Abstract
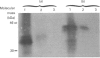
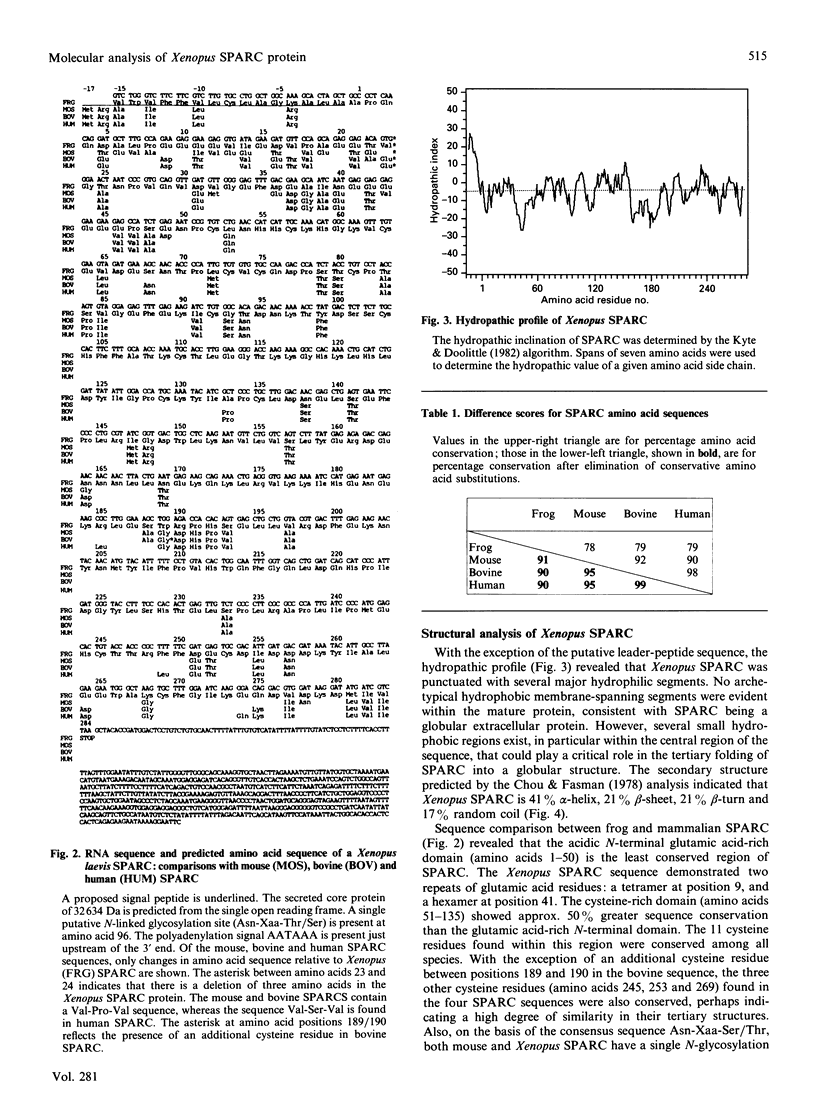
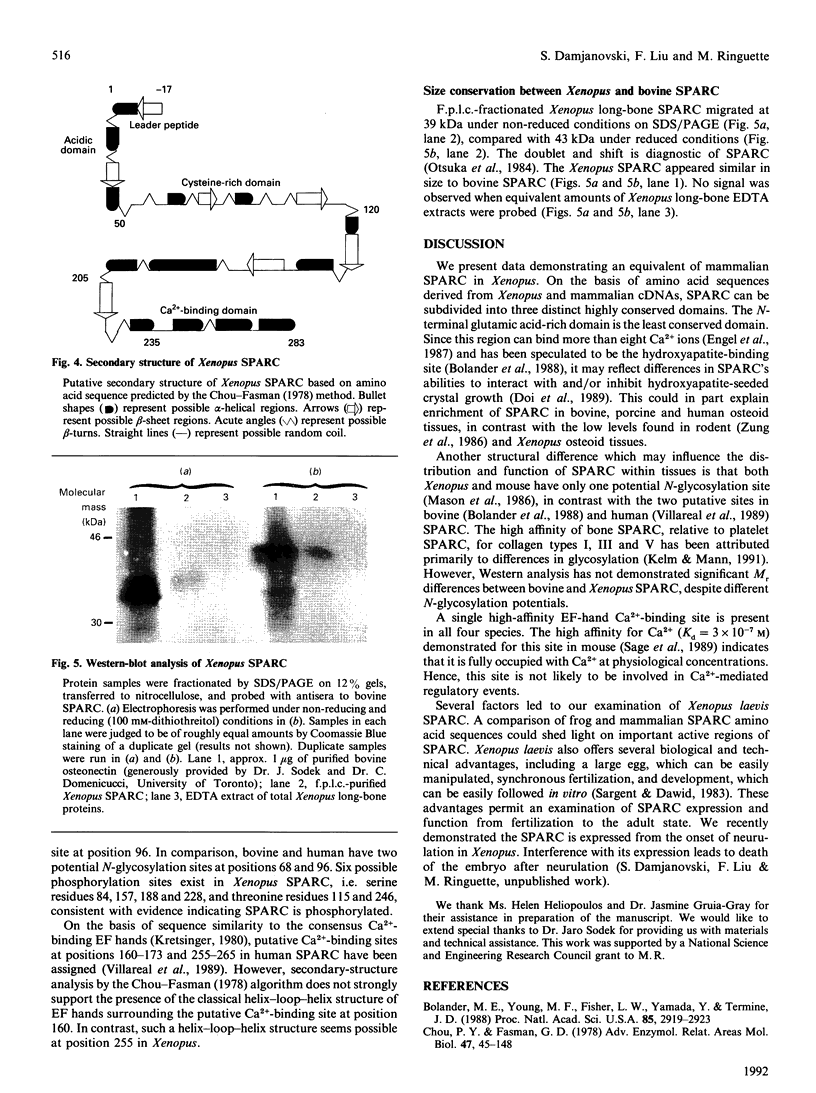
SPARC (Secreted Protein, Acidic, Rich in Cysteine) is expressed as a 1.6 kb mRNA in Xenopus laevis. On the basis of cDNA sequence analysis, Xenopus SPARC has a core Mr of 32643, with one potential N-glycosylation site. Western analysis of SPARC isolated from Xenopus long bone indicates that the mature protein has an Mr of 43,000. At the amino acid level, Xenopus SPARC has 78-79% sequence similarity to mouse, bovine and human SPARC. The least-conserved region is found within the N-terminal glutamic acid-rich domain, with the C-terminal Ca(2+)-binding domain being the most conserved. Adult Xenopus tissues show the same pattern of tissue-specific distribution of SPARC mRNAs as adult mouse.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolander M. E., Young M. F., Fisher L. W., Yamada Y., Termine J. D. Osteonectin cDNA sequence reveals potential binding regions for calcium and hydroxyapatite and shows homologies with both a basement membrane protein (SPARC) and a serine proteinase inhibitor (ovomucoid). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2919–2923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi Y., Okuda R., Takezawa Y., Shibata S., Moriwaki Y., Wakamatsu N., Shimizu N., Moriyama K., Shimokawa H. Osteonectin inhibiting de novo formation of apatite in the presence of collagen. Calcif Tissue Int. 1989 Mar;44(3):200–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02556565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenicucci C., Goldberg H. A., Hofmann T., Isenman D., Wasi S., Sodek J. Characterization of porcine osteonectin extracted from foetal calvariae. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):139–151. doi: 10.1042/bj2530139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Taylor W., Paulsson M., Sage H., Hogan B. Calcium binding domains and calcium-induced conformational transition of SPARC/BM-40/osteonectin, an extracellular glycoprotein expressed in mineralized and nonmineralized tissues. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6958–6965. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Harper S. J., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. In vivo expression of mRNA for the Ca++-binding protein SPARC (osteonectin) revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):473–482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelm R. J., Jr, Mann K. G. Human platelet osteonectin: release, surface expression, and partial characterization. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1105–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelm R. J., Jr, Mann K. G. The collagen binding specificity of bone and platelet osteonectin is related to differences in glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9632–9639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Structure and evolution of calcium-modulated proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):119–174. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. J., Murphy D., Münke M., Francke U., Elliott R. W., Hogan B. L. Developmental and transformation-sensitive expression of the Sparc gene on mouse chromosome 11. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1831–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A. Extracellular matrix assembly. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Yao K. L., Wasi S., Tung P. S., Aubin J. E., Sodek J., Termine J. D. Biosynthesis of osteonectin by fetal porcine calvarial cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9805–9812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringuette M., Damjanovski S., Wheeler D. Expression of SPARC/osteonectin in tissues of bony and cartilaginous vertebrates. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;69(4):245–250. doi: 10.1139/o91-037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romberg R. W., Werness P. G., Riggs B. L., Mann K. G. Inhibition of hydroxyapatite crystal growth by bone-specific and other calcium-binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1176–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Vernon R. B., Funk S. E., Everitt E. A., Angello J. SPARC, a secreted protein associated with cellular proliferation, inhibits cell spreading in vitro and exhibits Ca+2-dependent binding to the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):341–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Differential gene expression in the gastrula of Xenopus laevis. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):135–139. doi: 10.1126/science.6688681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termine J. D., Kleinman H. K., Whitson S. W., Conn K. M., McGarvey M. L., Martin G. R. Osteonectin, a bone-specific protein linking mineral to collagen. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal X. C., Mann K. G., Long G. L. Structure of human osteonectin based upon analysis of cDNA and genomic sequences. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6483–6491. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi S., Otsuka K., Yao K. L., Tung P. S., Aubin J. E., Sodek J., Termine J. D. An osteonectinlike protein in porcine periodontal ligament and its synthesis by periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;62(6):470–478. doi: 10.1139/o84-064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zung P., Domenicucci C., Wasi S., Kuwata F., Sodek J. Osteonectin is a minor component of mineralized connective tissues in rat. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;64(4):356–362. doi: 10.1139/o86-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]