Abstract
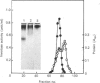
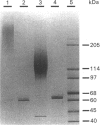
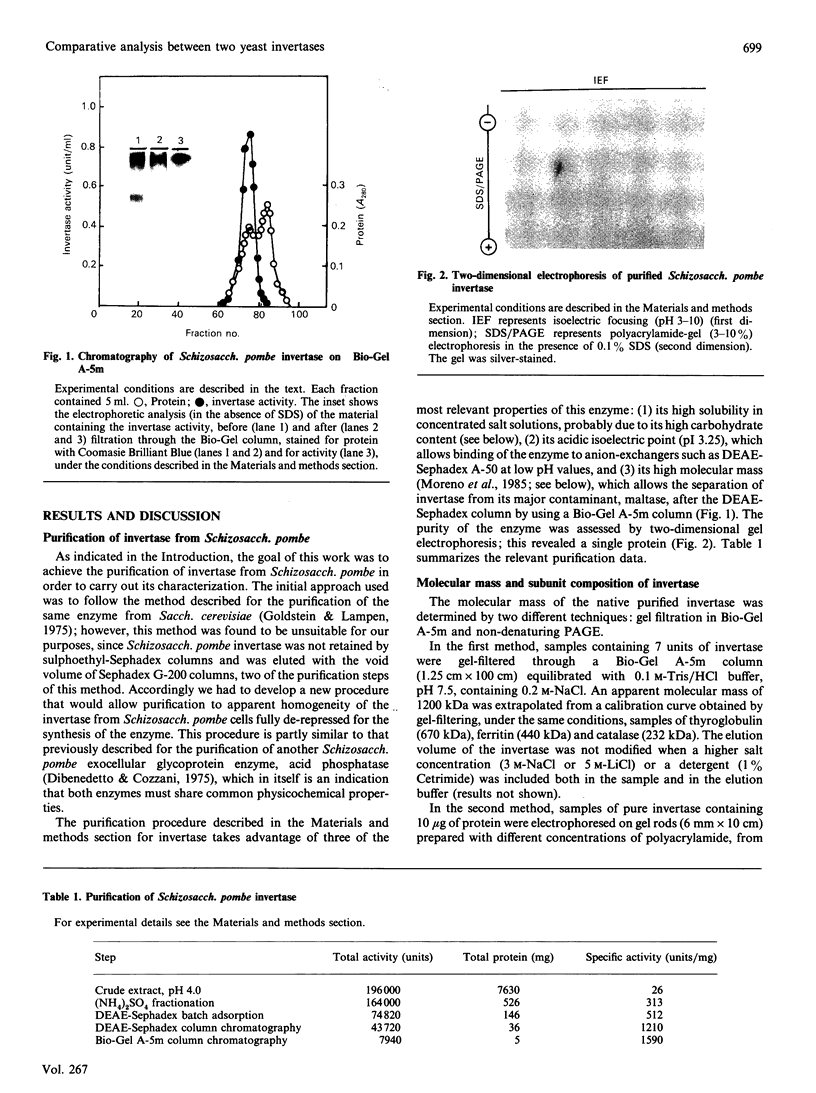
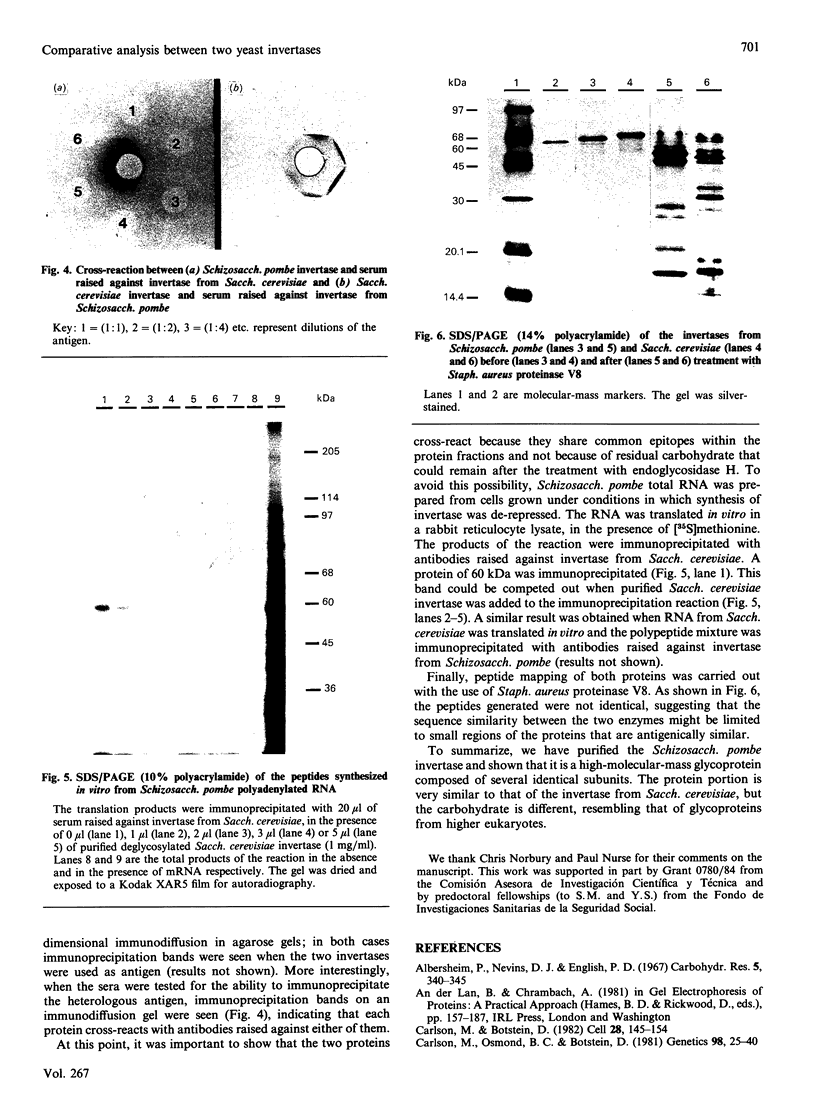
Invertase (EC 3.2.1.26) was purified to homogeneity from exponentially growing cells of Schizosaccharomyces pombe fully de-repressed for synthesis of the enzyme, and was shown to be a high-molecular-mass glycoprotein that can be dissociated in the presence of 8 M-urea/1% SDS into identical subunits with an apparent molecular mass of 205 kDa. The carbohydrate moiety, accounting for 67% of the total mass, is composed of equimolar amounts of mannose and galactose. There is a small amount of glucosamine, which is probably involved in the linkage to the protein moiety, since the enzyme is sensitive to treatment with endoglycosidase H. The composition of the carbohydrate moiety resembles that found in higher-eukaryotic glycoproteins and differs from glycoproteins found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The protein portion of each subunit is a polypeptide of molecular mass 60 kDa, very similar to the invertase of Sacch. cerevisiae. Both proteins cross-react with antibodies raised against the protein fractions of the other, indicating that the two enzymes are similar.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. Mutants of yeast defective in sucrose utilization. Genetics. 1981 May;98(1):25–40. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibenedetto G., Cozzani I. Nonspecific acid phosphatase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Purification and physical chemical properties. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2847–2852. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Rothman J. E. Compartmental organization of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel O., Wang S. F. Determination of enzymatic activity in polyacrylamide gels. I. Enzymes catalyzing the conversion of nonreducing substrates to reducing products. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón S., Lampen J. O. Purification of the internal invertase of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1567–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón S., Neumann N. P., Lampen J. O. Comparative study of the properties of the purified internal and external invertases from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1573–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón S., Ottolenghi P. Invertase isozymes and their localization in yeast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1967;36(5):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker T. C., Robbins P. W. Yeast mutants deficient in protein glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7466–7470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Simanis V., Nurse P. Fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe correctly excises a mammalian RNA transcript intervening sequence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):78–80. doi: 10.1038/318078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison J. M., Creanor J. Linear synthesis of sucrase and phosphatases during the cell cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 1969 Sep;5(2):373–391. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Ruíz T., Sánchez Y., Villanueva J. R., Rodríguez L. Subcellular localization and glycoprotein nature of the invertase from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Arch Microbiol. 1985 Sep;142(4):370–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00491906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann N. P., Lampen J. O. Purification and properties of yeast invertase. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):468–475. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]