). 2021;11 doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaa069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang T., Birsoy K., Hughes N.W., Krupczak K.M., Post Y., Wei J.J., Lander E.S., Sabatini D.M. Identification and characterization of essential genes in the human genome. Science. 2015;350:1096–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.aac7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Krishnan V., Schmidt F., Nawaz Z., Lee K.L., Nori Venkatesh P., Makheja M., Chan Z.E., Yu M., Arul Rayan N., Gek Liang Lim M., et al. A Single-Cell Atlas Identifies Pretreatment Features of Primary Imatinib Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood. 2022;140:792–794. doi: 10.1182/blood-2022-165758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Arede L., Foerner E., Wind S., Kulkarni R., Domingues A.F., Giotopoulos G., Kleinwaechter S., Mollenhauer-Starkl M., Davison H., Chandru A., et al. KAT2A complexes ATAC and SAGA play unique roles in cell maintenance and identity in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Blood Adv. 2022;6:165–180. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Adema V., Ma F., Kanagal-Shamanna R., Thongon N., Montalban-Bravo G., Yang H., Peslak S.A., Wang F., Acha P., Sole F., et al. Targeting the EIF2AK1 Signaling Pathway Rescues Red Blood Cell Production in SF3B1-Mutant Myelodysplastic Syndromes With Ringed Sideroblasts. Blood Cancer Discov. 2022;3:554–567. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-21-0220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu Z., Xu E., Zhao H.T., Cole T., West A.B. LRRK2 and Rab10 coordinate macropinocytosis to mediate immunological responses in phagocytes. EMBO J. 2020;39 doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang W., Jia W.-D., Hu B., Pan Y.-Y. RAB10 overexpression promotes tumor growth and indicates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:26434–26447. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shi P., Chandra J., Sun X., Gergely M., Cortes J.E., Garcia-Manero G., Arlinghaus R.B., Lai R., Amin H.M. Inhibition of IGF-IR tyrosine kinase induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010;14:1777–1792. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Feng M., Xie X., Han G., Zhang T., Li Y., Li Y., Yin R., Wang Q., Zhang T., Wang P., et al. YBX1 is required for maintaining myeloid leukemia cell survival by regulating BCL2 stability in an m6A-dependent manner. Blood. 2021;138:71–85. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Li H., Zhang D., Fu Q., Wang S., Wang Z., Zhang X., Chen X., Zhu X., An N., Chen Y., et al. YBX1 as an oncogenic factor in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2023;7:4874–4885. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lei H., Xu H.-Z., Shan H.-Z., Liu M., Lu Y., Fang Z.-X., Jin J., Jing B., Xiao X.-H., Gao S.-M., et al. Targeting USP47 overcomes tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance and eradicates leukemia stem/progenitor cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:51. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20259-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Panupinthu N., Yu S., Zhang D., Zhang F., Gagea M., Lu Y., Grandis J.R., Dunn S.E., Lee H.Y., Mills G.B. Self-reinforcing loop of amphiregulin and Y-box binding protein-1 contributes to poor outcomes in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33:2846–2856. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Teng X., Aouacheria A., Lionnard L., Metz K.A., Soane L., Kamiya A., Hardwick J.M. KCTD: A new gene family involved in neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019;25:887–902. doi: 10.1111/cns.13156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Burslem G.M., Schultz A.R., Bondeson D.P., Eide C.A., Savage Stevens S.L., Druker B.J., Crews C.M. Targeting BCR-ABL1 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by PROTAC-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation. Cancer Res. 2019;79:4744–4753. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Brockmann M., Blomen V.A., Nieuwenhuis J., Stickel E., Raaben M., Bleijerveld O.B., Altelaar A.F.M., Jae L.T., Brummelkamp T.R. Genetic wiring maps of single-cell protein states reveal an off-switch for GPCR signalling. Nature. 2017;546:307–311. doi: 10.1038/nature22376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nieborowska-Skorska M., Flis S., Skorski T. AKT-induced reactive oxygen species generate imatinib-resistant clones emerging from chronic myeloid leukemia progenitor cells. Leukemia. 2014;28:2416–2418. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zeng H., Castillo-Cabrera J., Manser M., Lu B., Yang Z., Strande V., Begue D., Zamponi R., Qiu S., Sigoillot F., et al. Genome-wide CRISPR screening reveals genetic modifiers of mutant EGFR dependence in human NSCLC. Elife. 2019;8 doi: 10.7554/eLife.50223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Magistroni V., Mauri M., D’Aliberti D., Mezzatesta C., Crespiatico I., Nava M., Fontana D., Sharma N., Parker W., Schreiber A., et al. De novo UBE2A mutations are recurrently acquired during chronic myeloid leukemia progression and interfere with myeloid differentiation pathways. Haematologica. 2019;104:1789–1797. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.179937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Jiang S., Wang X., He Y., Huang H., Cao B., Zhang Z., Liu J., Wang Q., Huang Z., Mao X. Suppression of USP7 induces BCR-ABL degradation and chronic myelogenous leukemia cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:456. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03732-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Potdar S., Ianevski A., Mpindi J.