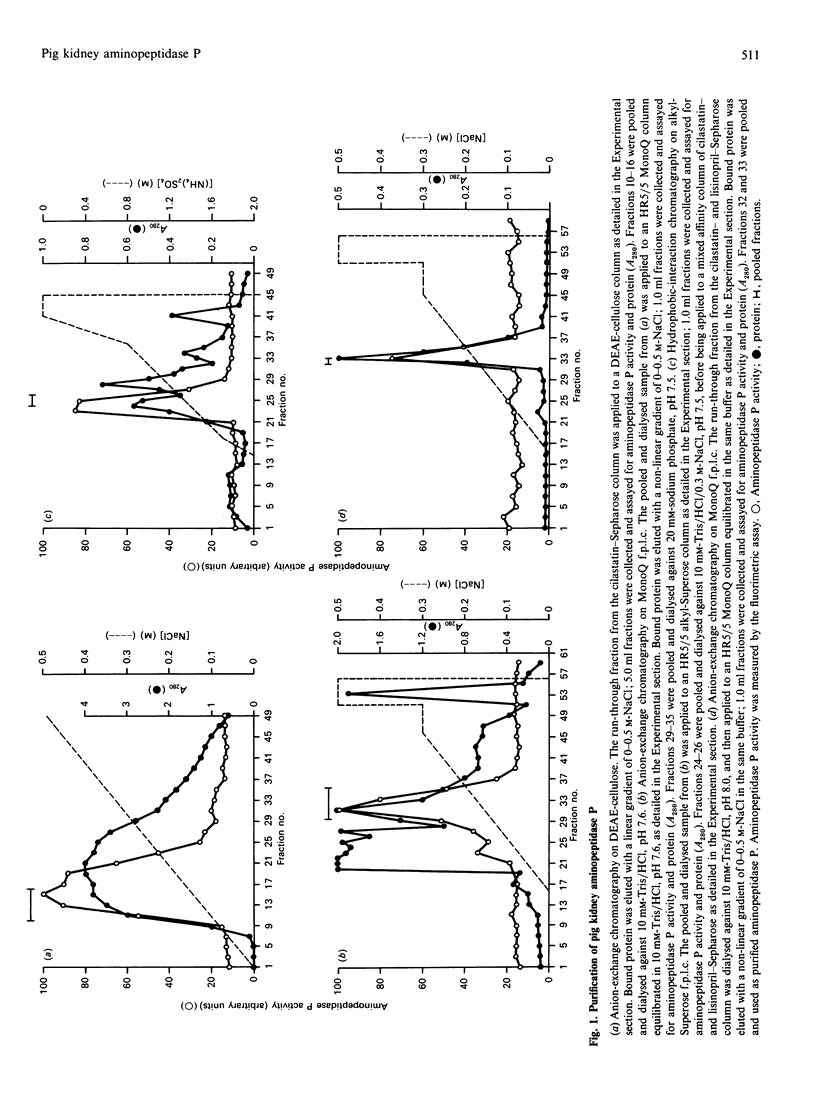
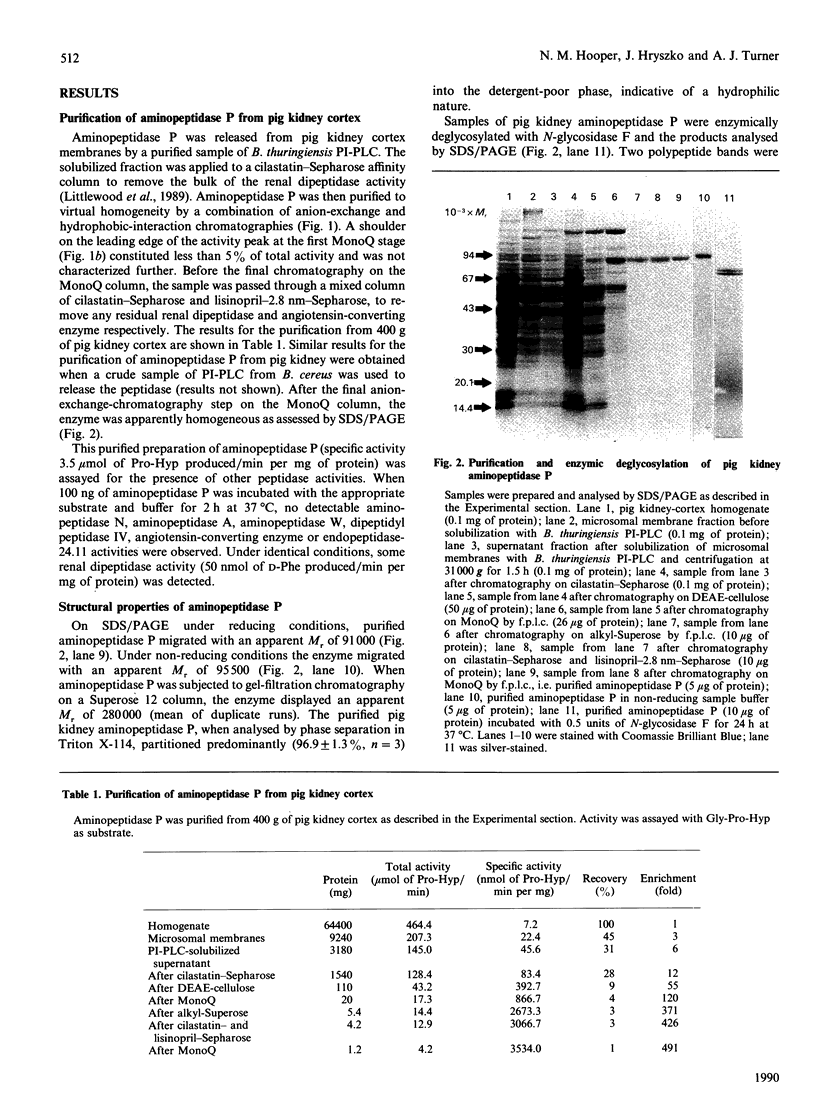
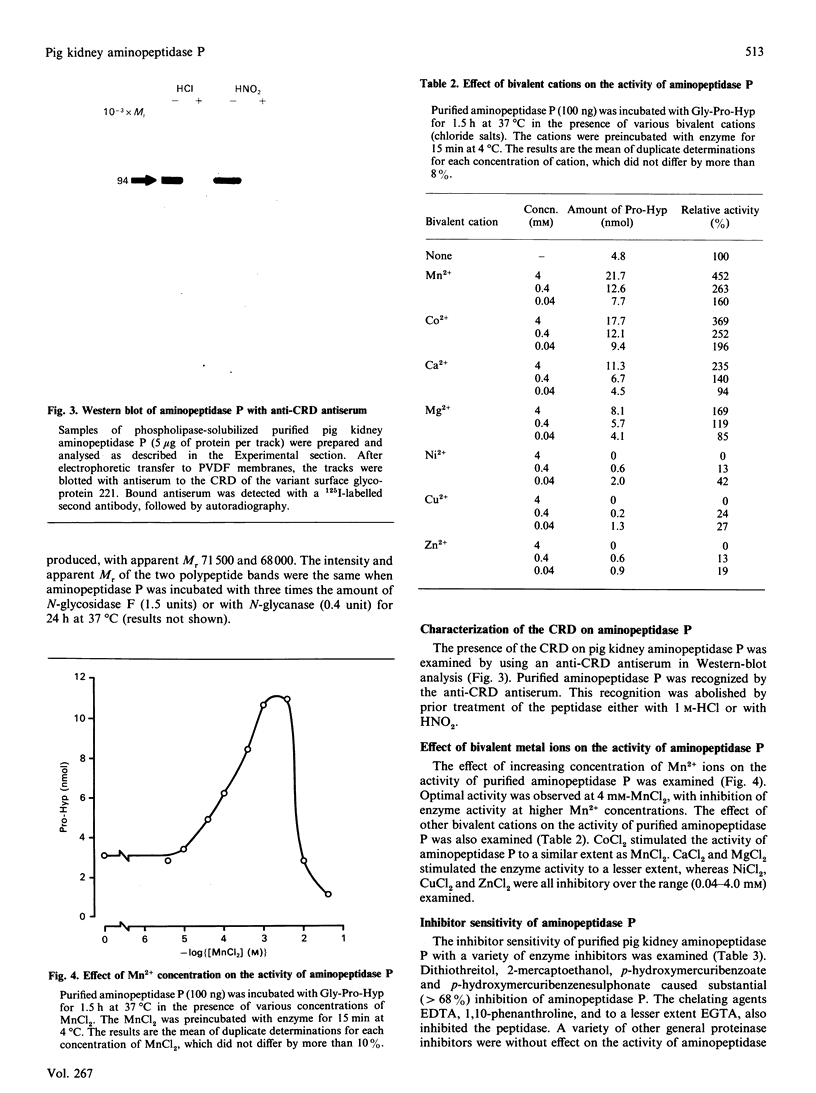
Abstract
Aminopeptidase P (EC 3.4.11.9) was solubilized from pig kidney membranes with bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) and then purified by a combination of anion-exchange and hydrophobic-interaction chromatographies. Contaminating peptidase activities were removed by selective affinity chromatography. The purified enzyme was apparently homogeneous on SDS/PAGE with an Mr of 91,000. Enzymic deglycosylation revealed that aminopeptidase P is a glycoprotein, with up to 25% by weight of the protein being due to the presence of N-linked sugars. The phospholipase-solubilized aminopeptidase P was recognized by an antiserum to the cross-reacting determinant (CRD) characteristic of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor. This recognition was abolished by mild acid treatment or deamination with HNO2, indicating that the CRD was due exclusively to the inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate ring epitope generated by the action of PI-PLC. The activity of aminopeptidase P was inhibited by chelating agents and was stimulated by Mn2+ or Co2+ ions, confirming the metallo-enzyme nature of this peptidase. Selective inhibitors of other aminopeptidases (actinonin, amastatin, bestatin and puromycin) had little or no inhibitory effect.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. J., Forrester L. J., Zahler W. L., Burks M. Beta-lactamase activity of purified and partially characterized human renal dipeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14586–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Turner M. J. The membrane form of variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):349–352. doi: 10.1038/302349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Nordwig A. Influence of serum albumin on the activity of a microsomal