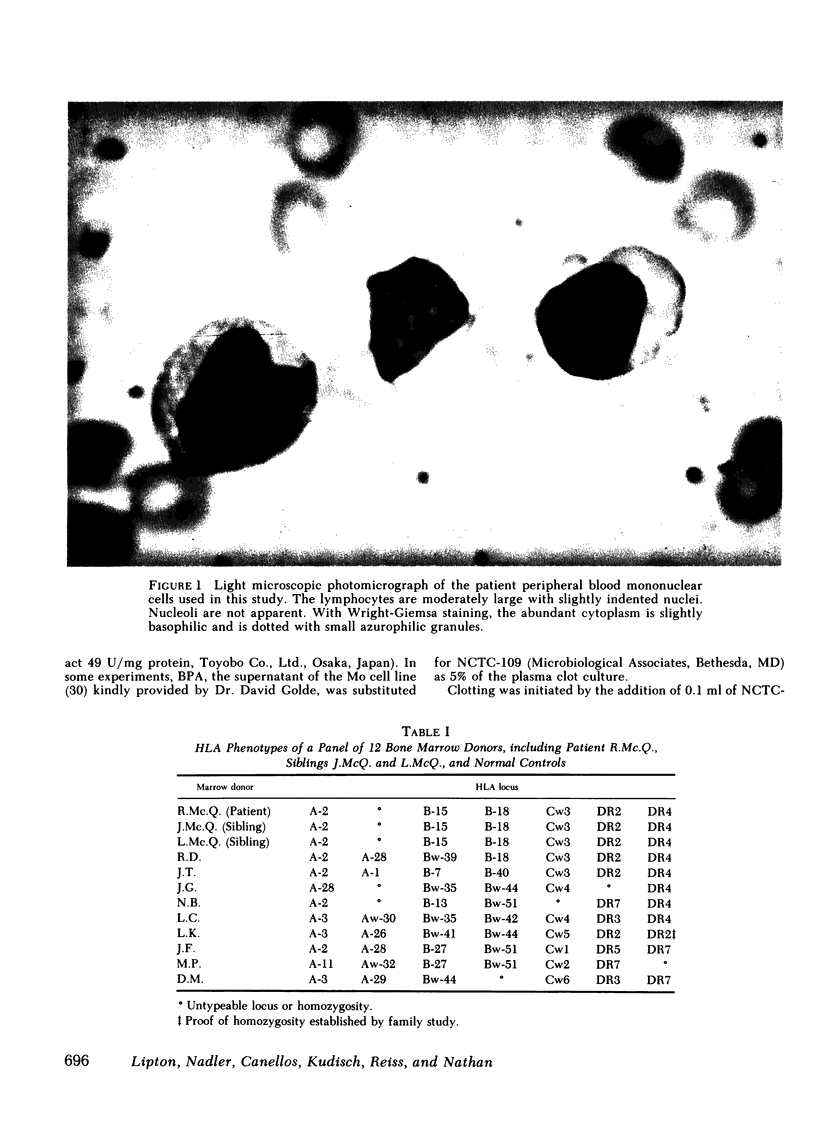
Abstract
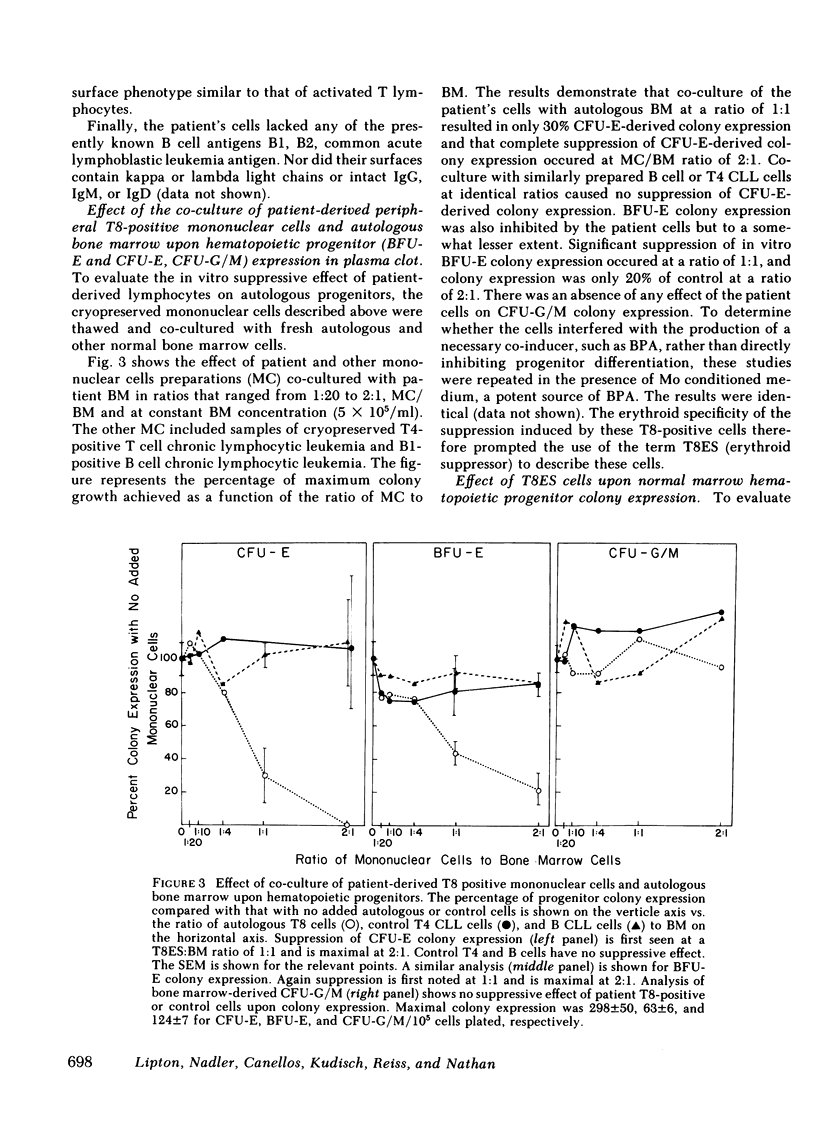
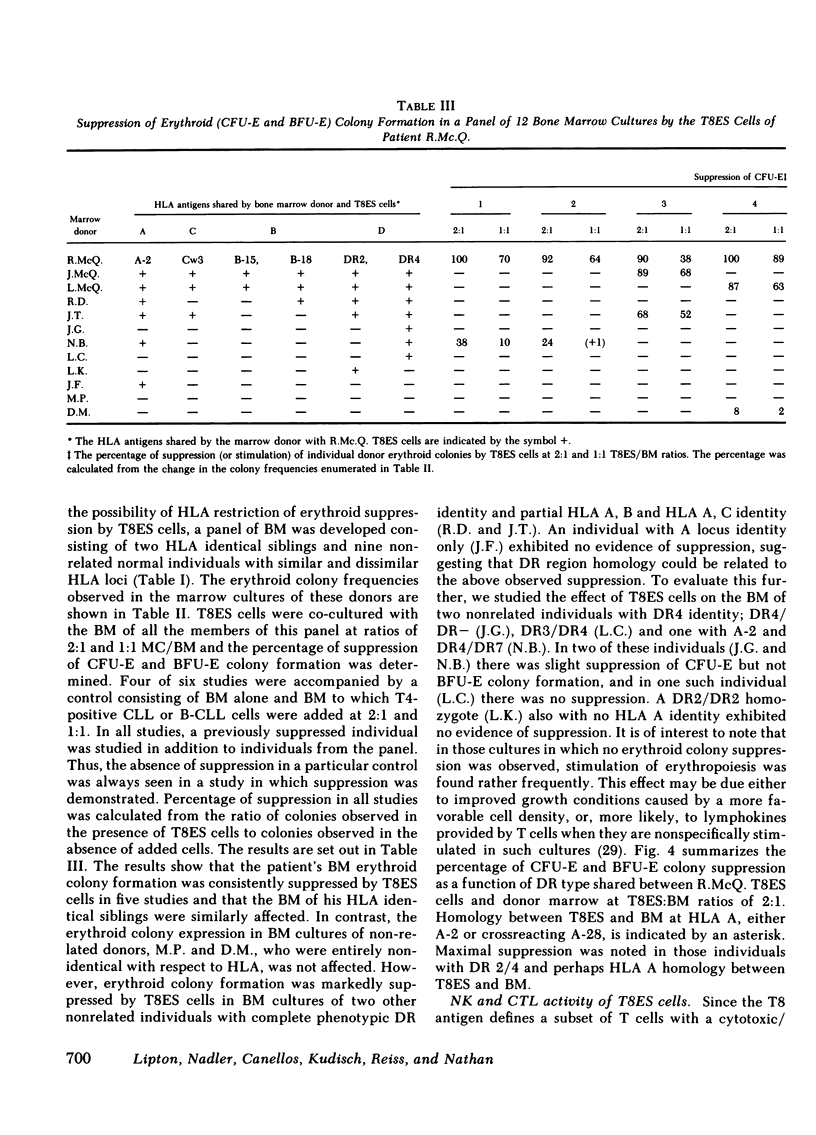
The suppression of erythropoiesis by lymphocytes from patients with a T cell lymphoproliferative syndrome and pure erythrocyte aplasia has been previously demonstrated. To study the nature of the suppressor cell and possible genetic restriction of this suppression, we investigated a patient with severe anemia, splenomegaly, lymphocytosis, and erythroid aplasia. A 3-mo course of low-dose daily oral cyclophosphamide achieved a complete remission for over 12 mo. The surface phenotype of his lymphocytes was analyzed by means of antibodies to lineage, differentiation, and activation-specific surface antigens. The cells expressed mature T cell antigens T3, T8, and T11, while lacking T1. Immature T cell, B cell, and the monocyte-specific antigen Mo2 were absent, while Mo1, a monocyte-associated antigen not normally expressed on T cells, was present. T10 and Ia expressed as activation antigens were also present. The cells, cryopreserved at diagnosis, were thawed and co-cultured in plasma clot with patient remission marrow samples at T cell/bone marrow ratios of 1:1 and 2:1. There was nearly 90% suppression of erythroid colony-forming unit expression and 60% suppression of erythroid burst-forming unit expression at 2:1 T cell to bone marrow ratios and somewhat less suppression at 1:1. Granulocyte/macrophage progenitor expression was unaffected. Erythroid progenitor differentiation in the marrows of two HLA identical siblings was similarly suppressed. The cells were co-cultured with the marrows of nine nonrelated donors to investigate the potential genetic restriction of this suppression. Colony suppression equal to that observed in the marrow of the patient and his siblings was found in studies of two partially HLA identical individuals. No suppression was detected in marrow co-cultures of two entirely HLA dissimilar individuals. These results show that suppression of erythropoiesis by a unique subset of T8, Mo1, Ia-positive lymphocytes isolated from a patient with lymphocytosis and erythrocyte aplasia is genetically restricted.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPEN E. L., CRANMORE D. Cellular kinetics and iron utilization in bone marrow as observed by Fe59 radioautography. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Jun 25;77:753–765. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb36938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisenberg A. C., Wilkes B. M., Harris N. L., Ault K. A., Carey R. W. Chronic T-cell lymphocytosis with neutropenia: report of a case studied with monoclonal antibody. Blood. 1981 Oct;58(4):818–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr T lymphocytes involved in inhibition of granulopoiesis in two neutropenic patients are of the cytotoxic/suppressor (T3+T8+) subset. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1597–1600. doi: 10.1172/JCI110415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck B. N., Frelinger J. G., Shigeta M., Infante A. J., Cummings D., Hämmerling G., Fathman C. G. T cell clones specific for hybrid I-A molecules. Discrimination with monoclonal anti-I-Ak antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1186–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Linch D. C., Beverley P. C. T cell disorders in haematological diseases. Clin Haematol. 