Abstract
The orchid genus Vietorchis comprises three species, all discovered in the 21 century. Each of these species is achlorophyllous, mycoheterotrophic and is known to be endemic to Vietnam. The type species of the genus, V. aurea, occurs in a single location in northern Vietnam within a lowland limestone karstic area. Vietorchis furcata and V. proboscidea, in contrast, are confined to mountains of southern Vietnam, far away from any limestone formations. Taxonomic placement of Vietorchis remained uncertain for the reason of inconclusive morphological affinities. At the same time, the genus has never been included into molecular phylogenetic studies. We investigate the phylogenetic relationships of two species of Vietorchis (V. aurea and V. furcata) based on three DNA datasets: (1) a dataset comprising two nuclear regions, (2) a dataset comprising two plastid regions, and (3) a dataset employing data on the entire plastid genomes. Our phylogenetic reconstructions support the placement of Vietorchis into the subtribe Orchidinae (tribe Orchideae, subfamily Orchidoideae). This leads to a conclusion that the previously highlighted similarities in the rhizome morphology between Vietorchis and certain mycoheterotrophic genera of the subfamilies Epidendroideae and Vanilloideae are examples of a convergence. Vietorchis is deeply nested within Orchidinae, and therefore the subtribe Vietorchidinae is to be treated as a synonym of Orchidinae. In the obtained phylogenetic reconstructions, Vietorchis is sister to the photosynthetic genus Sirindhornia. Sirindhornia is restricted to limestone mountains, which allows to speculate that association with limestone karst is plesiomorphic for Vietorchis. Flower morphology is concordant with the molecular data in placing Vietorchis into Orchidinae and strongly supports the assignment of the genus to one of the two major clades within this subtribe. Within this clade, however, Vietorchis shows no close structural similarity with any of its genera; in particular, the proximity between Vietorchis and Sirindhornia has never been proposed. Finally, we assembled the plastid genome of V. furcata, which is 65969 bp long and contains 45 unique genes, being one of the most reduced plastomes in the subfamily Orchidoideae. The plastome of Vietorchis lacks any rearrangements in comparison with the closest studied autotrophic species, and possesses substantially contracted inverted repeats. No signs of positive selection acting on the protein-coding plastid sequences were detected.
Keywords: genome reductive evolution, non-photosynthetic plants, Silvorchis, Sirindhornia, taxonomy, tribe Orchideae
Introduction
The genus Vietorchis Aver. & Averyanova was established to accommodate a newly described non-photosynthetic (presumably mycoheterotrophic) species, V. aurea Aver. & Averyanova, which appeared to be evidently distinct from all the other known genera of Orchidaceae (Averyanov and Averyanova, 2003). Ten years after the publication of the genus, its second species, V. furcata Aver. & Nuraliev, was described (Averyanov et al., 2013; see also Averyanov, 2013; Nuraliev et al., 2019). After another ten years, the third species of the genus, V. proboscidea Aver., Vuong & V.C.Nguyen, was introduced, which is extremely close morphologically to V. furcata (Averyanov et al., 2023). All three species of Vietorchis are currently known to be endemic to Vietnam. Of them, V. aurea is found only in Cuc Phuong National Park in the northern part of the country, whereas the other two species are confined to the southern part. Vietorchis furcata was reported from Chu Yang Sin National Park, Bao Loc forest and Hon Ba Nature Reserve, and V. proboscidea occurs in Dam Rong District, being nearly sympatric with V. furcata. The only known population of V. aurea is located within a vast limestone karst area (Tuan, 2020), where it inhabits lowland valley forest between rocky limestone hills (Averyanov, 2010). The other two species occur in mountainous areas devoid of limestone karstic formations.
Phylogenetic relationships and taxonomic placement of Vietorchis became a matter of continuous debates. Similarly to many other fully heterotrophic angiosperms, Vietorchis shows highly specialized morphology of both floral and underground parts, which complicates direct comparison with the proposed relatives. Initially Vietorchis was placed into the subfamily Orchidoideae, tribe Orchideae, subtribe Orchidinae (Averyanov and Averyanova, 2003). This placement was maintained by Averyanov (2010) who also indicated that Vietorchis is most close to Silvorchis J.J.Sm. Silvorchis is a poorly known Asian mycoheterotrophic genus; its type species, S. colorata J.J.Sm., was collected only once in 1907 in Java and is now probably extinct, and its second species, S. vietnamica Aver., Dinh & K.S.Nguyen, was recently discovered in Vietnam (Averyanov et al., 2018). Averyanov consistently accepted the subtribe Orchidinae in its narrow sense, i.e. separately from the subtribe Habenariinae (recognized e.g. in Averyanov, 2008; see also Averyanov et al., 2018) or Gymnadeniinae (recognized e.g. in Averyanov, 2010).
Averyanov et al. (2013) along with the description of V. furcata introduced a new subtribe, Vietorchidinae (within the tribe Orchideae), containing the genera Vietorchis and Silvorchis. Averyanov et al. (2013, 2018) have also provided a review of the opinions of various researchers on the affinities of Silvorchis; some taxonomists assumed this genus to be related to various representatives of the subfamily Orchidoideae, while the others argued for its relationship with the mycoheterotrophic genera Epipogium J.G.Gmel. ex Borkh. and Stereosandra Blume within the subfamily Epidendroideae. Meanwhile, Orchidoideae and Epidendroideae are the most diverse subfamilies of Orchidaceae. According to modern phylogenetic views (Chase et al., 2015), they crown the orchid evolution forming the terminal branch of a grade. The rest of the grade is formed by the subfamilies Cypripedioideae, Vanilloideae and the basalmost Apostasioideae, which altogether comprise about 1% of the species diversity of Orchidaceae. The striking contradictions regarding the relationships of Silvorchis, which is morphologically similar to Vietorchis, is a consequence of discrepancy in structure of above-ground and underground organs of these plants. Gynostemium and pollinaria of Silvorchis and Vietorchis are similar to those of some Orchidinae, for example Brachycorythis Lindl. and Orchis L. (Platanthera Rich. was erroneously mentioned by Averyanov et al., 2013). At the same time, the fleshy rootless rhizomes (described as tuberoid rhizomes and rhizome-like tubers) make them close to several mycoheterotrophic lineages belonging to Epidendroideae (Epipogium, Gastrodia R.Br., Yoania Maxim.), Vanilloideae (Cyrtosia Blume, Galeola Lour., Lecanorchis Blume) and Odontochilus Blume from Orchidoideae-Cranichideae-Goodyerinae (Averyanov et al., 2013, 2018).
In most recent accounts, the preference is given to the flower structure, and the placement of Vietorchis and Silvorchis in the subfamily Orchidoideae is accepted (e.g. Chase et al., 2015). Averyanov et al. (2018) maintained them in the subtribe Vietorchidinae. Olędrzyńska et al. (2016) synonymized Vietorchidinae with Orchidinae but provided no explanation in favor of their views. Averyanov et al. (2013) argued that the non-typical rhizome morphology could evolve within Orchidoideae in the course of adaptation to the mycoheterotrophic mode of life. However, the precise relationships of these genera cannot be confidently established on the basis of morphological features alone. As pointed by Chase et al. (2015), molecular data are needed to elucidate placement of these two genera within the taxonomic system of Orchidaceae.
Suggestions to merge the genus Vietorchis within Silvorchis were proposed, and corresponding nomenclatural combinations, Silvorchis aurea (Aver. & Averyanova) Szlach. and S. furcata (Aver. & Nuraliev) Olędrz. & Szlach., were published (Szlachetko et al., 2006; Olędrzyńska et al., 2016; see also Olędrzyńska and Szlachetko, 2021). These taxonomic transfers, however, were not accompanied by any additional data on these plants, and lack sufficient substantiations for the corresponding decisions. Besides, the synonymization of Vietorchis with Silvorchis leads to a loss of taxonomic information: the species within each of these genera are clearly highly similar to each other, whereas the similarity between the genera is not so high. This would be neglected if a single genus (containing five species) is accepted. For this reason, we prefer to consider Vietorchis a distinct genus, even though it is treated, rather groundlessly, as a synonym by Chase et al. (2015), Govaerts et al. (2022) and Wei et al. (2022).
Neither Silvorchis nor Vietorchis have ever been included into a molecular phylogenetic analysis. While no material of Silvorchis is currently available for such a study, our material of Vietorchis aurea and V. furcata allows a comprehensive DNA investigation, which is performed here in order to clarify the phylogenetic relationships of this genus as well as evolution of key morphological features in this group of Orchidaceae. We present phylogenetic reconstructions based on three datasets: (1) a dataset comprising selected nuclear regions, (2) a dataset comprising selected plastid regions, and (3) a dataset employing data on the entire plastid genomes. The two plastid datasets differ in taxonomic sampling and in number of molecular markers. Since an adequate taxon sampling is crucial for correct phylogeny reconstruction, we compiled a dataset representing the main lineages and genera of the subtribe Orchidinae s.l. (i.e., sensu Jin et al., 2017) using two plastid markers. At the same time, employment of longer matrices of complete plastome data allows to reduce stochastic error in phylogeny estimation; therefore, we sequenced plastid genomes of the two species of Vietorchis and used the obtained sequences in the dataset of complete plastomes, which was less representative in terms of species sampling. This approach allows more confident phylogenetic conclusions: similar results obtained from different datasets would indicate a robustly supported reconstruction.
Apart from the resolution of the phylogenetic questions, data on plastome of Vietorchis are important for understanding of plastid evolution in heterotrophic higher plants. Transitions from autotrophy to heterotrophy are usually accompanied by substantial structural changes of plastid genomes that lead to plastome reductions (Barrett and Davis, 2012; Barrett et al., 2014; Wicke et al., 2016; Graham et al., 2017), sometimes to the drastic ones, with the extreme known cases being those of Pilostyles Guill. from Apodanthaceae (Arias-Agudelo et al., 2019) and Pogoniopsis Rchb.f. from Orchidaceae (Klimpert et al., 2022). It is therefore of special interest if the plastome of Vietorchis shares the major trends of the nonphotosynthetic plant plastomes. Here we report for the first time the structure of the plastid genome in Vietorchis, accompanied by its comparative analysis.
Materials and methods
Plastid genome of Vietorchis: sequencing, assembly and comparative analyses
Total genomic DNAs were extracted from herbarium material (V. aurea) and silica gel-dried material (V. furcata) using the CTAB-based method (Doyle and Doyle, 1987) with the following modifications: chloroform extraction was performed twice. DNA of V. furcata was additionally extracted using the DiamondDNA kit (DiamondDNA, Russia) for clarification of the borders of the inverted repeat (IR) and single copy (SC) regions. For library preparation, we used NEBNext Ultra II DNA sample preparation kit for Illumina (New England Biolabs, USA). Before processing, DNA was sheared using Covaris S220 sonicator (Covaris, USA) with the following settings: time 40 s, peak power 175 W, duty cycle 10%. Libraries were sequenced using Hiseq2000 (V. aurea) or Nextseq (V. furcata) instruments (Illumina, USA).
We failed to combine a complete plastome of V. aurea as only short non-overlapping plastid contigs were assembled; nevertheless, these data were useful for employment in the phylogenetic analyses.
For the plastome of V. furcata, de novo assembly was performed using a CLC Genomics Workbench and IDBA version 1.1.3 (Peng et al., 2012). Contigs showing similarity to plastid genomes were joined by overlapping ends. To check the accuracy of assembly, trimmed paired reads were mapped onto the assembled plastome sequence and the mapping was examined in order to check that there are no regions with gaps in coverage (see Supplementary Figure 1 for the borders of inverted repeats); also, PCR and Sanger sequencing were used for the verification of IR-SC borders. The following primers flanking the IR-SC borders were used: Vf35037F: ATTTCGATTAGGGTCGTATTCTATGG, Vf35269R: CACGGCAATACATTTATACAAAACTTC; Vf35970F: TTCGTGGATCAATTTTAATTCAGTGG, Vf36190R: ATGAAAATATTCGCGATACTTGGTTG. PCR was run on T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, USA) using Encyclo PCR kit (Evrogen, Russia) under the following program: initial denaturation for 3 min at 95°C, followed by 35 cycles each comprising 15 s at 95°C, 25 s at 58°C and 40 s at 72°C. PCR products were visualized on agarose gel, cleaned using AMPure beads (Beckman Coulter, USA) and submitted for sequencing to “Genome” sequencing facility (Engelhardt Institute of Molecular Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences). Sequencing reaction was performed using BigDye Terminator v. 3.1 kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and run on a sequencing instrument Applied Biosystems 3730 DNA Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA).
