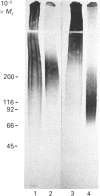
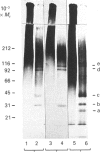
Abstract
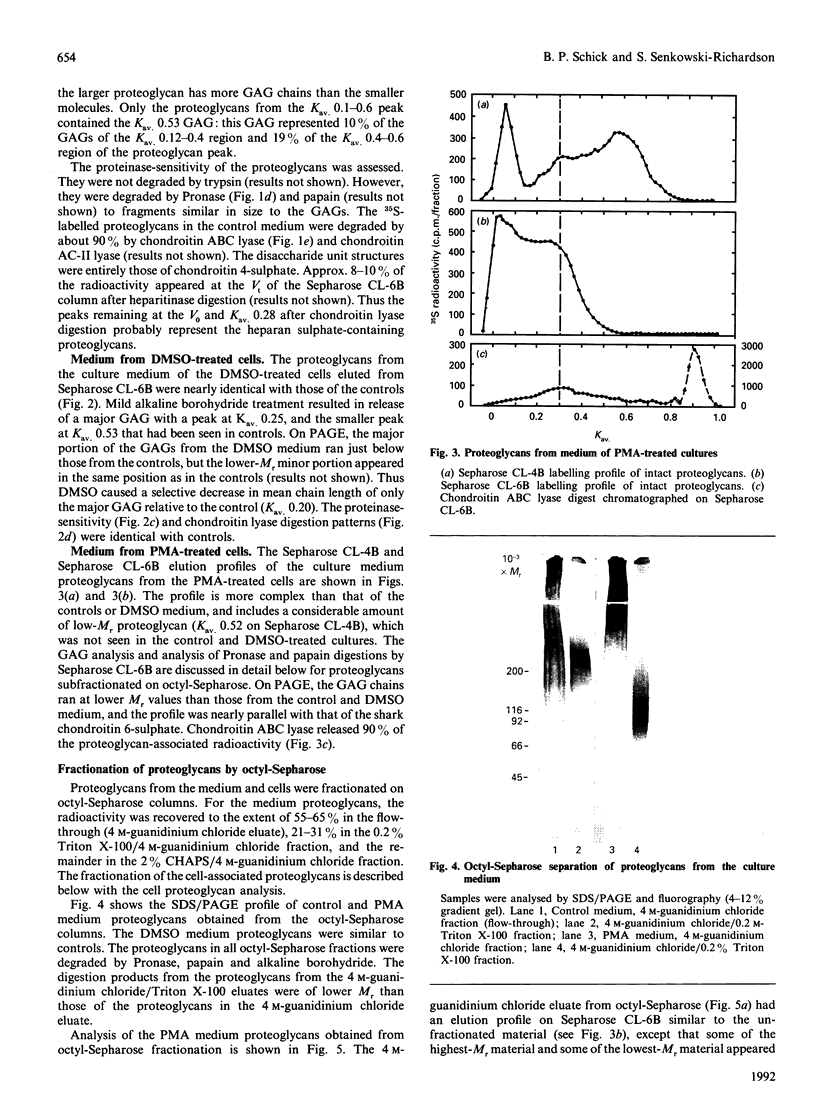
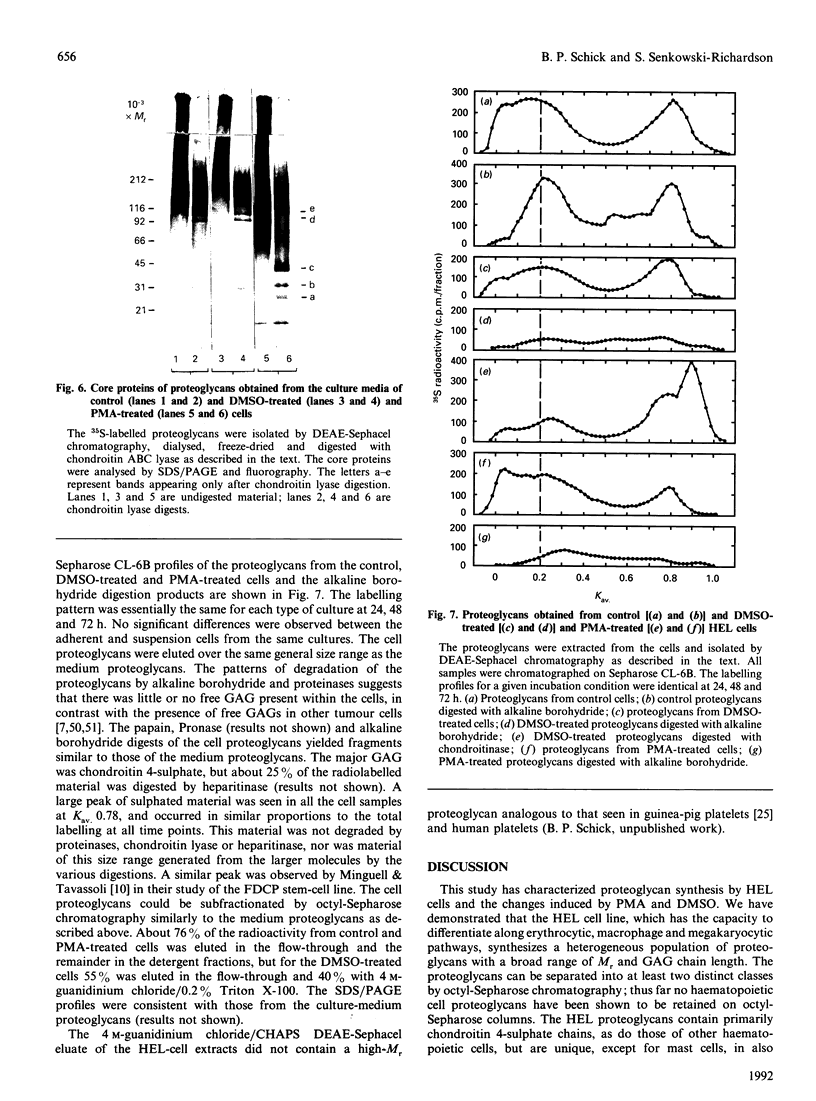
Synthesis of sulphated proteoglycans was compared in human erythroleukaemia (HEL) cells grown under control conditions and under stimulation by dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Synthesis of [35S]sulphate-labelled proteoglycans by DMSO-treated cells was decreased by about 35% relative to controls, but synthesis of proteoglycans by PMA-treated cells increased 3-4-fold. Control and DMSO-treated cells secreted 65% of the newly synthesized proteoglycans, but PMA-treated cells secreted more than 90%. Sepharose CL-6B chromatography and SDS/PAGE suggested the presence of several proteoglycans in the cells and culture medium. The PMA-treated cells synthesized a low-Mr proteoglycan (Kav. 0.3( that was not present in controls and DMSO-treated cultures. The proteoglycans of the cells and medium from control, DMSO-treated and PMA-treated cultures could be separated into three fractions by octyl-Sepharose chromatography. The proteoglycans were resistant to trypsin but were degraded by Pronase and papain to fragments similar in size to the NaOH/NaBH4-generated glycosaminoglycans. The average chain length of the glycosaminoglycans (Kav. 0.20 on Sepharose CL-6B for controls) was decreased by DMSO (Kav. 0.25) and by PMA (Kav. 0.30-0.38). Chondroitin ABC lyase digestion of the proteoglycans from the medium of the control cultures produced two core proteins at Mr 31,000 and 36,000. The DMSO medium proteoglycans had only the 31,000-Mr core protein, and the PMA culture medium proteoglycans had core proteins of Mr 27,000, 31,000 and 36,000. Changes in synthesis of proteoglycans induced by DMSO or PMA may have relevance for the maturation of haematopoietic cells.
