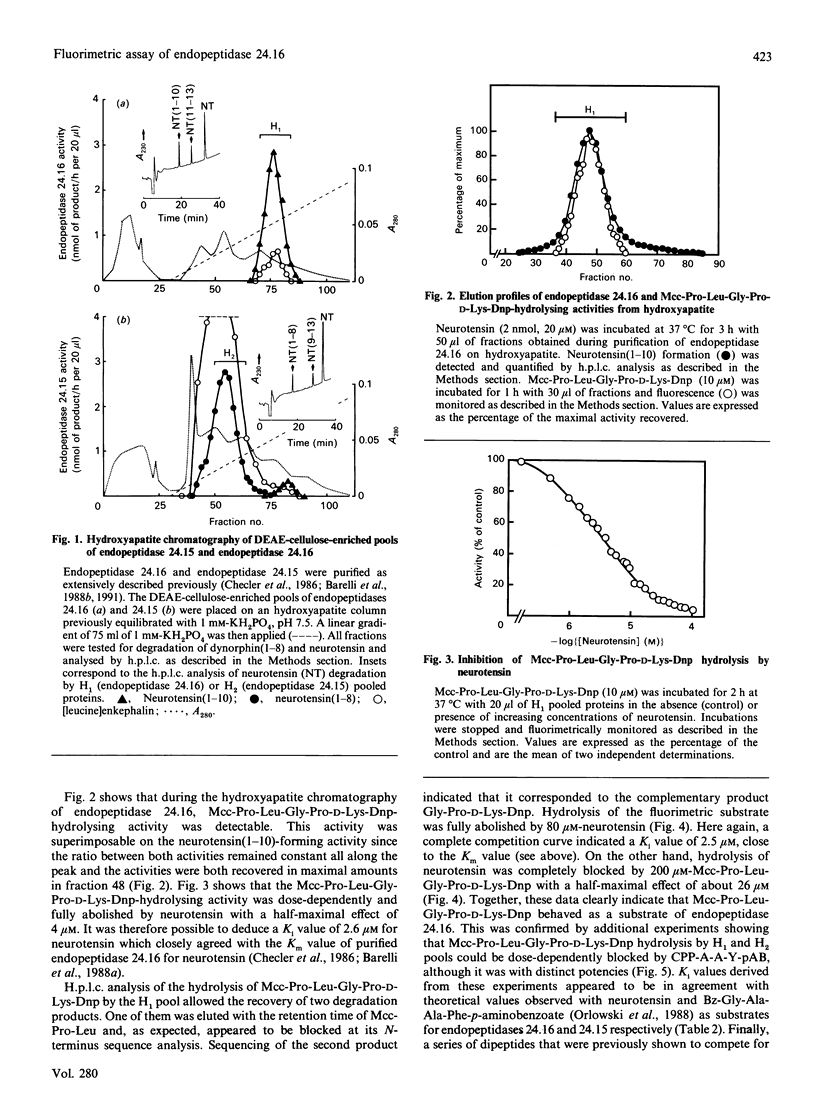
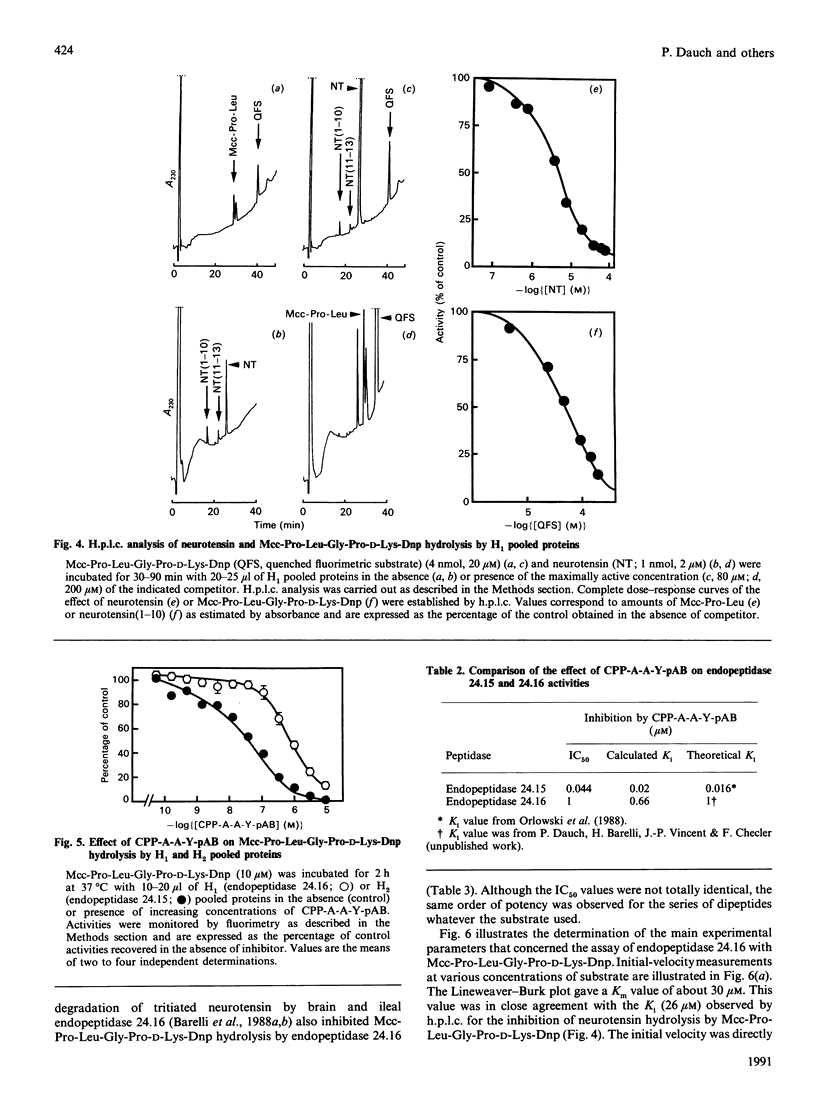
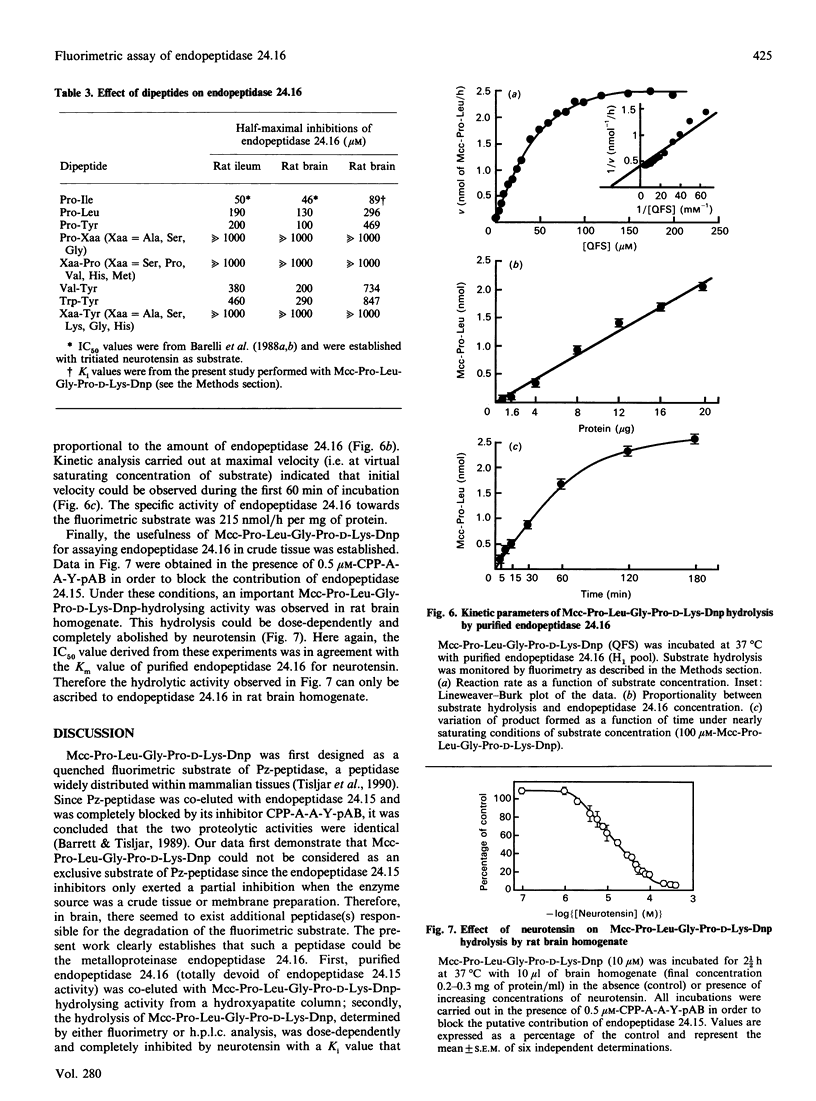
Abstract
Mcc-Pro-Leu-Gly-Pro-D-Lys-Dnp (Mcc = 3-carboxy-7-methoxycoumarin; Dnp = dinitrophenyl), a quenched fluorimetric substrate originally designed as a probe to measure Pz-peptidase (also called endopeptidase 24.15), was examined as a putative substrate of the neurotensin-degrading neutral metalloendopeptidase, endopeptidase 24.16. During the purification of endopeptidase 24.16 the neurotensin(1-10) and neurotensin(11-13) formation due to this enzyme was coeluted with Mcc-Pro-Leu-Gly-Pro-D-Lys-Dnp-hydrolysing activity. By both fluorimetric and h.p.l.c. analyses, we observed that the latter activity was dose-dependently and completely abolished by neurotensin with an IC50 value (2.6 microM) that closely corresponds to the affinity of purified endopeptidase 24.16 for neurotensin (Km = 2.5 microM). Furthermore, Mcc-Pro-Leu-Gly-Pro-D-Lys-Dnp hydrolysis was inhibited by a series of dipeptides with a rank of order of potencies that parallels that observed in competition experiments of tritiated neurotensin hydrolysis by brain and intestinal endopeptidase 24.16. Altogether, these data clearly demonstrate that, in addition to Pz-peptidase, Mcc-Pro-Leu-Gly-Pro-D-Lys-Dnp also behaves as a substrate of endopeptidase 