Abstract
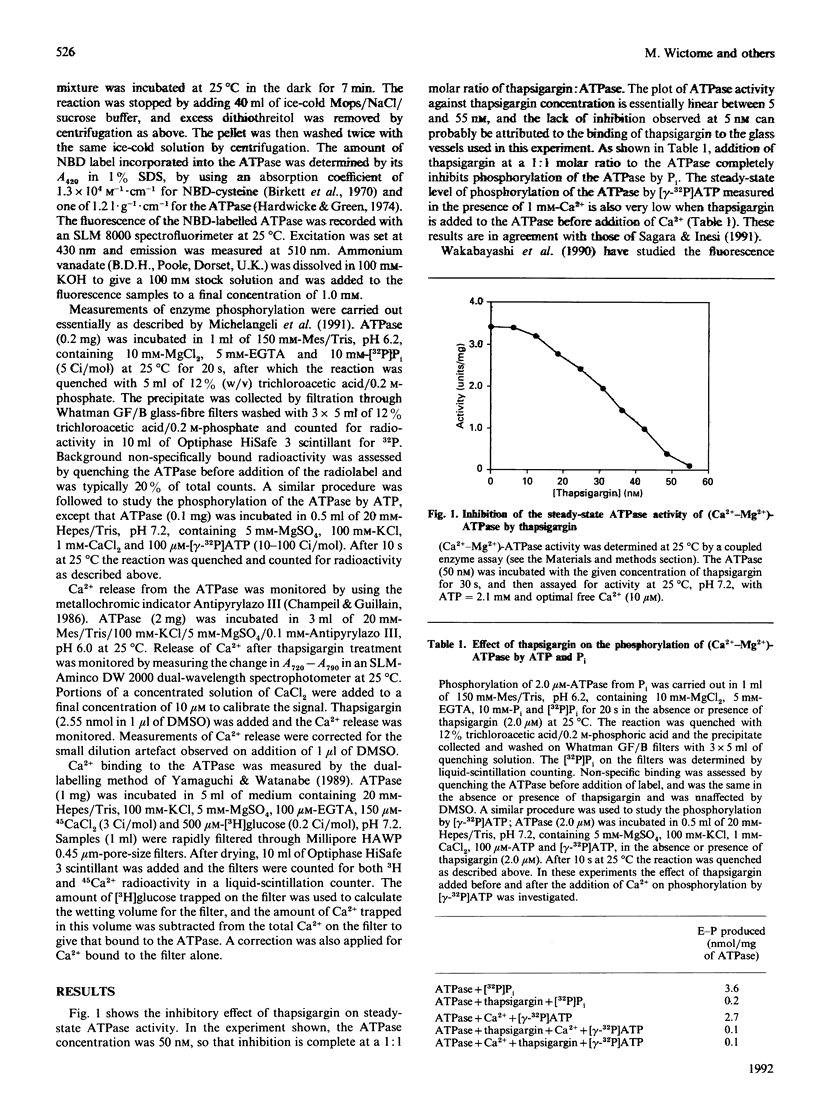
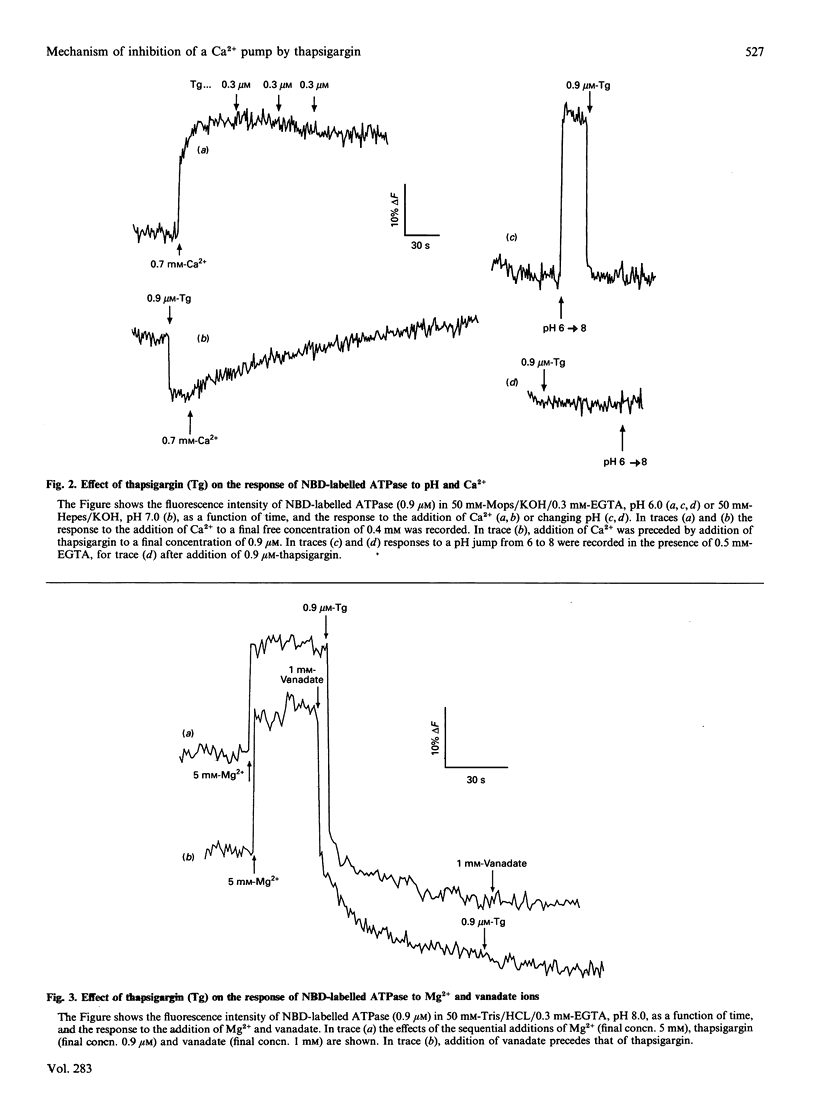
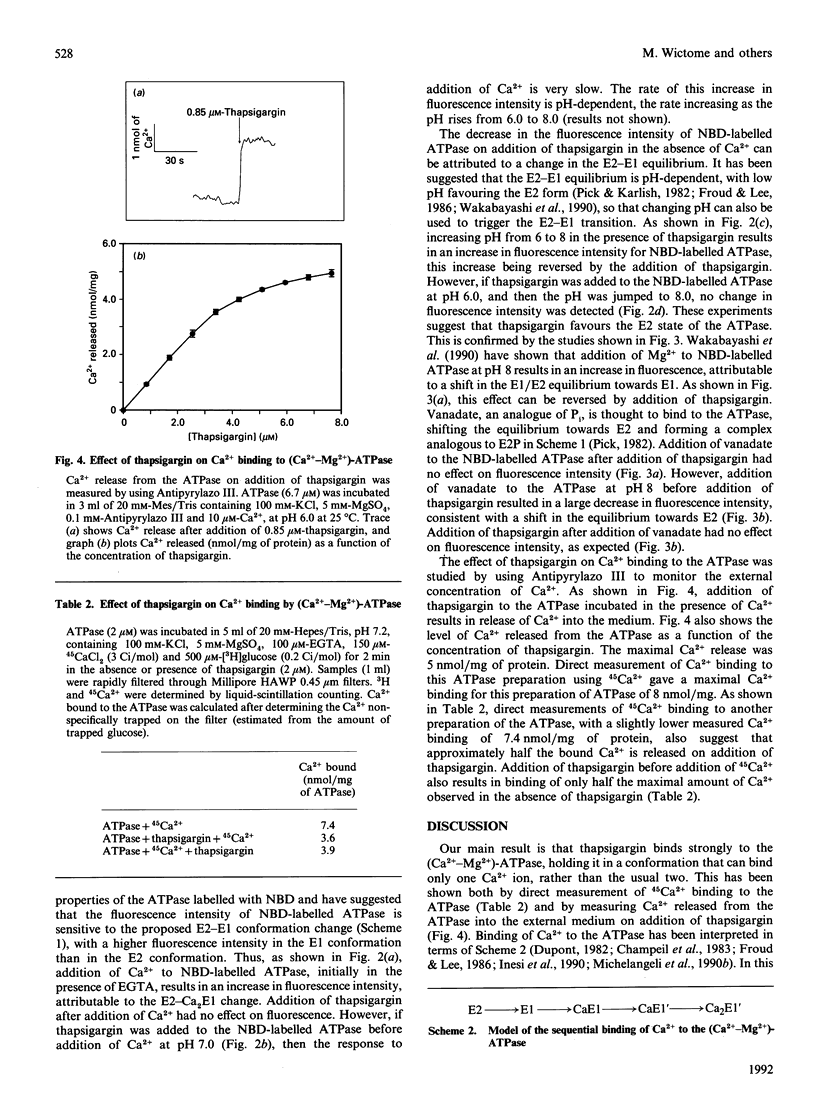
The steady-state ATPase activity of sarcoplasmic-reticulum (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase is inhibited by thapsigargin at a molar ratio of 1:1, with a dissociation constant for thapsigargin estimated to be in the sub-nanomolar range. In the presence of thapsigargin, only a single Ca2+ ion binds to the ATPase. Similarly, addition of thapsigargin to the ATPase incubated in the presence of Ca2+ results in the release of one of the two originally bound Ca2+ ions. As monitored by the fluorescence of nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-labelled ATPase, thapsigargin appears to shift the transition between E1 and E2 conformations towards E2. Addition of thapsigargin prevents phosphorylation of the ATPase by P(i) and results in a very low steady-state level of phosphorylation of the ATPase by ATP, as observed previously for nonylphenol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkett D. J., Price N. C., Radda G. K., Salmon A. G. The reactivity of SH groups with a fluorogenic reagent. FEBS Lett. 1970 Feb 25;6(4):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Gingold M. P., Guillain F., Inesi G. Effect of magnesium on the calcium-dependent transient kinetics of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase, studied by stopped flow fluorescence and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4453–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Guillain F. Rapid filtration study of the phosphorylation-dependent dissociation of calcium from transport sites of purified sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase and ATP modulation of the catalytic cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7623–7633. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Low-temperature studies of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Mechanisms of calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., East J. M., Rooney E. K., Lee A. G. Binding of long-chain alkyl derivatives to lipid bilayers and to (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7535–7544. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. Conformational transitions in the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase and the binding of Ca2+ ions. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):197–206. doi: 10.1042/bj2370197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwicke P. M., Green N. M. The effect of delipidation on the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Electron microscopy and physical properties. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):183–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Sumbilla C., Kirtley M. E. Relationships of molecular structure and function in Ca2(+)-transport ATPase. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):749–760. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Patterson S. I., Thastrup O., Hanley M. R. A novel tumour promoter, thapsigargin, transiently increases cytoplasmic free Ca2+ without generation of inositol phosphates in NG115-401L neuronal cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2530081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelangeli F., Grimes E. A., East J. M., Lee A. G. Effects of phospholipids on the function of (Ca2(+)-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 15;30(2):342–351. doi: 10.1021/bi00216a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelangeli F., Orlowski S., Champeil P., East J. M., Lee A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of the (Ca2(+)-Mg2+)-ATPase by nonylphenol. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):3091–3101. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelangeli F., Orlowski S., Champeil P., Grimes E. A., East J. M., Lee A. G. Effects of phospholipids on binding of calcium to (Ca2(+)-Mg2(+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8307–8312. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Karlish S. J. Regulation of the conformation transition in the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by pH, temperature, and calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6120–6126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. The interaction of vanadate ions with the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6111–6119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara Y., Inesi G. Inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport ATPase by thapsigargin at subnanomolar concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13503–13506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff O., Foder B., Thastrup O., Hofmann B., Møller J., Ryder L. P., Jacobsen K. D., Langhoff E., Dickmeiss E., Christensen S. B. Effect of thapsigargin on cytoplasmic Ca2+ and proliferation of human lymphocytes in relation to AIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 9;972(3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Imagawa T., Shigekawa M. Does fluorescence of 4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole incorporated into sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase monitor putative E1-E2 conformational transition? J Biochem. 1990 Apr;107(4):563–571. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Watanabe T. Modified membrane filtration methods for ligand binding on ATP-driven pumps during ATP hydrolysis. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:233–240. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