Annotation of plastid genes was performed using the GeSeq web tool (Tillich et al., 2017) with land plant plastid sequences as a reference set.
Colinearity of the sampled plastomes was estimated using the Mauve program (Darling et al., 2004).
Dispersed repeat content was explored using the repeat finder module in the Unipro UGENE package version 37.0 (Okonechnikov et al., 2012) with minimal length restricted to 20 bases for direct, inverted and palindrome repeats.
Estimation and comparison of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates in V. furcata and other orchid lineages were performed using the CodeML program from PAML package (Yang, 1997, 2007) with EasyCodeML interface (Gao et al., 2019). The tree inferred from the phylogenetic analysis of the 29-gene set was used as the input tree. A hypothesis that natural selection acting on the plastid proteins of V. furcata (25 of which were revealed in this study, see below) differs from those of other orchids was tested using two branch models, assuming a single omega value (ω, nonsynonymous to synonymous substitution rate ratio) for all branches versus different values of omega for the V. furcata branch (foreground) and the rest of the branches (background). Besides, the branch-site test was performed to detect signs of possible positive selection affecting a few sites of a protein in the V. furcata branch; Bonferroni correction was applied in both tests. Additionally, a similar gene-wide test for positive selection implemented in the BUSTED web tool (Murrell et al., 2015) was performed.
Taxon sampling for phylogenetic analyses
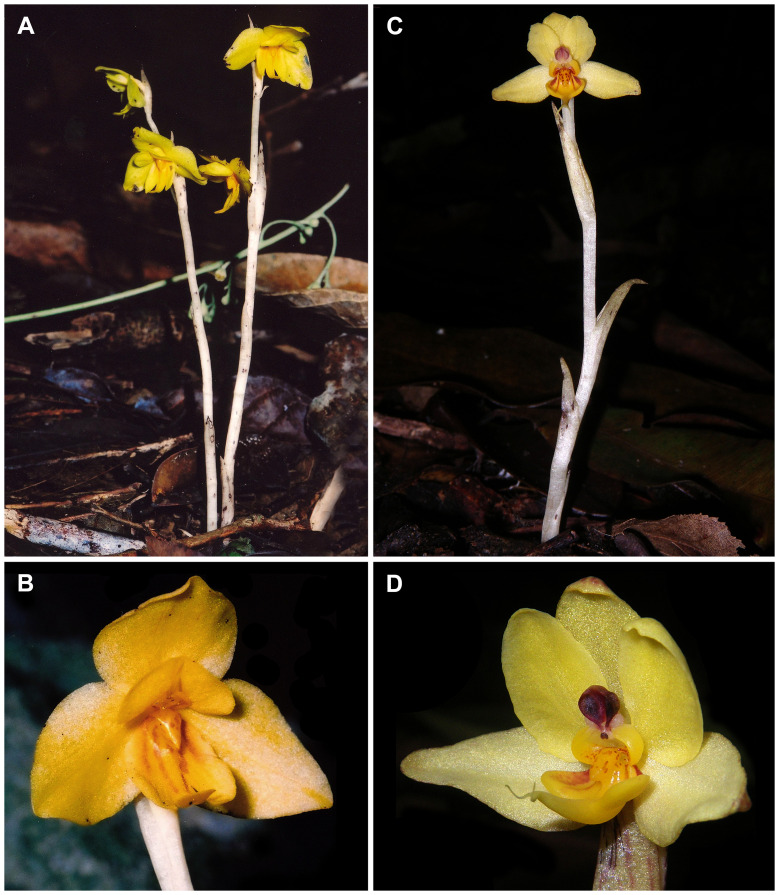
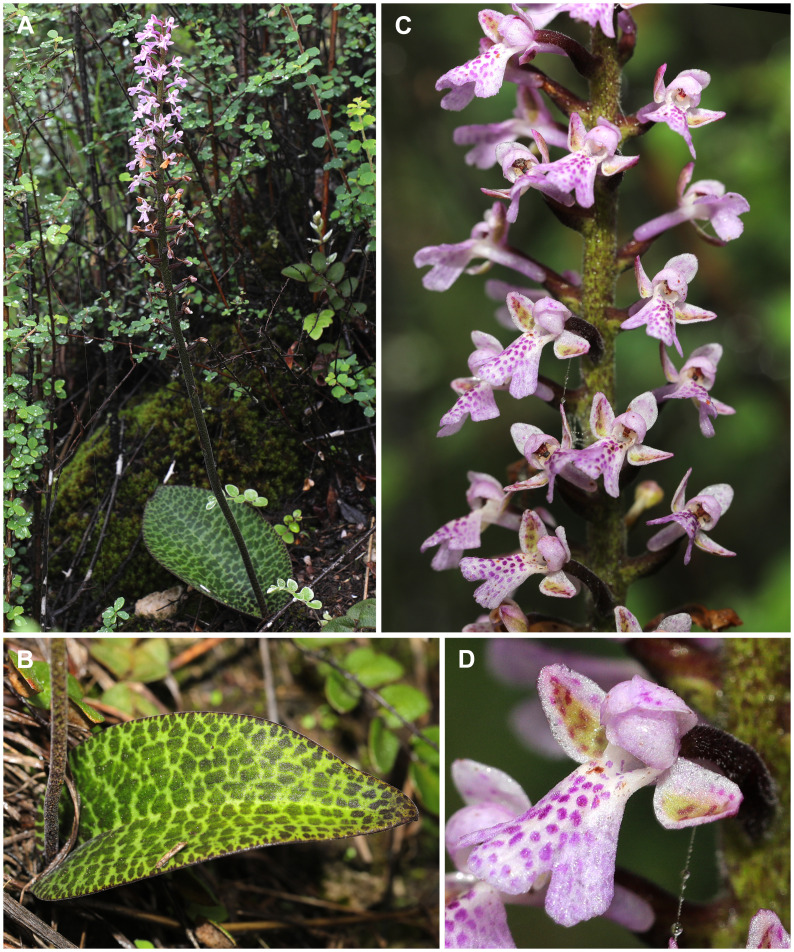
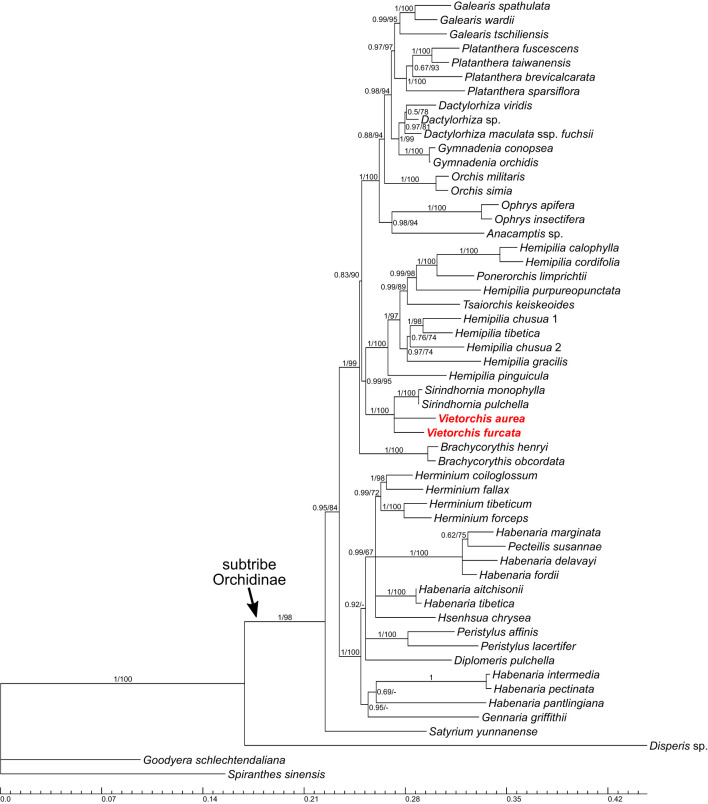
Sequences for Vietorchis aurea ( Figures 1A, B ) and V. furcata ( Figures 1C, D ) were generated de novo, representing the first DNA data obtained for this genus. In order to get rough estimates of the phylogenetic affinities of Vietorchis, the obtained ITS1–2 regions of both species were searched against the NCBI database using the BLAST tool. The analyses indicated high similarity with Sirindhornia H.A.Pedersen & Suksathan (93–95%) and the related genera from Orchidinae. Thus, in further phylogenetic analysis we focused on this subtribe. Additionally, sequences for Sirindhornia monophylla (Collett & Hemsl.) H.A.Pedersen & Suksathan ( Figure 2 ) were generated for the first time. The rest of the sequences were obtained from GenBank. The outgroup taxa were selected based on Jin et al. (2017).
Figure 1.
Studied species of Vietorchis. (A, B) Vietorchis aurea: habit and flower (May Van Xinh MVX 261; LE01076723, LE01122406). Photos by May Van Xinh. (C, D) Vietorchis furcata: habit (Nuraliev 747; LE01076758, LE01122414) and flower (Nuraliev et al. 810; LE01076727, LE01122413). Photos by M.S. Nuraliev.
Figure 2.
Sirindhornia monophylla in Yunnan, China (LE01093267). (A) Habit. (B) Leaf. (C) Inflorescence. (D) Flower. Photos by Qin-Chang Liao.
Our datasets employing selected nuclear and plastid DNA regions were based on the dataset for the subtribe Orchidinae used by Jin et al. (2017). We compiled a sampling of accessions following the idea that the generic diversity should be represented the best, as well as the basal lineages of the main clades. Fifty five specimens were employed in total (including those used by Jin et al., 2017 and studied here for the first time). These specimens belong to 54 species and 24 genera. Of them, Disperis sp., Goodyera schlechtendaliana Rchb.f. and Spiranthes sinensis (Pers.) Ames were included as outgroup taxa.
For the dataset based on the entire plastid genomes, all available published information (by March 30, 2023) on plastome structure of the species belonging to the subtribe Orchidinae was used. Goodyera pubescens (Willd.) R.Br. and Spiranthes sinensis were included as outgroup taxa. Altogether, this dataset covered 29 species (each represented by a single accession) and 13 genera.
Information on all the studied specimens is summarized in Appendices A1 and A2 . General taxonomy of Orchidaceae, including the generic placement of the studied species, follows Govaerts et al. (2022). In the Appendices, taxon names used in the cited papers are indicated in brackets for clarity, in case they are heterotypic synonyms of the currently accepted names, and also for the specimen of Herminium tibeticum X.H.Jin, Schuit. & Raskoti that was re-identified by Jin et al. (2017). The subtribe Orchidinae is accepted here in a wide sense, following Chase et al. (2015) and Jin et al. (2017), i.e. including the genera of the traditionally recognized subtribes Habenariinae and Satyriinae (e.g. Dressler, 1993; Bateman et al., 2003; Jin et al., 2012, Jin et al., 2014; Tang et al., 2015).
Phylogenetic inference
Low-coverage genome sequencing that we used for the assembly of the plastid genes/genome of Vietorchis species also allowed us to assemble the nuclear ribosomal RNA operon. Its genes and spacers, especially the 18S gene and the spacers ITS1 and ITS2, are valuable as phylogenetic markers.
Within the datasets employing selected DNA regions, we used four markers: the nuclear ribosomal ITS1–2 region (including internal transcribed spacer 1, the 5.8S rRNA gene and internal transcribed spacer 2; together referred to as ITS), a part of the nuclear Xdh gene, a part of the plastid matK gene and the plastid psbA-trnH intergenic spacer region (including the rps19 gene). These regions have previously been successfully used for phylogenetic analysis of Orchidinae (Jin et al., 2014; Tang et al., 2015; Jin et al., 2017).
The plastid dataset was composed of rRNA and protein-coding genes (29 genes in total) found in the plastome of V. furcata (accD, clpP, infA, matK, rpl14, rpl16, rpl2, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23, rpl32, rpl36, rps11, rps12, rps14, rps16, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7, rps8, rrn16, rrn23, rrn4.5, rrn5, ycf1, and ycf2). Sequences of the corresponding genes were manually extracted from 27 complete plastomes retrieved from Genbank. For V. aurea, partial sequences of 11 of these genes (accD, clpP, infA, matK, rpl14, rpl16, rpl2, rps2, rps3, ycf1, ycf2) were available from the obtained plastid contigs.
