Abstract
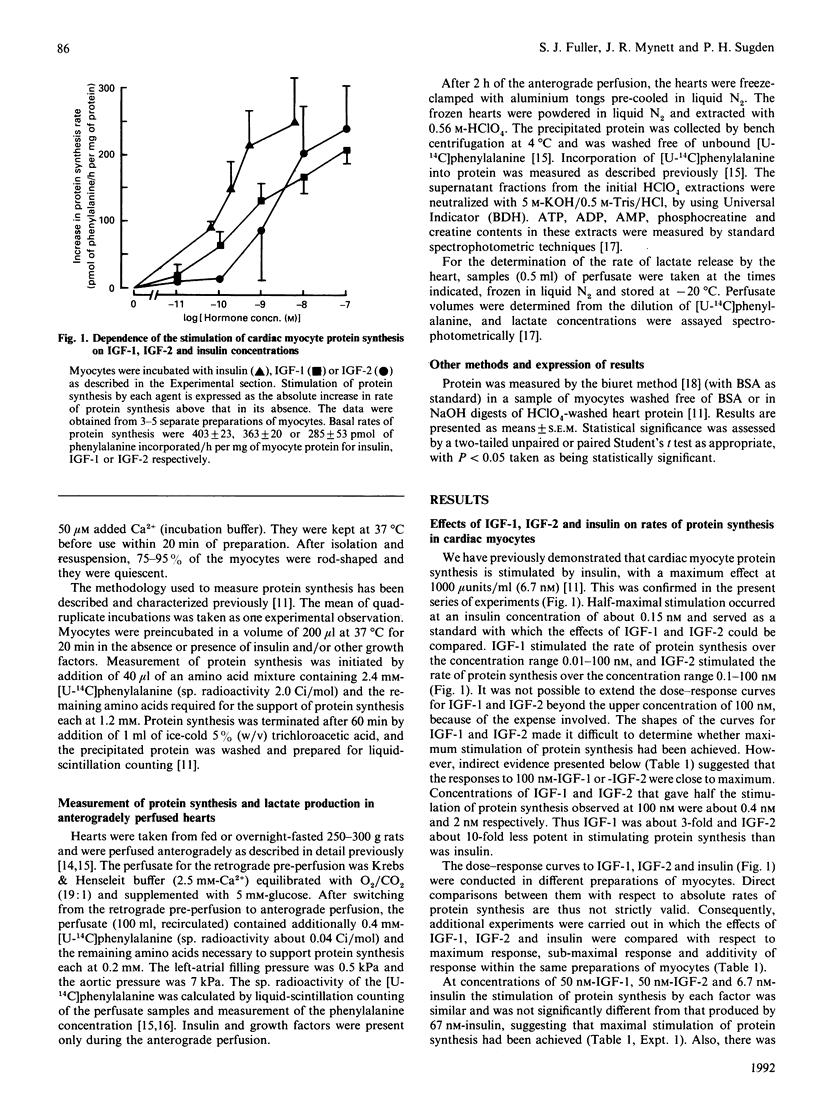
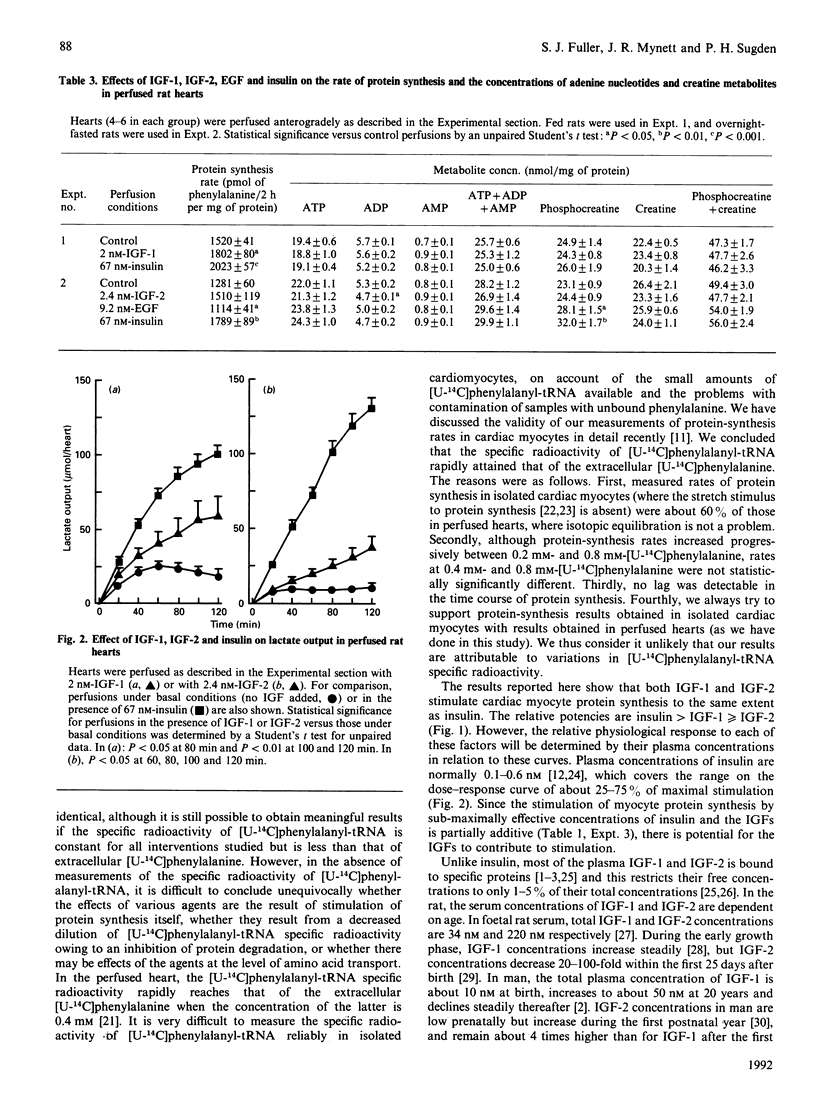
The effects of the insulin-like growth factors (IGF)-1 and -2 on the rates of protein synthesis in freshly isolated cardiac myocytes from adult rats were compared with those of insulin. At concentrations of 50-100 nM, each agent stimulated protein synthesis by about 70%. There was no additional stimulation upon combination of insulin with IGF-1 or IGF-2 at these high concentrations. When compared over a range of concentrations, the relative response to each agent was insulin greater than IGF-1 greater than or equal to IGF-2. Concentrations of 1 nM-IGF-1, 1 nM-IGF-2 or 0.2 nM-insulin enhanced the rates of protein synthesis by 36%, 30% or 34% respectively. A combination of 0.2 nM-insulin and 1 nM-IGF-1 or 1 nM-IGF-2 increased the stimulation of protein synthesis to 46%. In contrast, the effects of 1 nM-IGF-1 and 1 nM-IGF-2 were not additive. The possible mechanistic basis for this difference is discussed. At a concentration of 50 nM, epidermal growth factor (EGF), fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor were each without effect on protein synthesis. In anterogradely perfused rat heart preparations, 2 nM-IGF-1 or 2.4 nM-IGF-2 increased protein synthesis and lactate production, but 9.2 nM-EGF did not. From a consideration of the plasma free concentrations of IGF-1 and IGF-2, we suggest that these factors may contribute to the maintenance of rate of cardiac protein synthesis in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Airhart J., Arnold J. A., Stirewalt W. S., Low R. B. Insulin stimulation of protein synthesis in cultured skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):C81–C86. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.1.C81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Read L. C., Francis G. L., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Binding properties and biological potencies of insulin-like growth factors in L6 myoblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2330223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L. J., Goodman M. N., Kalish F. N., Ruderman N. B. Insulin binding and sensitivity in rat skeletal muscle: effect of starvation. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):E184–E190. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.2.E184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg G., Hall K. Immunoreactive IGF-II in serum of healthy subjects and patients with growth hormone disturbances and uraemia. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Oct;107(2):164–170. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1070164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayn K. N., Maycock P. F. Regulation of protein metabolism by a physiological concentration of insulin in mouse soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. Effects of starvation and scald injury. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):323–330. doi: 10.1042/bj1840323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. J., Gaitanaki C. J., Sugden P. H. Effects of catecholamines on protein synthesis in cardiac myocytes and perfused hearts isolated from adult rats. Stimulation of translation is mediated through the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):727–736. doi: 10.1042/bj2660727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. J., Gaitanaki C. J., Sugden P. H. Effects of increasing extracellular pH on protein synthesis and protein degradation in the perfused working rat heart. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):173–179. doi: 10.1042/bj2590173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. J., Sugden P. H. Acute inhibition of rat heart protein synthesis in vitro during beta-adrenergic stimulation or hypoxia. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):E537–E547. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.4.E537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. J., Sugden P. H. Stimulation of protein synthesis, glucose uptake and lactate output by insulin and adenosine deaminase in the rat heart. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 9;201(2):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80617-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. J., Sugden P. H. The effects of the exogenous provision of lactate and the endogenous production of lactate on protein synthesis in the heart. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):121–127. doi: 10.1042/bj2810121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J., D'Ercole A. J. Estimation of somatomedin-C levels in normals and patients with pituitary disease by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):648–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI108816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Butler J. H. Parturition-related changes in insulin-like growth factors-I and -II in the perinatal lamb. J Endocrinol. 1983 Nov;99(2):223–232. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0990223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulve E. A., Dice J. F. Regulation of protein synthesis and degradation in L8 myotubes. Effects of serum, insulin and insulin-like growth factors. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):377–387. doi: 10.1042/bj2600377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Sara V. R. Somatomedin levels in childhood, adolescence and adult life. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):91–112. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):445–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko R. A., Etlinger J. D. Inhibition of intracellular proteolysis in muscle cultures by multiplication-stimulating activity. Comparison of effects of multiplication-stimulating activity and insulin on proteolysis, protein synthesis, amino acid uptake, and sugar transport. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6292–6297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee E. E., Cheung J. Y., Rannels D. E., Morgan H. E. Measurement of the rate of protein synthesis and compartmentation of heart phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1030–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C. Effects of insulin and of NSILA-S on the perfused rat heart: glucose uptake, lactate production and efflux of 3-0-methyl glucose. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;5(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., White R. M., Knight A. B., Higa O. Z. Increased levels of multiplication-stimulating activity, an insulin-like growth factor, in fetal rat serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3649–3653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:425–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeds P. J., Hay S. M., Glennie R. T., Mackie W. S., Garlick P. J. The effect of indomethacin on the stimulation of protein synthesis by insulin in young post-absorptive rats. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):255–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2270255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin I. B., Goldstein G. An ultrasensitive isotope dilution method for the determination of L-amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):591–614. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K., Lins P. E., Fryklund L. Serum levels of immunoreactive somatomedin A in the rat: some developmental aspects. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):622–625. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Sugden P. H. Effects of pressure overload and insulin on protein turnover in the perfused rat heart. Prostaglandins are not involved although their synthesis is stimulated by insulin. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2430473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K. Immunological relationships between receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Evidence for structural heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor I receptors involving hybrids with insulin receptors. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):553–563. doi: 10.1042/bj2630553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Perkins G., Turner J., Edman J. C., Hari J., Pierce S. B., Stover C., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11486–11492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Fuller S. J. Correlations between cardiac protein synthesis rates, intracellular pH and the concentrations of creatine metabolites. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):339–346. doi: 10.1042/bj2730339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Fuller S. J. Regulation of protein turnover in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 1;273(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1042/bj2730021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Smith D. M. The effects of insulin on glucose uptake and lactate release in perfused working rat heart preparations. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2060473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xenophontos X. P., Gordon E. E., Morgan H. E. Effect of intraventricular pressure on protein synthesis in arrested rat hearts. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):C95–C98. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.1.C95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Jagars G., Sand I., Grunwald J., Froesch E. R. Inhibition of the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity on isolated rat fat cells by binding to its carrier protein. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI109377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


