Abstract
Two monomeric dihydrodiol dehydrogenases with pI values of 5.4 and 7.6 were co-purified with androsterone dehydrogenase activity to homogeneity from human liver. The two enzymes differed from each other on peptide mapping and in their heat-stabilities; with respect to the latter the dihydrodiol dehydrogenase and 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities of the respective enzymes were similarly inactivated. The pI 5.4 enzyme was equally active towards trans- and cis-benzene dihydrodiols, and towards (S)- and (R)-forms of indan-1-ol and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphth-1-ol and oxidized the 3 alpha-hydroxy group of C19-, C21- and C24-steroids, whereas the pI 7.6 enzyme showed high specificity for trans-benzene dihydrodiol, (S)-forms of the alicyclic alcohols and C19- and C21-steroids. Although the two enzymes reduced various xenobiotic carbonyl compounds and the 3-oxo group of C19- and C21-steroids, and were A-specific in the hydrogen transfer from NADPH, only the pI 5.4 enzyme showed reductase activity towards 7 alpha-hydroxy-5 beta-cholestan-3-one and dehydrolithocholic acid. The affinity of the two enzymes for the steroidal substrates was higher than that for the xenobiotic substrates. The two enzymes also showed different susceptibilities to the inhibition by anti-inflammatory drugs and bile acids. Whereas the pI-5.4 enzyme was highly sensitive to anti-inflammatory steroids, showing mixed-type inhibitions with respect to indan-1-ol and androsterone, the pI 7.6 enzyme was inhibited more potently by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bile acids than by the steroidal drugs, and the inhibitions were all competitive. These structural and functional differences suggest that the two enzymes are 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoenzymes.
Full text
PDF
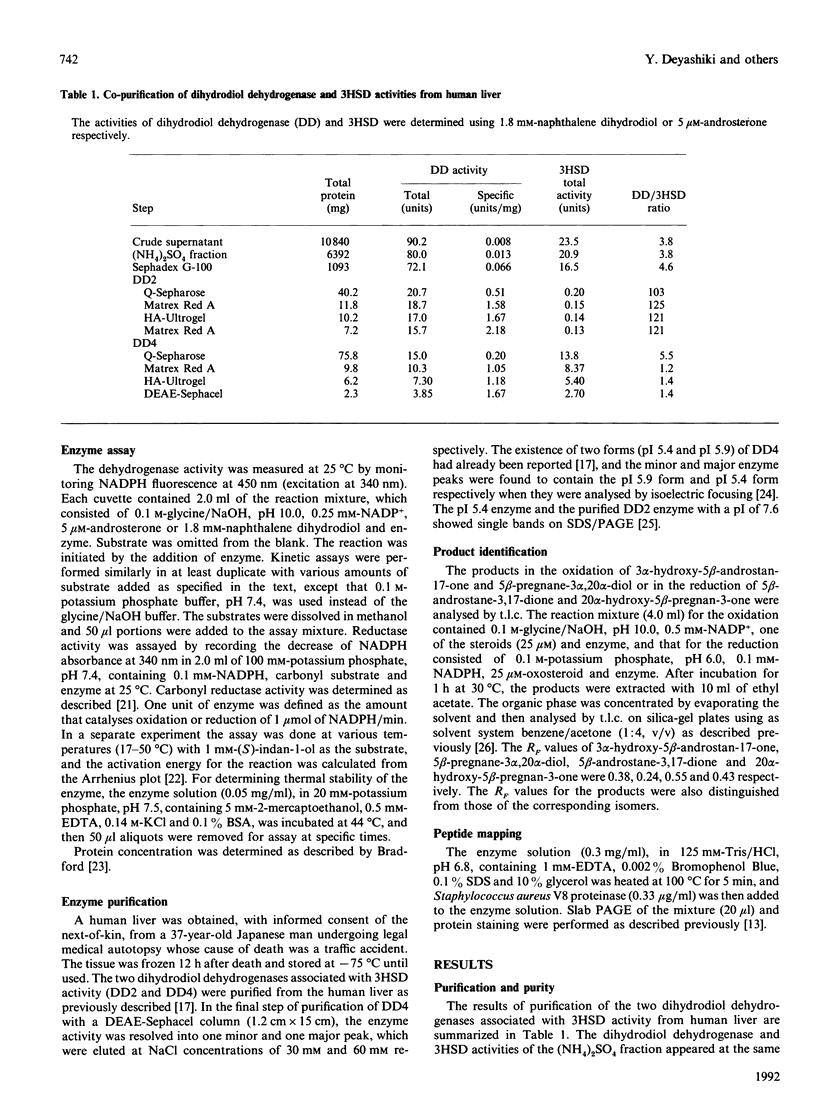
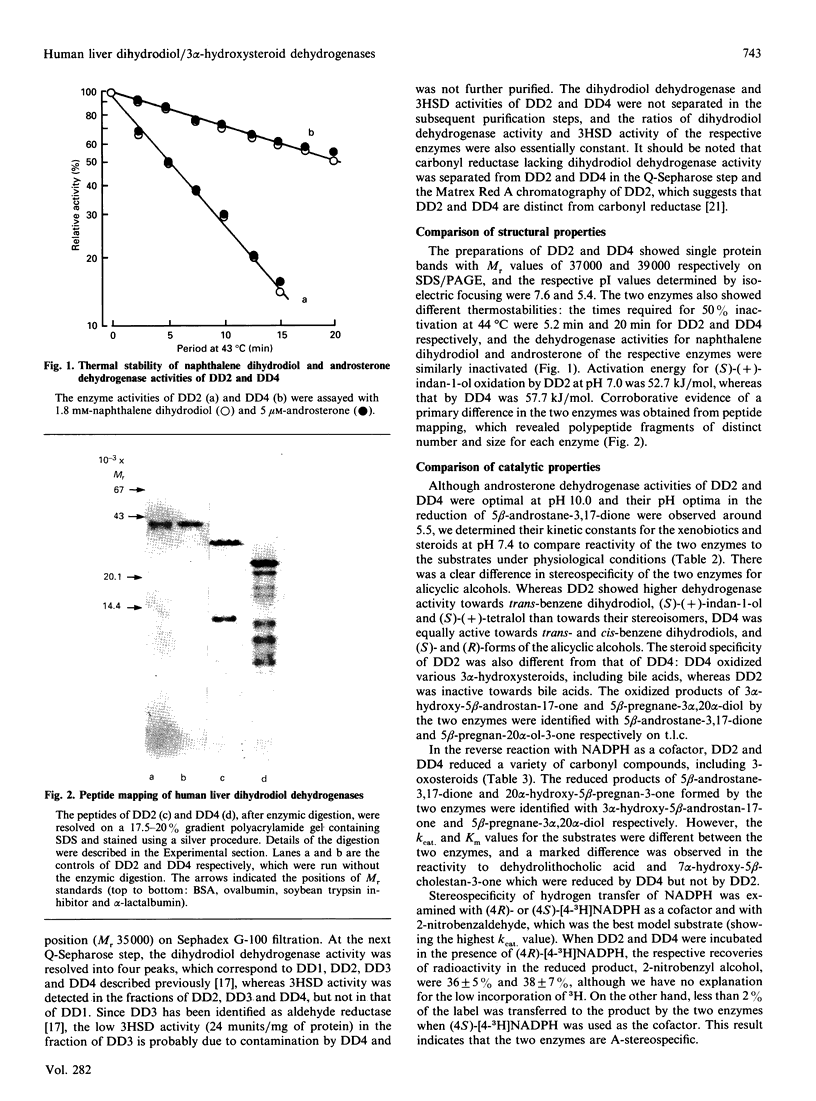
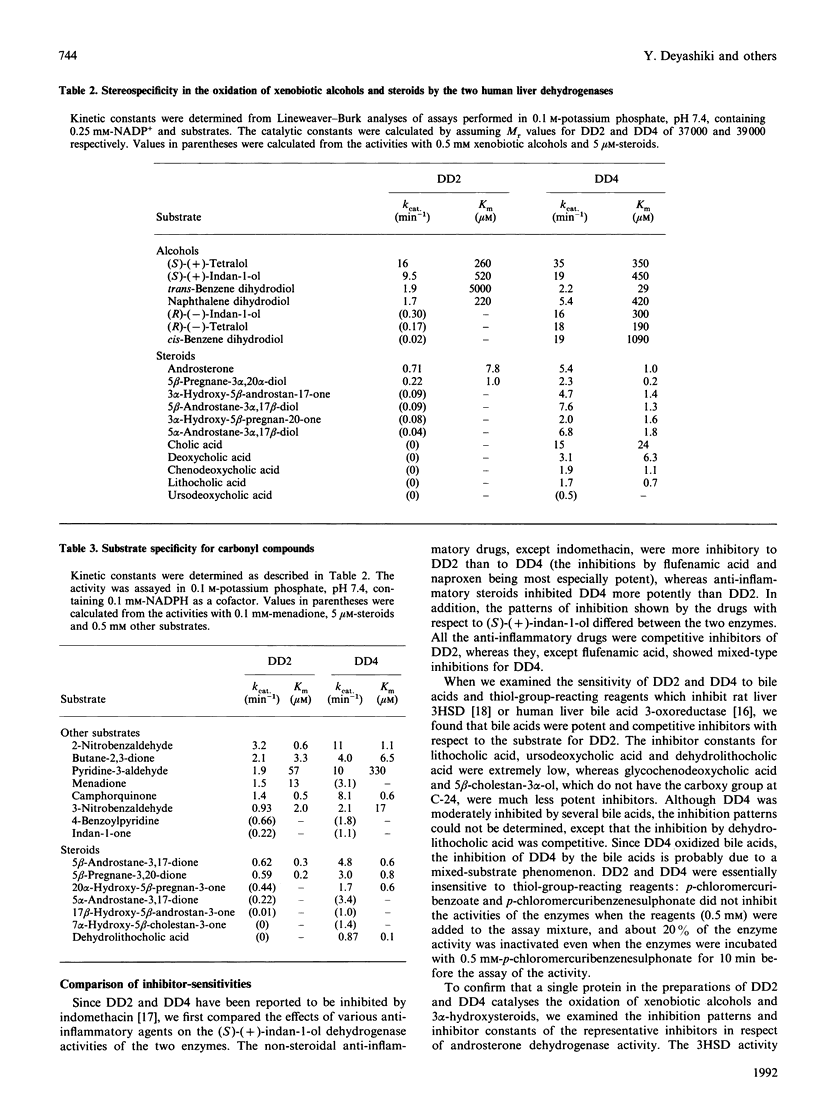

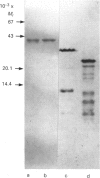
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Deyashiki Y., Nakagawa M., Nakayama T., Sawada H. Isolation of proteins with carbonyl reductase activity and prostaglandin-9-ketoreductase activity from chicken kidney. J Biochem. 1982 Dec;92(6):1753–1762. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Inoue Y., Nakagawa M., Naganeo F., Sawada H. Purification and characterization of NADP+-dependent 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from mouse liver cytosol. J Biochem. 1988 Jun;103(6):1027–1034. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Kariya K., Nakamura M., Nakayama T., Sawada H. Isolation of multiple forms of indanol dehydrogenase associated with 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity from male rabbit liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Aug 15;249(1):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Nakagawa M., Taniguchi H., Sawada H. 3(20)alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity of monkey liver indanol dehydrogenase. J Biochem. 