1982 Oct;11(3):661–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D., Hansen J. A., Newman W. Evidence for T cell nature and heterogeneity within natural killer (NK) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) effectors: a comparison with cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL). J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):448–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Cadoni A., Franzi A. T., Ghigliotti C., Leprini A., Zicca A., Grossi C. E. Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Similarities between the cells of the third population and TG lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):562–570. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Bersch N., Quan S. G., Lusis A. J. Production of erythroid-potentiating activity by a human T-lymphoblast cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):593–596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber S. E., Krantz S. B. Erythropoietin and the control of red cell production. Annu Rev Med. 1978;29:51–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.29.020178.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi C. E., Webb S. R., Zicca A., Lydyard P. M., Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Cooper M. D. Morphological and histochemical analyses of two human T-cell subpopulations bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1405–1417. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R., Kopel S., Hsu S. D., Dainiak N., Zanjani E. D. T cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: presence in bone marrow and peripheral blood of cells that suppress erythropoiesis in vitro. Blood. 1978 Jul;52(1):255–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Metcalf D. Pure and mixed erythroid colony formation in vitro stimulated by spleen conditioned medium with no detectable erythropoietin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3879–3882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Niskanen E., Cline M., Billing R., Golde D. Human myeloid precursors forming colonies in diffusion chambers expresses the Ia-like antigen. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):1188–1191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Taketani S., Biddison W. E., Strong D. M., Strominger J. L. Comparative structural analysis of HLA-A2 antigens distinguishable by cytotoxic T lymphocytes: variants M7 and DR1. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6313–6321. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAJTHA L. G., SUIT H. D. Uptake of radioactive iron (59Fe) by nucleated red cells in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1955 Jan;1(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1955.tb05488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linch D. C., Cawley J. C., MacDonald S. M., Masters G., Roberts B. E., Antonis A. H., Waters A. K., Sieff C., Lydyard P. M. Acquired pure red-cell aplasia associated with an increase of T cells bearing receptors for the Fc of IgG. Acta Haematol. 1981;65(4):270–274. doi: 10.1159/000207191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linch D. C., Cawley J. C., Worman C. P., Galvin M. C., Roberts B. E., Callard R. E., Beverley P. C. Abnormalities of T-cell subsets in patients with neutropenia and an excess of lymphocytes in the bone marrow. Br J Haematol. 