Abstract
The abundance of the alpha and beta subunits of the GTP-binding proteins (G-proteins) that transduce hormonal messages to adenylate cyclase was assessed in adipocyte membranes from lean (+/+) and obese (ob/ob) mice, using ADP-ribosylation with bacterial toxin and immunodetection. Both methods revealed two Gs alpha species (48 and 42 kDa) in the membranes. Compared with those of lean mice, the membranes from obese mice contained substantially less of the 48 kDa species of Gs alpha, as assessed by both methods. ADP-ribosylation by pertussis toxin showed that only half as much ADP-ribose was incorporated into Gi alpha in the membranes from obese as compared with lean mice. Immunodetection revealed two separate Gi alpha peptides (39 and 40 kDa) and showed that the 40 kDa species was less abundant in the membranes from obese mice, whereas the amount of the 39 kDa species was similar in membranes from both lean and obese animals. Based on ADP-ribosylation assays, in membranes from lean mice the ratio Gs alpha/Gi alpha was 1:16, whereas in the membranes from obese mice it was 1:10. Similar amounts of immunodetectable beta peptide were found in both types of membranes. On the basis of the currently accepted dissociation model of adenylate cyclase activation, the decrease in the abundance of the Gi alpha subunit in adipocyte membranes from obese mice could account for the abnormal kinetics of the enzyme in these membranes.
Full text
PDF

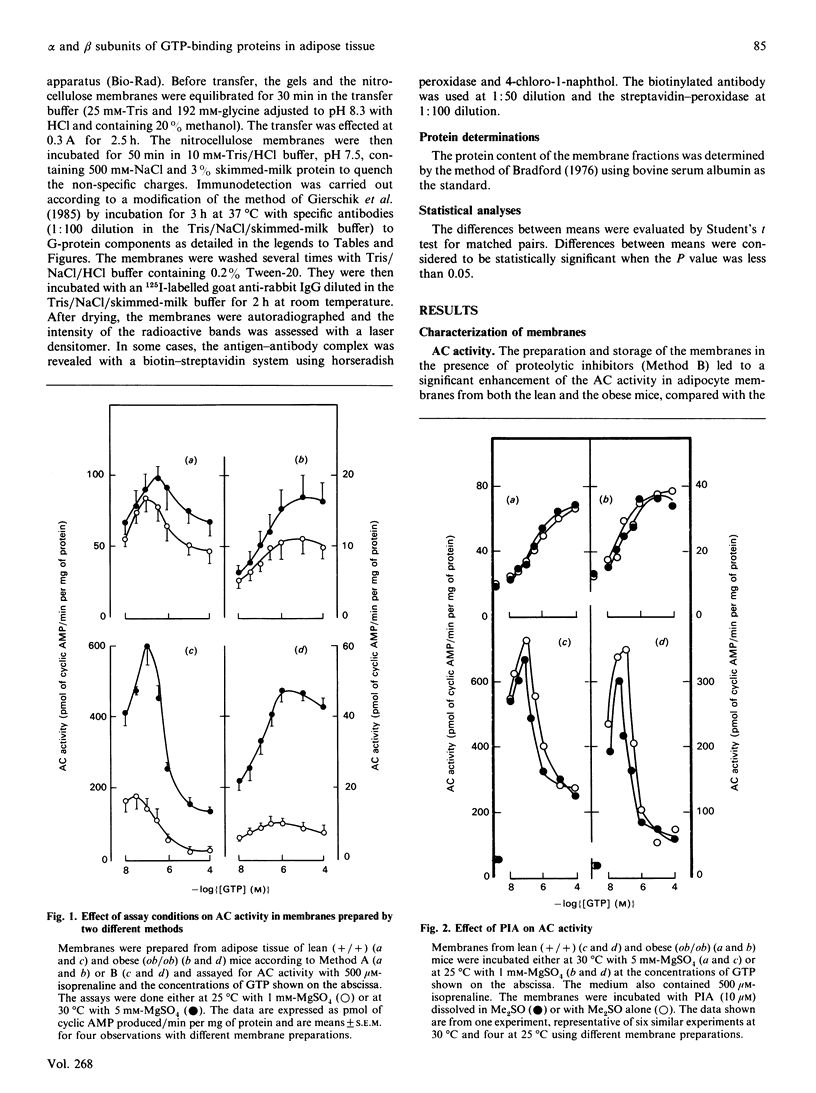
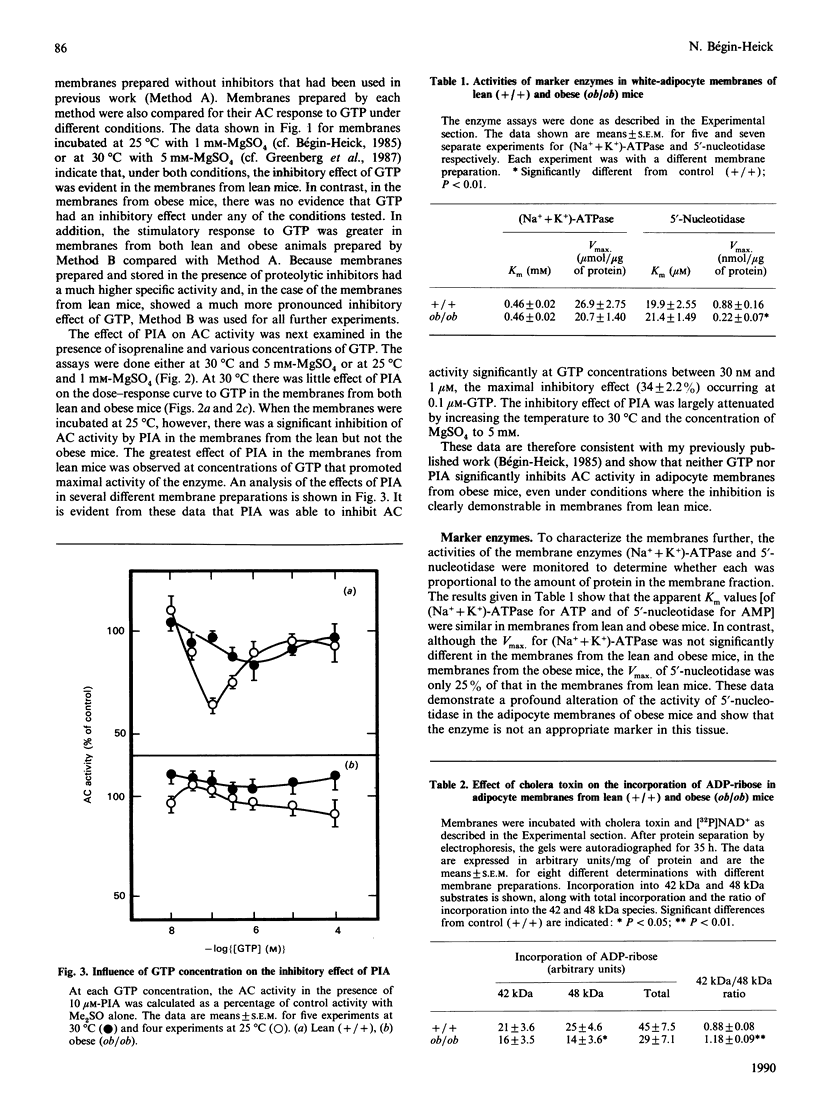
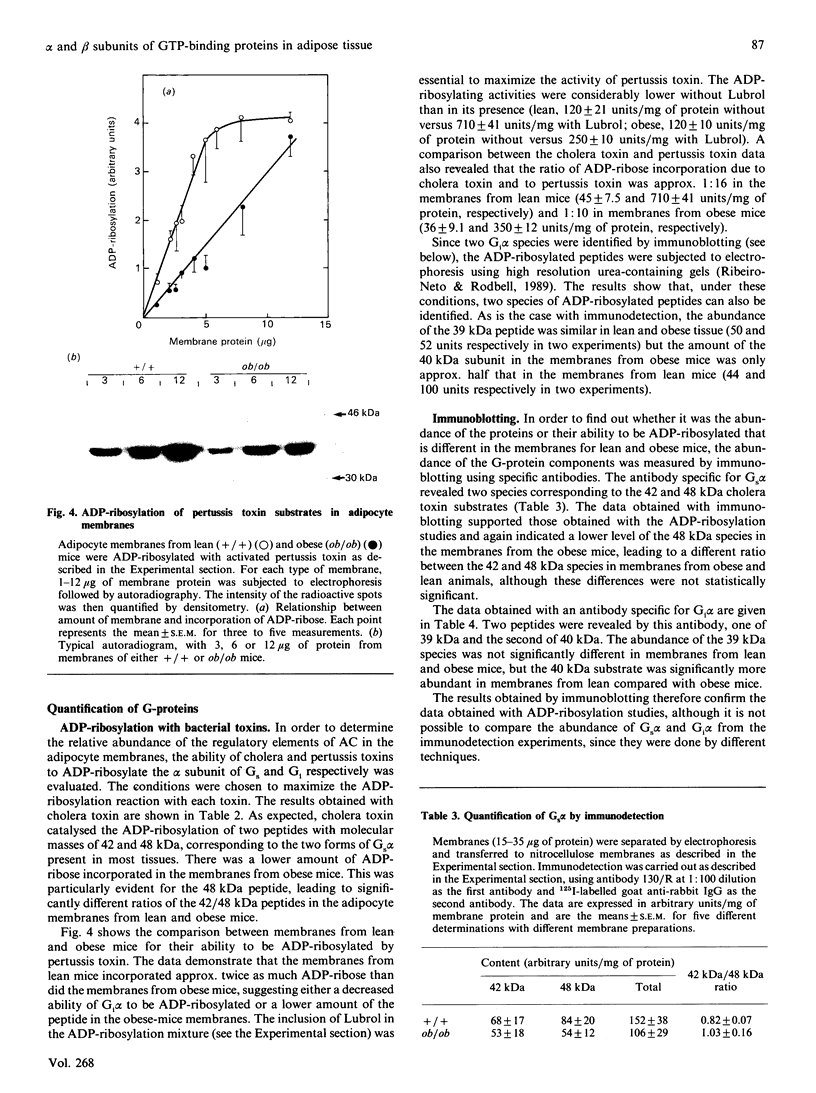


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley P. L., Ellison J., Sullivan K. A., Bourne H. R., Cox D. R. Chromosomal assignment of the murine Gi alpha and Gs alpha genes. Implications for the obese mouse. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15299–15301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Eversole-Cire P., Cohn V. H., Zollman S., Fournier R. E., Mohandas L. T., Nesbitt M., Lugo T., Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Chromosomal localization of genes encoding guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunits in mouse and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7642–7646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M. The presence of free G protein beta/gamma subunits in human neutrophils results in suppression of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Beiderman B., Steinberg F., Brothers V. M. Three adenylate cyclase phenotypes in S49 lymphoma cells produced by mutations of one gene. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;22(1):204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin-Heick N. Absence of the inhibitory effect of guanine nucleotides on adenylate cyclase activity in white adipocyte membranes of the ob/ob mouse. Effect of the ob gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6187–6193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin-Heick N., Coleman D. L. Effect of the genetic background and specific mutation on adenylate cyclase activity in obesity syndromes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;59(3):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin-Heick N., Welsh J. The regulation of adenylate cyclase in liver membranes of lean and obese mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;59(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A., Bardin C., Collins R., Simons C., Bray P., Spiegel A. Reduced expression of multiple forms of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory GTP-binding protein in pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7266–7269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M. ATPase and phosphatase activity of Na+,K+-ATPase: molar and specific activity, protein determination. Methods Enzymol. 1988;156:105–115. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)56013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Brown M. L., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K. Purification of the major GTP-binding proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7052–7059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Huerta-Bahena M. E., Malbon C. C. Hepatocyte beta-adrenergic responsiveness and guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C384–C389. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Codina J., Simons C., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. Antisera against a guanine nucleotide binding protein from retina cross-react with the beta subunit of the adenylyl cyclase-associated guanine nucleotide binding proteins, Ns and Ni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Freissmuth M., Gilman A. G. Expression of Gs alpha in Escherichia coli. Purification and properties of two forms of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):409–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Fisher M., Newsholme E. A. Maximum activities of enzymes involved in adenosine metabolism in adipose tissue of rats and mice under conditions of variations in insulin sensitivity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 5;676(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L. Evidence for altered expression of the GTP-dependent regulatory proteins, Gs and Gi, in adipocytes from aged rats. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):607–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2580607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. S., Taylor S. I., Londos C. Presence of a functional inhibitory GTP-binding regulatory component, Gi, linked to adenylate cyclase in adipocytes of ob/ob mice. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4564–4568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Ross E. M., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylate cyclase permanently uncoupled from hormone receptors in a novel variant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinsch K. D., Rosenthal W., Spicher K., Binder T., Gausepohl H., Frank R., Schultz G., Joost H. G. Adipocyte plasma membranes contain two Gi subtypes but are devoid of Go. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homburger V., Brabet P., Audigier Y., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Rouot B. Immunological localization of the GTP-binding protein Go in different tissues of vertebrates and invertebrates. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;31(4):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Gawler D. J., Milligan G., Wilson A. Multiple defects occur in the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein system in liver plasma membranes of obese (fa/fa) but not lean (Fa/Fa) Zucker rats: loss of functional Gi and abnormal Gs function. Cell Signal. 1989;1(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine F. J., Houslay M. D. Insulin and glucagon attenuate the ability of cholera toxin to activate adenylate cyclase in intact hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):447–452. doi: 10.1042/bj2510447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattera R., Codina J., Crozat A., Kidd V., Woo S. L., Birnbaumer L. Identification by molecular cloning of two forms of the alpha-subunit of the human liver stimulatory (GS) regulatory component of adenylyl cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Saggerson E. D. Chemically induced hypothyroidism produces elevated amounts of the alpha subunit of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein (Gi) and the beta subunit common to all G-proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Wolf L. G., Gill D. M. The stimulatory guanine-nucleotide regulatory unit of adenylate cyclase from bovine cerebral cortex. ADP-ribosylation and purification. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):325–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2410325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold C. I., Boyle D. B., Smith C. C., Brown K. N. Stage specific protein and nucleic acid synthesis during the asexual cycle of the rodent malaria Plasmodium chabaudi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Jan;5(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J., Milligan G. Guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins Gi and Gs in fat-cells from normal, hypothyroid and obese human subjects. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):843–847. doi: 10.1042/bj2600843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Rodbell M. Pertussis toxin induces structural changes in G alpha proteins independently of ADP-ribosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F., Mattera R., Grenet D., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L., Field J. B. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of G proteins by pertussis and cholera toxin in isolated membranes. Different requirements for and effects of guanine nucleotides and Mg2+. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jul;1(7):472–481. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-7-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Molecular basis for two forms of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. L., Kahn C. R. Insulin inhibits pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of G-proteins. Evidence for a novel interaction between insulin receptors and G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15546–15552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmer B. P., Tsao J. Isolation of forskolin-resistant adrenal cells defective in the adenylate cyclase system. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5376–5379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suki W. N., Abramowitz J., Mattera R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. The human genome encodes at least three non-allellic G proteins with alpha i-type subunits. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80900-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Regulation of G-proteins in differentiation. Altered ratio of alpha- to beta-subunits in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]