Abstract
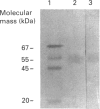
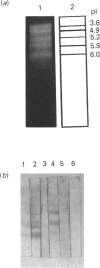
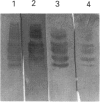
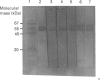
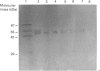
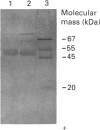
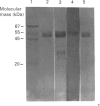
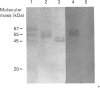
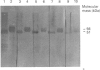
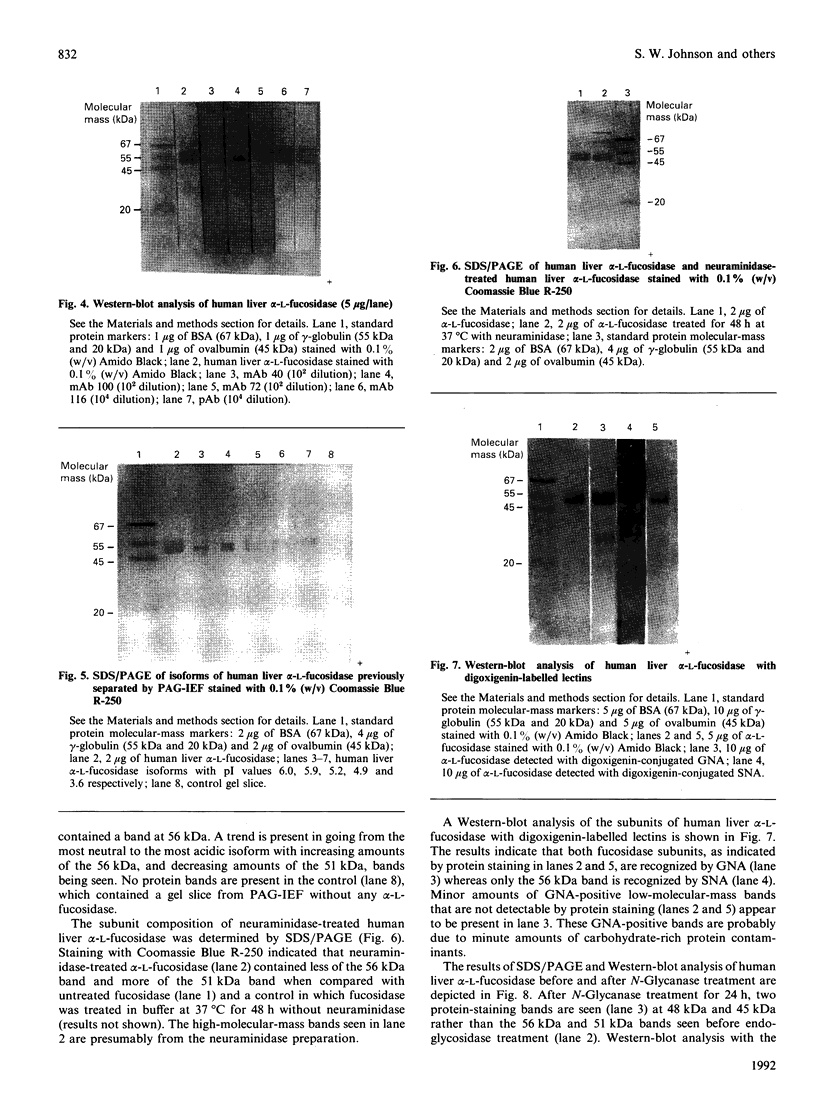
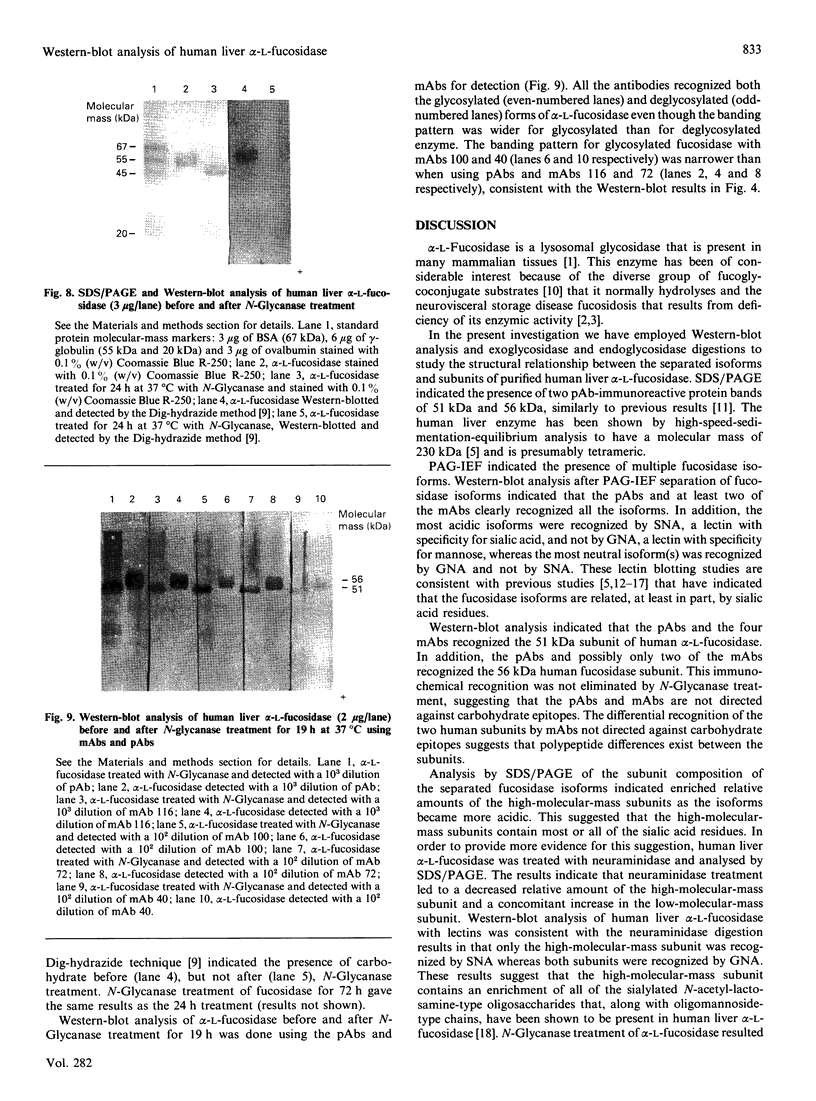
Western-blot analysis [with lectins, polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) and four monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)] was employed to investigate the structural relationship between the separated isoforms and subunits of purified human liver alpha-L-fucosidase. SDS/PAGE and Western-blot analysis indicated the presence of two protein bands of 51 kDa and 56 kDa that were recognized by the pAbs. Polyacrylamide-gel isoelectric focusing (PAG-IEF) followed by blotting indicated that the pAbs and mAbs recognized at least five fucosidase isoforms (pI values 3.6-6.0). Lectin blotting indicated an enrichment of sialic acid residues in the more acidic isoforms. Western-blot analysis indicated that four mAbs recognized the 51 kDa subunit and at least two mAbs recognized the 56 kDa subunit. The subunit composition of the isoforms (separated by PAG-IEF) of human liver alpha-L-fucosidase was investigated by SDS/PAGE. One or two closely spaced bands were found for each isoform with a trend of increasing relative amounts of the high-molecular-mass band in the more acidic isoforms relative to the more neutral isoforms. Neuraminidase treatment of alpha-L-fucosidase resulted in a decrease in the amount of the high-molecular-mass subunit and an increase in the amount of the low-molecular-mass subunit, suggesting that these subunits are related at least in part by sialic acid residues. In addition, blotting with lectins indicated the presence of sialic acid residues only in the high-molecular-mass subunit. N-Glycanase treatment led to the disappearance of the glycosylated 56 kDa and 51 kDa protein bands and the appearance of non-glycosylated protein bands at 48 kDa and 45 kDa. The overall results indicate that (1) N-glycosylation contributes to, but does not account completely for, structural differences in the fucosidase subunits and (2) the more acidic isoforms of fucosidase contain enriched relative amounts of the sialylated high-molecular-mass subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhadeff J. A., Cimino G., Janowsky A. Isoenzymes of human liver alpha-L-fucosidase: chemical relationship, kinetic studies, and immunochemical characterization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 May 31;19(3):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00225455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alhadeff J. A., Miller A. L., Wenaas H., Vedvick T., O'Brien J. S. Human liver alpha-L-fucosidase. Purification, characterization, and immunochemical studies. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7106–7113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alhadeff J. A., Tennant L., O'Brien J. S. Isoenzyme patterns of human liver alpha-L-fucosidase during development. Dev Biol. 1975 Dec;47(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90286-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews-Smith G. L., Alhadeff J. A. Radioimmunoassay determination of decreased amounts of alpha-L-fucosidase protein in fucosidosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 15;715(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argade S. P., Hopfer R. L., Strang A. M., van Halbeek H., Alhadeff J. A. Structural studies on the carbohydrate moieties of human liver alpha-L-fucosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Oct;266(1):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Matteo G., Orfeo M. A., Romeo G. Human alpha-fucosidase. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 8;429(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher K. J., Aronson N. N., Jr Isolation and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding rat liver alpha-L-fucosidase. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):695–701. doi: 10.1042/bj2640695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flowers H. M. Chemistry and biochemistry of D- and L-fucose. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1981;39:279–345. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., de Wet J. R., O'Brien J. S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for human alpha-L-fucosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1262–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley W. J., Canfield P. J., Donnelly T. M. A suspected new canine storage disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1982;56(3):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00690639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laury-Kleintop L. D., Damjanov I., Alhadeff J. A. Antibody-affinity purification of novel alpha-L-fucosidase from mouse liver. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):589–593. doi: 10.1042/bj2450589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Occhiodoro T., Beckmann K. R., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Human alpha-L-fucosidase: complete coding sequence from cDNA clones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91739-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe R., Robinson D. Isoelectric focusing of isoenzymes of human liver alpha-L-fucosidase. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 1;54(1):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Beratis N. G., Turner V. S., Hirschhorn K. Isozymes of human alpha-L-fucosidase detectable by starch gel electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Nov 20;57(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Turner V. S., Beratis N. G., Hirschhorn K. Polymorphism of human alpha fucosidase. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Sep;27(5):651–661. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Tichy D., Damjanov A., Paulsson M., Damjanov I. Distinct antigenic characteristics of murine parietal yolk sac laminin. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]