1981 May;48(1):137–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.00137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton J. M., Nathan D. G. Cell-cell interactions in the regulation of erythropoiesis. Br J Haematol. 1983 Mar;53(3):361–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton J. M., Reinherz E. L., Kudisch M., Jackson P. L., Schlossman S. F., Nathan D. G. Mature bone marrow erythroid burst-forming units do not require T cells for induction of erythropoietin-dependent differentiation. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):350–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmeyer J., Rieber P., Feucht H., Johnson J., Hadam M., Riethmüller G. A subset of human cells isolated and characterized by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Dec;11(12):997–1001. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan K. F., Chikkappa G., Bieler L. Z., Scharfman W. B., Parkinson D. R. Regulation of human blood erythroid burst-forming unit (BFU-E) proliferation by T-lymphocyte subpopulations defined by Fc receptors and monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):990–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan K. F., Chikkappa G., Farley P. C. T gamma (T gamma) cells suppress growth of erythroid colony-forming units in vitro in the pure red cell aplasia of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1148–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI110713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M., Axelrad A. A. Improved plasma culture system for production of erythrocytic colonies in vitro: quantitative assay method for CFU-E. Blood. 1974 Oct;44(4):517–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Ritz J., Hardy R., Pesando J. M., Schlossman S. F., Stashenko P. A unique cell surface antigen identifying lymphoid malignancies of B cell origin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):134–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI110005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., Pesando J. M., Yunis E. J., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining serologically distinct HLA-D/DR related Ia-like antigens in man. Hum Immunol. 1981 Feb;2(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody defining a lymphoma-associated antigen in man. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):570–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., van Agthoven A., Terhorst C., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B cell-specific antigen (B2) distinct from B1. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa T., Abe T., Nakagawa T. Pure red cell aplasia and hypogammaglobulinemia associated with Tr-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1025–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Chess L., Hillman D. G., Clarke B., Breard J., Merler E., Housman D. E. Human erythroid burst-forming unit: T-cell requirement for proliferation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):324–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid C. D., Baptista L. C., Chanarin I. Erythroid colony growth in vitro from human peripheral blood null cells: evidence for regulation by T-lymphocytes and monocytes. Br J Haematol. 