For phylogenetic purposes, the sequences of Sirindhornia monophylla were generated. Total genomic DNA was extracted from silica gel-dried leaves using a modified CTAB method (Smith et al., 1991). The primers used for amplification of the ITS, Xdh and matK regions are listed in Table 1 . The psbA-trnH region was not investigated. For the PCR, we used MightyAmp DNA polymerase (Takara Bio Inc., Japan) with corresponding buffer in a 30 mkl reaction mix. The PCR program consisted of 38–42 cycles, with each cycle as follows: denaturation for 20–30 s at 98°C, primer annealing for 30 s at 53°C, and elongation for 60–120 s at 68°C, with an initial denaturation for 3 min at 98°C and the final extension for 7 min at 68°C. The PCR products were run on 1.5% agarose gels to check the quality of amplified DNA. Commercial service of purification and Sanger sequencing was provided by the Invitrogen (China). Both forward and reverse sequences were edited and assembled using DNASTAR (http://www.dnastar.com/).
Table 1.
Primers used for amplification of the DNA regions of Sirindhornia monophylla.
| Primer | Sequence (5’ to 3’) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| ITS-17SE | ACGAATTCATGGTCCGGTGAAGTGTTCG | Sun et al. (1994) |
| ITS-26SE | GAATTCCCCGGTTCGCTCGCCGTTAC | Sun et al. (1994) |
| matK-19F | CGTTCTCATATTGCACTATG | Molvray et al. (2000) |
| matK-713F | AAGAAAAGATTCTTTTGGTTCC | Liu et al. (2011) |
| matK-969R | CTTTTCCTTGATATCGAACAT | Liu et al. (2011) |
| matK-1867R | TTGCAGTTTTCATTGCACACG | Liu et al. (2011) |
| Xdh-590F | GTGAATTCATTTGCCCATCATCT | Hu et al. (2020) |
| Xdh-1513R | GAGTGCAATATCATCTTCTCTCCG | Hu et al. (2020) |
For the specimens of Vietorchis, sequences of the regions ITS, matK and psbA-trnH were obtained from the results of the high-throughput sequencing (HTS, described above), but we were unable to get the Xdh sequences from the HTS data. We therefore used Sanger sequencing to obtain the Xdh sequence of one of the species, V. furcata. We used the following PCR primers: X502F (TGTGATGTCGATGTATGC), X1599R (G(AT)GAGAGAAA(CT)TGGAGCAAC), X551F (GAAGAGCAGATTGAAGA(AT)(AT)GCC) and X1591R (AA(CT)TGGAGCAACTCCACCA) (Górniak et al., 2010). The PCR program followed Górniak et al. (2010) and Jin et al. (2017). The PCR product was sent to the Majorbio Company (www.majorbio.com, China) for Sanger sequencing.
Sequences were aligned using MAFFT version 7.471 (Katoh et al., 2002; Katoh and Standley, 2013) and corrected manually in BioEdit (Hall, 1999). Regions where positional homology could not be firmly determined were excluded along with the gap-rich positions.
Phylogenetic reconstructions were performed for the concatenated alignments of the two nuclear markers (ITS+Xdh), for the concatenated alignments of the two plastid markers (matK+psbA-trnH), for the alignments of these four markers separately, and for the concatenated alignments of the 29 plastid genes.
The Bayesian phylogenetic reconstruction was performed by MrBayes v.3.2.7 (Ronquist et al., 2012) using four simultaneous runs of 20 million generations and four chains sampling every 1000th generation. The GTR+Γ model of nucleotide substitutions was selected for the data matrices (except for HKY+Γ for the Xdh set) as the most appropriate one according to the Akaike information criterion (Akaike, 1974) in PAUP version 4.0a (Swofford, 2003). The first million generations were discarded as burn-in, and the remaining trees were combined in a majority-rule consensus tree. Effective sample sizes were evaluated using Tracer v.1.7.1 (Rambaut et al., 2018). The effective sample sizes were > 200 for all statistics in all datasets, suggesting that the run length was adequate.
The maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic reconstruction was performed by IQ-tree (Minh et al., 2020). Internal branch support was assessed with the ultrafast bootstrap approximation (Hoang et al., 2018) using 10 thousand replications.
Results
Affinities of Vietorchis inferred from phylogenetic analysis
The main characteristics of the alignments are listed in Table 2 . The Bayesian and ML approaches for each dataset resulted in generally congruent tree topologies ( Figures 3 – 5 ; Supplementary Figures 2–12 ).
Table 2.
Statistics of multiple alignments.
| Marker(s) | Initial alignment length (bp) | Alignment length used in phylogeny inference (bp) | Number of variable sites used in phylogeny inference (bp) | Percent of variable sites used in phylogeny inference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| psbA-trnH | 1159 | 751 | 202 | 26.9 |
| matK | 1911 | 1628 | 619 | 38 |
| ITS | 874 | 800 | 505 | 63.1 |
| Xdh | 931 | 928 | 398 | 42.8 |
| plastome set | 30671 | 28254 | 4943 | 17.5 |
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree obtained from the Bayesian analysis of the combined nuclear ITS+Xdh dataset. Numbers near branches indicate posterior probabilities (PP) / ultrafast bootstrap percentages in the maximum likelihood analysis (BPML; see Supplementary Figure 2 ); “-” indicates absence of the branch in the maximum likelihood analysis. Scale bar shows number of substitutions per site. Accessions of Vietorchis are marked with red.
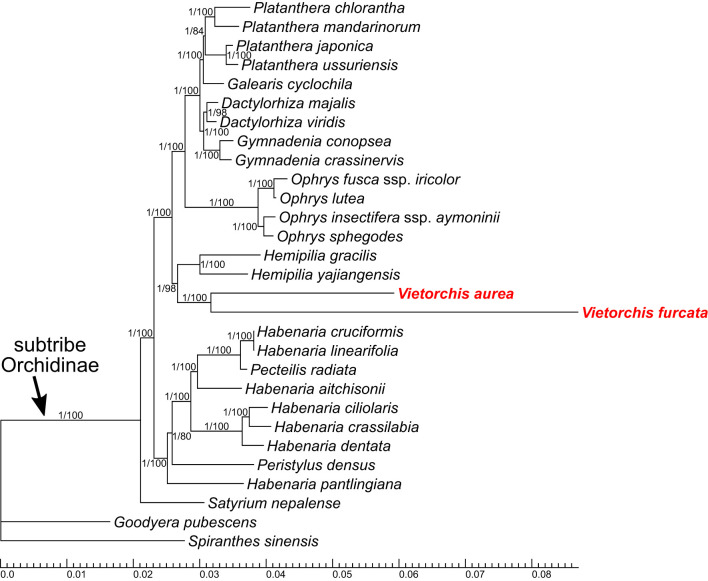
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree obtained from the Bayesian analysis of the combined 29-gene plastid dataset. Numbers near branches indicate posterior probabilities (PP) / ultrafast bootstrap percentages in the maximum likelihood analysis (BPML; see Supplementary Figure 4 ). Scale bar shows number of substitutions per site.
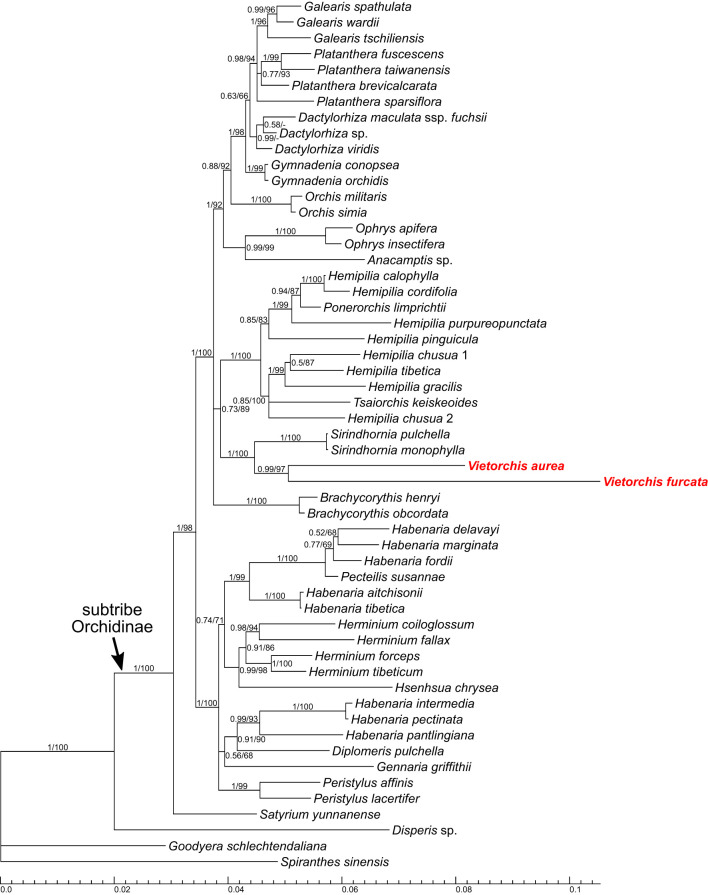
The analyses of four separate markers (ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH; Supplementary Figures 5–12 ) lack any well-supported incongruence with the two-marker trees ( Figures 3 , 4 ; Supplementary Figures 2, 3 ), but only show a lower resolution.
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree obtained from the Bayesian analysis of the combined plastid matK+psbA-trnH dataset. Numbers near branches indicate posterior probabilities (PP) / ultrafast bootstrap percentages in the maximum likelihood analysis (BPML; see Supplementary Figure 3 ); “-” indicates absence of the branch in the maximum likelihood analysis. Scale bar shows number of substitutions per site. Accessions of Vietorchis are marked with red.
In all the two-marker trees (i.e., the nuclear ITS+Xdh trees and the plastid matK+psbA-trnH trees), the genera belonging to the subtribe Orchidinae (as defined by Chase et al., 2015) form a well-supported clade [posterior probability (PP) 1.00 for both datasets, ultrafast bootstrap percentage in the maximum likelihood analysis (BPML) 98 and 100, respectively]. The genus Satyrium occupies a basal position within Orchidinae (the monophyly of the rest of Orchidinae is supported with PP 0.95, BPML 84 for the nuclear dataset and PP 1.00, BPML 98 for the plastid dataset). The rest of the accessions form two clades sister to each other. One of them (PP 1.00, BPML 100 for both datasets) comprises all the species of Habenaria studied, intermixed with the species of Diplomeris, Gennaria, Herminium, Hsenhsua, Pecteilis, and Peristylus. The second clade (PP 1.00 for both datasets, BPML 99 and 100, respectively) is subdivided into three subclades. One of them is Brachycorythis (PP 1.00, BPML 100 for both datasets; Brachycorythis occupies a sister position to the rest of the clade in the nuclear trees, and forms a polytomy with the two other subclades in the plastid trees). The second subclade (PP 1.00 for both datasets, BPML 100 and 92, respectively) contains species of the mostly extra-tropical genera (Anacamptis, Dactylorhiza, Galearis, Gymnadenia, Ophrys, Orchis, Platanthera). In the third subclade (PP 0.99, BPML 95 for the nuclear dataset and PP 0.73, BPML 89 for the plastid dataset), a clade comprising Sirindhornia and Vietorchis (PP 1.00, BPML 100 for both datasets) is sister to a clade containing the species of Hemipilia together with Ponerorchis limprichtii and Tsaiorchis keiskeoides (PP 1.00, BPML 100 for both datasets), i.e. corresponding to Hemipilia sensu latissimo as accepted by Tang et al. (2015) and Yang et al. (2022). The clade comprising Sirindhornia and Vietorchis shows a tritomy in the nuclear trees with the following branches: V. aurea, V. furcata and the monophyletic Sirindhornia (S. monophylla + S. pulchella; PP 1.00, BPML 100). In the plastid trees, both Sirindhornia (PP 1.00, BPML 100) and Vietorchis (PP 0.99, BPML 97) are monophyletic.
