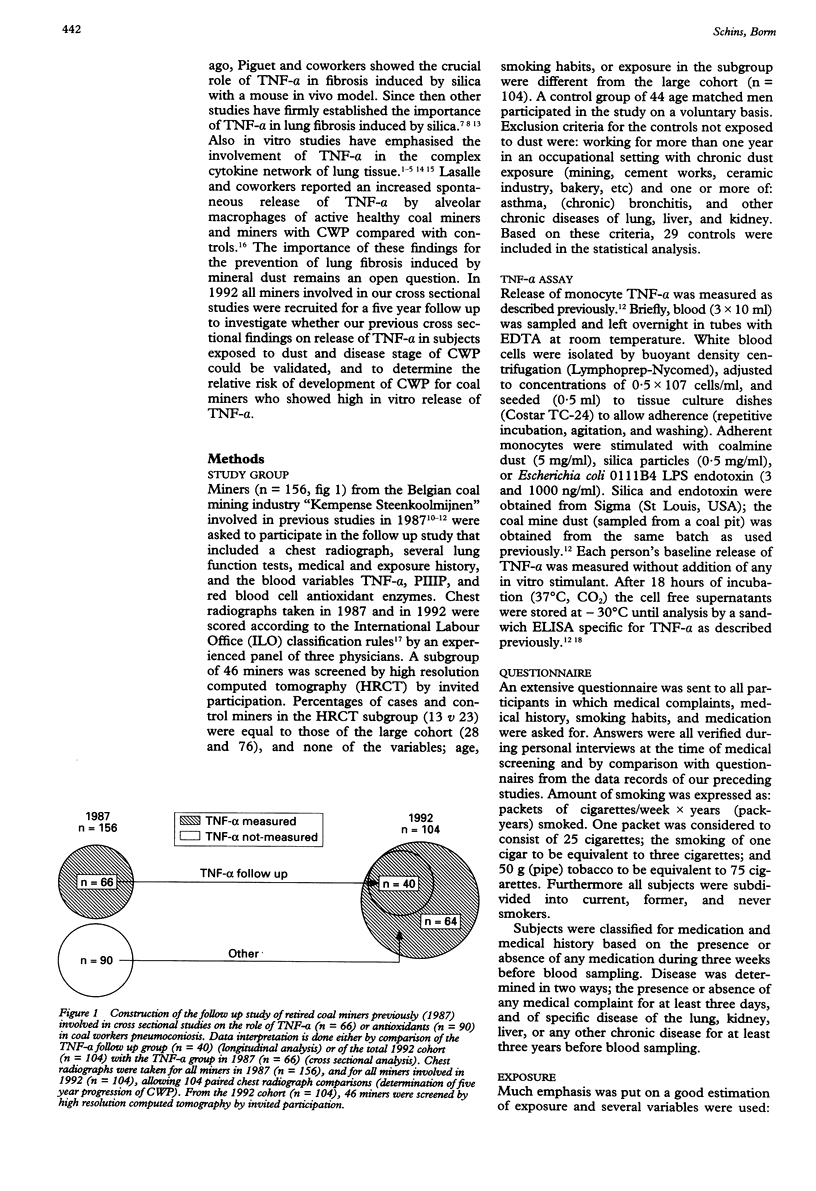
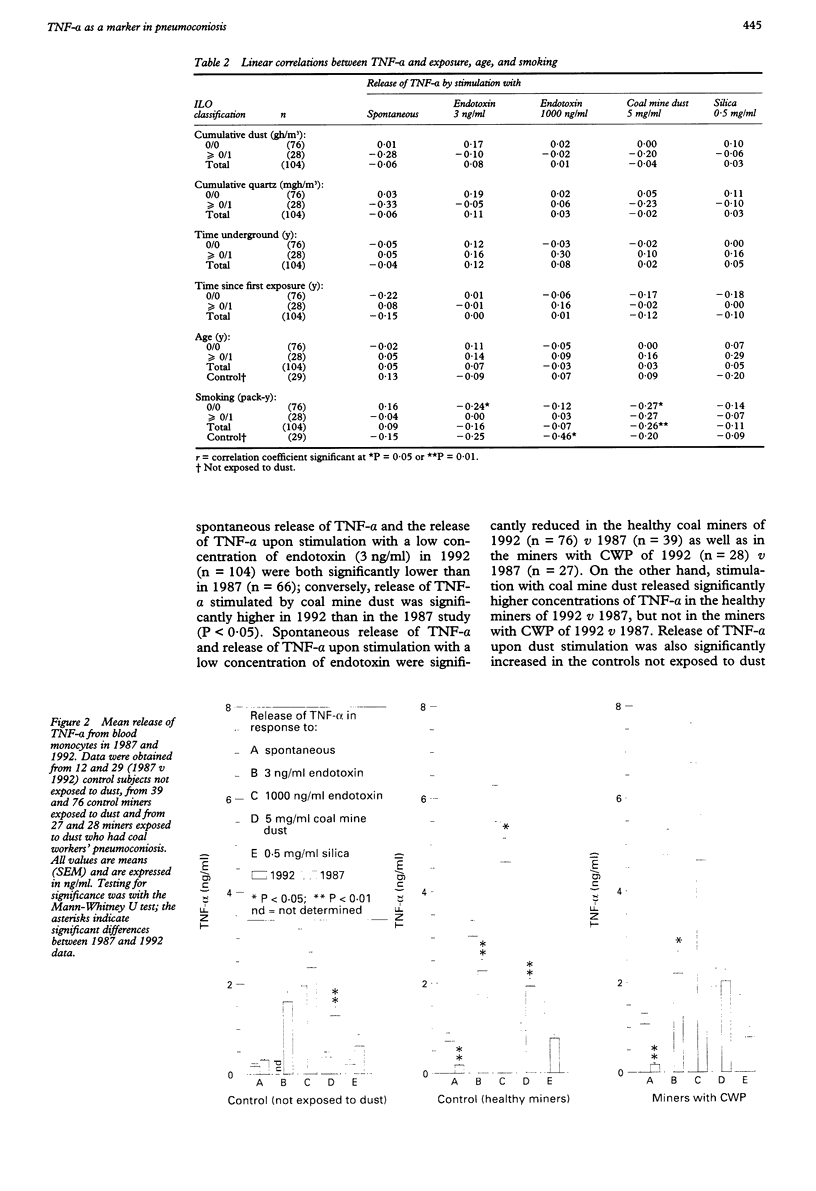
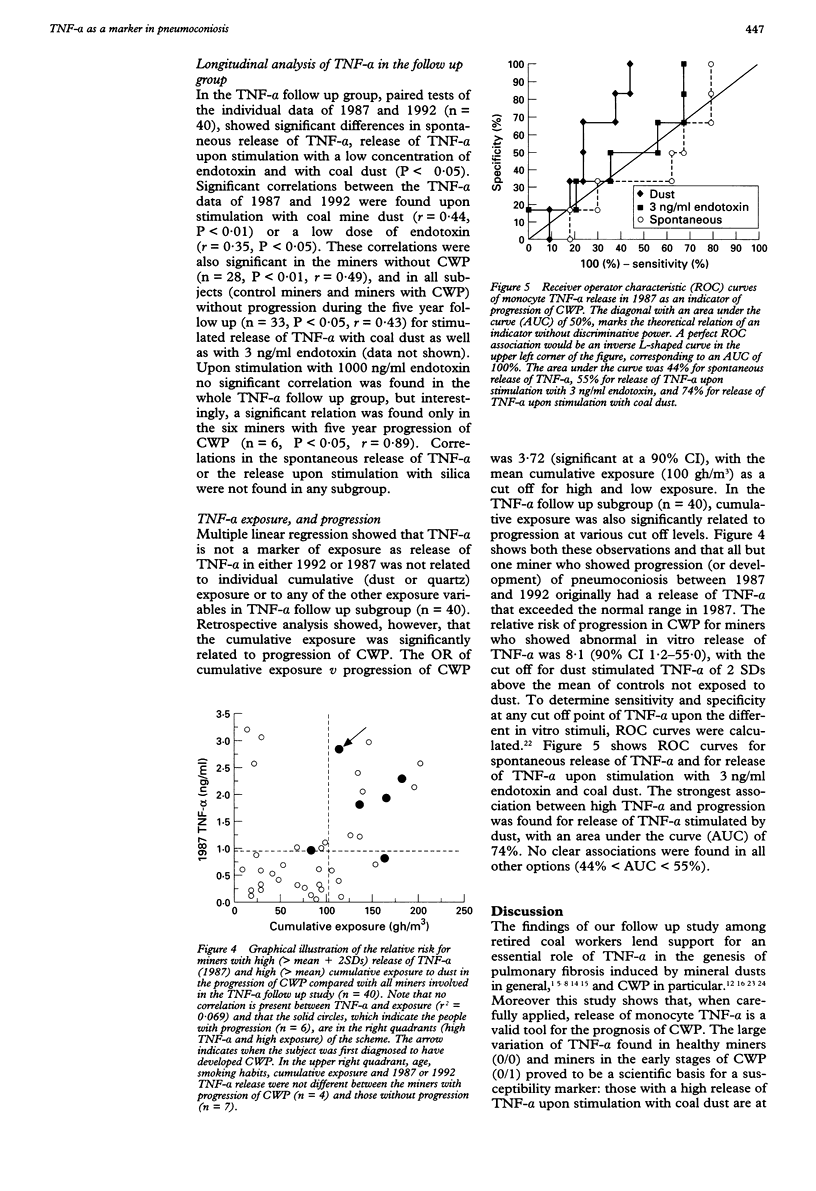
Abstract
OBJECTIVES--To determine (a) reproducibility with previous cross sectional findings, and (b) the predictive value of initial release of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) towards later progression of coalworkers' pneumoconiosis (CWP). METHODS--Release of monocyte TNF-alpha after in vitro stimulation with coal mine dust, silica, and endotoxin was measured in 104 retired miners and was related to stage of CWP (chest radiograph) and cumulative exposure. A subgroup of 46 miners was screened by high resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Prospective analysis of TNF-alpha (40 out of 104 miners involved in the previous TNF-alpha study) was done by relating initial TNF-alpha to five year progression of CWP measured by comparison of paired chest radiographs. RESULTS--As observed previously, dust stimulated release of TNF-alpha was increased in miners, especially in the early stages of pneumoconiosis. Cumulative exposure was related to pneumoconiotic stage but not to release of TNF-alpha. This excluded TNF-alpha as an exposure marker. Initial concentrations (1987) of TNF-alpha were related to later progression of CWP. Miners who showed abnormally high dust stimulated release of TNF-alpha had an increased risk of progression in CWP (relative risk 8.1). CONCLUSIONS--These results show (a) the significant involvement of TNF-alpha in pneumoconiosis in humans induced by coal dust and (b) that this routine test possibly constitutes a powerful tool to estimate individual prognosis of pneumoconiotic disease, even after the end of occupational exposure.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borm P. J., Palmen N., Engelen J. J., Buurman W. A. Spontaneous and stimulated release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) from blood monocytes of miners with coal workers' pneumoconiosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Dec;138(6):1589–1594. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.6.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R. Asbestos-induced lung disease. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Apr;100:21–30. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9310021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debets J. M., van der Linden C. J., Spronken I. E., Buurman W. A. T cell-mediated production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha by monocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Hassenbein D. G., Carter J., Poynter J., Asquith T. N., Grant R. A., Whitten J., Purdon M. P., Takigiku R. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: expression by rat alveolar macrophages, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells and in rat lung after mineral dust exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;8(3):311–318. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll K. E., Lindenschmidt R. C., Maurer J. K., Higgins J. M., Ridder G. Pulmonary response to silica or titanium dioxide: inflammatory cells, alveolar macrophage-derived cytokines, and histopathology. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):381–390. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubar V., Gosset P., Aerts C., Voisin C., Wallaert B., Tonnel A. B. In vitro acute effects of tobacco smoke on tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 production by alveolar macrophages. Exp Lung Res. 1993 May-Jun;19(3):345–359. doi: 10.3109/01902149309064351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Freundlich B., Kern J. A., Rosenbloom J. Cytokine networks in the regulation of inflammation and fibrosis in the lung. Chest. 1990 Jun;97(6):1439–1445. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.6.1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelen J. J., Borm P. J., van Sprundel M., Leenaerts L. Blood anti-oxidant parameters at different stages of pneumoconiosis in coal workers. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Mar;84:165–172. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9084165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson M. P., Chandler D. B. Changes in distribution, morphology, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion of alveolar macrophage subpopulations during the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):503–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley J. A., McNeil B. J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology. 1982 Apr;143(1):29–36. doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers R. J., Schins R. P., Wouters E. F., van Engelshoven J. M. High-resolution computed tomography of the lungs in coal miners with a normal chest radiograph. Exp Lung Res. 1994 Jul-Sep;20(5):411–419. doi: 10.3109/01902149409064397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassalle P., Gosset P., Aerts C., Fournier E., Lafitte J. J., Degreef J. M., Wallaert B., Tonnel A. B., Voisin