Abstract
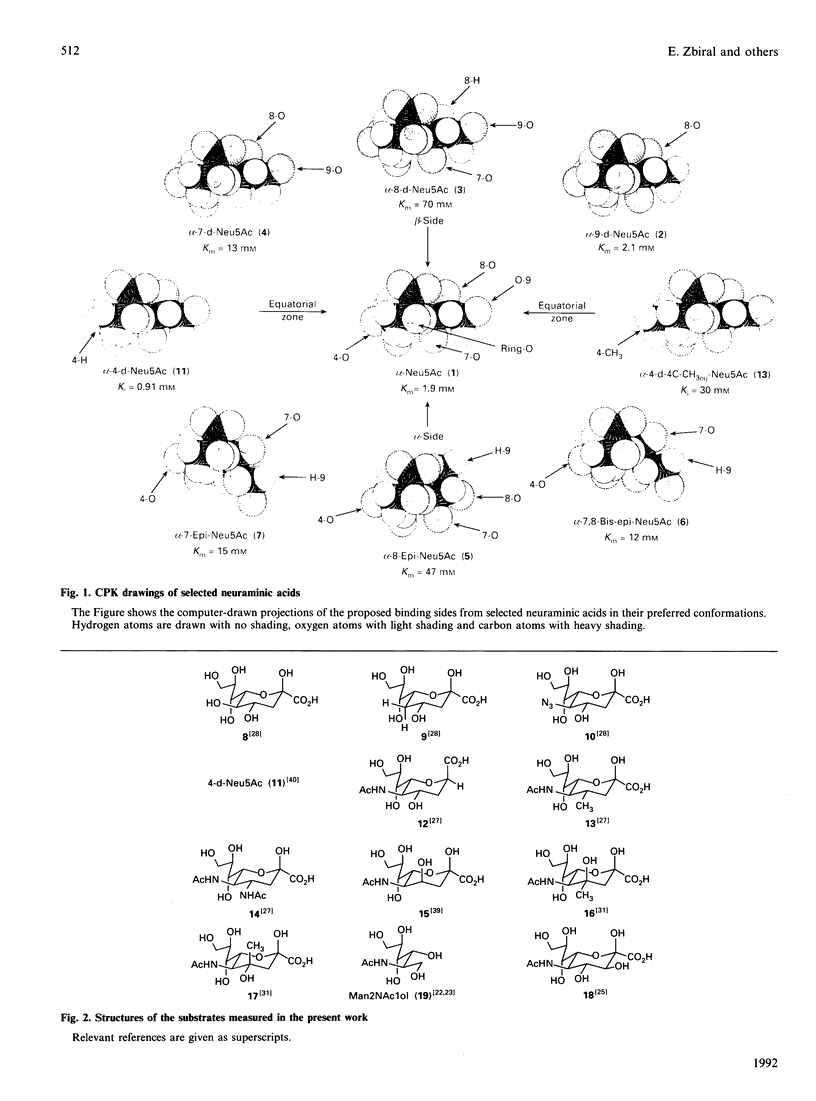
A series of neuraminic acid derivatives modified in the side chain or at C-3, C-4 or C-5 were tested as substrates of inhibitors of N-acetylneuraminate lyase (EC 4.1.3.3) from Clostridium perfringens. The results, together with Km and Ki values reported previously, indicate that the region most important for the binding of sialic acids is an equatorial zone reaching from C-8 via the ring oxygen atom to C-4 of the sugar molecule, whereas the substituents at C-9 and C-5 may be varied to a higher extent without significantly disturbing enzyme action. It is shown that stereo-electronic factors are responsible for the immediate heterolytic fragmentation of the cyclic sialic acid into pyruvic acid and 2-acetamidomannose or a related C-6 sugar.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann W., Freidenreich J., Weisshaar G., Brossmer R., Friebolin H. Spaltung und Synthese von Sialinsäuren mit Aldolase. 1H-NMR-Untersuchungen zur Stereochemie, zur Kinetik und zum Mechanismus. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Feb;370(2):141–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beau J. M., Schauer R. Metabolism of 4-O-methyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid a synthetic sialic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brossmer R., Rose U., Kaspar D., Smith T. L., Grasmuk H., Unger F. M. Enzymic synthesis of 5-acetamido-9-azido-3,5,9-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-2-nonulosonic acid, a 9-azido-9-deoxy derivative of N-acetylneuraminic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1282–1289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G., ROSEMAN S. The sialic acids. I. The structure and enzymatic synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2529–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian R., Schreiner E., Zbiral E., Schulz G. The side-chain conformations of N-acetyl-7-,8-,9-deoxy-, and -4,7-dideoxy-neuraminic acid and their effect on the activation of CTP:N-acylneuraminic acid cytidylyltransferase. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Dec 1;194:49–61. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)85005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian R., Schulz G., Brandstetter H. H., Zbiral E. On the side-chain conformation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and its epimers at C-7, C-8, and C-7,8. Carbohydr Res. 1987 Apr 15;162(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(87)80195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deijl C. M., Vliegenthart J. F. Configuration of substrate and products of N-acetylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase from Clostridium perfringens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):668–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90358-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faillard H., Ferreira do Amaral C., Blohm M. Untersuchungen zur enzymatischen Spezifität der Neuraminidase und N-Acyl-neuraminat-Lyase in bezug auf die N-Substitution. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Jul;350(7):798–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANTT R., MILLNER S., BINKLEY S. B. INHIBITION OF N-ACETYLNEURAMINIC ACID ALDOLASE BY 3-FLUOROSIALIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1952–1960. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H. J., Brossmer R. Inhibition of N-acetylneuraminate lyase by N-acetyl-4-oxo-D-neuraminic acid. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):145–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80404-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadano D., Iwasaki M., Endo S., Kitajima K., Inoue S., Inoue Y. A naturally occurring deaminated neuraminic acid, 3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nonulosonic acid (KDN). Its unique occurrence at the nonreducing ends of oligosialyl chains in polysialoglycoprotein of rainbow trout eggs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11550–11557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nees S., Schauer R., Mayer F. Purification and characterization of N-acetylneuraminate lyase from Clostridium perfringens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jun;357(6):839–853. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R. Chemistry, metabolism, and biological functions of sialic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1982;40:131–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R., Wember M., Wirtz-Peitz F., Ferreira do Amaral C. Studies on the substrate specificity of acylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Aug;352(8):1073–1080. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner E., Zbiral E., Kleineidam R. G., Schauer R. 2,3-Didehydro-2-deoxysialic acids structurally varied at C-5 and their behaviour towards the sialidase from Vibrio cholerae. Carbohydr Res. 1991 Sep 2;216:61–66. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(92)84150-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla A. K., Schauer R. Analysis of sialidase and N-acetylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase substrate specificity by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90604-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttajit M., Urban C., McLean R. L. N-acetylneuraminic acid analogues. II. The action of N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase on 8-carbon and 7-carbon analogues. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):810–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttajit M., Winzler R. J. Effect of modification of N-acetylneuraminic acid on the binding of glycoproteins to influenza virus and on susceptibility to cleavage by neuraminidase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3398–3404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



