Abstract
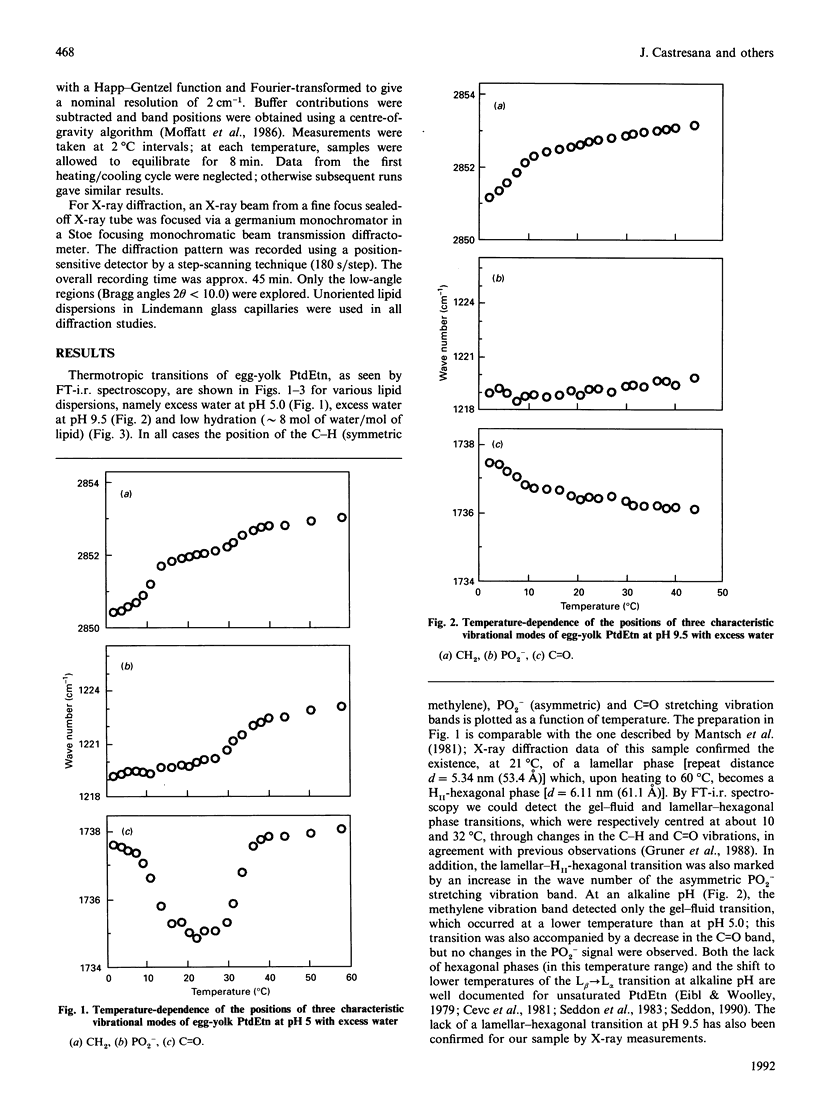
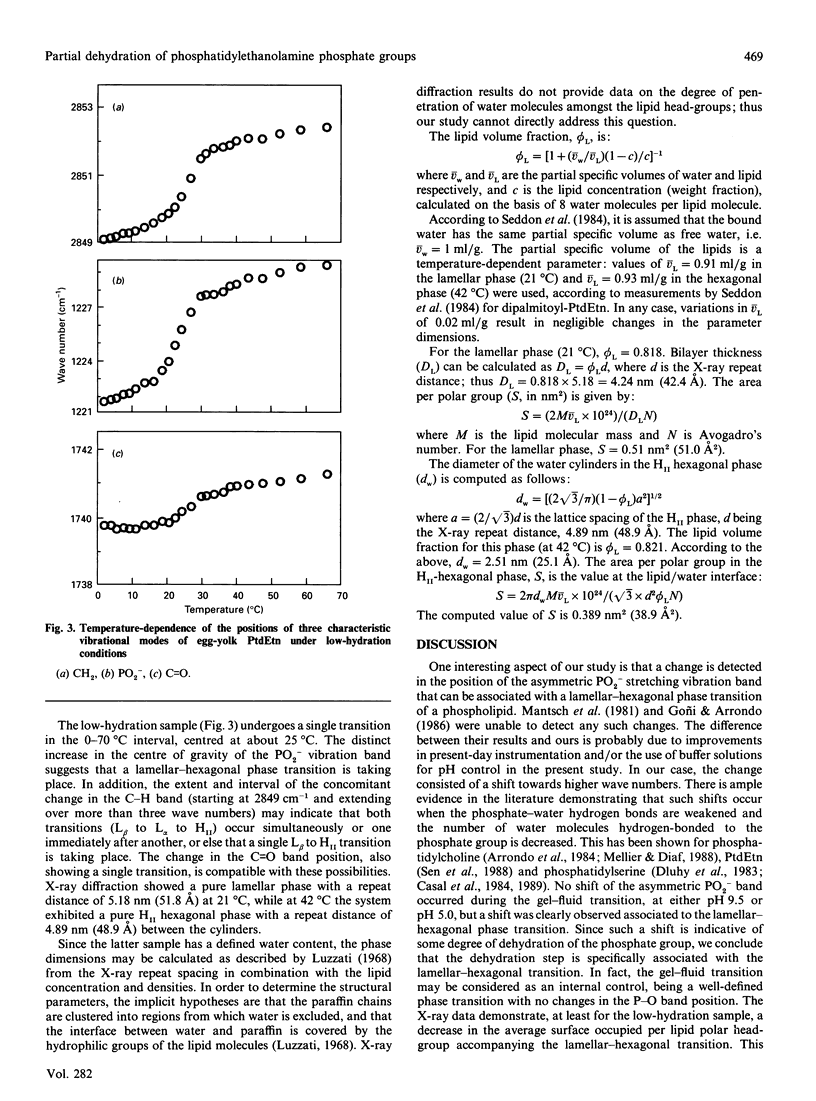
The gel-to-fluid and lamellar-to-HII-hexagonal thermotropic phase transitions of egg-yolk phosphatidylethanolamine have been examined by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy under a variety of conditions, namely excess water at pH 5.0, excess water at pH 9.5 and low hydration. The various lamellar and hexagonal phases have been characterized by X-ray diffraction. At pH 5.0, gel-fluid and lamellar-hexagonal transitions were detected at 10 and 32 degrees C respectively, in accordance with previous data. At pH 9.5, only the first of these two transitions was detected. In the partially hydrated sample a single phenomenon was observed, probably encompassing both transitions, so that, in practice, a gel-HII-hexagonal transition appears to occur. The region of the i.r. spectrum corresponding to the phospholipid phosphate group reveals that the lamellar-hexagonal, but not the gel-fluid, transition is accompanied by a weakening in the shell of hydrogen-bonded water, thus providing direct evidence that, in a pure lipid/water system, hexagonal phase formation requires partial dehydration of the phospholipid phosphate group. X-ray diffraction data support this conclusion, since, at least in the low-hydration system, the average surface area per lipid polar group decreases with the thermotropic lamellar-hexagonal transition.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrondo J. L., Goñi F. M., Macarulla J. M. Infrared spectroscopy of phosphatidylcholines in aqueous suspension. A study of the phosphate group vibrations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. M. Lipid intermolecular hydrogen bonding: influence on structural organization and membrane function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 5;906(3):353–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal H. L., Mantsch H. H., Hauser H. Infrared and 31P-NMR studies of the interaction of Mg2+ with phosphatidylserines: effect of hydrocarbon chain unsaturation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 10;982(2):228–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal H. L., Mantsch H. H. Polymorphic phase behaviour of phospholipid membranes studied by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 4;779(4):381–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevc G., Watts A., Marsh D. Titration of the phase transition of phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Effects of pH, surface electrostatics, ion binding, and head-group hydration. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4955–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., Hope M. J., Tilcock C. P. Lipid polymorphism and the roles of lipids in membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Jun-Jul;40(2-4):127–144. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. The polymorphic phase behaviour of phosphatidylethanolamines of natural and synthetic origin. A 31P NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Woolley P. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. Hydrogen bonds in lipid membrane surfaces. Biophys Chem. 1979 Nov;10(3-4):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(79)85015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fringeli U. P., Günthard H. H. Infrared membrane spectroscopy. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1981;31:270–332. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81537-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goñi F. M., Arrondo J. L. A study of phospholipid phosphate groups in model membranes by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Faraday Discuss Chem Soc. 1986;(81):117–126. doi: 10.1039/dc9868100117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M., Cullis P. R., Hope M. J., Tilcock C. P. Lipid polymorphism: the molecular basis of nonbilayer phases. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:211–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M., Tate M. W., Kirk G. L., So P. T., Turner D. C., Keane D. T., Tilcock C. P., Cullis P. R. X-ray diffraction study of the polymorphic behavior of N-methylated dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2853–2866. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman P. D. Spin-label characterisation of the lamellar-to-hexagonal (HII) phase transition in egg phosphatidylethanolamine aqueous dispersions. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Chapman D. Infrared spectroscopic studies of biomembranes and model membranes. Biosci Rep. 1986 Mar;6(3):235–256. doi: 10.1007/BF01115153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., Mannock D. A., McElhaney R. N., Turner D. C., Gruner S. M. Effect of fatty acyl chain length and structure on the lamellar gel to liquid-crystalline and lamellar to reversed hexagonal phase transitions of aqueous phosphatidylethanolamine dispersions. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):541–548. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantsch H. H., Martin A., Cameron D. G. Characterization by infrared spectroscopy of the bilayer to nonbilayer phase transition of phosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3138–3145. