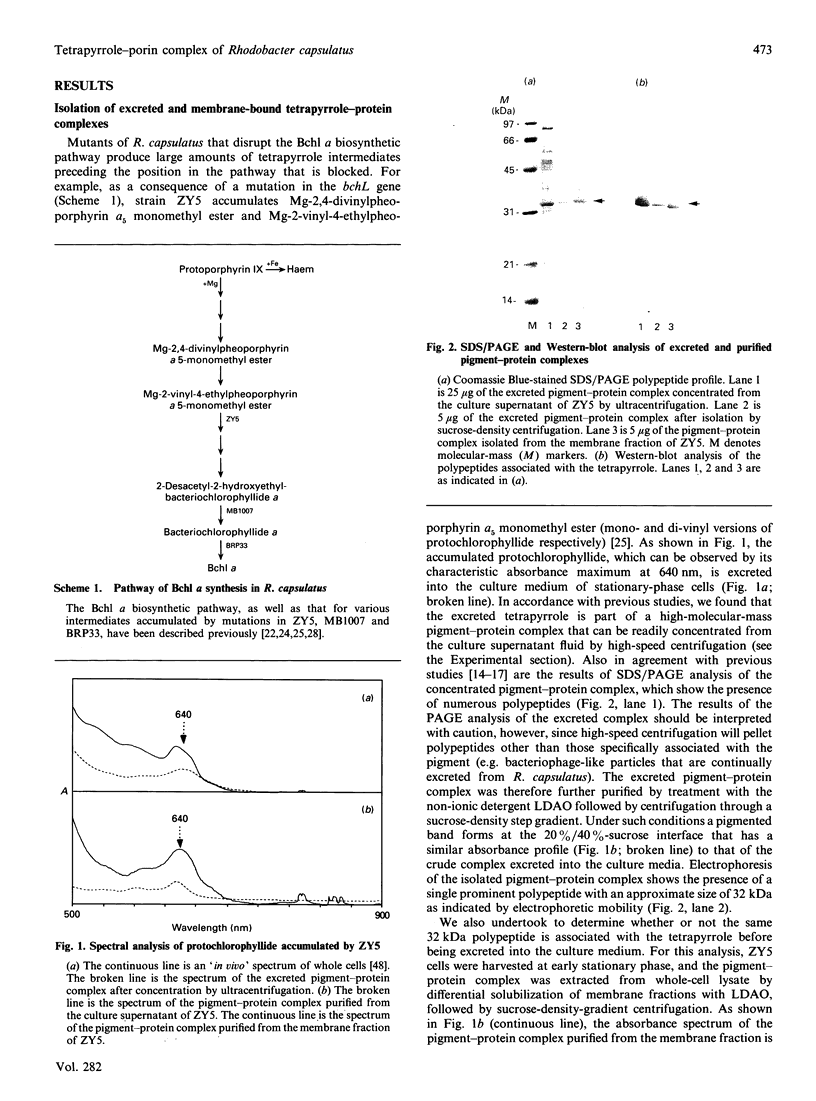
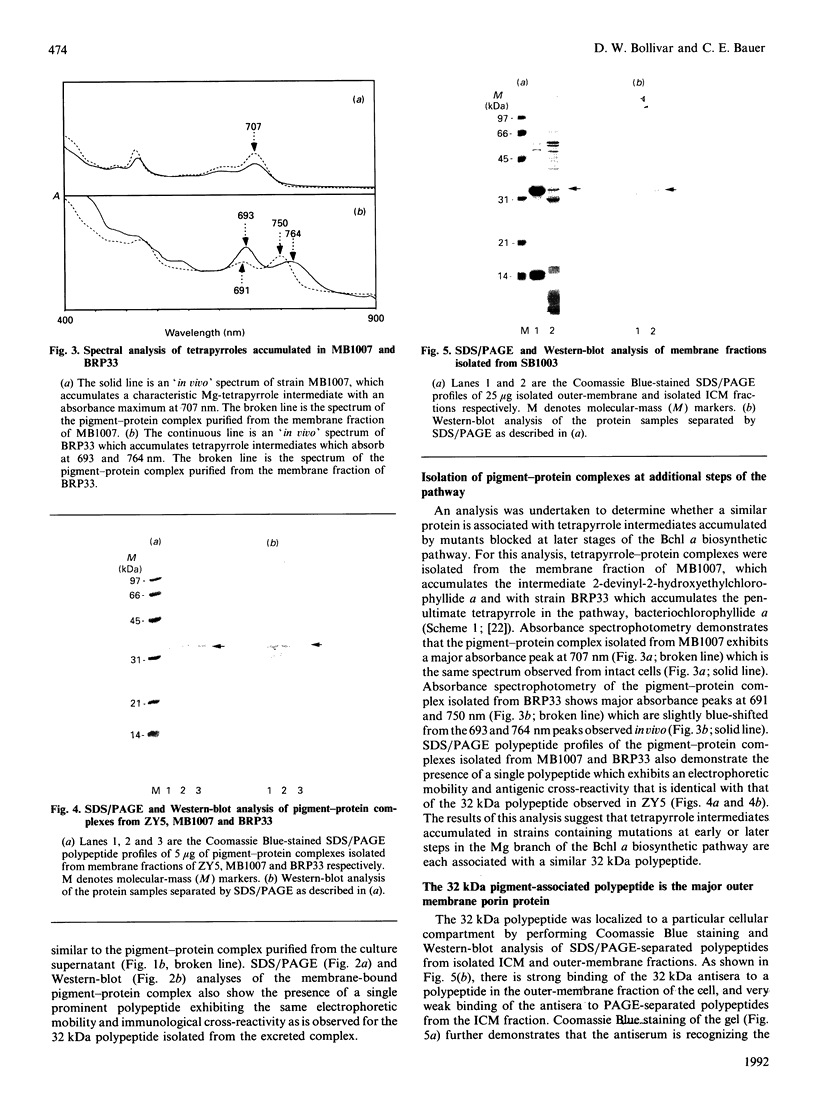
Abstract
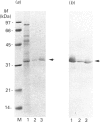
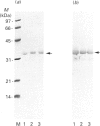
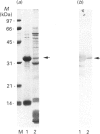
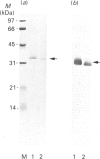
Rhodobacter capsulatus regulates synthesis of bacteriochlorophyll a in response to changes in oxygen partial pressure and light intensity. One early model proposed that this regulation involved a carrier polypeptide that functions to tether tetrapyrrole intermediates to the membrane. In the present study we isolated tetrapyrrole intermediates accumulated in three strains of R. capsulatus that contain mutations which block bacteriochlorophyll a biosynthesis at different steps of the magnesium branch of the pathway. Each of the tetrapyrrole intermediates was shown to be associated with the same 32 kDa polypeptide, as indicated by similar electrophoretic mobility and antigenic cross-reactivity with polyclonal antisera. The 32 kDa pigment-associated protein was further found to have an electrophoretic mobility, antigenic cross-reactivity and N-terminal sequence identical with those of the previously characterized major outer-membrane porin protein of R. capsulatus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer C. E., Marrs B. L. Rhodobacter capsulatus puf operon encodes a regulatory protein (PufQ) for bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7074–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel A. J. Characterization of a coproporphyrin-protein complex from Rhodobacter capsulatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jun 1;65(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90468-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel A. J., Marrs B. L. Transcriptional regulation of several genes for bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata in response to oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.686-694.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. G., Davidson E., Marrs B. L. Variation of levels of mRNA coding for antenna and reaction center polypeptides in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata in response to changes in oxygen concentration. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):945–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.945-948.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flammann H. T., Weckesser J. Characterization of the cell wall and outer membrane of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.191-198.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flammann H. T., Weckesser J. Porin isolated from the cell envelope of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):410–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.410-412.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., NEUBERGER A., TAIT G. H. Studies on the biosynthesis of porphyrin and bacteriochlorophyll by Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. 2. The effects of ethionine and threonine. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:550–559. doi: 10.1042/bj0830550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING T. E. RECONSTITUTION OF RESPIRATORY CHAIN ENZYME SYSTEMS. XI. USE OF ARTIFICIAL ELECTRON ACCEPTORS IN THE ASSAY OF SUCCINATE-DEHYDROGENATING ENZYMES. