Abstract
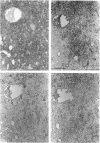
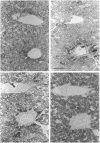
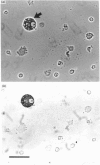
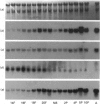
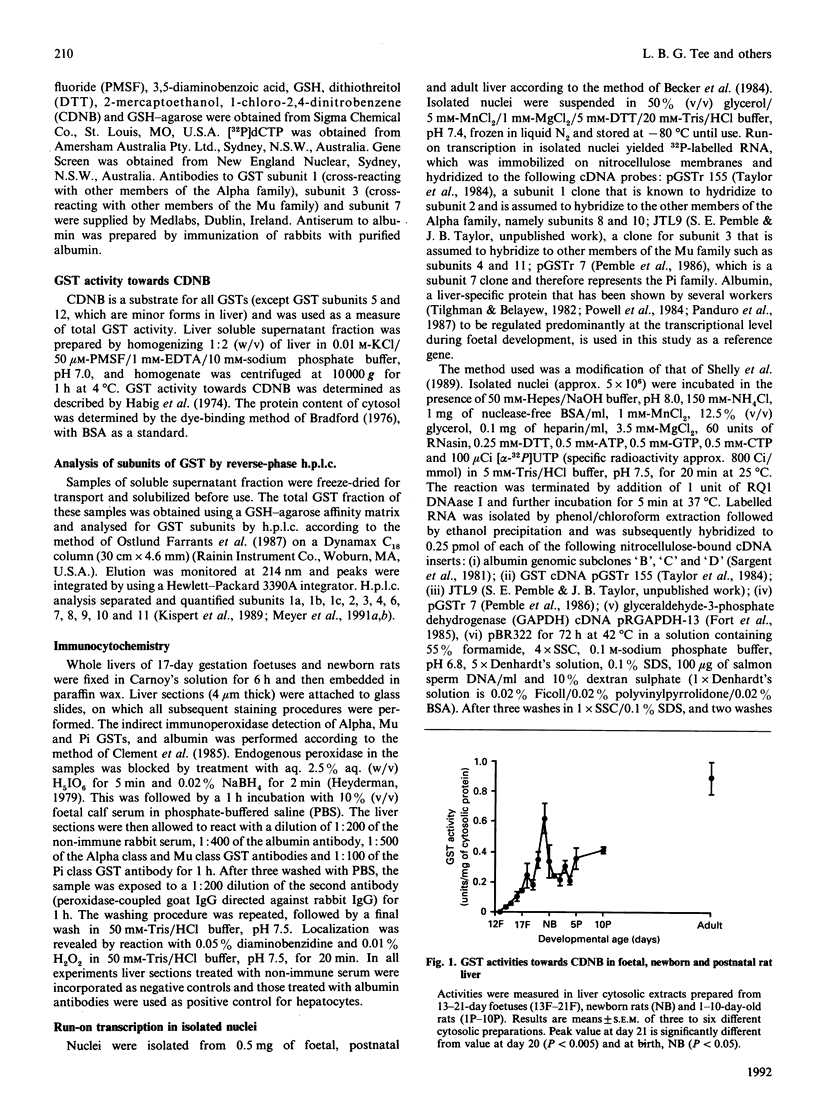
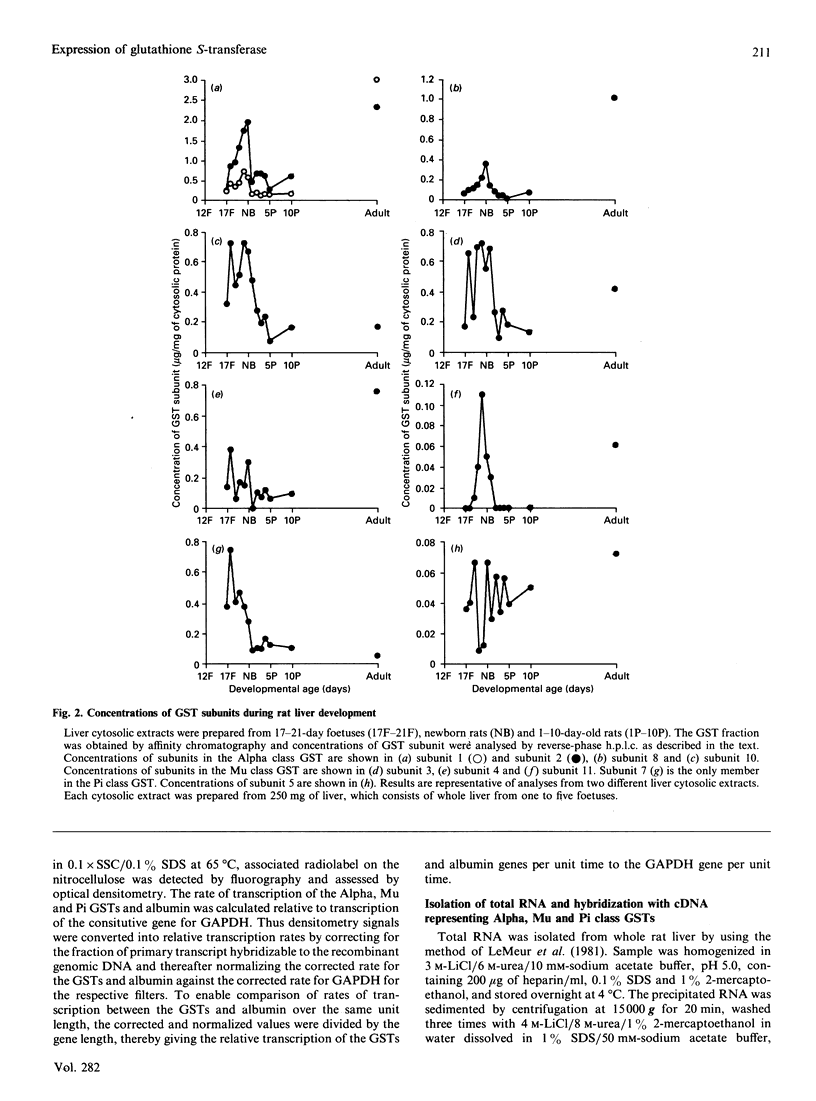
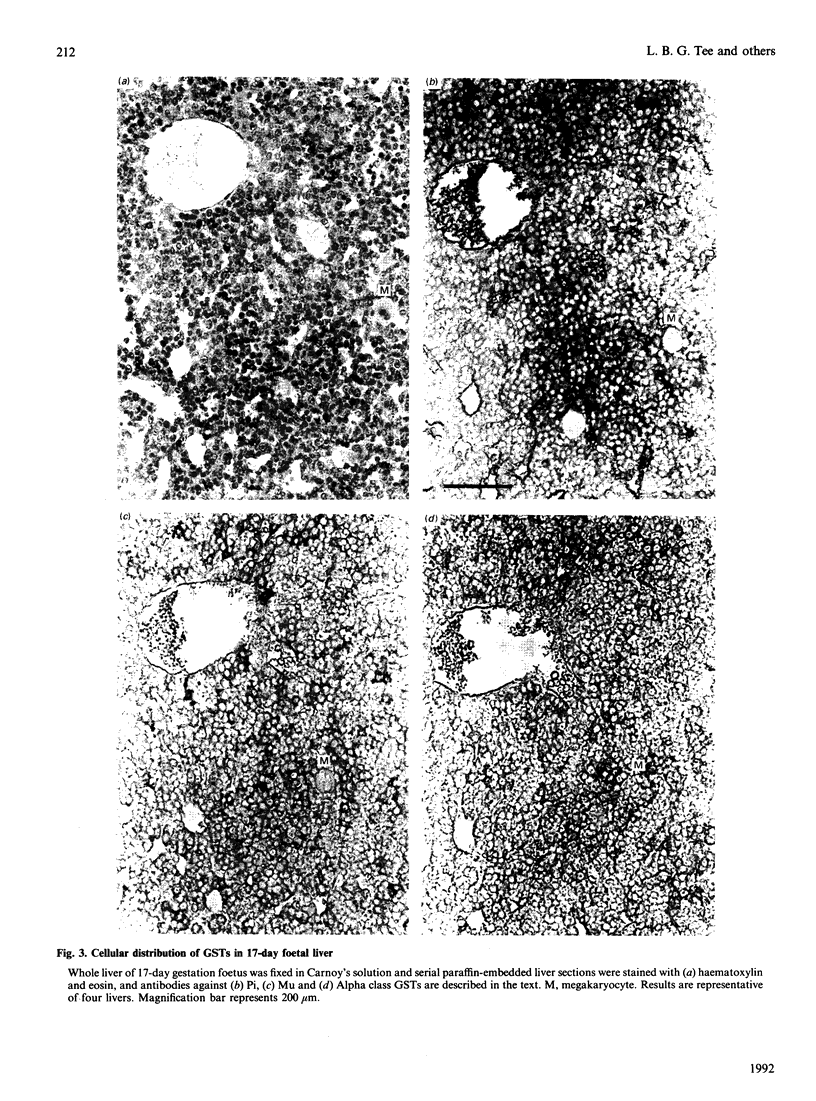
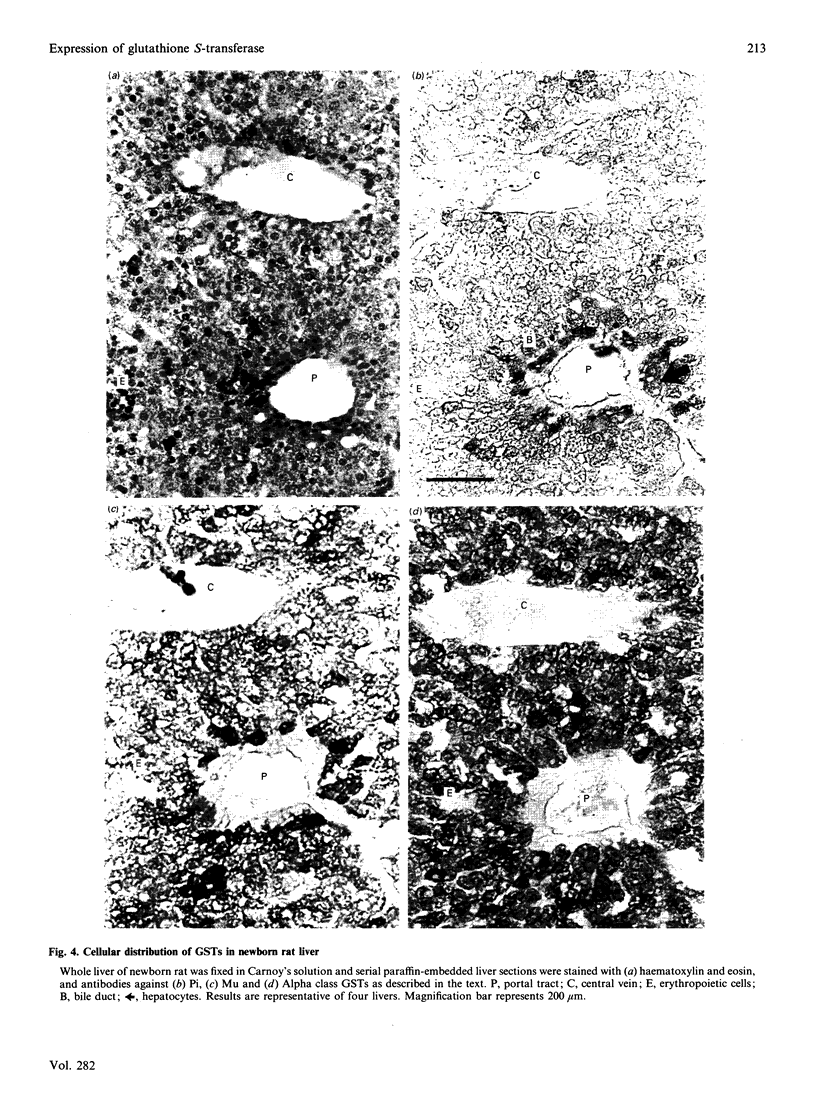
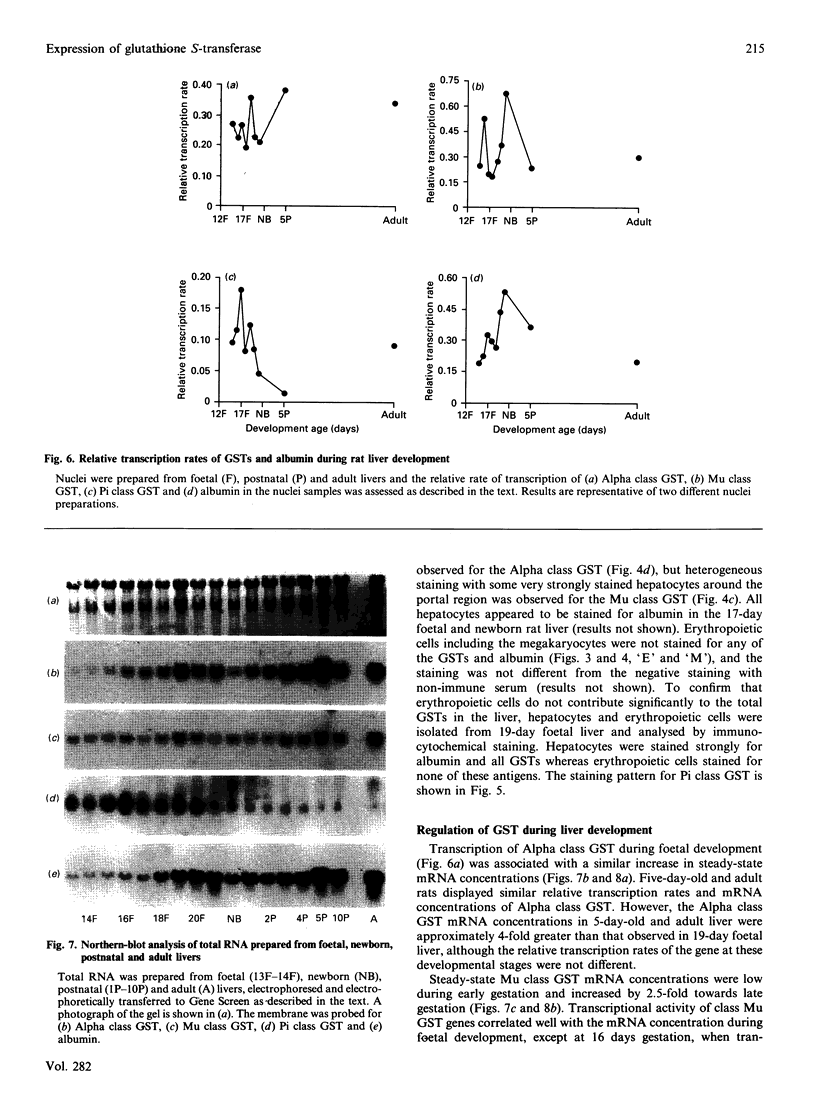
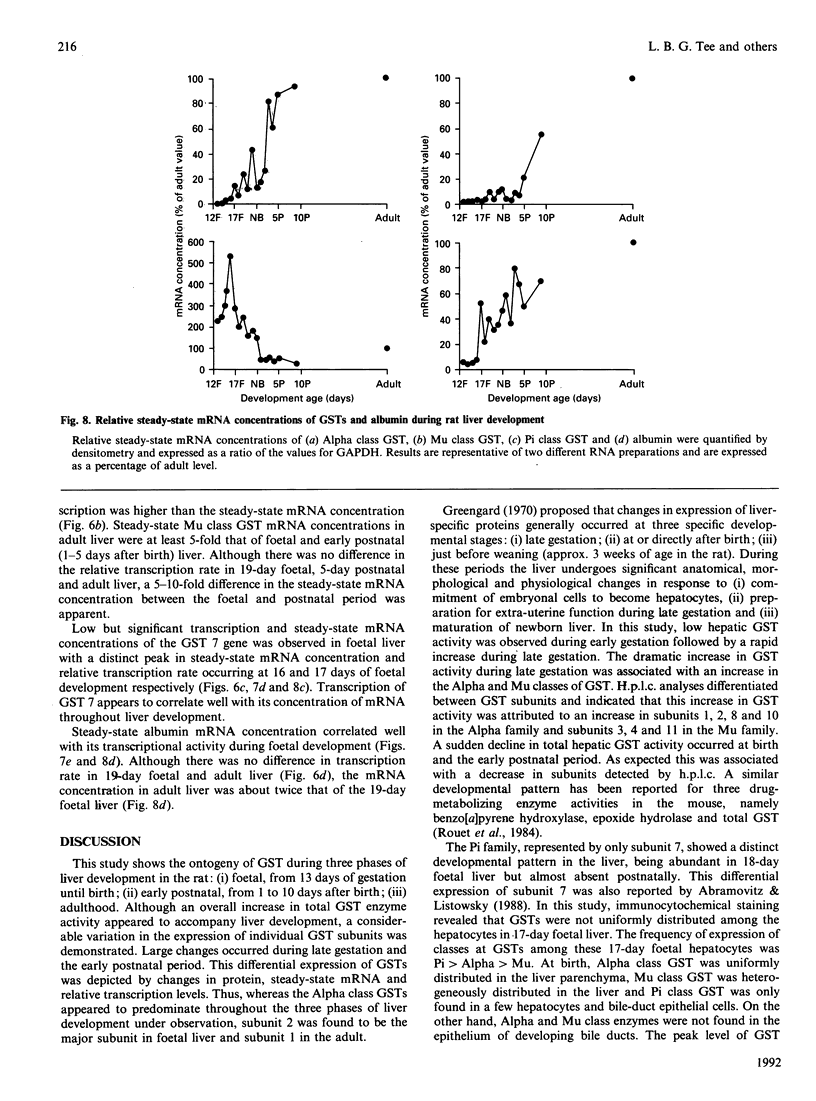
The ontogeny of rat liver glutathione S-transferase (EC 2.5.1.18) (GSTs) during foetal and postnatal development was investigated. The GSTs are dimers, the subunits of which belong to three multigene families, Alpha (subunits 1, 2, 8 and 10), Mu (subunits 3, 4, 6, 9 and 11) and Pi (subunit 7) [Mannervik, Alin, Guthenberg, Jennsson, Tahir, Warholm & Jörnvall (1985) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 7202-7206; Kispert, Meyer, Lalor, Coles & Ketterer (1989) Biochem. J. 260, 789-793]. There is considerable structural homology within each gene family, with the result that whereas reverse-phase h.p.l.c. successfully differentiates individual subunits, immunocytochemical and Northern-blotting analyses may only differentiate families. Enzymic activity, h.p.l.c. and Northern blotting indicated that expression of GST increased from very low levels at 12 days of foetal growth to substantial amounts at day 21. At birth, GST concentrations underwent a dramatic decline and remained low until 5-10 days post partum, after which they increased to adult levels. During the period under study, GST subunits underwent differential expression. The Mu family had a lower level of expression than the Alpha family, and, within the Alpha family, subunit 1 was more dominant in the adult than the foetus. Subunit 2 is the major form in the foetus. Most noteworthy were