Abstract
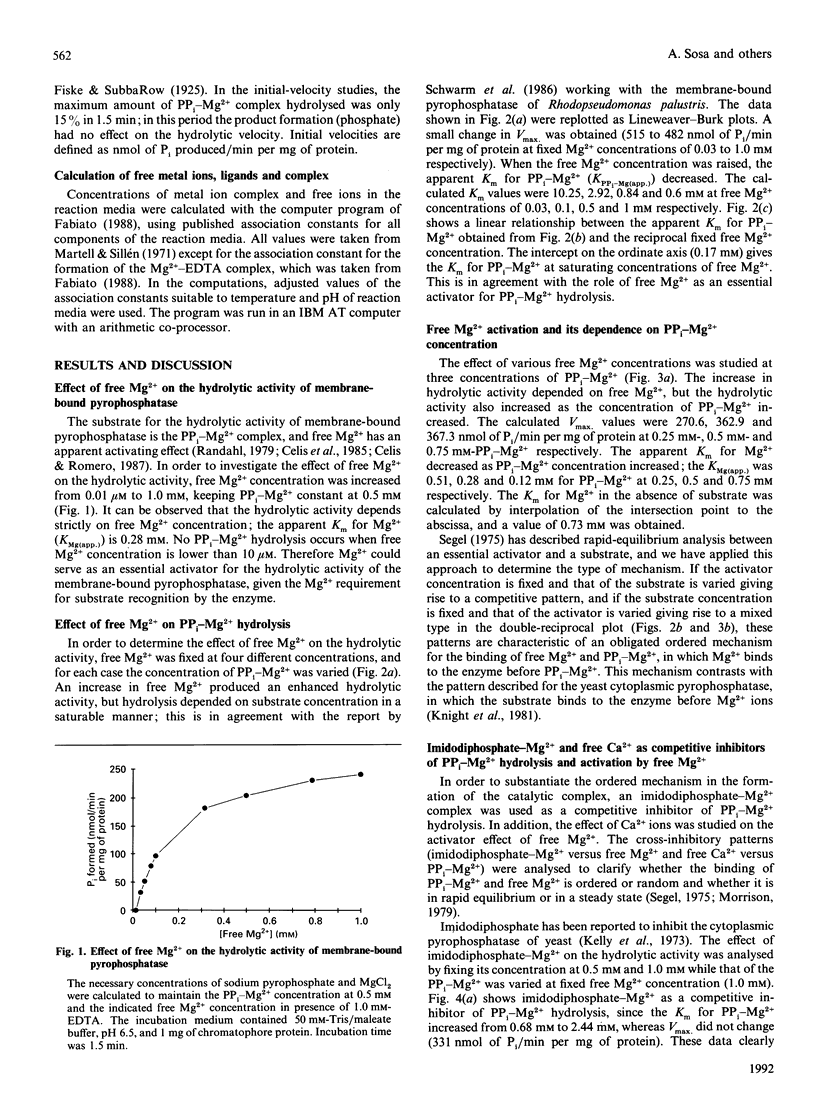
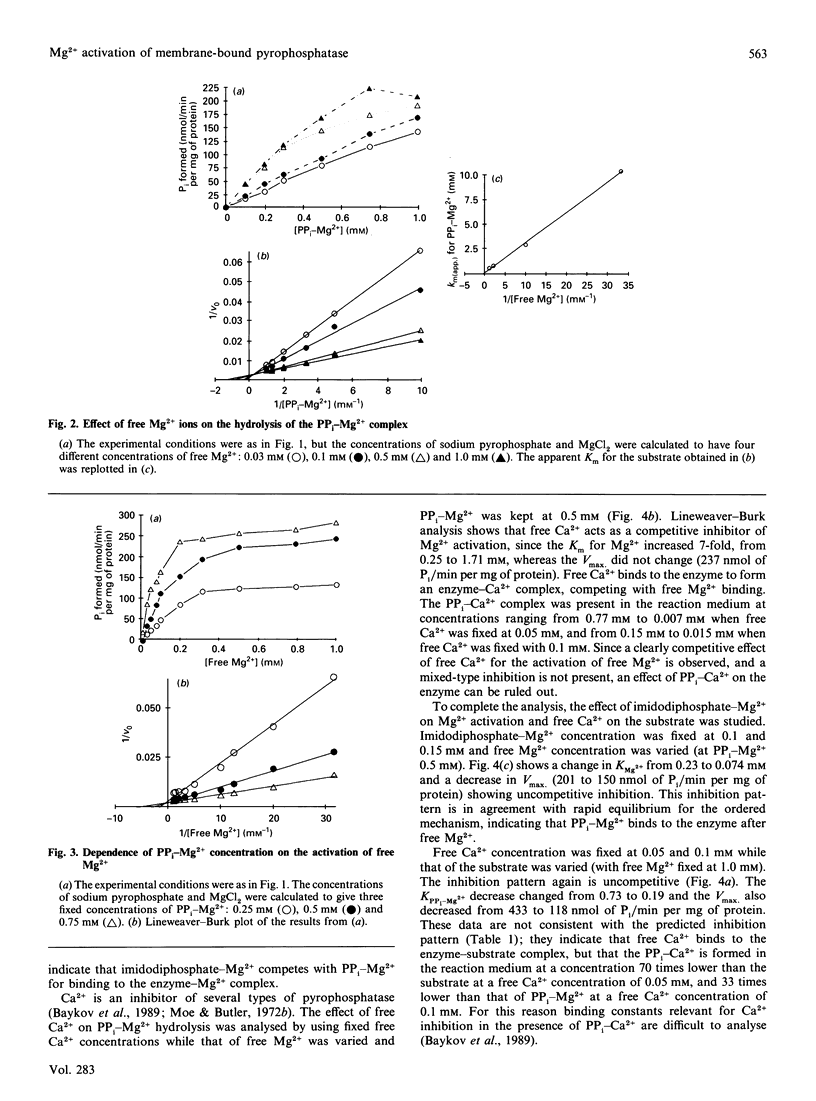
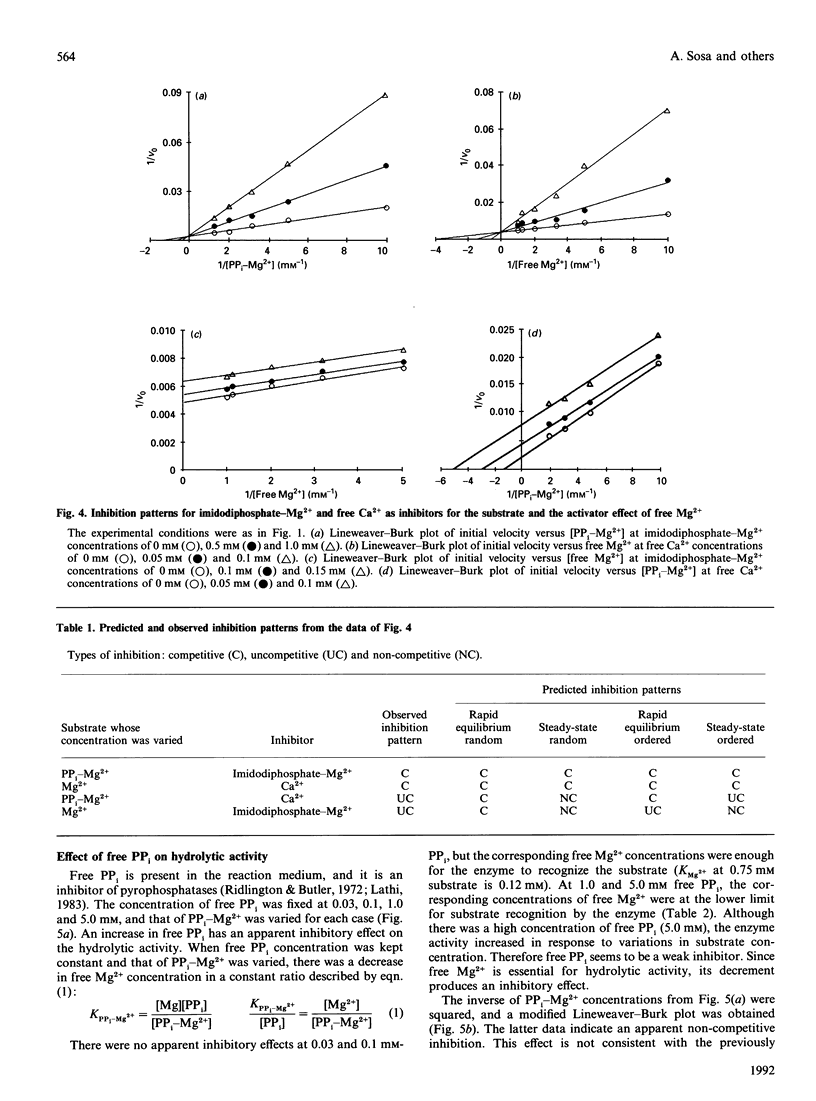
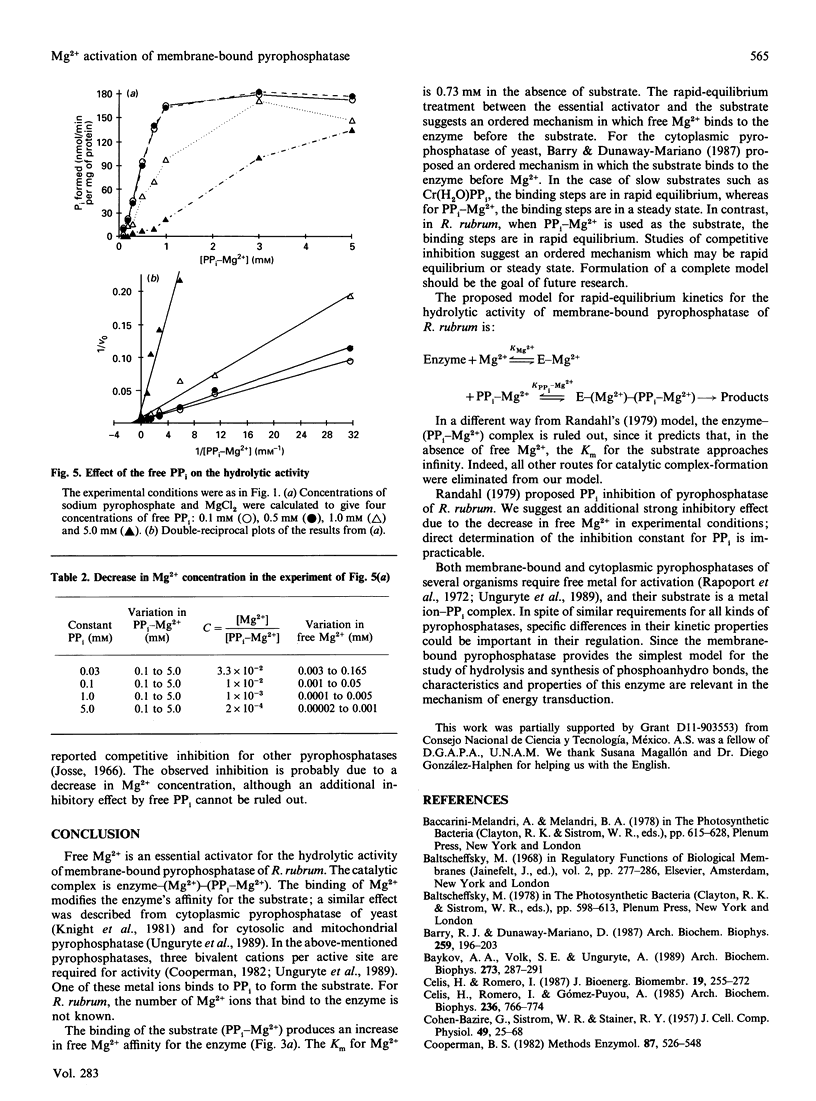
The substrate for the hydrolytic activity of membrane-bound pyrophosphatase is the PP(i)-Mg2+ complex. The enzyme has no activity when the free Mg2+ concentration is lower than 10 microM (at 0.5 mM-PP(i)-Mg2+), and therefore free Mg2+ is an essential activator of the hydrolytic activity. The Km for the substrate changes in response to variation in free Mg2+ concentration, from 10.25 to 0.6 mM when free Mg2+ is increased from 0.03 to 1.0 mM respectively. The Km for Mg2+ depends on the substrate concentration: the Km decreases from 0.52 to 0.14 mM from 0.25 to 0.75 mM-PP(i)-Mg2+ respectively. The extrapolated Km for Mg2+ in the absence of the substrate is 0.73 mM. Imidodiphosphate-Mg2+ and free Ca2+ were used as competitive inhibitors of substrate and activator respectively. The equilibrium binding kinetics suggest an ordered mechanism for the activator and the substrate: Mg2+ ions bind the enzyme before PP(i)-Mg2+ in the formation of the catalytic complex, membrane-bound pyrophosphatase-(Mg2+)-(PP(i)-Mg2+).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry R. J., Dunaway-Mariano D. The kinetic mechanism of yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 15;259(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90486-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baykov A. A., Volk S. E., Unguryte A. Inhibition of