Abstract
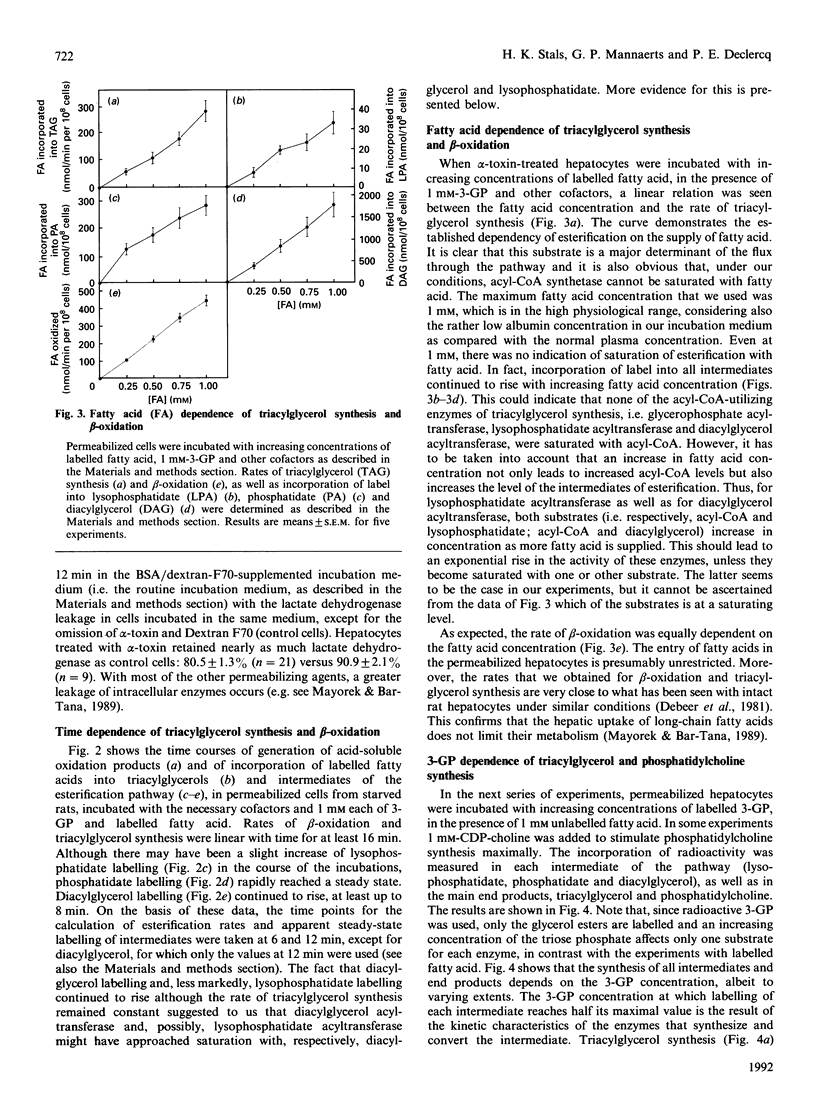
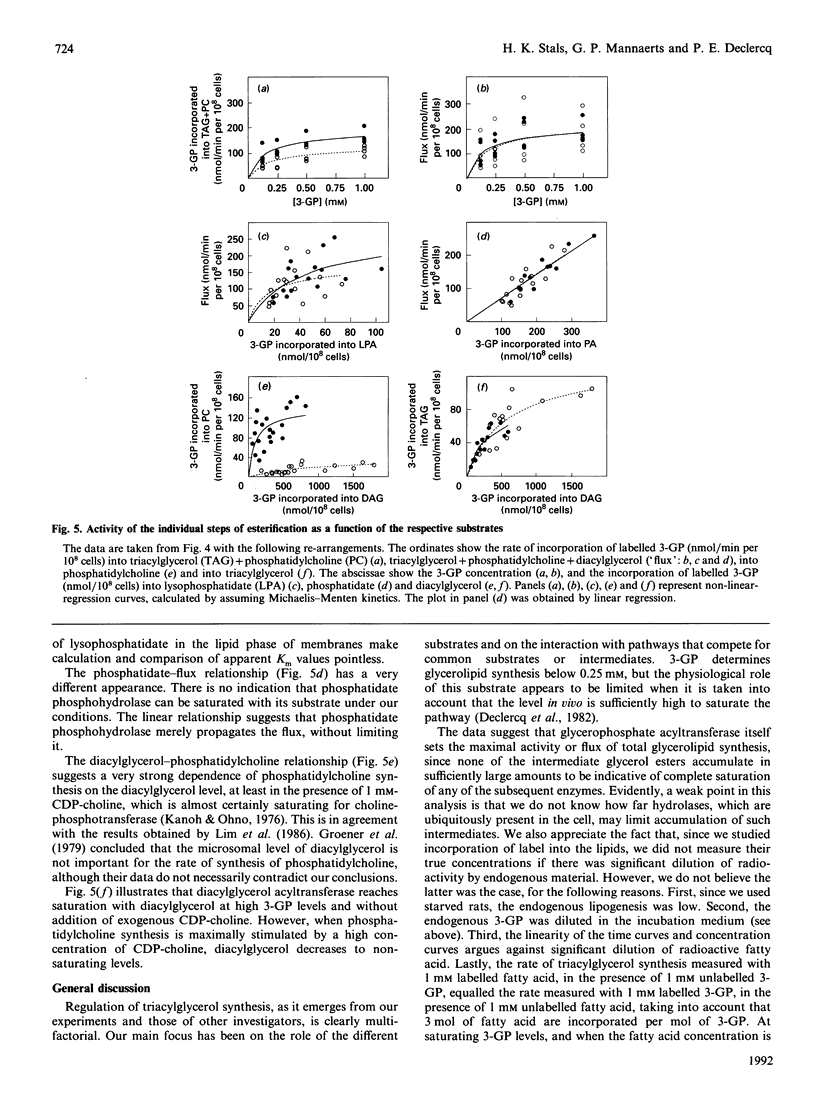
Rat hepatocytes were treated with Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin to permeabilize their plasma membrane for low-molecular-mass compounds. During incubation with 1 mM labelled fatty acid, phosphatidate and, less clearly, lysophosphatidate rapidly reached a steady state, whereas labelled diacylglycerol accumulated to some extent, at least in the absence of exogenous CDP-choline. Esterification and oxidation were linearly related to the fatty acid concentration, and there was no indication for saturation with acyl-CoA. However, when permeabilized cells were incubated with labelled sn-glycerol 3-phosphate and 1 mM unlabelled fatty acid, glycerolipid synthesis and the level of esterification intermediates reached a plateau between 0.25 and 0.50 mumol of the triose phosphate/ml. The synthesis of phosphatidylcholine was dependent on addition of CDP-choline. In presence of the latter, diacylglycerol no longer accumulated and triacylglycerol synthesis was suppressed, although the sum of synthesized diacylglycerol, triacylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine remained constant. This indicates that the same pool of diacylglycerol is shared by choline-phosphotransferase and diacylglycerol acyltransferase and that the relative activity of these enzymes depends on the CDP-choline supply. Comparison of the levels of the esterification intermediates with the activity of the respective steps of the pathway reveals that, at a fixed fatty acid concentration, glycerophosphate acyltransferase determines the esterification rate, whereas lysophosphatidate acyltransferase and, at low CDP-choline levels, diacylglycerol acyltransferase approach saturation at elevated sn-glycerol 3-phosphate concentration. There is, however, no indication for a regulatory role of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in this system. The significance of these findings for the regulation of triacylglycerol synthesis under conditions in vivo is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bhakdi S., Gratzl M. Minimal requirements for exocytosis. A study using PC 12 cells permeabilized with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12730–12734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvord W. G., Driver J. H., Claxton L., Creason J. P. Methods for comparing Salmonella mutagenicity data sets using nonlinear models. Mutat Res. 1990 Mar;240(3):177–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(90)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Thiersé D., Aunis D., Ahnert-Hilger G., Gratzl M. Characterization of hormone and protein release from alpha-toxin-permeabilized chromaffin cells in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5777–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Coleman R. A. Enzymes of glycerolipid synthesis in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:459–487. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Rudy B. Interactions between membranes and cytolytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 12;864(1):123–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Angelin B., Backman L., Liljeqvist L., Nilsell K., Einarsson K. Triglyceride metabolism in human liver: studies on hepatic phosphatidic-acid phosphatase in obese and non-obese subjects. Eur J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;14(3):233–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1984.