C. Abnormal secretion of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha by alveolar macrophages in coal worker's pneumoconiosis: comparison between simple pneumoconiosis and progressive massive fibrosis. Exp Lung Res. 1990 Jan;16(1):73–80. doi: 10.3109/01902149009064700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C., Gemsa D., Graebner C., Hemenway D. R., Leslie K. O., Absher P. M., Davis G. S. Systemic macrophage stimulation in rats with silicosis: enhanced release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;5(4):395–402. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins R. C., Scheule R. K., Hamilton R., Gomes G., Freidman G., Holian A. Human alveolar macrophage cytokine release in response to in vitro and in vivo asbestos exposure. Exp Lung Res. 1993 Jan-Mar;19(1):55–65. doi: 10.3109/01902149309071080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Kunkel S. L. Lung cytokine production in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res. 1992 Jan-Mar;18(1):29–43. doi: 10.3109/01902149209020649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Collart M. A., Grau G. E., Sappino A. P., Vassalli P. Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):245–247. doi: 10.1038/344245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy-Jardin M., Degreef J. M., Beuscart R., Voisin C., Remy J. Coal worker's pneumoconiosis: CT assessment in exposed workers and correlation with radiographic findings. Radiology. 1990 Nov;177(2):363–371. doi: 10.1148/radiology.177.2.2217770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar C. A., Maclaren W. M., Annis R., Melville A. W. Quantitative relations between exposure to respirable coalmine dust and coalworkers' simple pneumoconiosis in men who have worked as miners but have left the coal industry. Br J Ind Med. 1986 Jan;43(1):29–36. doi: 10.1136/oem.43.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner W. G., Welborn M. B., Shepherd V. L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 alpha synergistically enhance phorbol myristate acetate-induced superoxide production by rat bone marrow-derived macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Oct;7(4):379–384. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S., Kunkel S. L., Cunningham T. W., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Macrophage-derived cytokines amplify immune complex-triggered O2-. responses by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):489–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


