Abstract
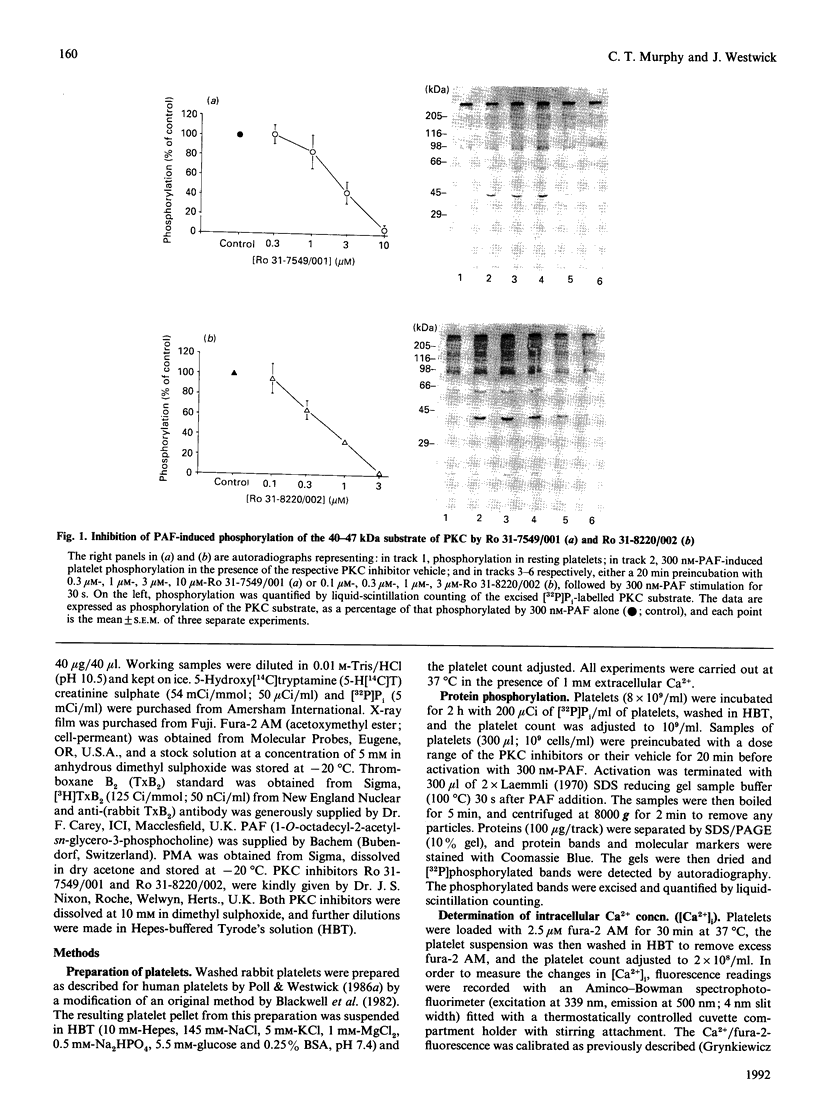
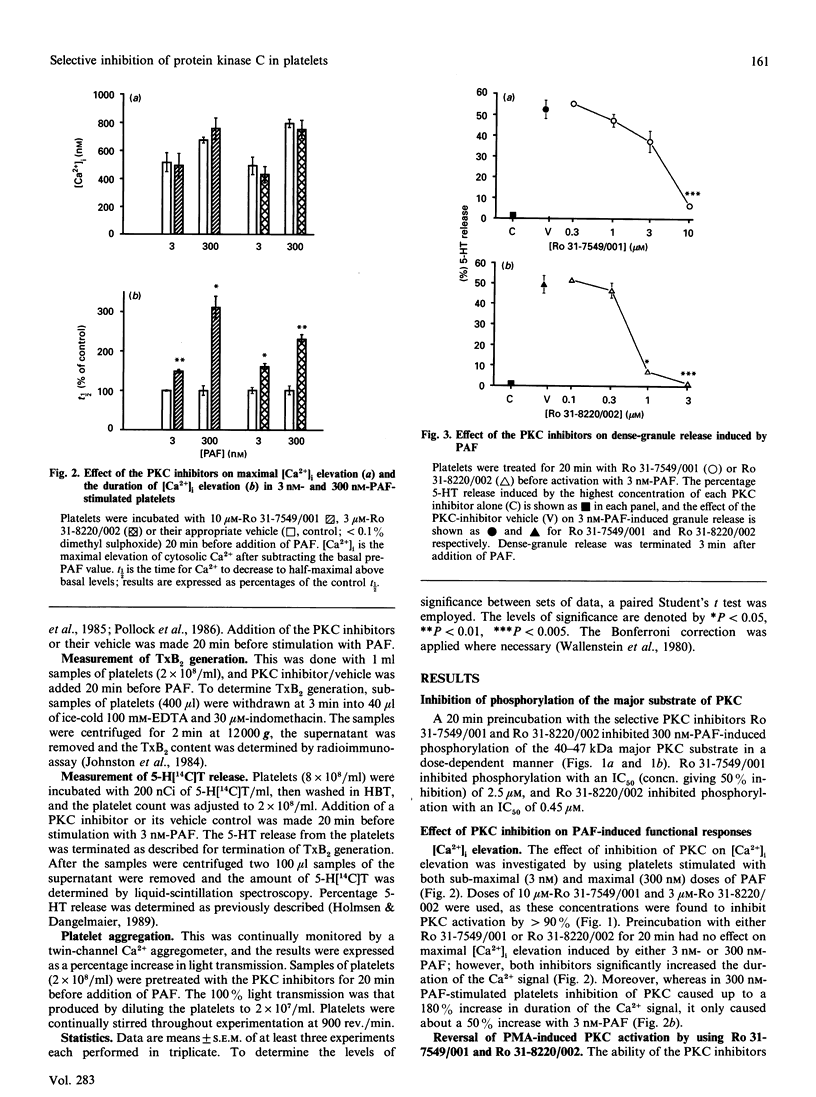
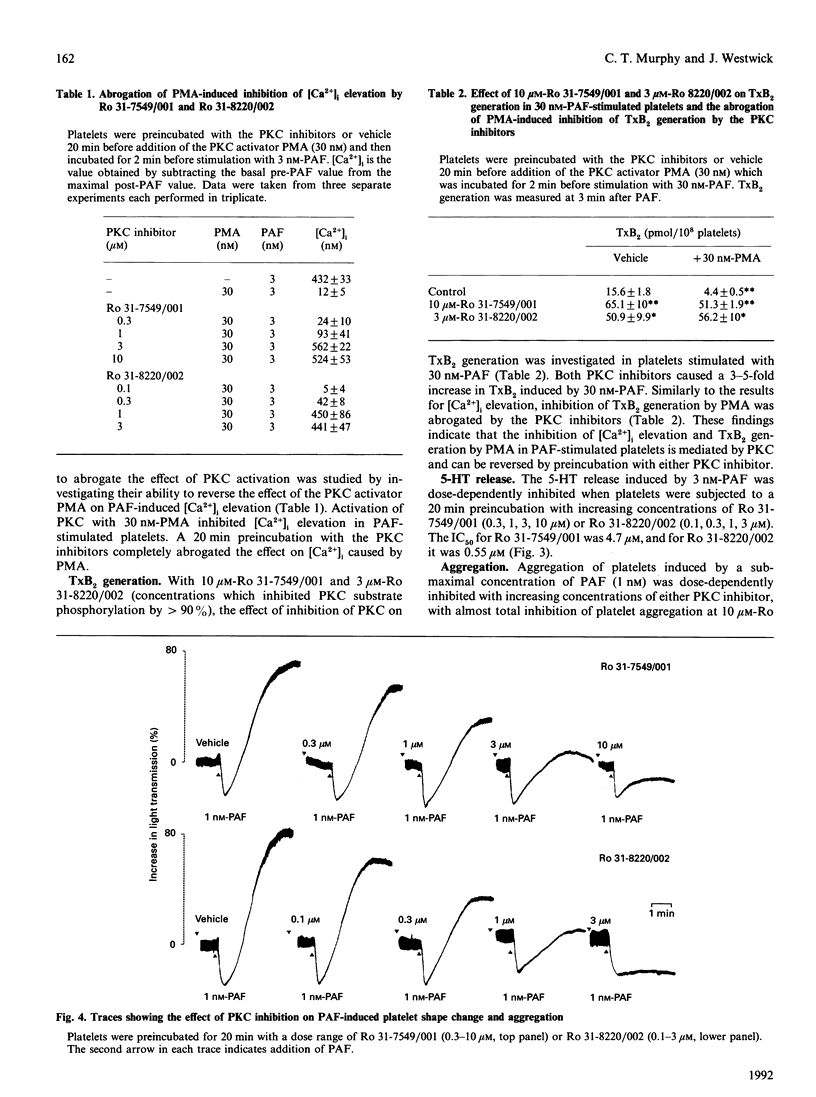
The role of protein kinase C (PKC) in platelet-activating-factor (PAF)-induced platelet activation was examined by using two selective inhibitors of PKC, namely Ro 31-7549/001 and Ro 31-8220/002. Both inhibitors dose-dependently inhibited PAF-induced phosphorylation of the major 40-47 kDa protein substrate of PKC, with 50% inhibition at 4.5 microM-Ro 31-7549/001 and 0.7 microM-Ro 31-8220/002. Inhibition of PKC had no effect on maximal elevation of intracellular Ca2+ [Ca2+]i produced by either a high or a low dose of PAF, but significantly increased the duration of the Ca2+ signal and the thromboxane B2 (TxB2) generation in high-dose PAF-stimulated platelets. The inhibitors also abrogated the effect of the PKC activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate on PAF-induced [Ca2+]i elevation. Sub-maximal PAF-induced dense-granule release and platelet aggregation were dose-dependently inhibited by Ro 31-7549/001 and Ro 31-8220/002. The findings suggest that endogenously activated PKC holds a bifurcating role in PAF-activated platelets, negatively affecting duration of both [Ca2+]i and TxB2 generation, and positively influencing dense-granule release and aggregation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Differences in the effects of phorbol esters and diacylglycerols on protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9317–9323. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignon E., Ogita K., Kishimoto A., Gilbert J., Abecassis J., Miquel J. F., Nishizuka Y. Modes of inhibition of protein kinase C by triphenylacrylonitrile antiestrogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 29;163(3):1377–1383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blache D., Ciavatti M., Ponsin G., Nargeot J. Direct evidence for the modulation of human platelet cytosolic free Ca2+ by intracellular cyclic AMP produced with a photoactivatable derivative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Radomski M., Vargas J. R., Moncada S. Prostacyclin prolongs viability of washed human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 17;718(1):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Brasseur R., Pavoine C., Bredoux R., Mely B., Ruysschaert J. M., Levy-Toledano S. Protein kinase C and granule release in human platelets. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;192:249–263. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9442-0_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Lawing W. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. Protein kinase C phosphorylates human platelet inositol trisphosphate 5'-phosphomonoesterase, increasing the phosphatase activity. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Keech E., Lawton G., Nixon J. S., Sedgwick A. D., Wadsworth J., Westmacott D., Wilkinson S. E. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Zavoico G. B., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol esters and oleoyl acetoyl glycerol enhance release of arachidonic acid in platelets stimulated by Ca2+ ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12484–12491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Aminoacridines, potent inhibitors of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5124–5131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Dangelmaier C. A. Measurement of secretion of serotonin. Methods Enzymol. 1989;169:205–210. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)69061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How do inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate regulate intracellular Ca2+? Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Feb;17(1):6–9. doi: 10.1042/bst0170006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C., Carey F., Forder R. A., Haworth D. Prostacyclin and thromboxane in non-insulin dependent diabetes: the chlorpropamide alcohol flush reaction revisited. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Dec;67(6):633–638. doi: 10.1042/cs0670633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiyama Y., Murayama T., Nomura Y. Pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding proteins may regulate phospholipase A2 in response to thrombin in rabbit platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):200–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. 1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7) is a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C in rabbit platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):258–264. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., Pollock W. K. Platelet-activating factor stimulates phosphatidylinositol turnover in human platelets. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):433–437. doi: 10.1042/bj2120433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. Diacylglycerol lipase pathway is a minor source of released arachidonic acid in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1327–1333. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei G. J., Katoh N., Kuo J. F. Polymyxin B is a more selective inhibitor for phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase than for calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91894-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley A., Tai H. H. Synergistic stimulation of thromboxane biosynthesis by calcium ionophore and phorbol ester or thrombin in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90475-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A. Arachidonate metabolism in blood cells and the vessel wall. Clin Haematol. 1986 May;15(2):273–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy C. T., Elmore M., Kellie S., Westwick J. The relationship between cytosolic Ca2+, sn-1,2-diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate elevation in platelet-activating-factor-stimulated rabbit platelets. Influence of protein kinase C on production of signal molecules. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):255–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2780255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C. A., Liskamp R. M., Solomon D. H., Weinstein I. B. Inhibition of protein kinase C by tamoxifen. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2462–2465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poll C., Westwick J. Phorbol esters modulate thrombin-operated calcium mobilisation and dense granule release in human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 29;886(3):434–440. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Stimulation of Ca2+ efflux from fura-2-loaded platelets activated by thrombin or phorbol myristate acetate. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 5;210(2):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricouart A., Tartar A., Sergheraert C. Inhibition of protein kinase C by retro-inverso pseudosubstrate analogues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1382–1390. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg U. T., Burgess G. M. Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):218–220. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schächtele C., Seifert R., Osswald H. Stimulus-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation by the protein kinase C inhibitors polymyxin B, H-7 and staurosporine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90628-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk S. T., Clejan S., Witkom K. Evidence of GTP-binding protein regulation of phospholipase A2 activity in isolated human platelet membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21466–21469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., Kathuria S., De Meyts P. Acridine orange, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, abolishes insulin and growth hormone stimulation of lipogenesis in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):465–468. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spacey G. D., Bonser R. W., Randall R. W., Garland L. G. Selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors in human intact platelets. Cell Signal. 1990;2(4):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90062-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Rachubinski R. A., Stewart M. I., Varrichio A. M., Shorr R. G., Haslam R. J., Harley C. B. Molecular cloning and expression of the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):470–473. doi: 10.1038/333470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Johnson B. Modulation of platelet-activating-factor-induced calcium influx and intracellular calcium release in platelets by phorbol esters. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2470669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Hambleton S. Phosphorylation-dependent and -independent pathways of platelet aggregation. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj2580479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McNally J., Shipman L. J., Godfrey P. P. The action of the protein kinase C inhibitor, staurosporine, on human platelets. Evidence against a regulatory role for protein kinase C in the formation of inositol trisphosphate by thrombin. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):345–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2490345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler-Jones C. P., Patel Y., Kakkar V. V., Krishnamurthi S. Role of protein kinase C in the regulation of phospholipase A2 activity in human platelets. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Jun;18(3):467–468. doi: 10.1042/bst0180467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Iwahashi K., Kase H. K252a, a new inhibitor of protein kinase C, concomitantly inhibits 40K protein phosphorylation and serotonin secretion in a phorbol ester-stimulated platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Troll W., Belman S. The tumor-promoter phorbol ester (12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate), a potent aggregating agent for blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):325–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]