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:4032–4036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. Adaptation to form bacteriochlorophyll in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: changes in activity of enzymes concerned in pyrrole synthesis. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:508–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0720508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. The synthesis of enzymes concerned in bacteriochlorophyll formation in growing cultures of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:487–498. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. C., Hurlbert R. E. Characterization of the cell wall and cell wall proteins of Chromatium vinosum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1386–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1386-1398.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J., Altshuler T. Some properties of mutant strains of Rhodopseudomoas spheroides which do not form bacteriochlorophyll. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):204–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00406333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J. The accumulation of bacteriochlorophyll precursors by mutant and wild-type strains of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):175–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1000175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Nikaido H. Specificity of diffusion channels produced by lambda phage receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs B. Mobilization of the genes for photosynthesis from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata by a promiscuous plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1003–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1003-1012.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel U., Wacker T., Woitzik D., Weckesser J., Kreutz W., Welte W. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J., Drews G. Dei Ausscheidung von partikelgebundenen Bacteriochlorophyllvorstufen durch die Mutante F9 von Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;73(1):19–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel J., Clement-Metral J. D. A 4-vinylprotochlorophyllide complex accumulated by "phofil" mutant of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. An authentic intermediate in the development of the photosynthetic apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 14;430(2):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudek M. R., Richards W. R. A possible alternate pathway of bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis in a mutant of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3132–3137. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. R., Lascelles J. The biosynthesis of bacteriochlorophyll. The characterization of latter stage intermediates from mutants of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3473–3482. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. R., Wallace R. B., Tsao M. S., Ho E. The nature of a pgiment-protein complex excreted from mutants of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 30;14(26):5554–5561. doi: 10.1021/bi00697a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. Observations on the relationship between the formation of photopigments and the synthesis of protein in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;28:599–605. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-4-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick J., Drews G. The morphogenesis of the bacterial photosynthetic apparatus. 3. The features of a pheophytin-protein-carbohydrate complex excreted by the mutant M 46 of Rodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 3;183(1):215–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sojka G. A., Freeze H. H., Gest H. Quantitative estimation of bacteriochlorophyll in situ. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Feb;136(2):578–580. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. P., Cohen S. N., Clark W. G., Marrs B. L. Alignment of genetic and restriction maps of the photosynthesis region of the Rhodopseudomonas capsulata chromosome by a conjugation-mediated marker rescue technique. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):580–590. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.580-590.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver P. F., Wall J. D., Gest H. Characterization of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Nov 7;105(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00447139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Porin from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):199–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.199-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woitzik D., Weckesser J., Benz R., Stevanovic S., Jung G., Rosenbusch J. P. Porin of Rhodobacter capsulatus: biochemical and functional characterization. Z Naturforsch C. 1990 Jun;45(6):576–582. doi: 10.1515/znc-1990-0602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. M., Bauer C. E. Rhodobacter capsulatus genes involved in early steps of the bacteriochlorophyll biosynthetic pathway. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5001–5010. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5001-5010.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen H. C., Marrs B. Map of genes for carotenoid and bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):619–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.619-629.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Bauer C. E., Williams J. C., Marrs B. L. Genetic evidence for superoperonal organization of genes for photosynthetic pigments and pigment-binding proteins in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00330558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. S., Cook D. N., Leach F., Armstrong G. A., Alberti M., Hearst J. E. Oxygen-regulated mRNAs for light-harvesting and reaction center complexes and for bacteriochlorophyll and carotenoid biosynthesis in Rhodobacter capsulatus during the shift from anaerobic to aerobic growth. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1180–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1180-1188.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. S., Hearst J. E. Regulation of expression of genes for light-harvesting antenna proteins LH-I and LH-II; reaction center polypeptides RC-L, RC-M, and RC-H; and enzymes of bacteriochlorophyll and carotenoid biosynthesis in Rhodobacter capsulatus by light and oxygen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7613–7617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]