The trees based on the 29-gene plastid dataset ( Figure 5 , Supplementary Figure 4 ) are highly congruent to the two-marker trees (ITS+Xdh and matK+psbA-trnH), despite it employed a smaller sampling that was quite different at the species level. In the 29-gene trees, the monophyly of the subtribe Orchidinae is supported (PP 1.00, BPML 100). Satyrium is the basalmost taxon within Orchidinae, and the other accessions are distributed within two clades. One of these clades comprises the species of Habenaria intermixed with Pecteilis and Peristylus (PP 1.00, BPML 100). Within the second clade (PP 1.00, BPML 100), the subclade containing species of the mostly extra-tropical genera (Dactylorhiza, Galearis, Gymnadenia, Ophrys, Platanthera; PP 1.00, BPML 100) is sister to a subclade (PP 1.00, BPML 98) with the following topology: (Hemipilia gracilis + Hemipilia yajiangensis; PP 1.00, BPML 100) + (Vietorchis aurea + Vietorchis furcata; PP 1.00, BPML 100).
Plastome of Vietorchis furcata: structure, gene content and selective pressure
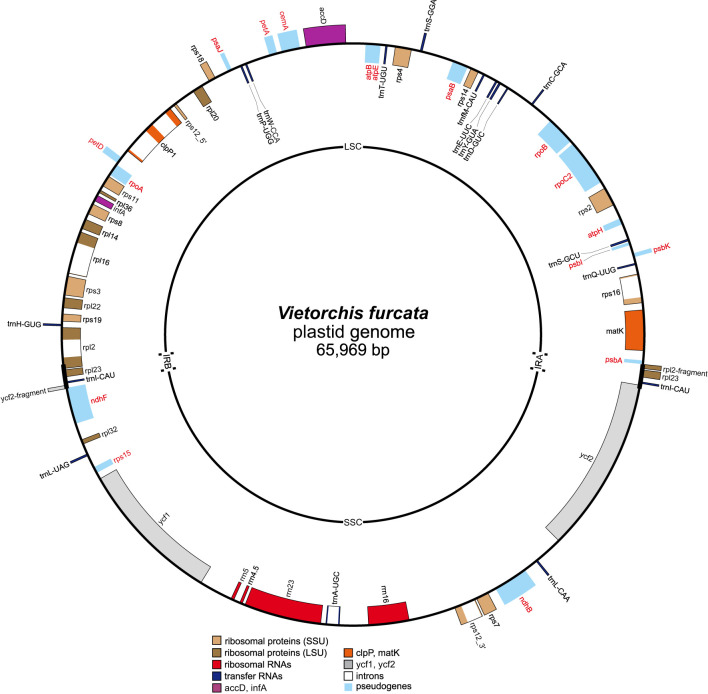
The newly assembled complete plastid genome of Vietorchis furcata is 65,969 base pairs (bp) in length with the typical quadripartite structure containing a large (LSC) and a small single copy (SSC) region (35,123 and 29,056 bp, respectively) separated with inverted repeats (IR) of 895 bp ( Figure 6 ). The overall GC content was 33.58%.
Figure 6.
Circular map of the plastid genome of Vietorchis furcata. Genes shown outside of the circle are transcribed counterclockwise and those inside are transcribed clockwise. Names of pseudogenes are marked with red color. LSC, large single copy region; SSC, small single copy region; IRA and IRB, inverted repeats A and B, respectively.
Forty five unique genes were revealed in the plastome ( Table 3 ), including those of 4 rRNAs, 16 tRNAs, 11 proteins of small ribosomal subunit, 8 proteins of large ribosomal subunit, and 6 other proteins. Of these genes, 31 were situated in the LSC, 11 were in the SSC, and the trans-spliced rps12 was spread in both single copy regions. The inverted repeats contained two genes (rpl23 and trnI-CAU) and partial sequences of rpl2 and ycf2 genes (with their other parts being in the LSC and SSC, respectively). Fraction of the coding DNA was 44.01%.
Table 3.
Gene content in the plastome of Vietorchis furcata.
| Gene groups | Gene names |
|---|---|
| NDH complex | - |
| Photosynthesis | - |
| ATP synthesis | - |
| Plastid RNA polymerase subunits | - |
| Ribosomal RNA genes | rrn5, rrn4.5, rrn16, rrn23 |
| Transfer RNA genes | trnA-UGC, trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnfM-CAU, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU*, trnL-CAA, trnL-UAG, trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnT-UGU, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA |
| Small subunit ribosomal proteins | rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7, rps8, rps11, rps12, rps14, rps16, rps18, rps19 |
| Large subunit ribosomal proteins | rpl2, rpl14, rpl16, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23*, rpl32, rpl36 |
| Maturase | matK |
| Subunit of acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD |
| ATP-dependent protease, subunit P | clpP |
| Translational initiation factor | infA |
| Conserved open reading frames (ycf) | ycf1, ycf2 |
The genes located in inverted repeats are marked with asterisks.
No intact photosynthesis-related genes were found, but 17 pseudogenes were annotated in the plastome: atpB, atpE, atpH, cemA, rpoA, rpoB, rpoC2, ndhB, ndhF, petA, petD, psaB, psaJ, psbA, psbI, psbK, and rps15 ( Figure 6 ); all of them except for rps15 are derived from the photosynthesis-related genes. All of the pseudogenes contained multiple internal termination codons. Of the six intron-containing genes, five were protein-coding sequences (rps16, rpl16, rpl2, rps12, clpP; the last one contained two introns) and one was the tRNA gene (trnA-UGC).
The genes and pseudogenes in the plastome of V. furcata retained the same relative position as in the phylogenetically closest known plastomes, i.e. those of the photosynthetic Hemipilia gracilis and Hemipilia yajiangensis ( Supplementary Figure 13 ).
A total of 13 dispersed repeats were found in the plastome of V. furcata, with the longest repeat being 68 bases long ( Supplementary Figure 14 ). The numbers of direct, inverted and palindrome repeats were almost equal: 4, 4 and 5, respectively. Comparison of the plastomes of Vietorchis furcata and Hemipilia yajiangensis showed similar relative amount of dispersed repeats (~0.20 vs. ~0.19 repeats per 1000 bases) and their relative length (0.50% vs. 0.47% of the plastome length).
The likelihood ratio tests (LRTs) based on the branch models (and performed using CodeML) showed that the “single ω model” was preferable for 23 (of 25) protein-coding genes, whereas the difference in ω values between the foreground and background branches can be considered statistically significant (implying the alternative model) for the two remaining genes (rps2 and rps11, Table 4 ). However, for all the genes, an averaged omega ratio was below 1, suggesting that all of them undergo negative selection. The performed branch-site tests also did not reveal any signs of positive selection acting on the amino acid residues ( Supplementary Table 1 ). Similarly, the LRTs performed using BUSTED showed no evidence of episodic diversifying selection in any of the analyzed genes in the plastome of V. furcata ( Table 4 ).
Table 4.
Nonsynonymous (Dn) to synonymous (Ds) substitution rate ratio for plastid gene sequences in the photosynthetic lineages of the subfamily Orchidoideae studied here and in Vietorchis furcata.
| Gene names | Dn/Ds ratio in photosynthetic lineages (PAML) | Dn/Ds ratio in Vietorchis furcata (PAML) | LRT p-value (PAML) | LRT p-value (BUSTED) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| accD | 0.4661 | 0.3156 | 0.1492 | 0.50 |
| clpP | 0.0884 | 0.1678 | 0.2820 | 0.50 |
| infA | 0.0573 | 0.1788 | 0.1716 | 0.50 |
| matK | 0.4562 | 0.6255 | 0.2042 | 0.47 |
| rpl14 | 0.1144 | 0.4381 | 0.0459 | 0.50 |
| rpl16 | 0.1938 | 0.2353 | 0.7362 | 0.50 |
| rpl2 | 0.2622 | 0.2108 | 0.7211 | 0.50 |
| rpl20 | 0.3854 | 0.5069 | 0.5860 | 0.28 |
| rpl22 | 0.2649 | 0.508 | 0.2601 | 0.50 |
| rpl23 | 0.1322 | 0.8199 | 0.0368 | 0.50 |
| rpl32 | 0.2493 | 0.5702 | 0.3551 | 0.32 |
| rpl36 | 0.1594 | 0.3429 | 0.4964 | 0.50 |
| rps11 | 0.1108 | 0.3899 | **0.0103 | 0.50 |
| rps12 | 0.1626 | 0.5786 | 0.1714 | 0.50 |
| rps14 | 0.2570 | 0.2526 | 0.9789 | 0.50 |
| rps16 | 0.1719 | 0.2997 | 0.3906 | 0.50 |
| rps18 | 0.1462 | 0.5851 | 0.0312 | 0.50 |
| rps19 | 0.2742 | 0.1985 | 0.7472 | 0.50 |
| rps2 | 0.1115 | 0.4894 | **0.0013 | 0.26 |
| rps3 | 0.1470 | 0.3548 | 0.0347 | 0.19 |
| rps4 | 0.2017 | 0.5588 | 0.0271 | 0.50 |
| rps7 | 0.3321 | 0.5061 | 0.6065 | 0.50 |
| rps8 | 0.1525 | 0.3366 | 0.1044 | 0.42 |
| ycf1 | 0.5984 | 0.5630 | 0.6778 | 0.50 |
| ycf2 | 0.7460 | 0.6457 | 0.3707 | 0.50 |
** indicates that the differеnce is statistically significant after Bonferroni correction.
Discussion
Subfamily placement of Vietorchis, and homoplastic evolution of rhizomes in mycoheterotrophic Orchidaceae
In our reconstructions, Vietorchis is deeply nested within the subfamily Orchidoideae, and thus the earlier discussed possibility of the placement of Vietorchis outside Orchidoideae is now decisively refuted. Taking into account the implied close relationship between Vietorchis and Silvorchis, we extrapolate this conclusion to the latter genus. The reason of doubts regarding the subfamily placement of these two genera was the structure of their underground organs, i.e. the “Epipogium-Cyrtosia-like” plagiotropic thick fleshy branching rootless tuber-like rhizomes (in S. colorata and in the genus Vietorchis; Averyanov et al., 2013) or “Gastrodia-like” rhizome-like tubers (in S. vietnamica; Averyanov et al., 2018). It is noteworthy that Smith (1907) described the underground organs of S. colorata as short fleshy rhizome bearing 0.6 cm thick roots. This was reproduced in subsequent accounts (e.g. Pridgeon et al., 2005) since no material was available to clarify the morphology. Similarly, Averyanov (2010) initially described V. aurea as having tuber-like roots due to the lack of appropriate material at that time. Based on the newly obtained material of Silvorchis and Vietorchis, as well as on the drawing from the protologue of S. colorata (Smith, 1907), Averyanov et al. (2013, 2018) concluded that the two genera share fleshy rootless underground stems ranging from thick rhizomes to somewhat elongate tubers. There is also a possibility that the underground plant part in Silvorchis and Vietorchis is a root-stem tuberoid (see also Averyanov et al., 2023), i.e. a storage root with its basal portion surrounding a core of stem tissue with a bud (as defined by Dressler, 1993), but anyway these genera lack morphologically distinct roots of typical shape and structure.
Thus, our molecular phylogenetic data support the idea that the similarities in the rhizome morphology between Vietorchis (and the supposedly related Silvorchis) and the genera from the subfamilies Epidendroideae and Vanilloideae are examples of a convergence, and are likely caused by the mycoheterotrophic lifestyle shared by these genera. At the same time, the rhizomes of Vietorchis are markedly different from those of its closest photosynthetic relatives within Orchidoideae. In particular, Sirindhornia, the closest genus to Vietorchis in our reconstructions based on the datasets employing selected nuclear and plastid regions, is characterized by root-bearing tubers/tuberoids (Pedersen et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2009; Pedersen, 2011).
Relationships of Vietorchis within the subtribe Orchidinae
Our reconstructions based on the nuclear dataset and two plastid datasets demonstrate that Vietorchis is placed within the subtribe Orchidinae, where it (together with Sirindhornia, when included in analysis) forms a sister group to Hemipilia s.l. (including Ponerorchis and Tsaiorchis). Molecular phylogenetic evidence therefore supports the synonymization of the subtribe Vietorchidinae with Orchidinae suggested by Olędrzyńska et al. (2016). Since the latter authors have not indicated the reasons of their decision, our study is the first one to provide a basis for such a taxonomic rearrangement.