Full text
PDF
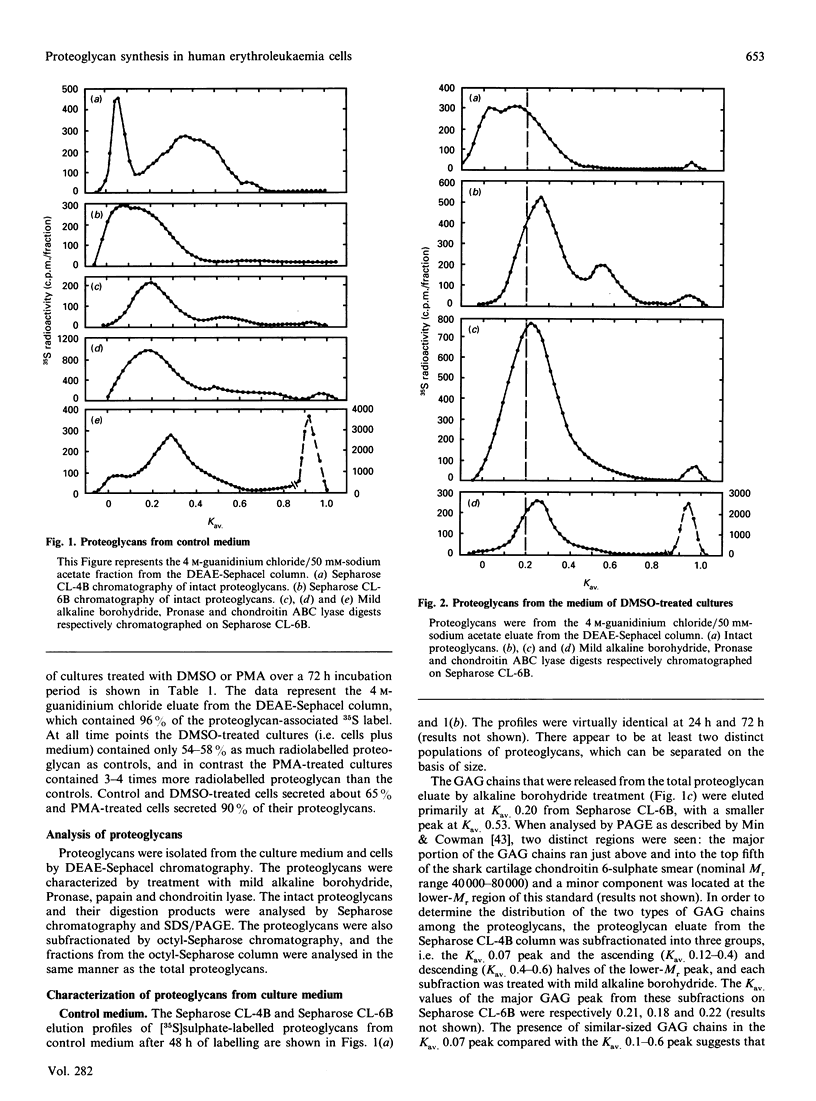



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alliel P. M., Périn J. P., Maillet P., Bonnet F., Rosa J. P., Jollès P. Complete amino acid sequence of a human platelet proteoglycan. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres J. L., Stanley K., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3137–3145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham S., Stevens R. L., Gartner M. C., Austen K. F., Lalley P. A., Weis J. H. Isolation of a cDNA that encodes the peptide core of the secretory granule proteoglycan of rat basophilic leukemia-1 cells and assessment of its homology to the human analogue. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7292–7296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham S., Stevens R. L., Nicodemus C. F., Gartner M. C., Austen K. F., Weis J. H. Molecular cloning of a cDNA that encodes the peptide core of a mouse mast cell secretory granule proteoglycan and comparison with the analogous rat and human cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartold P. M., Harkin D. G., Bignold L. P. Proteoglycans synthesized by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes in vitro. Immunol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;67(Pt 1):9–17. doi: 10.1038/icb.1989.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley S. A., Kirby S. L. Biosynthesis of proteochondroitin sulfate by HL-60 human promyelocytic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jan;45(1):46–54. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland C. E., Rosenthal K. L., Pluznik D. H., Dennert G., Hengartner H., Bienenstock J., Metcalfe D. D. Glycosaminoglycan profiles in cloned granulated lymphocytes with natural killer function and in cultured mast cells: their potential use as biochemical markers. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1937–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouakka M., Legendre P., Jouis V., Langris M., Béliard R., Loyau G., Bocquet J. Calcium ionophore and phorbol myristate acetate synergistically inhibited proteoglycan biosynthesis in articular chondrocytes by prostaglandin independent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):690–698. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Shiga M., Ruoslahti E. Identification from cDNA of the precursor form of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan core protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12534–12537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P. F., Rosa J. P., Johnston G. I., Shiu D. T., Cook R. G., Lau C., Kan Y. W., McEver R. P., Shuman M. A. Platelet glycoprotein IIb. Chromosomal localization and tissue expression. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1812–1817. doi: 10.1172/JCI113277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. M. Structures and immunochemical properties of oligosaccharides isolated from pig submaxillary mucins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):616–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. L., Baxter C. S. Decreased sulfation of cellular chondroitin sulfate in response to activators of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):909–914. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C., Wight T. N. Proteoglycans synthesized by smooth muscle cells derived from monkey (Macaca nemestrina) aorta. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5679–5688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Andres J. L., Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta receptor type III is a membrane proteoglycan. Domain structure of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16984–16991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christner J. E. Biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan by P388D1 macrophage-like cell line. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Sep-Oct;8(5):535–543. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.5.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso M., Cappelletti R., Dini G., Fibbi G., Vannucchi S., Chiarugi V., Guazzelli C. Involvement of glycosaminoglycans in detachment of early myeloid precursors from bone-marrow stromal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 17;676(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson K. G., Lindahl U. Degradation of heparin proteoglycan in cultured mouse mastocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):409–415. doi: 10.1042/bj2460409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O., Ivhed I., Overvatn A., Nilsson K. Differentiation-associated changes in the expression of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan in induced U-937 cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 1;48(21):6103–6108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O., Kjellén L., Seljelid R., Lindahl U. Changes in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis during differentiation in vitro of human monocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):661–667. doi: 10.1042/bj2100661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O. Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan in cultured human peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O. Proteoglycans in normal and neoplastic monocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Feb;168(2):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Ho P. L. Induction of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan synthesis and secretion in lymphocytes and monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):351–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Papayannopoulou T., Roth G. J. Cloning of the alpha chain of human platelet glycoprotein Ib: a transmembrane protein with homology to leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luikart S. D. Inability of HL-60 cells induced by phorbol myristate acetate to produce macrophage-associated glycosaminoglycans. Exp Hematol. 1986 Aug;14(7):672–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luikart S. D., Maniglia C. A., Sartorelli A. C. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis during differentiation of HL60/HGPRT-leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1984 Jul;44(7):2907–2912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luikart S. D., Sackrison J. L. Glycosaminoglycan metabolism of HL-60 cells during differentiation induction by tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Leuk Res. 1986;10(9):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(86)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Schmidt R. E., Caulfield J. P., Hein A., Bartley G. T., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Proteoglycans in cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Identification, localization, and exocytosis of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan from human cloned natural killer cells during target cell lysis. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1771–1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Papayannopoulou T. HEL cells: a new human erythroleukemia cell line with spontaneous and induced globin expression. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1233–1235. doi: 10.1126/science.6177045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillan D. J., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C., Bickel M. Proteoglycan biosynthesis in murine monocytic leukemic (M1) cells before and after differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13245–13251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe D. D., Bland C. E., Wasserman S. I. Biochemical and functional characterization of proteoglycans isolated from basophils of patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1943–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H., Cowman M. K. Combined alcian blue and silver staining of glycosaminoglycans in polyacrylamide gels: application to electrophoretic analysis of molecular weight distribution. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jun;155(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minguell J. J., Tavassoli M. Proteoglycan synthesis by hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1821–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Dexter T. M., Gallagher J. T. Metabolic properties of a homogeneous proteoglycan of a haemopoietic stem cell line, FDCP-mix. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):479–486. doi: 10.1042/bj2600479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL T. T., Jr, TAUSCHE F. G., GUDE W. D. Uptake of radioactive sulfate by elements of the blood and the bone marrow of rats. Am J Physiol. 1955 Mar;180(3):491–494. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.180.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S., Lindahl U. Cleavage of macromolecular heparin by an enzyme from mouse mastocytoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2690–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike Y., Kimata K., Shinomura T., Nakazawa K., Suzuki S. Structural analysis of chick-embryo cartilage proteoglycan by selective degradation with chondroitin lyases (chondroitinases) and endo-beta-D-galactosidase (keratanase). Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):193–207. doi: 10.1042/bj1910193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama M., Oguri K., Fujiwara Y., Nakanishi H., Yonekura H., Kondo T., Ui N. Purification and characterization of human platelet proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):73–81. doi: 10.1042/bj2330073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Nakamoto B., Yokochi T., Chait A., Kannagi R. Human erythroleukemia cell line (HEL) undergoes a drastic macrophage-like shift with TPA. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):832–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Raines E., Collins S., Nakamoto B., Tweeddale M., Ross R. Constitutive and inducible secretion of platelet-derived growth factor analogs by human leukemic cell lines coexpressing erythroid and megakaryocytic markers. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):859–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI112895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Eisman R., Heidenreich R., Silver S. M., Vilaire G., Surrey S., Schwartz E., Bennett J. S. Structure of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb. Homology to the alpha subunits of the vitronectin and fibronectin membrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8476–8482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Surrey S., LaRocco P., Weiss M. J., Rappaport E. F., Conway T. M., Schwartz E. Cloning and characterization of platelet factor 4 cDNA derived from a human erythroleukemic cell line. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):219–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Maillet P., Jollès P. Characterization and N-terminal sequence of human platelet proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):1007–1013. doi: 10.1042/bj2551007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Endo E., Koda J., Bernfield M. The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11046–11052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Stevens R. L., Akiyama F., Schmid K., Austen K. F. Culture from mouse bone marrow of a subclass of mast cells possessing a distinct chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with glycosaminoglycans rich in N-acetylgalactosamine-4,6-disulfate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7229–7236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. C., Choi H. U., Tang L. H., Johnson T. L., Pal S., Webber C., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Isolation of dermatan sulfate proteoglycans from mature bovine articular cartilages. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6304–6313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg M. E., Caulfield J. P., Austen K. F., Hein A., Edmiston K., Newburger P. E., Stevens R. L. Biochemical and morphological characterization of basophilic leukocytes from two patients with myelogenous leukemia. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2616–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Yamagata T., Suzuki S. Enzymatic methods for the determination of small quantities of isomeric chondroitin sulfates. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1536–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Cullen S. E., Giacoletto K. S., Schwartz B. D. Invariant chain is the core protein of the Ia-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1916–1934. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick B. P., Walsh C. J., Jenkins-West T. Sulfated proteoglycans and sulfated proteins in guinea pig megakaryocytes and platelets in vivo. Relevance to megakaryocyte maturation and platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1052–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick P. K., Schick B. P., Williams-Gartner K. Characterization of guinea pig megakaryocyte subpopulations at different phases of maturation prepared with a Celsep separation system. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1801–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., MacDermott R. P., Bartley G., Bertovich M., Amato D. A., Austen K. F., Schlossman S. F., Stevens R. L., Ritz J. Specific release of proteoglycans from human natural killer cells during target lysis. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):289–291. doi: 10.1038/318289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R., Seyedin S. M. The high molecular weight receptor to transforming growth factor-beta contains glycosaminoglycan chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8366–8370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin D. C., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Purification and characterization of protease-resistant secretory granule proteoglycans containing chondroitin sulfate di-B and heparin-like glycosaminoglycans from rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11131–11139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Avraham S., Gartner M. C., Bruns G. A., Austen K. F., Weis J. H. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA that encodes the peptide core of the secretory granule proteoglycan of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7287–7291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Otsu K., Austen K. F. Purification and analysis of the core protein of the protease-resistant intracellular chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan from the interleukin 3-dependent mouse mast cell. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14194–14200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Otsu K., Weis J. H., Tantravahi R. V., Austen K. F., Henkart P. A., Galli M. C., Reynolds C. W. Co-sedimentation of chondroitin sulfate A glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans with the cytolytic secretory granules of rat large granular lymphocyte (LGL) tumor cells, and identification of a mRNA in normal and transformed LGL that encodes proteoglycans. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):863–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabilio A., Rosa J. P., Testa U., Kieffer N., Nurden A. T., Del Canizo M. C., Breton-Gorius J., Vainchenker W. Expression of platelet membrane glycoproteins and alpha-granule proteins by a human erythroleukemia cell line (HEL). EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):453–459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeo E., Furie B. C., Furie B. PADGEM protein in human erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimrin A. B., Eisman R., Vilaire G., Schwartz E., Bennett J. S., Poncz M. Structure of platelet glycoprotein IIIa. A common subunit for two different membrane receptors. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1470–1475. doi: 10.1172/JCI113478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]