1989 Nov;106(5):900–903. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara A., Taniguchi H., Nakayama T., Sawada H. Purification and properties of multiple forms of dihydrodiol dehydrogenase from human liver. J Biochem. 1990 Aug;108(2):250–254. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Hattori H., Ikeda N., Hayakawa S., Ohmori S. Purification and characterization of the multiple forms of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in rat liver cytosol. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Mar;365(3):377–391. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Hattori H., Ohmori S. Properties of NADPH-dependent carbonyl reductases in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 15;33(24):3957–3961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Hayakawa S., Ezaki M., Ohmori S. An NADP-dependent 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of rat liver active against C19, C20, C23, C24, C25 and C26 steroids. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 May;362(5):511–520. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.1.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo K., Amuro Y., Hada T., Higashino K. Purification and properties of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase as a 3-keto bile acid reductase from human liver cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 28;1046(1):12–18. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90088-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa M., Harada T., Hara A., Nakayama T., Sawada H. Purification and properties of multiple forms of dihydrodiol dehydrogenase from monkey liver. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1989 Oct;37(10):2852–2854. doi: 10.1248/cpb.37.2852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Hara A., Yashiro K., Sawada H. Reductases for carbonyl compounds in human liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 1;34(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmura M., Hara A., Nakagawa M., Sawada H. Demonstration of 3 alpha(17 beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase distinct from 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in hamster liver. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):583–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Mukharji I., Barrows S., Talalay P. Purification and properties of a 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of rat liver cytosol and its inhibition by anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):601–611. doi: 10.1042/bj2220601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Sharp R. B. Characterization of dihydrodiol dehydrogenase in human liver and lung. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jul;11(7):1203–1208. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.7.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning T. M., Smithgall T. E., Askonas L. J., Sharp R. B. Rat liver 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Steroids. 1986 Apr-May;47(4-5):221–247. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(86)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Hara A., Nakagawa M., Tsukada F., Ohmura M., Matsuura K. Separation and properties of multiple forms of dihydrodiol dehydrogenase from hamster liver. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(4):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithgall T. E., Penning T. M. Electrophoretic and immunochemical characterization of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenases of rat tissues. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):715–721. doi: 10.1042/bj2540715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz A., Takikawa H., Sugiyama Y., Kuhlenkamp J., Kaplowitz N. 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity of the Y' bile acid binders in rat liver cytosol. Identification, kinetics, and physiologic significance. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):427–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI112829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa H., Stolz A., Kuroki S., Kaplowitz N. Oxidation and reduction of bile acid precursors by rat hepatic 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and inhibition by bile acids and indomethacin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 2;1043(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90289-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa H., Stolz A., Sugiyama Y., Yoshida H., Yamanaka M., Kaplowitz N. Relationship between the newly identified bile acid binder and bile acid oxidoreductases in human liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2132–2136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui E., Okuda K. Identification of 7 alpha,12 alpha-dihydroxy-5 beta-cholestan-3-one 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 11;877(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K., Bentley P., Platt K. L., Oesch F. Rat liver cytoplasmic dihydrodiol dehydrogenase. Purification to apparent homogeneity and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9621–9625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wörner W., Oesch F. Identity of dihydrodiol dehydrogenase and 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in rat but not in rabbit liver cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 21;170(2):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]