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Seddon J. M. Gel-to-inverted hexagonal (L beta-HII) phase transitions in phosphatidylethanolamines and fatty acid-phosphatidylcholine mixtures, demonstrated by 31P-NMR spectroscopy and x-ray diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 25;690(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Fuller N. L., Gruner S. M., Parsegian V. A. Membrane curvature, lipid segregation, and structural transitions for phospholipids under dual-solvent stress. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):76–87. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Husson F. Structure des phases liquide-cristallines de différents phospholipides, monoglycérides, sphingolipides, anhydres ou en présence d'eau. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):363–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M., Cevc G., Kaye R. D., Marsh D. X-ray diffraction study of the polymorphism of hydrated diacyl- and dialkylphosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2634–2644. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M., Cevc G., Marsh D. Calorimetric studies of the gel-fluid (L beta-L alpha) and lamellar-inverted hexagonal (L alpha-HII) phase transitions in dialkyl- and diacylphosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M. Structure of the inverted hexagonal (HII) phase, and non-lamellar phase transitions of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 28;1031(1):1–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90002-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Yang P. W., Mantsch H. H., Hui S. W. Extended hydrogen-bonded structures of phosphatidylethanolamine. Chem Phys Lipids. 1988 Jun;47(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(88)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. P. Inverted micellar intermediates and the transitions between lamellar, cubic, and inverted hexagonal lipid phases. II. Implications for membrane-membrane interactions and membrane fusion. Biophys J. 1986 Jun;49(6):1171–1183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83745-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate M. W., Gruner S. M. Lipid polymorphism of mixtures of dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine and saturated and monounsaturated phosphatidylcholines of various chain lengths. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):231–236. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate M. W., Gruner S. M. Temperature dependence of the structural dimensions of the inverted hexagonal (HII) phase of phosphatidylethanolamine-containing membranes. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4245–4253. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


