Abstract
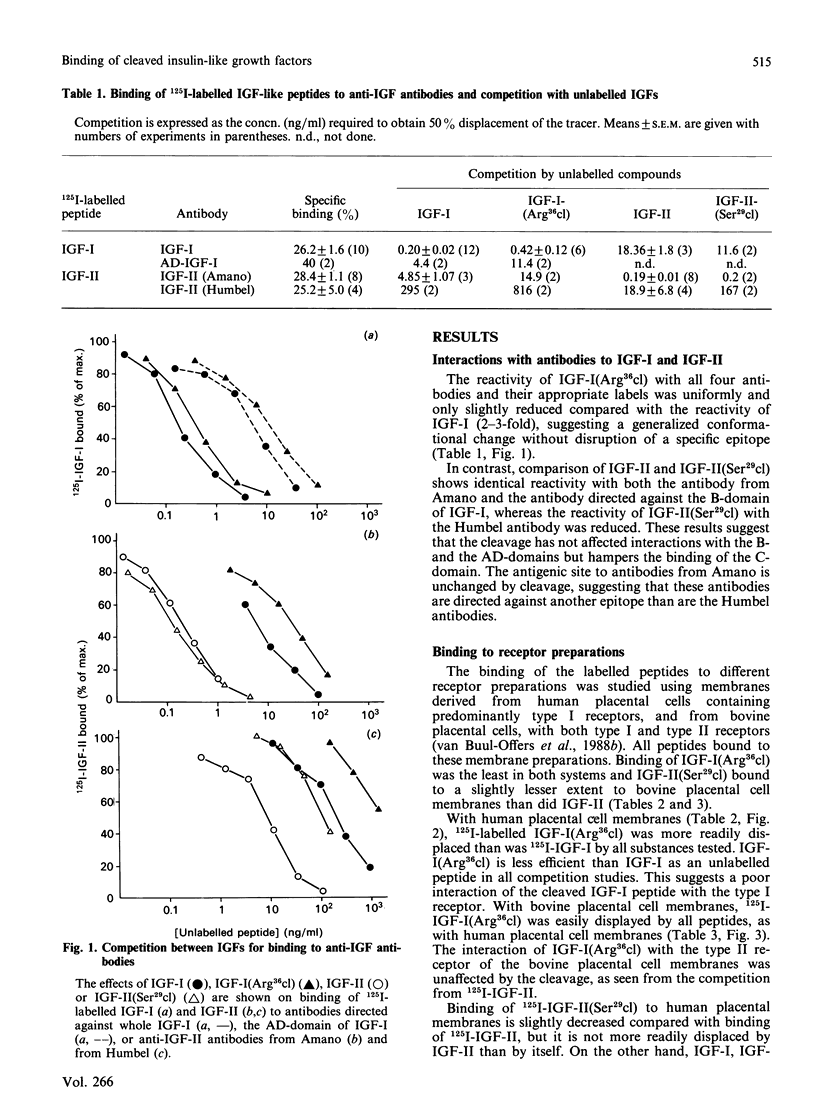
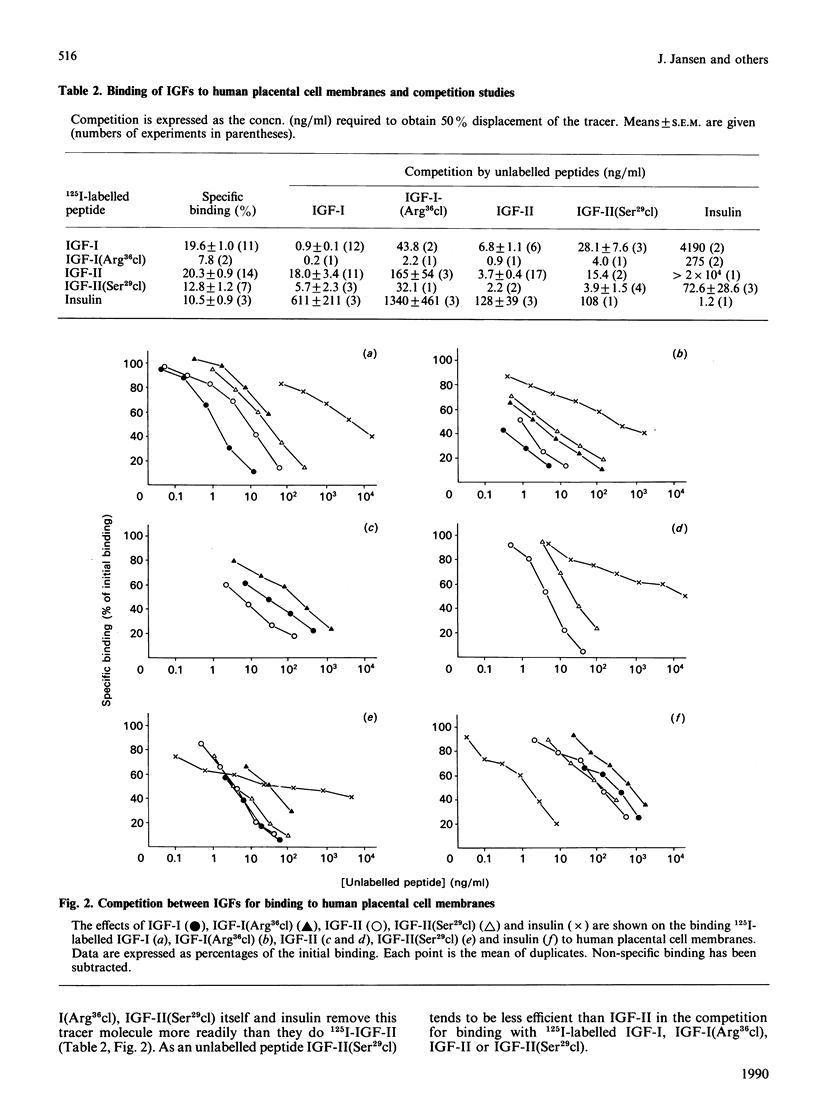
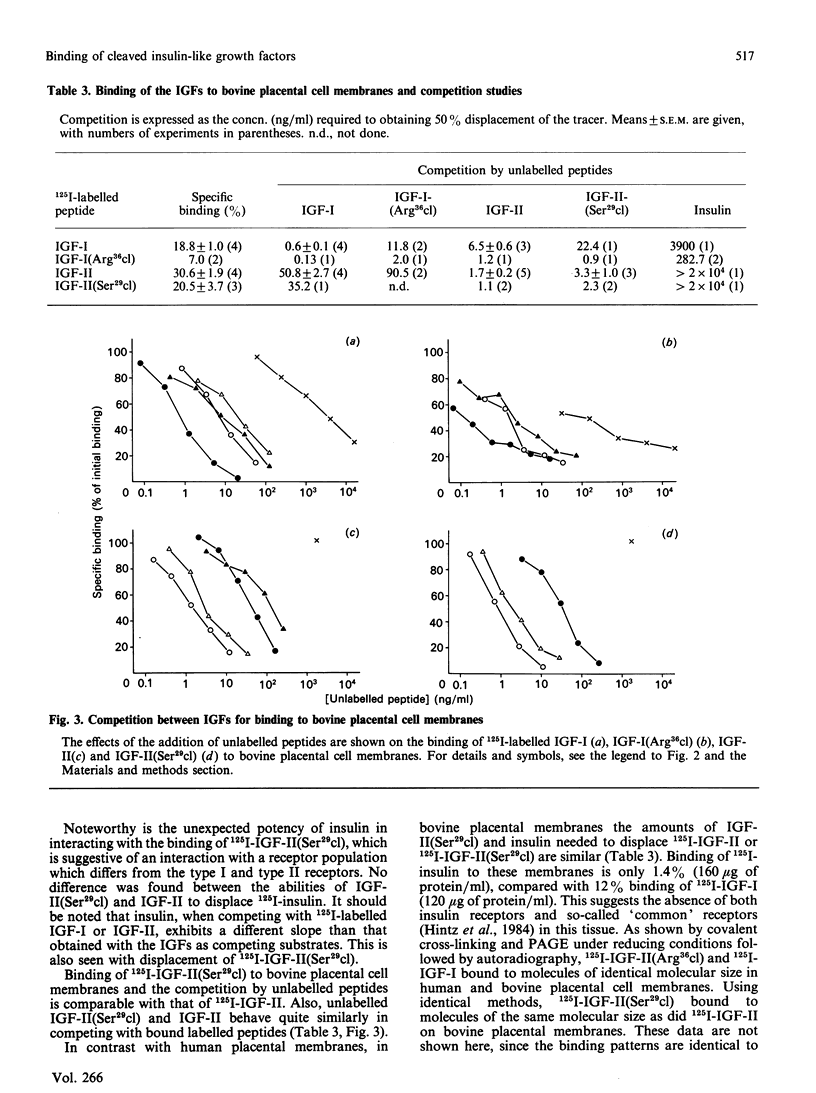
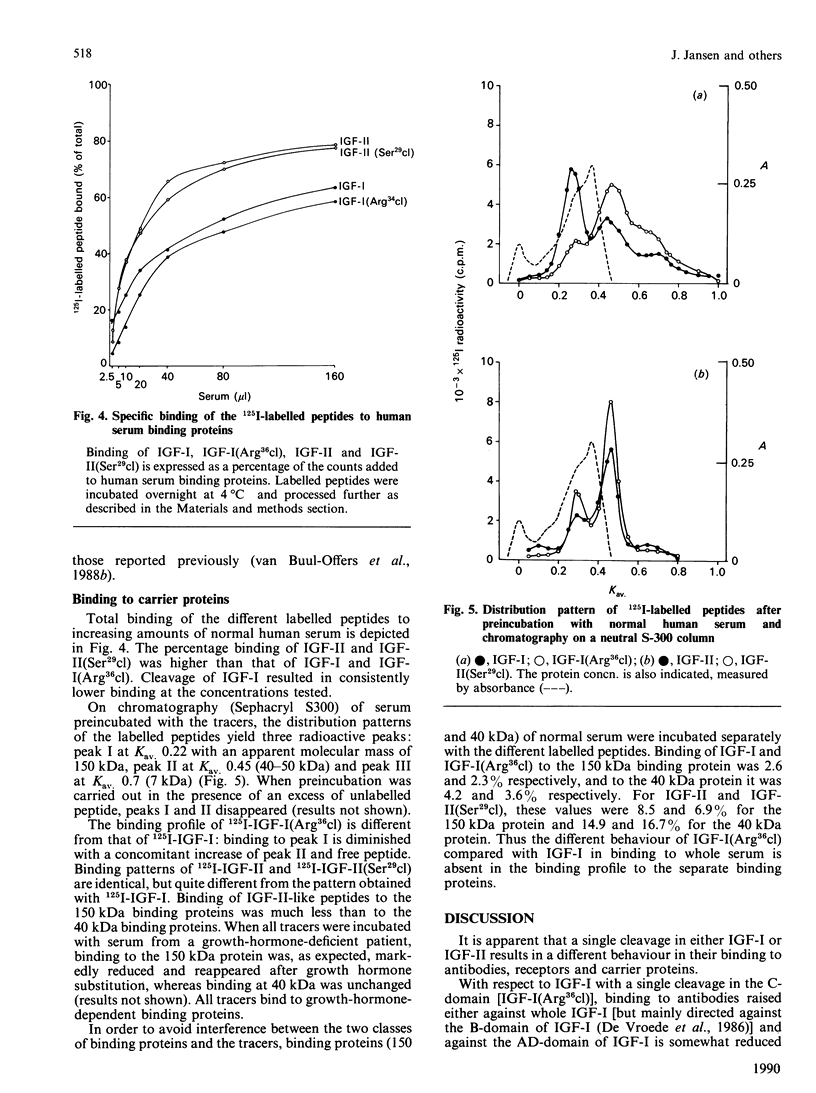
Two somatomedin-like peptides were extracted from Cohn fraction IV of human plasma and brought to homogeneity: one focused at pH 7.8 and the other at pH less than 5.6. Each consisted of two peptide chains interlinked by disulphide bonds. The basic peptide was identical to insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and had a single cleavage in the C-domain before Arg37 [IGF-I(Arg36cl)]. The acid peptide showed identity with IGF-II, with a cleavage in the B-domain before Arg30 [IGF-II(Ser29cl)]. The effects of these cleavages on the characteristics of binding to type I and type II receptor sites, to binding proteins and to antibodies was studied. Binding of IGF-I(Arg36cl) to antibodies directed against the B-domain or against the AD-domain of IGF-I was the same as IGF-I binding. Thus the cleavage does not influence these antigenic sites. In contrast, binding of IGF-I(Arg36cl) to the type I receptor on human and bovine placental cell membranes was markedly decreased compared with IGF-I binding. Binding to the insulin receptor on human placental cell membranes was slightly diminished, whereas the interaction with specific type II receptors on bovine placental cell membranes was unaffected. There was only a minor influence of the cleavage on the region involved in binding to binding proteins. The cleavage in IGF-II(Ser29cl) diminished binding to antibodies directed against the C-domain of IGF-II, compared with binding of IGF-II itself. Binding to receptors (type I and type II) was changed less profoundly. With 125I-labelled IGF-II(Ser29cl), less insulin was needed in order to obtain 50% displacement of the tracer compared with displacement of 125I-labelled IGF-II. The cleaved form of IGF-II probably has a greater affinity towards the common receptor population than does native IGF-II. Binding to binding proteins was not affected by the cleavage in IGF-II.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banskota N. K., Carpentier J. L., King G. L. Processing and release of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I by macro- and microvascular endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Nov;119(5):1904–1913. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-5-1904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Yorek M. Processing of insulin-like growth factors I and II by capillary and large vessel endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Mar;118(3):1072–1080. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-3-1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne M. L., Applebaum J., Chicchi G. G., Hayes N. S., Green B. G., Cascieri M. A. Structural analogs of human insulin-like growth factor I with reduced affinity for serum binding proteins and the type 2 insulin-like growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6233–6239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W. F., Ranke M. B., Bierich J. R. Isolation and partial characterization of six somatomedin-like peptides from human plasma Cohn fraction IV. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1986 Feb;111(2):271–284. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1110271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Humbel R. E. Tertiary structures, receptor binding, and antigenicity of insulinlike growth factors. Fed Proc. 1983 Jun;42(9):2592–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor: a model for tertiary structure accounting for immunoreactivity and receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Chicchi G. G., Applebaum J., Hayes N. S., Green B. G., Bayne M. L. Mutants of human insulin-like growth factor I with reduced affinity for the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3229–3233. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Insulin-like growth factor II binding to the type I somatomedin receptor. Evidence for two high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9268–9273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J. The effect of different isolation procedures on the yields of insulin-like growth factors from human plasma. Prep Biochem. 1982;12(1):57–76. doi: 10.1080/00327488208065550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dafgård E., Bajaj M., Honegger A. M., Pitts J., Wood S., Blundell T. The conformation of insulin-like growth factors: relationships with insulins. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;3:53–64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_3.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Kapadia M., Mariz I. Serum somatomedin binding proteins: physiologic significance and interference in radioligand assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Mar;109(3):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vroede M. A., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P., Joshi S., Burke G. T., Katsoyannis P. G. Hybrid molecules containing the B-domain of insulin-like growth factor I are recognized by carrier proteins of the growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vroede M. A., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P., Ogawa H., Joshi S., Burke G. T., Katsoyannis P. G. Mitogenic activity and receptor reactivity of hybrid molecules containing portions of the insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-II, and insulin molecules. Diabetes. 1986 Mar;35(3):355–361. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.3.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg G., Holmgren A. Degradation of somatomedins by the thioredoxin system. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 8;183(1):52–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80952-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Thorsson A. V., Enberg G., Hall K. IGF-II binding on human lymphoid cells: demonstration of a common high affinity receptor for insulin like peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):774–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in fetal and adult bovine serum. Purification, primary structures, and immunological cross-reactivities. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi S., Burke G. T., Katsoyannis P. G. Synthesis of an insulin-like compound consisting of the A chain of insulin and a B chain corresponding to the B domain of human insulin-like growth factor I. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4208–4214. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi S., Ogawa H., Burke G. T., Tseng L. Y., Rechler M. M., Katsoyannis P. G. Structural features involved in the biological activity of insulin and the insulin-like growth factors: A27 insulin/BIGF-I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90923-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Samuels B., Danho W., Bullesbach E. E., Gattner H. G. Synthesis and characterization of molecular hybrids of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. The role of the A-chain extension peptide. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10869–10873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Purification of somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:798–816. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. Y., Schwartz G. P., Sheikh M., Chen Z. Z., Joshi S., Wang J. F., Nissley S. P., Burke G. T., Katsoyannis P. G., Rechler M. M. Hybrid molecules containing the A-domain of insulin-like growth factor-I and the B-chain of insulin have increased mitogenic activity relative to insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):672–679. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schravendijk C. F., Hooghe-Peters E. L., Van den Brande J. L., Pipeleers D. G. Receptors for insulin-like growth factors and insulin on murine fetal cortical brain cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):228–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90967-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Biological and immunological properties of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) I and II. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):3–30. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buul-Offers S., Hoogerbrugge C. M., Branger J., Feijlbrief M., Van den Brande J. L. Growth-stimulating effects of somatomedin-/insulin-like peptides in Snell dwarf mice. Horm Res. 1988;29(5-6):229–236. doi: 10.1159/000181009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buul-Offers S., Hoogerbrugge C. M., de Poorter T. L. The bovine placenta: a specific radioreceptor assay for both insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor II. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Jun;118(2):306–313. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