subunits 7 and 10, which were prominent in the foetus, but present at low levels post partum. Immunocytochemical analysis of the 17-day foetal and newborn rat livers showed marked differences in the distribution of GSTs in hepatocytes. In the 17-day foetal liver Pi greater than Alpha greater than Mu whereas in the newborns Alpha greater than Mu much greater than Pi. Erythropoietic cells were not stained for any of the three GST families. Steady-state mRNA concentrations in the foetus correlated with the relative transcription of the Alpha, Mu and Pi class genes. However, in those genes expressed post partum, namely the Alpha and Mu class, low transcriptional activity was associated with high concentrations of mRNA. This suggests that there is a switch from transcriptional control to post-transcriptional control at birth. GST 7-7 appears to be regulated predominantly by transcription throughout the period of liver development under observation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovitz M., Listowsky I. Developmental regulation of glutathione S-transferases. Xenobiotica. 1988 Nov;18(11):1249–1254. doi: 10.3109/00498258809042248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. Tissue-specific DNaseI hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking sequences of the tryptophan oxygenase and the tyrosine aminotransferase genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2015–2020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement B., Rissel M., Peyrol S., Mazurier Y., Grimaud J. A., Guillouzo A. A procedure for light and electron microscopic intracellular immunolocalization of collagen and fibronectin in rat liver. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 May;33(5):407–414. doi: 10.1177/33.5.3886779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannan G. A., Guengerich F. P., Waxman D. J. Hormonal regulation of rat liver microsomal enzymes. Role of gonadal steroids in programming, maintenance, and suppression of delta 4-steroid 5 alpha-reductase, flavin-containing monooxygenase, and sex-specific cytochromes P-450. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10728–10735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstone D. I. Regulation of blood flow through the ductus venosus. J Dev Physiol. 1980 Aug;2(4):219–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstone D. I., Rudolph A. M., Heymann M. A. Effects of hypoxemia and decreasing umbilical flow liver and ductus venosus blood flows in fetal lambs. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):H656–H663. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.5.H656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthenberg C., Jensson H., Nyström L., Osterlund E., Tahir M. K., Mannervik B. Isoenzymes of glutathione transferase in rat kidney cytosol. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2300609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Jakoby W. B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7130–7139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. F., Jaeger V., Neims A. H. Isoelectric focusing of glutathione S-transferases from rat liver and kidney. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):937–943. doi: 10.1042/bj1750937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman E. Immunoperoxidase technique in histopathology: applications, methods, and controls. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):971–978. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kispert A., Meyer D. J., Lalor E., Coles B., Ketterer B. Purification and characterization of a labile rat glutathione transferase of the Mu class. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):789–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2600789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara A., Satoh K., Nishimura K., Ishikawa T., Ruike K., Sato K., Tsuda H., Ito N. Changes in molecular forms of rat hepatic glutathione S-transferase during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1984 Jun;44(6):2698–2703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M., Glanville N., Mandel J. L., Gerlinger P., Palmiter R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: hormonal control of X and Y gene transcription and mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack G., Ketterer B., Arias I. M. Ligandin: a hepatic protein which binds steroids, bilirubin, carcinogens and a number of exogenous organic anions. Nature. 1971 Dec 24;234(5330):466–467. doi: 10.1038/234466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Alin P., Guthenberg C., Jensson H., Tahir M. K., Warholm M., Jörnvall H. Identification of three classes of cytosolic glutathione transferase common to several mammalian species: correlation between structural data and enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7202–7206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Danielson U. H. Glutathione transferases--structure and catalytic activity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(3):283–337. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Beale D., Tan K. H., Coles B., Ketterer B. Glutathione transferases in primary rat hepatomas: the isolation of a form with GSH peroxidase activity. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80670-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Coles B., Pemble S. E., Gilmore K. S., Fraser G. M., Ketterer B. Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2740409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Gilmore K. S., Coles B., Dalton K., Hulbert P. B., Ketterer B. Structural distinction of rat GSH transferase subunit 10. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):619–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2740619a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund Farrants A. K., Meyer D. J., Coles B., Southan C., Aitken A., Johnson P. J., Ketterer B. The separation of glutathione transferase subunits by using reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):423–428. doi: 10.1042/bj2450423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panduro A., Shalaby F., Shafritz D. A. Changing patterns of transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of liver-specific gene expression during rat development. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemble S. E., Taylor J. B., Ketterer B. Tissue distribution of rat glutathione transferase subunit 7, a hepatoma marker. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):885–889. doi: 10.1042/bj2400885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. J., Friedman J. M., Oulette A. J., Krauter K. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of specific messenger RNAs in adult and embryonic liver. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouet P., Dansette P., Frayssinet C. Ontogeny of benzo(a)pyrene hydroxylase, epoxide hydrolase and glutathione-S transferase in the brain, lung and liver of C57Bl/6 mice. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1984;7(4):245–258. doi: 10.1159/000457171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jagodzinski L. L., Yang M., Bonner J. Fine structure and evolution of the rat serum albumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):871–883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelly L. L., Tynan W., Schmid W., Schütz G., Yeoh G. C. Hepatocyte differentiation in vitro: initiation of tyrosine aminotransferase expression in cultured fetal rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3403–3410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahir M. K., Ozer N., Mannervik B. Isoenzymes of glutathione transferase in rat small intestine. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):759–764. doi: 10.1042/bj2530759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatematsu M., Mera Y., Ito N., Satoh K., Sato K. Relative merits of immunohistochemical demonstrations of placental, A, B and C forms of glutathione S-transferase and histochemical demonstration of gamma-glutamyl transferase as markers of altered foci during liver carcinogenesis in rats. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Nov;6(11):1621–1626. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.11.1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. B., Craig R. K., Beale D., Ketterer B. Construction and characterization of a plasmid containing complementary DNA to mRNA encoding the N-terminal amino acid sequence of the rat glutathione transferase Ya subunit. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):223–231. doi: 10.1042/bj2190223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Dannan G. A., Guengerich F. P. Regulation of rat hepatic cytochrome P-450: age-dependent expression, hormonal imprinting, and xenobiotic inducibility of sex-specific isoenzymes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4409–4417. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]