In the two-marker trees (i.e. those based on ITS+Xdh and matK+psbA-trnH datasets), which employed a broader sampling with respect to the trees based on the plastomes, Vietorchis is most close to Sirindhornia. Vietorchis is therefore inferred here to be a part of the clade XVIII recognized by Jin et al. (2017). All the three species of Sirindhornia are restricted to limestone mountains (Pedersen et al., 2003; Pedersen, 2011), and one species of Vietorchis (V. aurea) also inhabits limestone karsts. With this evidence, our phylogenetic results suggest that association with limestone is possibly a plesiomorphic condition for Vietorchis. This assumption is to be tested after establishment of the phylogenetic position of Silvorchis, a putative closest relative of Vietorchis known exclusively in non-limestone areas.
Morphologically, Vietorchis is unique among Orchidinae (and among the entire tribe Orchideae) in having a lip with a massive callus and a raised longitudinal keel (Averyanov, 2013; Averyanov et al., 2013). In addition, Vietorchis and Silvorchis are remarkable in their spurless lips, which is a very rare feature in Orchidinae (Dressler, 1993), known, for example, in Ophrys and Serapias L. No morphological proximity between Vietorchis and Sirindhornia has ever been proposed. Indeed, with respect to the flower structure, Vietorchis (together with Silvorchis, for which the molecular phylogenetic data are still lacking) is equally close to a number of genera traditionally associated with Orchis as Orchidinae s.s., of which the ones inhabiting tropical mainland Asia being Sirindhornia and Hemipilia s.l. (including Ponerorchis, Tsaiorchis, the formerly recognized Amitostigma Schltr. and Neottianthe (Rchb.) Schltr. and possibly Apetalanthe Aver. & Vuong, the latter genus not yet included in a phylogenetic analysis). All genera of this alliance share such characters as small plant habit, fleshy tuber-like roots, erect anther with closely spaced almost parallel thecae, thecae with short bases supported by small rostellum having no rostellar arms, large hemispheric or conoid auricles on the sides of the anther, clavate pollinia with long caudicles terminated by closely spaced viscidia, viscidia completely separated or united into a single body, viscidia naked or covered by bursiculum (or bursicula), entire concave stigma without any extensions. Except for the roots, this set of characters is also found in Vietorchis and Silvorchis.
Thus, flower morphology is concordant with the molecular data in placing Vietorchis into Orchidinae, but appears to be only moderately instructive in determination of its phylogenetic relationships within the subtribe. Morphology strongly supports the assignment of Vietorchis to the second major clade (the one containing Orchis, etc), but fails to guide its affinities within the clade. At the same time, the two subclades of this clade are correlated with the geographical evidence, and Vietorchis fits this pattern as it occupies the predominantly tropical subclade. Therefore, characteristics of flower morphology combined with the geographical distribution exhibit considerable phylogenetic signal.
Plastid genome of Vietorchis furcata in comparison with other reduced plastomes
While the typical plastomes of autotrophic angiosperms are 120–170 kb in length and encode 120–130 genes (Ruhlman and Jansen, 2021), the plastome of the non-photosynthetic Vietorchis furcata is substantially reduced in both length and gene content, in line with the tendency observed in heterotrophic plants (Barrett and Davis, 2012; Barrett et al., 2014; Wicke et al., 2016; Graham et al., 2017). Vietorchis furcata possesses one of the most reduced plastomes in the subfamily Orchidoideae (65969 bp), the other ones being those of the two other fully mycoheterotrophic species, Rhizanthella gardneri R.S.Rogers (59190 bp: Delannoy et al., 2011) and Corybas cryptanthus Hatch (69300 bp: Murray, 2019). The plastome of Vietorchis furcata lacks intact photosynthesis-related genes and contains some genes of ribosome components and transfer RNAs in addition to several other “housekeeping” genes (matK, accD, clpP, infA, ycf1, ycf2). The retained protein-coding genes in Vietorchis furcata appear to undergo the same negative selection as in its photosynthetic relatives from the subfamily Orchidoideae, although the stabilizing constraints are likely to be relaxed in the rps2 and rps11 sequences in V. furcata.
In terms of functional gene content, the plastome of Vietorchis furcata seems to be at one of the last stages of degradation (sensu Barrett et al., 2014), because it has lost several genes of tRNA and the rps15 ribosomal protein has been pseudogenized. Similar gene content is characteristic of the most reduced plastomes in Orchidaceae, e.g., in Epipogium (Schelkunov et al., 2015), Gastrodia (Wen et al., 2022), Pogoniopsis (Klimpert et al., 2022), Rhizanthella (Delannoy et al., 2011). However, in spite of their similar gene content, the plastomes of Epipogium, Gastrodia and Pogoniopsis are considerably shorter than those of Rhizanthella and Vietorchis. This is due to a larger fraction of non-coding DNA in the plastomes of Rhizanthella and Vietorchis, and particularly, the presence of multiple pseudogenes in the latter. Pseudogenes are usually rapidly purged from the plastomes of heterotrophic plants, and their abundant presence is associated with very recent transition to heterotrophy (see e.g. Barrett et al., 2014; Samigullin et al., 2016). The other types of non-coding DNA (intergenic spacers and introns) are also scarce in highly reduced plastomes (Schelkunov et al., 2015, 2019; Su et al., 2019). Thus, the plastome of Vietorchis represents an interesting example of heterochrony: it has a highly reduced gene set (with the reduction affecting even the ribosomal protein genes, which is typical for the last steps of plastome degradation, following the model of Barrett and Davis, 2012) but keeps a large amount of pseudogenes and non-coding DNA of the other types (which is typical for the earliest steps of degradation). It should also be noted that though ribosome is a necessary component of virtually any cell (and plastids and mitochondria as well, since they are derivatives of a bacterial cell), the essentiality of different ribosomal proteins is considerably unequal (see Nikolaeva et al., 2021). It might be beneficial to update the model of plastome reduction in heterotrophic plants taking this idea into account.
In the phylogenetic trees based on the plastid datasets, both studied species of Vietorchis occupy long terminal branches, which assume a substantial overall elevation of substitution rates. The phenomenon of long branches is characteristic of plastomes of many heterotrophic lineages (Lam et al., 2018), and the elevated substitution rates in plastomes of fully heterotrophic plants seem to be frequent (see a review by Sanchez-Puerta et al., 2023), although not obligatory (e.g., Cephalanthera humilis X.H.Jin: Lam et al., 2018, Petrosavia stellaris Becc.: Logacheva et al., 2014).
The small length of the inverted repeats in Vietorchis furcata (895 bp) is a remarkable feature, which is shared by this species with Epipogium roseum Lindl. (about 250–300 bp in different accessions: Schelkunov et al., 2015) and Pogoniopsis schenckii Cogn. (1509 bp: Klimpert et al., 2022). The IR reduction is the only apparent structural alteration in the plastome of Vietorchis furcata with respect to the typical plastomes of photosynthetic angiosperms. Both large contractions and expansions of the IRs are often documented in heterotrophic plant lineages (Wicke et al., 2013; Feng et al., 2016; Logacheva et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2020b; Yudina et al., 2021), sometimes even within a single genus (e.g., Epipogium: Schelkunov et al., 2015, Neottia Guett.: Feng et al., 2016, Thismia Griff.: Yudina et al., 2021).
The retention of plastome gene order revealed in Vietorchis furcata is rather typical for the species with recent transition to heterotrophy and low degree of plastome reduction (e.g. Barrett et al., 2014; Samigullin et al., 2016). And vice versa, numerous deeply reduced plastomes of mycoheterotrophic (e.g., Schelkunov et al., 2015; Lim et al., 2016; Li et al., 2019; Yudina et al., 2021; Wen et al., 2022) as well as holoparasitic (e.g., Schelkunov et al., 2019; Su et al., 2019) species show a highly altered gene order, although the retained colinearity was also demonstrated for some of such taxa (e.g., Logacheva et al., 2011; Lam et al., 2015; Klimpert et al., 2022). Thus, the plastome of Vietorchis furcata, being colinear to the plastomes of the autotrophic genus Hemipilia (which are the most close phylogenetically to Vietorchis among the available orchid plastomes) again demonstrates the same heterochronic pattern as outlined above. It should be noted, however, that the major determinant of the rearrangements (inversions and translocations) in plant plastomes are the dispersed repeats, and therefore the number of such rearrangements relates largely to the repeat richness, and not to the nutrition type. Indeed, numerous autotrophic plant groups with highly rearranged plastomes are known (e.g. within Campanulaceae: Haberle et al., 2008, Ericaceae: Logacheva et al., 2016, Geraniaceae: Guisinger et al., 2011, Oleaceae: Lee et al., 2007); all of these plastomes have high fraction of repetitive DNA, which is supposed in the cited studies to relieve rearrangements. The presence of abundant dispersed repeats seems to be one of the necessary conditions for the occurrence of rearrangements; in line with this idea, the unrearranged plastome of Vietorchis furcata has low abundance of repeats.
Conclusions
We provided for the first time the results of molecular phylogenetic analysis of Vietorchis, a genus of mycoheterotrophic orchids with unusual morphology and continuously debated evolutionary relationships. The obtained results were largely obtained through the high-throughput sequencing approaches and covered two of the three species of the genus. We confirmed that Vietorchis is a member of the subfamily Orchidoideae, which implies a homoplastic evolution of orchid subterranean shoots related to transitions to heterotrophy: the similarities of the rhizomes of Vietorchis to those of the mycoheterotrophic taxa of Epidendroideae and Vanilloideae are proved to have a convergent nature.
Our study demonstrated that Vietorchis belongs to the tribe Orchideae, where it is deeply nested within the subtribe Orchidinae. Our findings therefore corroborate the necessity of synonymization of the subtribe Vietorchidinae with Orchidinae. The inclusion of Vietorchis into one of the two major clades of Orchidinae is in strong agreement with floral morphology. Vietorchis is shown to be phylogenetically placed in the vicinity of the species-rich genus Hemipilia and sister to Sirindhornia (both genera being entirely autotrophic). Among the members (and putative members) of the subfamily Orchidoideae not included into the phylogenetic analysis, the poorly known mycoheterotrophic genus Silvorchis is the only one that has ever been proposed to be allied to Vietorchis. The currently available morphological evidence suggest a sister relationship between Silvorchis and Vietorchis (and then these two genera are sister to Sirindhornia); however, the phylogenetic placement of Silvorchis is to be verified by utilizing molecular data, along with the question of a common versus independent transition to heterotrophy in Silvorchis and Vietorchis.
Finally, we characterized the plastid genome of one of the species of Vietorchis, V. furcata, and performed its comparative analysis with plastomes of other mycoheterotropic as well as autrotrophic orchids. The plastome is found to be 65969 bp long and comprise 45 unique genes along with 17 pseudogenes. On the one side, the plastome structure is typical for a non-photosynthetic plant in a lack of any functional photosynthesis-related genes. On the other side, however, the plastome structure demonstrates unusual heterochronic patterns expressed in co-occurring of a highly reduced gene set with the retention of pseudogenes and other non-coding DNA and the absence of rearrangements compared with the closest studied autotrophic species.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: Nucleotide sequences generated in this study are available in the GenBank online public database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) under the accession numbers OQ318186–OQ318196, OQ318871, OQ331227, OQ331229, OQ331230, OQ344206, OQ344207, OQ344208, OQ352447.
Author contributions
TS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ML: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. LA: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. S-JZ: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. L-FF: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MN: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Qin-Chang Liao for providing photographs of Sirindhornia monophylla.
Appendix A1.
APPENDIX TABLE 1.
