Abstract
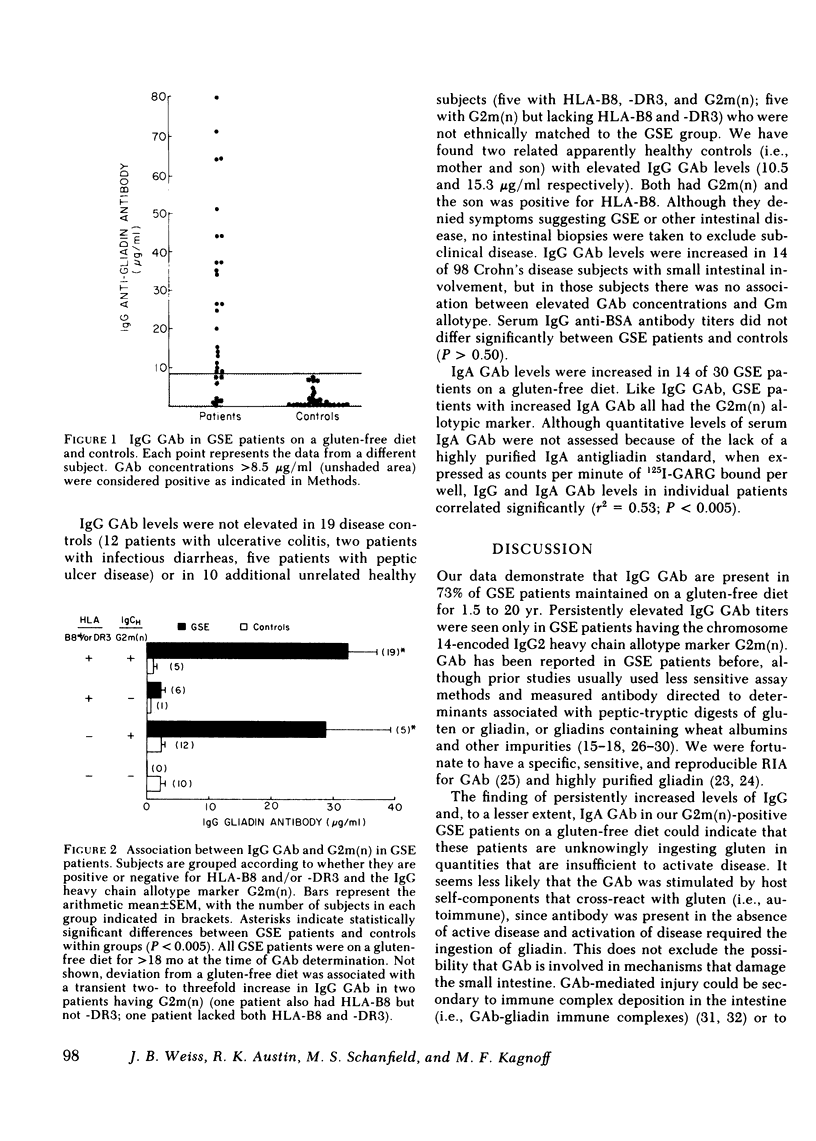
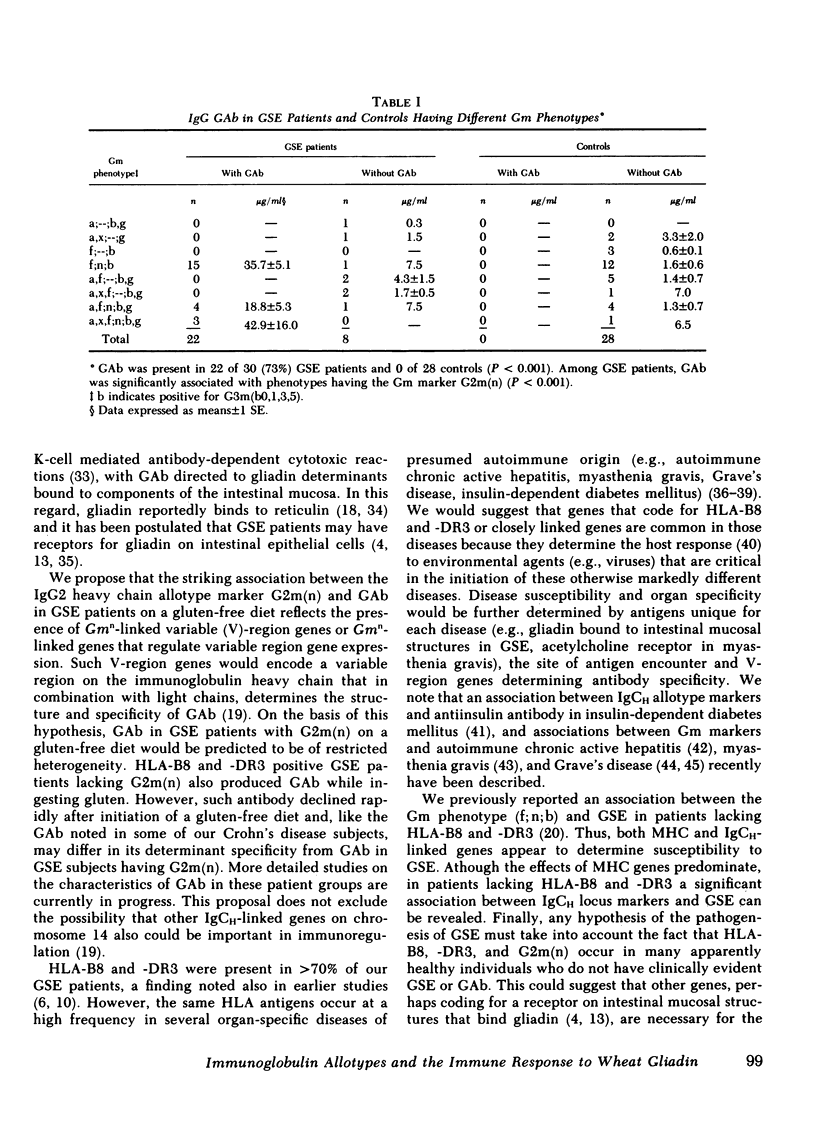
Anti-gliadin antibody was measured by radioimmunoassay in 30 Caucasians with gluten-sensitive enteropathy (GSE). 22 GSE patients maintained on a gluten-free diet for 1.5 to 20 yr (mean duration 76 mo) had elevated serum concentrations of IgG antigliadin antibody. Among GSE patients on a gluten-free diet, antigliadin antibody was seen only in those having the chromosome 14-encoded IgG immunoglobulin heavy chain allotype marker G2m(n). IgG antigliadin antibody was found in GSE patients with G2m(n) regardless of whether the HLA-B8 and/or -DR3 major histocompatibility complex antigens that occur frequently in GSE were present. No patient lacking G2m(n) had significant levels of antigliadin antibody. The association between antigliadin antibody and the immunoglobulin heavy chain allotype marker G2m(n) in GSE patients likely reflects the presence of Gmn-linked variable region genes or Gmn-linked genes that regulate variable region gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALARCON SEGOVIA D., HERSKOVIC T., WAKIM K. G., GREEN P. A., SCUDAMORE H. H. PRESENCE OF CIRCULATING ANTIBODIES TO GLUTEN AND MILK FRACTIONS IN PATIENTS WITH NONTROPICAL SPRUE. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:485–499. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert E. D., Harms K., Wank R., Steinbauer-Rosenthal I., Scholz S. Segregation analysis of HL-A antigens and haplotypes in 50 families of patients with coeliac disease. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1785–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek J., Albrechtsen D., Solheim B. G., Thorsby E. Strong association between the HLA-Dw3-related B cell alloantigen -DRw3 and coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(2):229–233. doi: 10.3109/00365527809181753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eterman K. P., Feltkamp T. E. Antibodies to gluten and reticulin in gastrointestinal diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):92–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Rogentine G. N., Strober W. Predominance of histocompatibility antigen HL-A8 in patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1602–1605. doi: 10.1172/JCI106958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M. Update on gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Am J Med. 1979 Dec;67(6):1085–1096. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., MacDonald T. T., McClure J. P., Holden R. J. Cell-mediated immunity to gliadin within the small-intestinal mucosa in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1975 Apr 19;1(7912):895–897. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91689-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. V., Kagnoff M. F., Hatlen L. H. Immune responses in human colon cancer. II. Cytotoxic antibody detected in patients' sera. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Apr;60(4):779–784. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.4.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K., Asquith P., Stokes P. L., Cooke W. T. Cellular infiltrate of jejunal biopsies in adult coeliac disease in relation to gluten withdrawal. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):278–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson J., Schilling W. Some characteristics of immunofluorescence tests for antibodies against gluten, using wheat grain sections or gliadin coated sepharose beads. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Aug;89(4):253–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIVEL R. M., KEARNS D. H., LIEBOWITZ D. SIGNIFICANCE OF ANTIBODIES TO DIETARY PROTEINS IN THE SERUMS OF PATIENTS WITH NONTROPICAL SPRUE. N Engl J Med. 1964 Oct 8;271:769–772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196410082711504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Johnson H. C., Bernardin J. E., Dietler M. D., Kasarda D. D. Celiac sprue: correlation with murine T cell responses to wheat gliadin components. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2693–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Two genetic loci control the murine immune response to A-gliadin, a wheat protein that activates coeliac sprue. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):158–160. doi: 10.1038/296158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Weiss J. B., Brown R. J., Lee T., Schanfield M. S. Immunoglobulin allotype markers in gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Lancet. 1983 Apr 30;1(8331):952–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenrick K. G., Walker-Smith J. A. Immunoglobulins and dietary protein antibodies in childhood coeliac disease. Gut. 1970 Aug;11(8):635–640. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.8.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster-Smith M., Kumar P., Marks R., Clark M. L., Dawson A. M. Jejunal mucosal immunoglobulin-containing cells and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis. Gut. 1974 May;15(5):371–376. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.5.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley T. J., Hall R. P., Fauci A. S., Katz S. I., Hamburger M. I., Frank M. M. Defective Fc-receptor functions associated with the HLA-B8/DRw3 haplotype: studies in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis and normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 22;304(4):185–192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101223040401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay I. R., Tait B. D. HLA associations with autoimmune-type chronic active hepatitis: identification of B8-DRw3 haplotype by family studies. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Katz S. I., Nelson D. L., Abelson L. D. Specific B-cell antigens associated with gluten-sensitive enteropathy and dermatitis herpetiformis. Lancet. 1976 Jan 17;1(7951):110–111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Mizuno N., Arima N., Wakisaka A., Okimoto K., Akazawa Y., Tsuji K., Fujita T. IgG heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and immune response to insulin in insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):407–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Nishitani H., Ota K., Fujita T., Tsuji K. Gm allotypes in myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1980 Mar 29;1(8170):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Mann D. L., Hague N. E., Heck J. A., van Leeuwen H. A., van Rood J. J., Strober W. Genetic basis of gluten-sentitive enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN W., FAUCI A. S., MARVIN S. F., SLEISENGER M. H., JEFRIES G. H. IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STUDIES IN ADULT CELIAC DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:475–485. doi: 10.1172/JCI105161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood J. J., Hooff J. P., Keuning J. J. Disease predisposition, immune responsiveness and the fine structure of the HL-A supergene. A need for a reappraisal. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:75–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. B., Scott D. G., Losowsky M. S. Jejunal mucosal immunoglobulins and complement in untreated coeliac disease. J Pathol. 1977 Apr;121(4):219–223. doi: 10.1002/path.1711210405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiner M., Ballard J. Antigen-antibody reactions in jejunal mucosa in childhood coeliac disease after gluten challenge. Lancet. 1972 Jun 3;1(7762):1202–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90924-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E., Bürgin-Wolff A., Berger R., Birbaumer A., Just M. Antibodies to gliadin as a screening test for coeliac disease. A prospective study. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1979 Feb;34(1):41–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M., Fischer K., Grüttner R. Immunofluorescent serum gliadin antibodies in children with coeliac disease and various malabsorptive disorders. II. Specificity of Gliadin antibodies: immunoglobulin classes, immunogenic properties of wheat protein fractions, and pathogenic significance of food antibodies in coeliac disease. Eur J Pediatr. 1979 Mar 1;130(3):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00455262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes P. L., Asquith P., Holmes G. K., Mackintosh P., Cooke W. T. Histocompatibility antigens associated with adult coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Jul 22;2(7769):162–164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR K. B., TRUELOVE S. C., WRIGHT R. SEROLOGIC REACTIONS TO GLUTEN AND COW'S MILK PROTEINS IN GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE. Gastroenterology. 1964 Feb;46:99–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trefts P. E., Kagnoff M. F. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. I. The T-dependent anti-A-gliadin antibody response maps to the murine major histocompatibility locus. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2249–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno H., Sasazuki T., Tamai H., Matsumoto H. Two major genes, linked to HLA and Gm, control susceptibility to Graves' disease. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):768–770. doi: 10.1038/292768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Johnson G. D., Haffenden G., Fry L., Holborow E. J. Binding of wheat gliadin in vitro to reticulum in normal and dermatitis herpetiformis skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Feb;76(2):88–93. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Manuel P. D., Walker-Smith J. A., Campbell C. A., Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J. New immunofluorescent blood test for gluten sensitivity. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Nov;56(11):864–868. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.11.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mathews J. D., Schanfield M. S., Tait B. D., Mackay I. R. Interaction of HLA and Gm in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jan;43(1):80–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