inorganic pyrophosphatase of animal mitochondria by calcium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90486-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis H., Romero I., Gómez-Puyou A. The phosphate-pyrophosphate exchange and hydrolytic reactions of the membrane-bound pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum: effects of Mg2+, phosphate, and pyrophosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Feb 1;236(2):766–774. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90682-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis H., Romero I. The phosphate-pyrophosphate exchange and hydrolytic reactions of the membrane-bound pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum: effects of pH and divalent cations. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Jun;19(3):255–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00762416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperman B. S. The mechanism of action of yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1982;87:526–548. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)87030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josse J. Constitutive inorganic pyrophosphatase of Escherichia coli. II. Nature and binding of active substrate and the role of magnesium. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):1948–1955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. L., Minton N. J. Energy-linked reactions in photosynthetic bacteria. VI. Inorganic pyrophosphate-driven ATP synthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Nov;147(1):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. J., Feldman F., Sperow J. W., Butler L. G. Kinetic effects of inorganic pyrophosphate analogs on several inorganic pyrophosphate hydrolyzing enzymes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3338–3341. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemme J. H., Gest H. Regulation of the cytoplasmic inorganic pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 26;22(4):529–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight W. B., Fitts S. W., Dunaway-Mariano D. Investigation of the catalytic mechanism of yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4079–4086. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. Microbial inorganic pyrophosphatases. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):169–178. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.169-178.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. A., Butler L. G. Yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. 3. Kinetics of Ca 2+ inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7315–7319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. A., Butler L. G. Yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. II. Kinetics of Mg 2+ activation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7308–7314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F. Approaches to kinetic studies on metal-activated enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:257–294. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle J., Mitchell R., Mitchell P. Proton-translocating pyrophosphatase of Rhodospirillum rubrum. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 15;23(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randahl H. Characterization of the membrane-bound inorganic pyrophosphatase in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec;102(1):251–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb06287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport T. A., Höhne W. E., Reich J. G., Heitmann P., Rapoport S. M. A kinetic model for the action of the inorganic pyrophosphatase from bakers' yeast. The activating influence of magnesium ions. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 27;26(2):237–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridlington J. W., Butler L. G. Yeast inorganic pyrophosphatase. I. Binding of pyrophosphate, metal ion, and metal ion-pyrophosphate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7303–7307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarm H. M., Vigenschow H., Knobloch K. Kinetic characterization and partial purification of the membrane-bound inorganic pyrophosphatase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Feb;367(2):127–133. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unguryte A., Smirnova I. N., Baykov A. A. Kinetic models for the action of cytosolic and mitochondrial inorganic pyrophosphatases of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