Nuclear and plastid regions used in this study: species sampled, voucher information, geographical origin, and GenBank (NCBI) accession numbers. Asterisk denotes newly generated sequences.
| Species | Voucher | Source or label data | GenBank number for ITS | GenBank number for Xdh | GenBank number for matK | GenBank number for psbA-trnH (including rps19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anacamptis sp. | 1351 | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944260 | MF945073 | MF945394 | MF944716 |
| Brachycorythis henryi (Schltr.) Summerh. | X.H. Jin 13860 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944262 | MF945034 | MF945438 | MF944675 |
| Brachycorythis obcordata (Lindl. ex Wall.) Summerh. | B.B. Raskoti 2014106 (KATH) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944263 | MF945098 | MF945500 | MF944742 |
| Dactylorhiza maculata ssp. fuchsii (Druce) Hyl. | X.H. Jin 14625 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944265 | MF944992 | MF945400 | MF944633 |
| Dactylorhiza viridis (L.) R.M.Bateman, Pridgeon & M.W.Chase | China, Yunnan, STET 0772 (PE) | ITS: Jin et al. (2012); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017); matK: Jin et al. (2014) | JN696446 | MF945117 | KJ452797 | MF944762 |
| Dactylorhiza sp. | 1245 / X.H. Jin 14263 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944266 | MF944993 | MF945401 | MF944634 |
| Diplomeris pulchella D.Don | X.H. Jin, L. Zhang 11553 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944270 | MF945181 | MF945535 | MF944826 |
| Galearis spathulata (Lindl.) P.F.Hunt | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, S.Z. Xu 13234 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | KJ460094 | MF945156 | KJ452850 | MF944801 |
| Galearis tschiliensis (Schltr.) P.J.Cribb, S.W.Gale & R.M.Bateman | STET 09281 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | KJ460057 | MF945128 | KJ452813 | MF944773 |
| Galearis wardii (W.W.Sm.) P.F.Hunt | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14576 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944274 | MF945011 | MF945417 | MF944652 |
| Gennaria griffithii (Hook.f.) X.H.Jin & D.Z.Li | China, Yunnan, X.H. Jin 10879 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2012); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | JN696445 | MF944987 | JN696430 | MF944627 |
| Gymnadenia conopsea (L.) R.Br. | China, Yunnan, X.H. Jin 9896 (PE) | ITS: Jin et al. (2012); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017); matK: Jin et al. (2014) | JN696449 | MF945115 | KJ452795 | MF944760 |
| Gymnadenia orchidis Lindl. | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14459 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944276 | MF945088 | MF945491 | MF944732 |
| Habenaria aitchisonii Rchb.f. | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14680 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944279 | MF945017 | MF945422 | MF944658 |
| Habenaria delavayi Finet | X.H. Jin 10396 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944290 | MF945056 | MF945461 | MF944699 |
| Habenaria fordii Rolfe | W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14362 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944294 | MF945027 | MF945431 | MF944668 |
| Habenaria intermedia D.Don | B.B. Raskoti 201446 (KATH) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944298 | MF945094 | MF945496 | MF944738 |
| Habenaria marginata Colebr. | B.B. Raskoti 201459 (KATH) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944307 | MF945101 | MF945503 | MF944745 |
| Habenaria pantlingiana Kraenzl. | B.B. Raskoti 201335 (KATH) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944309 | MF945118 | MF945513 | MF944763 |
| Habenaria pectinata D.Don | X.F. Gao, Z.M. Zhu, W.B. Ju, W.T. Jin 14714 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944310 | MF945185 | MF945539 | MF944830 |
| Habenaria tibetica Schltr. | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, S.Z. Xu 13108 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944325 | MF945177 | MF945531 | MF944822 |
| Hemipilia calophylla C.S.P.Parish & Rchb.f. | W.T. Jin 11798 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | KJ460095 | MF945158 | KJ452852 | MF944803 |
| Hemipilia chusua (D.Don) Y.Tang & H.Peng 1 | X.H. Jin 8272 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944401 | MF945055 | MF945460 | MF944698 |
| Hemipilia chusua (D.Don) Y.Tang & H.Peng 2 | X.H. Jin 9138 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) (listed as Ponerorchis nana (King & Pantl.) Soó) | MF944404 | MF945070 | MF945475 | MF944713 |
| Hemipilia cordifolia Lindl. | X.H. Jin 11052 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) (listed as Hemipilia cruciata Finet) | MF944330 | MF945057 | MF945462 | MF944700 |
| Hemipilia gracilis (Blume) Y.Tang, H.Peng & T.Yukawa | China, Yunnan, X.H. Jin 9257 (PE) | ITS: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017); matK: Jin et al. (2012) | KJ460036 | MF945003 | JN696435 | MF944644 |
| Hemipilia pinguicula (Rchb.f. & S.Moore) Y.Tang & H.Peng | W.T. Jin 16006 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944417 | MF945093 | MF945495 | MF944737 |
| Hemipilia purpureopunctata (K.Y.Lang) X.H.Jin, Schuit. & W.T.Jin | X.H. Jin 13198 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | KJ460051 | MF945123 | KJ452807 | MF944768 |
| Hemipilia tibetica (Schltr.) Y.Tang & H.Peng | X.H. Jin, L. Zhang 11075 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944412 | MF945043 | MF945449 | MF944685 |
| Herminium coiloglossum Schltr. | X.H. Jin 8273 (PE) | ITS, matK, psbA-trnH: Raskoti al. (2016); Xdh: Jin et al. (2017) | KR350153 | MF945161 | KR350189 | KR350299 |
| Herminium fallax (Lindl.) Hook.f. | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, S.Z. Xu 13248 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Raskoti al. (2016) | KR350164 | KR350453 | KR350200 | KR350310 |
| Herminium forceps (Finet) Schltr. | X.H. Jin 9360 (PE) | ITS: Jin et al. (2012); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Raskoti al. (2016); matK: Jin et al. (2014) | JN696461 | KR350423 | KJ452789 | KR350280 |
| Herminium tibeticum X.H.Jin, Schuit. & Raskoti | China, Tibet, STET 1293 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2012) (listed as Herminium monorchis (L.) R.Br.); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Raskoti al. (2016) (listed as Herminium sp.) | JN696453 | KR350417 | JN696439 | KR350273 |
| Hsenhsua chrysea (W.W.Sm.) X.H.Jin, Schuit., W.T.Jin & L.Q.Huang | X.H. Jin, L. Zhang 11082 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Raskoti al. (2016) | KJ460056 | KR350430 | KJ452812 | KR350286 |
| Ophrys apifera Huds. | ITS, matK: M.W. Chase 536 (K); psbA-trnH: England, M.W. Chase 13839 (K) | ITS, matK: Salazar et al. (2003); psbA-trnH: Devey et al. (2008) | AJ539529 | – | AJ543953 | AM711642 |
| Ophrys insectifera L. | unknown | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944348 | MF945090 | MF945396 | MF944734 |
| Orchis militaris L. | Switzerland, Valais, A. Widmer (Z/ZT) | ITS: Soliva et al. (2001); matK: unpublished | AY014548 | – | KF997352 | – |
| Orchis simia Lam. | (NAP) | ITS: Aceto et al. (1999); matK: unpublished |
Z94107+ Z94108 |
– | KF997476 | – |
| Pecteilis susannae (L.) Raf. | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14631 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944350 | MF945018 | MF945423 | MF944659 |
| Peristylus affinis (D.Don) Seidenf. | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14623 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944353 | MF944999 | MF945406 | MF944640 |
| Peristylus lacertifer (Lindl.) J.J.Sm. | X.H. Jin 11645 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944365 | MF945074 | MF945477 | MF944717 |
| Platanthera brevicalcarata Hayata | X.H. Jin 10024 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | KJ460067 | MF945136 | KJ452823 | MF944781 |
| Platanthera fuscescens (L.) Kraenzl. | China, Yunnan, X.H. Jin 10385 (PE) | ITS: Jin et al. (2012); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017); matK: Jin et al. (2014) | JN696467 | MF945109 | KJ452788 | MF944754 |
| Platanthera sparsiflora (S.Watson) Schltr. | B. Bartholomew, A. Anderson, H.W. Li, T.S. Ying 2313 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944389 | MF945102 | MF945504 | MF944746 |
| Platanthera taiwanensis (S.S.Ying) S.C.Chen, S.W.Gale & P.J.Cribb | Hsu 5942 (TAIF) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944393 | MF945038 | MF945443 | MF944680 |
| Ponerorchis limprichtii (Schltr.) Soó | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14466 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944398 | MF945020 | MF945425 | MF944661 |
| Satyrium yunnanense Rolfe | X.H. Jin, W.T. Jin, Y.Q. Cui 14710 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944415 | MF945086 | MF945489 | MF944730 |
| Sirindhornia monophylla (Collett & Hemsl.) H.A.Pedersen & Suksathan | China, Yunnan, Z.J. Liu 7951 (NOCC) | Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture, Mangshi City, 26.05.2014 | OQ331227* | OQ344206* | OQ344208* | – |
| Sirindhornia pulchella H.A.Pedersen & Indham. | X.H. Jin 11012 (PE) | ITS, matK: Jin et al. (2014); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | KJ460045 | MF945119 | KJ452801 | MF944764 |
| Tsaiorchis keiskeoides (Gagnep.) X.H.Jin, Schuit. & W.T.Jin | China, Yunnan, YNET 507 (PE) | ITS: Jin et al. (2012); Xdh, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017); matK: Jin et al. (2014) | JN696466 | MF945114 | KJ452794 | MF944759 |
| Vietorchis aurea Aver. & Averyanova | Vietnam, Ninh Binh, May Van Xinh MVX 261 (LE: LE01076723) | Cuc Phuong National Park, 200‒300 m, 05.2004 | OQ331229* | – | OQ318186* | OQ352447* |
| Vietorchis furcata Aver. & Nuraliev | Vietnam, Dak Lak, M.S. Nuraliev 998 (LE: LE01076759) | Lak distr., Bong Krang munic., Chu Yang Sin national park, 12 km S of Krong Kmar village, forest, near small river, c. 1100 m, 12°23’41”N 108°20’55”E, 28.05.2014 | OQ331230* | OQ344207* | OQ318871* | OQ318871* |
| Outgroups | ||||||
| Disperis sp. | 1520 / CPG 29216 (PE) | ITS, Xdh, matK, psbA-trnH: Jin et al. (2017) | MF944272 | MF945082 | MF945484 | MF944725 |
| Goodyera schlechtendaliana Rchb.f. | South Korea, Jeju, N. Lee 0510011 (EWH) | ITS, psbA-trnH: Lee et al. (2012); matK: unpublished | HM021571 | – | KC704635 | HM021618 |
| Spiranthes sinensis (Pers.) Ames | eastern Asia, M.W. Chase 10450 (K) | ITS, matK: Salazar and Jost (2012); Xdh: unpublished | HE575518 | – | HE575508 | KC704395 |
Asterisk denotes newly generated sequences.
Appendix A2.
APPENDIX TABLE 2.
Plastid genomes used in this study: species sampled, voucher information, geographical origin, and GenBank (NCBI) accession numbers. In cases where two numbers are indicated, the first one is the accession containing a reference to the original plastome annotation. Asterisk denotes newly generated sequences.