aminopeptidase. FEBS Lett. 1970 Aug 17;9(4):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Nordwig A. The cleavage of prolyl peptides by kidney peptidases. Partial purification of an "X-prolyl-aminopeptidase" from swine kidney microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):364–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. J., Pillay G., Rosenthal T., Yaron A. Aminopeptidase P activity in rat organs and human serum. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):476–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90423-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Keen J. N., Turner A. J. Characterization of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored human renal dipeptidase reveals that it is more extensively glycosylated than the pig enzyme. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):429–433. doi: 10.1042/bj2650429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Keen J., Pappin D. J., Turner A. J. Pig kidney angiotensin converting enzyme. Purification and characterization of amphipathic and hydrophilic forms of the enzyme establishes C-terminal anchorage to the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):85–93. doi: 10.1042/bj2470085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Aminopeptidase P is anchored by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Differential solubilization by detergents can predict a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):865–869. doi: 10.1042/bj2500865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Isolation and characterization of the amphipathic form of renal dipeptidase and hydrolysis of its glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor by an activity in plasma. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2610811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Isolation of two differentially glycosylated forms of peptidyl-dipeptidase A (angiotensin converting enzyme) from pig brain: a re-evaluation of their role in neuropeptide metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2410625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., Macnair R. D. Peptidases of the kidney microvillus membrane. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(11-12):1575–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasch J., Koelsch R., Ladhoff A. M., Hartrodt B. Is the proline-specific aminopeptidase P of the intestinal brush border an integral membrane enzyme? Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(7):833–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasch J., Koelsch R., Steinmetzer T., Neumann U., Demuth H. U. Enzymic properties of intestinal aminopeptidase P: a new continuous assay. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80891-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood G. M., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Affinity purification, characterization and localization of the phospholipase C-solubilized form of renal dipeptidase. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2570361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol: a versatile anchor for cell surface proteins. FASEB J. 1989 Mar;3(5):1600–1608. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.5.2522071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orawski A. T., Susz J. P., Simmons W. H. Aminopeptidase P from bovine lung: solubilization, properties, and potential role in bradykinin degradation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Jun;75(2):123–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00229900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamze S. E., Ferguson M. A., Collins R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Characterization of the cross-reacting determinant (CRD) of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):527–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]