Abstract
Peptido-keratan sulphate fragments were isolated from the nucleus pulposus of bovine intervertebral discs (2-year-old animals) after digestion with chondroitin ABC lyase followed by digestion with diphenylcarbamoyl chloride-treated trypsin of A1D1 proteoglycans and gel-permeation chromatography on Sepharose CL-6B. The peptido-keratan sulphate fragments were subjected to alkaline borohydride reduction. The reduced chains were treated with keratanase in the presence of the sialidase inhibitor 2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy-N-acetylneuraminic acid, and the digest was subjected to alkaline borohydride reduction. This produced oligosaccharides with galactitol at their reducing ends. This reduced digest was chromatographed on a Nucleosil 5 SB anion-exchange column and individual oligosaccharides were isolated. One of these was shown by 600 MHz 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy to have the following structure: NeuAc alpha 2-6Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc(6-SO4)beta 1-3Gal-ol The structure of this oligosaccharide shows that keratan sulphate chains from bovine intervertebral disc have non-reducing termini with N-acetylneuraminic acid linked alpha(2----6) as well as alpha(2----3) to an unsulphated galactose.
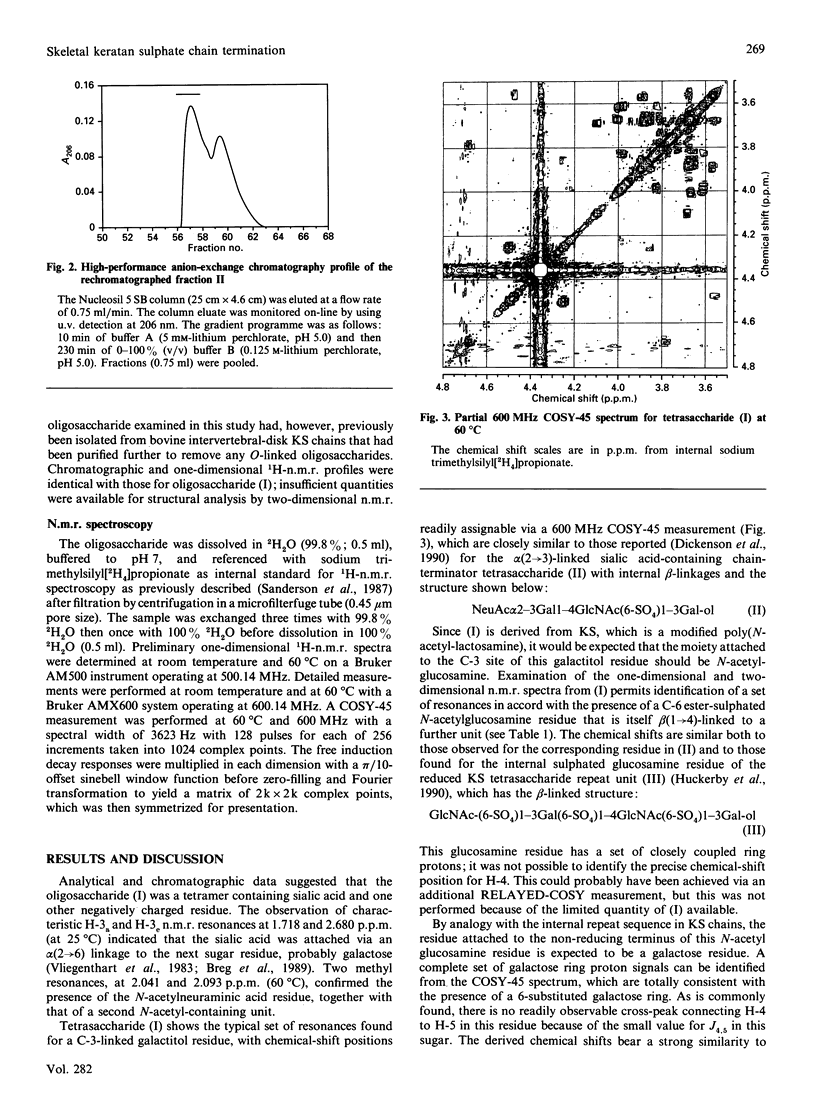
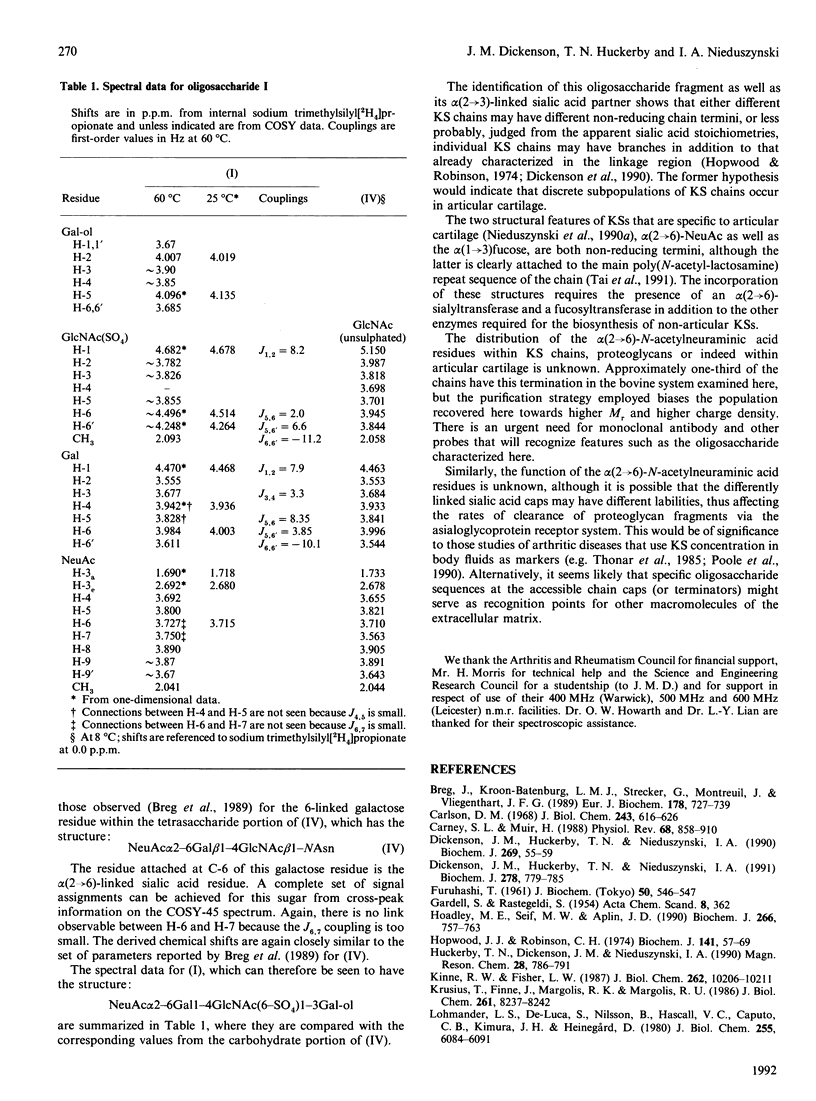
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breg J., Kroon-Batenburg L. M., Strecker G., Montreuil J., Vliegenthart J. F. Conformational analysis of the sialyl alpha(2----3/6)N-acetyllactosamine structural element occurring in glycoproteins, by two-dimensional NOE 1H-NMR spectroscopy in combination with energy calculations by hard-sphere exo-anomeric and molecular mechanics force-field with hydrogen-bonding potential. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):727–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. M. Structures and immunochemical properties of oligosaccharides isolated from pig submaxillary mucins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):616–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. L., Muir H. The structure and function of cartilage proteoglycans. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jul;68(3):858–910. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.3.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Huckerby T. N., Nieduszynski I. A. A non-reducing terminal fragment from tracheal cartilage keratan sulphate chains contains alpha (2-3)-linked N-acetylneuraminic acid. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):779–785. doi: 10.1042/bj2780779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Huckerby T. N., Nieduszynski I. A. Two linkage-region fragments isolated from skeletal keratan sulphate contain a sulphated N-acetylglucosamine residue. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2690055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUHASHI T. Polysulfated mucopolysaccharides of elasmobranch cartilage. J Biochem. 1961 Dec;50:546–547. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoadley M. E., Seif M. W., Aplin J. D. Menstrual-cycle-dependent expression of keratan sulphate in human endometrium. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):757–763. doi: 10.1042/bj2660757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Robinson H. C. The alkali-labile linkage between keratan sulphate and protein. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):57–69. doi: 10.1042/bj1410057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne R. W., Fisher L. W. Keratan sulfate proteoglycan in rabbit compact bone is bone sialoprotein II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10206–10211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Finne J., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U. Identification of an O-glycosidic mannose-linked sialylated tetrasaccharide and keratan sulfate oligosaccharides in the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8237–8242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., De Luca S., Nilsson B., Hascall V. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Heinegard D. Oligosaccharides on proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6084–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K., HOFFMAN P., LINKER A. Mucopolysaccharides of costal cartilage. Science. 1958 Oct 17;128(3329):896–896. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3329.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K., LINKER A., DAVIDSON E. A., WEISSMANN B. The mucopolysaccharides of bovine cornea. J Biol Chem. 1953 Dec;205(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieduszynski I. A., Huckerby T. N., Dickenson J. M., Brown G. M., Tai G. H., Bayliss M. T. Structural aspects of skeletal keratan sulphates. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Oct;18(5):792–793. doi: 10.1042/bst0180792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieduszynski I. A., Huckerby T. N., Dickenson J. M., Brown G. M., Tai G. H., Morris H. G., Eady S. There are two major types of skeletal keratan sulphates. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):243–245. doi: 10.1042/bj2710243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Witter J., Roberts N., Piccolo F., Brandt R., Paquin J., Baron M. Inflammation and cartilage metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Studies of the blood markers hyaluronic acid, orosomucoid, and keratan sulfate. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):790–799. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson P. N., Huckerby T. N., Nieduszynski I. A. Conformational equilibria of alpha-L-iduronate residues in disaccharides derived from heparin. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):175–181. doi: 10.1042/bj2430175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai G. H., Brown G. M., Morris H. G., Huckerby T. N., Nieduszynski I. A. Fucose content of keratan sulphates from bovine articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):307–310. doi: 10.1042/bj2730307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thonar E. J., Lenz M. E., Klintworth G. K., Caterson B., Pachman L. M., Glickman P., Katz R., Huff J., Kuettner K. E. Quantification of keratan sulfate in blood as a marker of cartilage catabolism. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1367–1376. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton D. J., Morris H. G., Cockin G. H., Huckerby T. N., Nieduszynski I. A. Structural studies of two populations of keratan sulphate chains from mature bovine articular cartilage. Glycoconj J. 1989;6(2):209–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01050649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