-P., Bychkov D., Fiere C., Ianevski P., Yadav B., Wennerberg K., Aittokallio T., Kallioniemi O., et al. Breeze: an integrated quality control and data analysis application for high-throughput drug screening. Bioinformatics. 2020;36:3602–3604. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yadav B., Pemovska T., Szwajda A., Kulesskiy E., Kontro M., Karjalainen R., Majumder M.M., Malani D., Murumägi A., Knowles J., et al. Quantitative scoring of differential drug sensitivity for individually optimized anticancer therapies. Sci. Rep. 2014;4:5193. doi: 10.1038/srep05193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Li W., Xu H., Xiao T., Cong L., Love M.I., Zhang F., Irizarry R.A., Liu J.S., Brown M., Liu X.S. MAGeCK enables robust identification of essential genes from genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens. Genome Biol. 2014;15:554. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0554-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Brinkman E.K., Chen T., Amendola M., van Steensel B. Easy quantitative assessment of genome editing by sequence trace decomposition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:e168. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Dobin A., Davis C.A., Schlesinger F., Drenkow J., Zaleski C., Jha S., Batut P., Chaisson M., Gingeras T.R. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15–21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liao Y., Smyth G.K., Shi W. The Subread aligner: fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Robinson M.D., McCarthy D.J., Smyth G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K., Mukherjee S., Ebert B.L., Gillette M.A., Paulovich A., Pomeroy S.L., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kuleshov M.V., Jones M.R., Rouillard A.D., Fernandez N.F., Duan Q., Wang Z., Koplev S., Jenkins S.L., Jagodnik K.M., Lachmann A., et al. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W90–W97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chen E.Y., Tan C.M., Kou Y., Duan Q., Wang Z., Meirelles G.V., Clark N.R., Ma’ayan A. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinf. 2013;14:128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Schneider C.A., Rasband W.S., Eliceiri K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:671–675. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Arber D.A., Orazi A., Hasserjian R., Thiele J., Borowitz M.J., Le Beau M.M., Bloomfield C.D., Cazzola M., Vardiman J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–2405. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Pemovska T., Kontro M., Yadav B., Edgren H., Eldfors S., Szwajda A., Almusa H., Bespalov M.M., Ellonen P., Elonen E., et al. Individualized systems medicine strategy to tailor treatments for patients with chemorefractory acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:1416–1429. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Adnan Awad S., Dufva O., Ianevski A., Ghimire B., Koski J., Maliniemi P., Thomson D., Schreiber A., Heckman C.A., Koskenvesa P., et al. RUNX1 mutations in blast-phase chronic myeloid leukemia associate with distinct phenotypes, transcriptional profiles, and drug responses. Leukemia. 2021;35:1087–1099. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01011-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ianevski A., Giri A.K., Gautam P., Kononov A., Potdar S., Saarela J., Wennerberg K., Aittokallio T. Prediction of drug combination effects with a minimal set of experiments. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019;1:568–577. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0122-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kuusanmäki H., Dufva O., Vähä-Koskela M., Leppä A.-M., Huuhtanen J., Vänttinen I.M., Nygren P.J., Klievink J., Bouhlal J.O.V., Pölönen P., et al. Erythroid/megakaryocytic differentiation confers BCL-XL dependency and venetoclax resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2022;141:1610–1625. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Adnan-Awad S., Kim D., Hohtari H., Javarappa K.K., Brandstoetter T., Mayer I., Potdar S., Heckman C.A., Kytölä S., Porkka K., et al. Characterization of p190-Bcr-Abl chronic myeloid leukemia reveals specific signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Leukemia. 2021;35:1964–1975. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01082-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Robinson M.D., Oshlack A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010;11 doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Storey J.D. A Direct Approach to False Discovery Rates. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B. 2002;64:479–498. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kim D., Park G., Huuhtanen J., Lundgren S., Khajuria R.K., Hurtado A.M., Muñoz-Calleja C., Cardeñoso L., Gómez-García de Soria V., Chen-Liang T.H., et al. Somatic mTOR mutation in clonally expanded T lymphocytes associated with chronic graft versus host disease. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:2246. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16115-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
-
•
The amplicon sequencing data from CRISPR-Cas9 screens as well as RNA-sequencing data from individual gene-KO cell lines are deposited to Zenodo (zenodo.org). De-identified individual participants’ gene expression data are deposited to Zenodo (zenodo.org) under restricted access due to GDPR, and access request for research use can be sent to the corresponding authors. DOIs are listed in the key resources table. This paper does not generate original code.
-
•
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this work paper is available from the lead contact upon request.