1981 May;48(1):155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.00155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2894–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss C. S., Hemler M. E., Englehard V. H., Mier J. W., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J. Development and characterization of allospecific long-term human cytolytic T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5432–5436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Notis-McConarty J., Lazarus H., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody to human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):583–585. doi: 10.1038/283583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Sieff C., Delia D., Edwards P. A., Greaves M. Expression of cell-surface HLA-DR, HLA-ABC and glycophorin during erythroid differentiation. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):68–71. doi: 10.1038/289068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlimok G., Thiel E., Rieber E. P., Huhn D., Feucht H., Lohmeyer J., Riethmüller G. Chronic leukemia with a hybrid surface phenotype (T lymphocytic/myelomonocytic): leukemic cells displaying natural killer activity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1157–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer G., Verma D. S. Cells with Fc gamma receptors from normal donors suppress granulocytic macrophage colony formation. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):758–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., Parham P., Mann D. L., Strominger J. L. Structure of HLA antigens: amino-acid and carbohydrate compositions and NH2-terminal sequences of four antigen preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., van Agthoven A., LeClair K., Snow P., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. Biochemical studies of the human thymocyte cell-surface antigens T6, T9 and T10. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. F., 3rd, Nadler L. M., Schlossman S. F. Antigens on human monocytes identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1435–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torok-Storb B., Hansen J. A. Modulation of in vitro BFU-E growth by normal Ia-positive T cells is restricted by HLA-DR. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):473–474. doi: 10.1038/298473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torok-Storb B., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A. Regulation of in vitro erythropoiesis by normal T cells: evidence for two T-cell subsets with opposing function. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J., Goossens J., Decock W., Kung P., Goldstein G. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis and E-rosette formation by the monoclonal antibody OKT11A. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):865–871. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Cannon G. B., Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes against a myeloid cell line: characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker R. B., Kauffman R. S., Che M., Finberg R. CT hybridomas: tumor cells capable of lysing virally infected target cells. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):900–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Meyers P. A., Broxmeyer H. E., Wang C. Y., Moore M. A., Kunkel H. G. Inhibition of human erythropoietic colony formation in culture by treatment with Ia antisera. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):613–618. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]