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon M. R., Zammit V. A. Use of a selectively permeabilized isolated rat hepatocyte preparation to study changes in the properties of overt carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity in situ. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):645–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2490645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindley D. N. Intracellular translocation of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and its possible role in the control of glycerolipid synthesis. Prog Lipid Res. 1984;23(3):115–133. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(84)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung C. W., Cohen N. S., Raijman L. Channeling of urea cycle intermediates in situ in permeabilized hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4038–4044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W. Rapid fractionation of cell suspensions with the use of brominated hydrocarbons. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik J. D., Elliott K. R. Kinetics of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):503–508. doi: 10.1042/bj1820503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debeer L. J., Declercq P. E., Mannaerts G. P. Glycerol-3-phosphate content and triacylglycerol synthesis in isolated hepatocytes from fed and starved rats. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 9;124(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debeer L. J., Thomas J., Mannaerts G., DeSchepper P. J. Effect of sulfonylureas on triglyceride metabolism in the rat liver: possible role of the lysosomes in hepatic lipolysis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):185–192. doi: 10.1172/JCI108628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declercq P. E., Debeer L. J., Mannaerts G. P. Role of glycerol 3-phosphate and glycerophosphate acyltransferase in the nutritional control of hepatic triacylglycerol synthesis. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):247–256. doi: 10.1042/bj2040247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groener J. E., Klein W., Van Golde L. M. The effect of fasting and refeeding on the composition and synthesis of triacylglycerols, phosphatidylcholines, and phosphatidylethanolamines in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Nov;198(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groener J. E., van Golde L. M. Effect of fasting and feeding a high-sucrose, fat-free diet on the synthesis of hepatic glycerolipids in vivo and in isolated hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 26;487(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines D. S., Rose C. I. Impaired labelling of liver phosphatidylethanolamine from ethanolamine-14C in choline deficiency. Can J Biochem. 1970 Aug;48(8):885–892. doi: 10.1139/o70-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Ohno K. Solubilization and purification of rat liver microsomal 1,2-diacylglycerol: CDP-choline cholinephosphotransferase and 1,2-diacylglycerol: CDP-ethanolamine ethanolaminephosphotransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):201–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim P., Cornell R., Vance D. E. The supply of both CDP-choline and diacylglycerol can regulate the rate of phosphatidylcholine synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;64(7):692–698. doi: 10.1139/o86-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannaerts G. P., Thomas J., Debeer L. J., McGarry J. D., Foster D. W. Hepatic fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis after clofibrate treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 25;529(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorek N., Bar-Tana J. Lipid synthesis in permeabilized cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4450–4455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. F., Arion W. J. Permeabilization of rat hepatocytes with Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1922–1929. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mick G. J., Bonn T., Steinberg J., McCormick K. Preservation of intermediary metabolism in saponin-permeabilized rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10667–10673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney R. A. Use of digitonin-permeabilized adipocytes for cAMP studies. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:193–202. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ontko J. A. Metabolism of free fatty acids in isolated liver cells. Factors affecting the partition between esterification and oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1788–1800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Vance D. E. Regulation of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 25;779(2):217–251. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittner R. A., Fears R., Brindley D. N. Effects of cyclic AMP, glucocorticoids and insulin on the activities of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase, tyrosine aminotransferase and glycerol kinase in isolated rat hepatocytes in relation to the control of triacylglycerol synthesis and gluconeogenesis. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj2250455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz I. Permeabilizing cells: some methods and applications for the study of intracellular processes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:280–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92077-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. I. Effect of Ca 2+ on enzymatic dispersion of isolated, perfused liver. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Oct;74(2):450–454. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens T. W., Harris R. A. Effect of starvation and diabetes on the sensitivity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I to inhibition by 4-hydroxyphenylglyoxylate. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):405–412. doi: 10.1042/bj2430405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijburg L. B., Geelen M. J., van Golde L. M. Regulation of the biosynthesis of triacylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 17;1004(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahlten R. N., Stratman F. W. The isolation of hormone-sensitive rat hepatocytes by a modified enzymatic technique. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Aug;163(2):600–608. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit V. A. Mechanisms of regulation of the partition of fatty acids between oxidation and esterification in the liver. Prog Lipid Res. 1984;23(1):39–67. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(84)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