24.16, with a Km of about 26 microM. In addition, we show that, even in crude membrane preparations, Mcc-Pro-Leu-Gly-Pro-D-Lys-Dnp behaves as a useful tool to monitor and accurately quantify endopeptidase 24.16.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barelli H., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Peripheral inactivation of neurotensin. Isolation and characterization of a metallopeptidase from rat ileum. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Tisljar U. The activities of 'Pz-peptidase' and 'endopeptidase 24.15' are due to a single enzyme. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):1047–1050. doi: 10.1042/bj2611047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabry J., Checler F., Vincent J. P., Mazella J. Colocalization of neurotensin receptors and of the neurotensin-degrading enzyme endopeptidase 24-16 in primary cultures of neurons. J Neurosci. 1990 Dec;10(12):3916–3921. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-12-03916.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Barelli H., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P. Neurotensin metabolism in various tissues of central and peripheral origins: ubiquitous involvement of a novel neurotensin degrading metalloendopeptidase. Biochimie. 1988 Jan;70(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Barelli H., Vincent J. P. Tissue distribution of a novel neurotensin-degrading metallopeptidase. An immunological approach using monospecific polyclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):549–554. doi: 10.1042/bj2570549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Emson P. C., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Inactivation of neurotensin by rat brain synaptic membranes. Cleavage at the Pro10-Tyr11 bond by endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and a peptidase different from proline-endopeptidase. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1295–1301. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Purification and characterization of a novel neurotensin-degrading peptidase from rat brain synaptic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11274–11281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C., Molineaux C. J. Substrate-related potent inhibitors of brain metalloendopeptidase. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):597–602. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisljar U., Knight C. G., Barrett A. J. An alternative quenched fluorescence substrate for Pz-peptidase. Anal Biochem. 1990 Apr;186(1):112–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90582-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