| Species | Voucher | Source or label data | GenBank reference for plastid genome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dactylorhiza majalis (Rchb.) P.F.Hunt & Summerh. | Poland, SG-13237 (UGDA) | May et al. (2019) |
NC_044644 MK984209 |
| Dactylorhiza viridis (L.) R.M.Bateman, Pridgeon & M.W.Chase | unknown | unpublished |
NC_056192 MN824430 |
| Galearis cyclochila (Franch. & Sav.) Soó | PDBK2000-0786 (KB, KUS) | Kim et al. (2020b) |
NC_046818 MN200388 |
| Gymnadenia conopsea (L.) R.Br. | PDBK2011-0894 (KB, KUS) | Kim et al. (2020b) |
NC_046820 MN200391 |
| Gymnadenia crassinervis Finet | unknown | unpublished | MW322684 |
| Habenaria aitchisonii Rchb.f. | unknown | unpublished | MW316693 |
| Habenaria ciliolaris Kraenzl. | China, Fujian, YT-MTYFH (FAFU) |
Chen et al. (2019) | MN495954 |
| Habenaria crassilabia Kraenzl. | PDBK2018-1246 (KB, KUS) | Kim et al. (2020b) (listed as Habenaria chejuensis Y.N.Lee & K.Lee) |
NC_046821 MN200392 |
| Habenaria cruciformis Ohwi | South Korea, Gangwon, GCU190036385 (GCU) | Kim et al. (2020a) |
NC_059695 MT863537 |
| Habenaria dentata (Sw.) Schltr. | China, Guangxi, SFC-20201015012 (IBK) |
Zhang et al. (2022) | OK012095 |
| Habenaria linearifolia Maxim. | unknown | Kim et al. (2020a) |
NC_059696 MT863538 |
| Habenaria pantlingiana Kraenzl. | unknown | Lin et al. (2015) (as Habenaria longidenticulata, nom. nud.) |
NC_026775 KJ524104 |
| Hemipilia gracilis (Blume) Y.Tang, H.Peng & T.Yukawa | PDBK2008-0404 (KB, KUS) | Kim et al. (2020b) |
NC_046810 MN200376 |
| Hemipilia yajiangensis G.W.Hu, Jia X.Yang & Q.F.Wang | China, Sichuan, J.X. Yang, S. Peng, Y. Wang, S.X. Ding, J.J. Wang PS-00264 (HIB: 0188766, 0188768, 0188767, paratypes) | Yang et al. (2022) |
NC_067080 OM009241 |
| Ophrys fusca ssp. iricolor (Desf.) K.Richt. | Greece, Crete | Roma et al. (2018) | AP018716 |
| Ophrys insectifera ssp. aymoninii Breistr. | France, Occitania | Bertrand et al. (2021) | MW309825 |
| Ophrys lutea Cav. | France, Occitania | Bertrand et al. (2021) |
NC_058525 MW309826 |
| Ophrys sphegodes Mill. | Italy, Apulia | Roma et al. (2018) | AP018717 |
| Pecteilis radiata (Thunb.) Raf. | PDBK2015-1271 | Kim et al. (2020a) |
NC_035834 KX871237 |
| Peristylus densus (Lindl.) Santapau & Kapadia | PDBK2018-1247 (KB, KUS) | Kim et al. (2020b) (listed as Habenaria flagellifera Makino) |
NC_046801 MN200366 |
| Platanthera chlorantha (Custer) Rchb. | Poland, SG-13236 (UGDA) |
Lallemand et al. (2019) |
NC_044626 MK937914 |
| Platanthera japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. | China, Shaanxi (WNU) | Dong et al. (2018) |
NC_037440 MG925368 |
| Platanthera mandarinorum Rchb.f. | PDBK2013-0398 (KB, KUS) | Kim et al. (2020b) |
NC_046805 MN200370 |
| Platanthera ussuriensis (Regel) Maxim. | China, Liaoning, B. Qu, X. Chen s.n. |
Han et al. (2022) | MN686021 |
| Satyrium nepalense D.Don | China, Yunnan, X.K. Ma 006 (FAFU) |
Ma et al. (2019) | MN497244 |
| Vietorchis aurea Aver. & Averyanova | Vietnam, Ninh Binh, May Van Xinh MVX 261 (LE: LE01076723) | Cuc Phuong National Park, 200‒300 m, 05.2004 |
OQ318186*–OQ318196* (11 individual regions) |
| Vietorchis furcata Aver. & Nuraliev | Vietnam, Dak Lak, M.S. Nuraliev 998 (LE: LE01076759) | Lak distr., Bong Krang munic., Chu Yang Sin national park, 12 km S of Krong Kmar village, forest, near small river, c. 1100 m, 12°23’41”N 108°20’55”E, 28.05.2014 | OQ318871* |
| Outgroups | |||
| Goodyera pubescens (Willd.) R.Br. | USA, Wisconsin, JH170809001 (GCU) | Kim and Kim (2022) |
NC_064116 OM314912 |
| Spiranthes sinensis (Pers.) Ames | South Korea, Jeju, TH200805012 (GCU) | Kim and Kim (2022) |
NC_064118 OM314917 |
Asterisk denotes newly generated sequences.
Funding Statement
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The work of TS and MN was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project 21-74-10006).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1393225/full#supplementary-material
References
- Aceto S., Caputo P., Cozzolino S., Gaudio L., Moretti A. (1999). Phylogeny and evolution of Orchis and allied genera based on ITS DNA variation: morphological gaps and molecular continuity. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 13, 67–76. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1999.0628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19, 716–723. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Agudelo L. M., González F., Isaza J. P., Alzate J. F., Pabón-Mora N. (2019). Plastome reduction and gene content in New World Pilostyles (Apodanthaceae) unveils high similarities to African and Australian congeners. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 135, 193–202. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.03.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V. (2008). The orchids of Vietnam. Illustrated survey. Part 1. Subfamilies Apostasioideae, Cypripedioideae and Spiranthoideae. Turczaninowia 11, 5–168. [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V. (2010). The orchids of Vietnam. Illustrated survey. Part 2. Subfamily Orchidoideae. Turczaninowia 13, 5–98. [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V. (2013). The orchids of Vietnam illustrated survey. Part 4. Subfamily Epidendroideae (tribes Arethuseae and Malaxideae). Turczaninowia 16, 5–163. [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V., Averyanova A. L. (2003). Updated checklist of the orchids of Vietnam (Hanoi: Vietnam National University Publishing House; ). [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V., Nguyen V. D., Nguyen K. S., Dinh Q. D., Maisak T. V. (2018). Silvorchis vietnamica (Orchidaceae, Orchidoideae, Vietorchidinae), a new miniature mycotrophic species from southern Vietnam. Nordic J. Bot. 36, e01883. doi: 10.1111/njb.01883 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V., Nguyen V. C., Truong B. V., Nguyen K. S., Nuraliev M. S., Nguyen C. H., et al. (2023). New orchids in the flora of Vietnam VII (Orchidaceae: tribes Cypripedieae, Cranichideae, Orchideae, and Collabieae). Phytotaxa 619, 255–276. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.619.4.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov L. V., Nuraliev M. S., Kuznetsov A. N., Kuznetsova S. P. (2013). Vietorchis furcata (Orchidaceae, Vietorchidinae) – a new species from Southern Vietnam. Taiwania 58, 251–256. doi: 10.6165/tai.2013.58.251 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. F., Davis J. I. (2012). The plastid genome of the mycoheterotrophic Corallorhiza striata (Orchidaceae) is in the relatively early stages of degradation. Am. J. Bot. 99, 1513–1523. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1200256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. F., Freudenstein J. V., Li J., Mayfield-Jones D. R., Perez L., Pires J. C., et al. (2014). Investigating the path of plastid genome degradation in an early-transitional clade of heterotrophic orchids, and implications for heterotrophic angiosperms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 31, 3095–3112. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman R. M., Hollingsworth P. M., Preston J., Luo Y.-B., Pridgeon A. M., Chase M. W. (2003). Molecular phylogenetics and evolution of Orchidinae and selected Habenariinae (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 142, 1–40. doi: 10.1046/j.1095-8339.2003.00157.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand J. A., Gibert A., Llauro C., Panaud O. (2021). Whole plastid genome-based phylogenomics supports an inner placement of the O. insectifera group rather than a basal position in the rapidly diversifying Ophrys genus (Orchidaceae). Bot. Lett. 168, 452–457. doi: 10.1080/23818107.2021.1893216 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chase M. W., Cameron K. M., Freudenstein J. V., Pridgeon A. M., Salazar G., Berg C., et al. (2015). An updated classification of Orchidaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 177, 151–174. doi: 10.1111/boj.12234 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. K., Chen J., Zhou J., Ma S. H., Zheng Q. D., Xie T. X., et al. (2019). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Habenaria ciliolaris (Orchidaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 4, 4132–4133. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1692727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Liu Z. J., Zhu G. H., Lang K. Y., Ji Z. H., Luo Y. B., et al. (2009). “Orchidaceae,” in Flora of China, vol. 25. Eds. Wu Z. Y., Raven P. H., Hong D. Y. (Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden, Beijing and St. Louis: ), 1–506. [Google Scholar]
- Darling A. C. E., Mau B., Blattner F. R., Perna N. T. (2004). Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 14, 1394–1403. doi: 10.1101/gr.2289704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delannoy E., Fujii S., Colas des Francs-Small C., Brundrett M., Small I. (2011). Rampant gene loss in the underground orchid Rhizanthella gardneri highlights evolutionary constraints on plastid genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2077–2086. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey D. S., Bateman R. M., Fay M. F., Hawkins J. A. (2008). Friends or relatives? Phylogenetics and species delimitation in the controversial European orchid genus. Ophrys. Ann. Bot. 101, 385–402. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcm299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong W. L., Wang R. N., Zhang N. Y., Fan W. B., Fang M. F., Li Z. H. (2018). Molecular evolution of chloroplast genomes of orchid species: insights into phylogenetic relationship and adaptive evolution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 716. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030716 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle J. J., Doyle J. L. (1987). A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dressler R. L. (1993). Phylogeny and classification of the orchid family (Portland: Dioscorides Press; ). [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. L., Wicke S., Li J. W., Han Y., Lin C. S., Li D. Z., et al. (2016). Lineage-specific reductions of plastid genomes in an orchid tribe with partially and fully mycoheterotrophic species. Genome Biol. Evol. 8, 2164–2175. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evw144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Chen C., Arab D. A., Du Z., He Y., Ho S. Y. W. (2019). EasyCodeML: A visual tool for analysis of selection using CodeML. Ecol. Evol. 9, 3891–3898. doi: 10.1002/ece3.5015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Górniak M., Paun O., Chase M. W. (2010). Phylogenetic relationships within Orchidaceae based on a low-copy nuclear coding gene, Xdh: Congruence with organellar and nuclear ribosomal DNA results. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 56, 784–795. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts R., Bernet P., Kratochvil K., Gerlach G., Carr G., Alrich P., et al. (2022) Orchidaceae. POWO: Plants of the World Online (Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; ). Available online at: http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ (Accessed 13 October, 2022). [Google Scholar]
- Graham S. W., Lam V. K. Y., Merckx V. S. F. T. (2017). Plastomes on the edge: the evolutionary breakdown of mycoheterotroph plastid genomes. New Phytol. 214, 48–55. doi: 10.1111/nph.14398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guisinger M. M., Kuehl J. V., Boore J. L., Jansen R. K. (2011). Extreme reconfiguration of plastid genomes in the angiosperm family Geraniaceae: rearrangements, repeats, and codon usage. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 583–600. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberle R. C., Fourcade H. M., Boore J. L., Jansen R. K. (2008). Extensive rearrangements in the chloroplast genome of Trachelium caeruleum are associated with repeats and tRNA genes. J. Mol. Evol. 66, 350–361. doi: 10.1007/s00239-008-9086-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. A. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Ding R., Zong X., Zhang L., Chen X., Qu B. (2022). Structural characterization of Platanthera ussuriensis chloroplast genome and comparative analyses with other species of Orchidaceae. BMC Genomics 23, 84. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08319-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang D. T., Chernomor O., Von Haeseler A., Minh B. Q., Vinh L. S. (2018). UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 35, 518–522. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu A. Q., Gale S. W., Liu Z. J., Suddee S., Hsu T. C., Fischer G. A., et al. (2020). Molecular phylogenetics and floral evolution of the Cirrhopetalum alliance (Bulbophyllum, Orchidaceae): evolutionary transitions and phylogenetic signal variation. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 143, 106689. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin W.-T., Jin X.-H., Schuiteman A., Li D.-Z., Xiang X.-G., Huang W.-C., et al. (2014). Molecular systematics of subtribe Orchidinae and Asian taxa of Habenariinae (Orchideae, Orchidaceae) based on plastid matK, rbcL and nuclear ITS. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 77, 41–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin X. H., Li D. Z., Xiang X. G., Lai Y. J., Shi X. C. (2012). Nujiangia (Orchidaceae: Orchideae): a new genus from the Himalayas. J. Syst. Evol. 50, 64–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1759-6831.2011.00167.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jin W. T., Schuiteman A., Chase M. W., Li J. W., Chung S. W., Hsu T. C., et al. (2017). Phylogenetics of subtribe Orchidinae s.l. (Orchidaceae; Orchidoideae) based on seven markers (plastid matK, psaB, rbcL, trnL-F, trnH-psba, and nuclear nrITS, Xdh): implications for generic delimitation. BMC Plant Biol. 17, 222. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1160-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh K., Misawa K., Kuma K. I., Miyata T. (2002). MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 3059–3066. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh K., Standley D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C., Do H. D. K., Jung J., Kim D. K., Kim J. H. (2020. a). Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Korean endemic, Habenaria cruciformis (Orchidaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 5, 3269–3271. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1812448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Jo S., Cheon S. H., Joo M. J., Hong J. R., Kwak M., et al. (2020. b). Plastome evolution and phylogeny of Orchidaceae, with 24 new sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 22. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim T. H., Kim J. H. (2022). Molecular phylogeny and historical biogeography of Goodyera R. Br. (Orchidaceae): a case of the vicariance between East Asia and North America. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 850170. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.850170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpert N. J., Mayer J. L. S., Sarzi D. S., Prosdocimi F., Pinheiro F., Graham S. W. (2022). Phylogenomics and plastome evolution of a Brazilian mycoheterotrophic orchid, Pogoniopsis schenckii . Am. J. Bot. 109, 2030–2050. doi: 10.1002/ajb2.16084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallemand F., May M., Ihnatowicz A., Jąkalski M. (2019). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Platanthera chlorantha (Orchidaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 4, 2683–2684. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1644551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam V. K. Y., Darby H., Merckx V. S. F. T., Lim G., Yukawa T., Neubig K. M., et al. (2018). Phylogenomic inference in extremis: A case study with mycoheterotroph plastomes. Am. J. Bot. 105, 480–494. doi: 10.1002/ajb2.1070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam V. K. Y., Soto Gomez M., Graham S. W. (2015). The highly reduced plastome of mycoheterotrophic Sciaphila (Triuridaceae) is colinear with its green relatives and is under strong purifying selection. Genome Biol. Evol. 7, 2220–2236. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. L., Jansen R. K., Chumley T. W., Kim K. J. (2007). Gene relocations within chloroplast genomes of Jasminum and Menodora (Oleaceae) are due to multiple, overlapping inversions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1161–1180. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. S., Kim S. C., Yeau S. H., Lee N. S. (2012). Nuclear and cpDNA sequences demonstrate spontaneous hybridization between Goodyera schlechtendaliana Rchb. f. and G. velutina Maxim. (Orchidaceae) in Jeju Island, Korea. Syst. Bot. 37, 356–364. doi: 10.1600/036364412X635421 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. X., Li Z. H., Schuiteman A., Chase M. W., Li J. W., Huang W. C., et al. (2019). Phylogenomics of Orchidaceae based on plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 139, 106540. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim G. S., Barrett C. F., Pang C. C., Davis J. I. (2016). Drastic reduction of plastome size in the mycoheterotrophic Thismia tentaculata relative to that of its autotrophic relative Tacca chantrieri . Am. J. Bot. 103, 1129–1137. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1600042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Chen J. J. W., Huang Y. T., Chan M. T., Daniell H., Chang W. J., et al. (2015). The location and translocation of ndh genes of chloroplast origin in the Orchidaceae family. Sci. Rep. 5, 9040. doi: 10.1038/srep09040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. J., Chen L. J., Chen S. C., Cai J., Tsai W. C., Hsiao Y. Y., et al. (2011). Paraholcoglossum and Tsiorchis, two new orchid genera established by molecular and morphological analyses of the Holcoglossum alliance. PloS One 6, e24864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logacheva M. D., Schelkunov M. I., Nuraliev M. S., Samigullin T. H., Penin A. A. (2014). The plastid genome of mycoheterotrophic monocot Petrosavia stellaris exhibits both gene losses and multiple rearrangements. Genome Biol. Evol. 6, 238–246. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logacheva M. D., Schelkunov M. I., Penin A. A. (2011). Sequencing and analysis of plastid genome in mycoheterotrophic orchid Neottia nidus-avis . Genome Biol. Evol. 3, 1296–1303. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evr102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logacheva M. D., Schelkunov M. I., Shtratnikova V. Y., Matveeva M. V., Penin A. A. (2016). Comparative analysis of plastid genomes of non-photosynthetic Ericaceae and their photosynthetic relatives. Sci. Rep. 6, 30042. doi: 10.1038/srep30042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X., Lin H., Chen Y., Lan S., Ming R. (2019). The complete chloroplast genome of a gynodioecious deciduous orchid Satyrium ciliatum (Orchidaceae) female. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 4, 3876–3877. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1687359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M., Novotná A., Minasiewicz J., Selosse M. A., Jąkalski M. (2019). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Dactylorhiza majalis (Rchb.) P.F. Hunt et Summerh. (Orchidaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 4, 2821–2823. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1660282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minh B. Q., Schmidt H. A., Chernomor O., Schrempf D., Woodhams M. D., von Haeseler A., et al. (2020). IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37, 1530–1534. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molvray M., Kores P. J., Chase M. W. (2000). “Polyphyly of mycoheterotrophic orchids and functional influences on floral and molecular characters,” in Monocots: systematics and evolution. Eds. Wilson K. L., Morrison D. A. (Collingwood: CSIRO: ), 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J. H. (2019). Chloroplast genome evolution in New Zealand mycoheterotrophic Orchidaceae. Massey University, Manawatu, New Zealand. [Google Scholar]
- Murrell B., Weaver S., Smith M. D., Wertheim J. O., Murrell S., Aylward A., et al. (2015). Gene-wide identification of episodic selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32, 1365–1371. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaeva D. D., Gelfand M. S., Garushyants S. K. (2021). Simplification of ribosomes in bacteria with tiny genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 58–66. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuraliev M. S., Kuznetsov A. N., Kuznetsova S. P., Averyanov L. V. (2019). Towards inventory of non-photosynthetic plants in Vietnam: a progress report. Wulfenia 26, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Okonechnikov K., Golosova O., Fursov M., UGENE team . (2012). Unipro UGENE: a unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 28, 1166–1167. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts091 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olędrzyńska N., Szlachetko D. L. (2021). Contribution to the taxonomic revision of Brachycorythis-complex (Orchidaceae, Orchidoideae). Biodiv. Res. Conserv. 62, 5–117. doi: 10.2478/biorc-2021-0004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Olędrzyńska N., Szlachetko D. L., Mieszkowska A. (2016). Notes on the genera Silvorchis and Vietorchis (Orchidaceae-Orchidoideae). Phyton 56, 193–200. doi: 10.12905/0380.phyton56(2)2016-0193 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen H.Æ. (2011). “32. Sirindhornia ,” in Flora of Thailand Volume 12 (part 1). Eds. Santisuk T., Larsen K. (the Forest Herbarium, National Park, Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department, Bangkok: ), 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen H.Æ., Suksathan P., Indhamusika S. (2003). Sirindhornia, a new orchid genus from Southeast Asia. Nordic J. Bot. 22, 391–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-1051.2002.tb01390.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y., Leung H. C., Yiu S. M., Chin F. Y. (2012). IDBA-UD: a de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 28, 1420–1428. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pridgeon A. M., Cribb P. J., Chase M. W., Rasmussen F. N. (2005). Genera Orchidacearum. Volume 4: Epidendroideae (Part 1) (Oxford: Oxford University Press; ). doi: 10.1093/oso/9780198507123.001.0001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut A., Drummond A. J., Xie D., Baele G., Suchard M. A. (2018). Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 67, 901–904. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syy032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskoti B. B., Jin W. T., Xiang X. G., Schuiteman A., Li D. Z., Li J. W., et al. (2016). A phylogenetic analysis of molecular and morphological characters of Herminium (Orchidaceae, Orchideae): evolutionary relationships, taxonomy, and patterns of character evolution. Cladistics 32, 198–210. doi: 10.1111/cla.12125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roma L., Cozzolino S., Schlüter P. M., Scopece G., Cafasso D. (2018). The complete plastid genomes of Ophrys iricolor and O. sphegodes (Orchidaceae) and comparative analyses with other orchids. PloS One 13, e0204174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist F., Teslenko M., van der Mark P., Ayres D. L., Darling A., Höhna S., et al. (2012). MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 61, 539–542. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/sys029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhlman T. A., Jansen R. K. (2021). “Plastid genomes of flowering plants: essential principles,” in Methods in molecular biology. Chloroplast biotechnology: methods and protocols. Ed. Maliga P. (Springer US, New York, NY: ), 3–47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1472-3_1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar G. A., Chase M. W., Soto Arenas M. A., Ingrouille M. (2003). Phylogenetics of Cranichideae with emphasis on Spiranthinae (Orchidaceae, Orchidoideae): evidence from plastid and nuclear DNA sequences. Am. J. Bot. 90, 777–795. doi: 10.3732/ajb.90.5.777 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar G. A., Jost L. (2012). Quechua, a new monotypic genus of Andean Spiranthinae (Orchidaceae). Syst. Bot. 37, 78–86. doi: 10.1600/036364412X616657 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Samigullin T. H., Logacheva M. D., Penin A. A., Vallejo-Roman C. M. (2016). Complete plastid genome of the recent holoparasite Lathraea squamaria reveals earliest stages of plastome reduction in Orobanchaceae. PloS One 11, e0150718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Puerta M. V., Ceriotti L. F., Gatica-Soria L. M., Roulet M. E., Garcia L. E., Sato H. A. (2023). Beyond parasitic convergence: unravelling the evolution of the organellar genomes in holoparasites. Ann. Bot. 132, 909–928. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelkunov M. I., Nuraliev M. S., Logacheva M. D. (2019). Rhopalocnemis phalloides has one of the most reduced and mutated plastid genomes known. PeerJ 7, e7500. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelkunov M. I., Shtratnikova V. Y., Nuraliev M. S., Selosse M.-A., Penin A. A., Logacheva M. D. (2015). Exploring the limits for reduction of plastid genomes: a case study of the mycoheterotrophic orchids Epipogium aphyllum and Epipogium roseum . Genome Biol. Evol. 7, 1179–1191. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. J. (1907). Die orchideen von Java. Bull. Dép. Agric. Indes Néerl. 13, 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. F., Sytsma K. J., Shoemaker J. S., Smith R. L. (1991). A qualitative comparison of total cellular DNA extraction protocols. Phytochem. Bull. 23, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Soliva M., Kocyan A., Widmer A. (2001). Molecular phylogenetics of the sexually deceptive orchid genus Ophrys (Orchidaceae) based on nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequences. Mol. Phyl. Evol. 20, 78–88. doi: 10.1006/mpev.2001.0953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H. J., Barkman T. J., Hao W., Jones S. S., Naumann J., Skippington E., et al. (2019). Novel genetic code and record-setting AT-richness in the highly reduced plastid genome of the holoparasitic plant Balanophora . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 934–943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816822116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Skinner D., Liang G., Hulbert S. (1994). Phylogenetic analysis of Sorghum and related taxa using internal transcribed spacers of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89, 26–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00226978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swofford D. (2003). PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and other methods), Version 4 (Sunderland, MA, USA: Sinauer Associates; ). [Google Scholar]
- Szlachetko D. L., Kras M., Mytnik J. (2006). Matériaux pour la révision taxinomique du complexe Brachycorytis (Orchidaceae, Orchidoideae). Richardiana 6, 72–90. [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y., Yukawa T., Bateman R. M., Jiang H., Peng H. (2015). Phylogeny and classification of the East Asian Amitostigma alliance (Orchidaceae: Orchideae) based on six DNA markers. BMC Evol. Biol. 15, 96. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0376-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillich M., Lehwark P., Pellizzer T., Ulbricht-Jones E. S., Fischer A., Bock R., et al. (2017). GeSeq – versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W6–W11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx391 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan L. C. (2020). Characteristics of karst polje in Vietnam and associated geohazards. Int. J. Sci. Res. 9, 1391–1398. doi: 10.21275/SR20323154210 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y. G., Do T. V., Wen F. (2022). A checklist to the plants of northern Vietnam (Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House; ). [Google Scholar]
- Wen Y., Qin Y., Shao B., Li J., Ma C., Liu Y., et al. (2022). The extremely reduced, diverged and reconfigured plastomes of the largest mycoheterotrophic orchid lineage. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 448. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03836-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicke S., Müller K. F., dePamphilis C. W., Quandt D., Bellot S., Schneeweiss G. M. (2016). Mechanistic model of evolutionary rate variation en route to a nonphotosynthetic lifestyle in plants. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 113, 9045–9050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1607576113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicke S., Müller K. F., dePamphilis C. W., Quandt D., Wickett N. J., Zhang Y., et al. (2013). Mechanisms of functional and physical genome reduction in photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic parasitic plants of the broomrape family. Plant Cell 25, 3711–3725. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.113373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. (1997). PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 13, 555–556. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/13.5.555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. (2007). PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1586–1591. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Peng S., Wang J., Wang Y., Ding S., Tian J., et al. (2022). Hemipilia yajiangensis (Orchidoideae, Orchidaceae), a new species from western Sichuan, China, based on molecular and morphological evidence. Kew Bull. 77, 973–982. doi: 10.1007/s12225-022-10049-w [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yudina S. V., Schelkunov M. I., Nauheimer L., Crayn D., Chantanaorrapint S., Hroneš M., et al. (2021). Comparative analysis of plastid genomes in the non-photosynthetic genus Thismia reveals ongoing gene set reduction. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 602598. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.602598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Yang Y., Tang J., Luo Y., Lv H., Chai S. (2022). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Habenaria dentata (Orchidaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 7, 969–970. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2022.2080016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: Nucleotide sequences generated in this study are available in the GenBank online public database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) under the accession numbers OQ318186–OQ318196, OQ318871, OQ331227, OQ331229, OQ331230, OQ344206, OQ344207, OQ344208, OQ352447.