Abstract
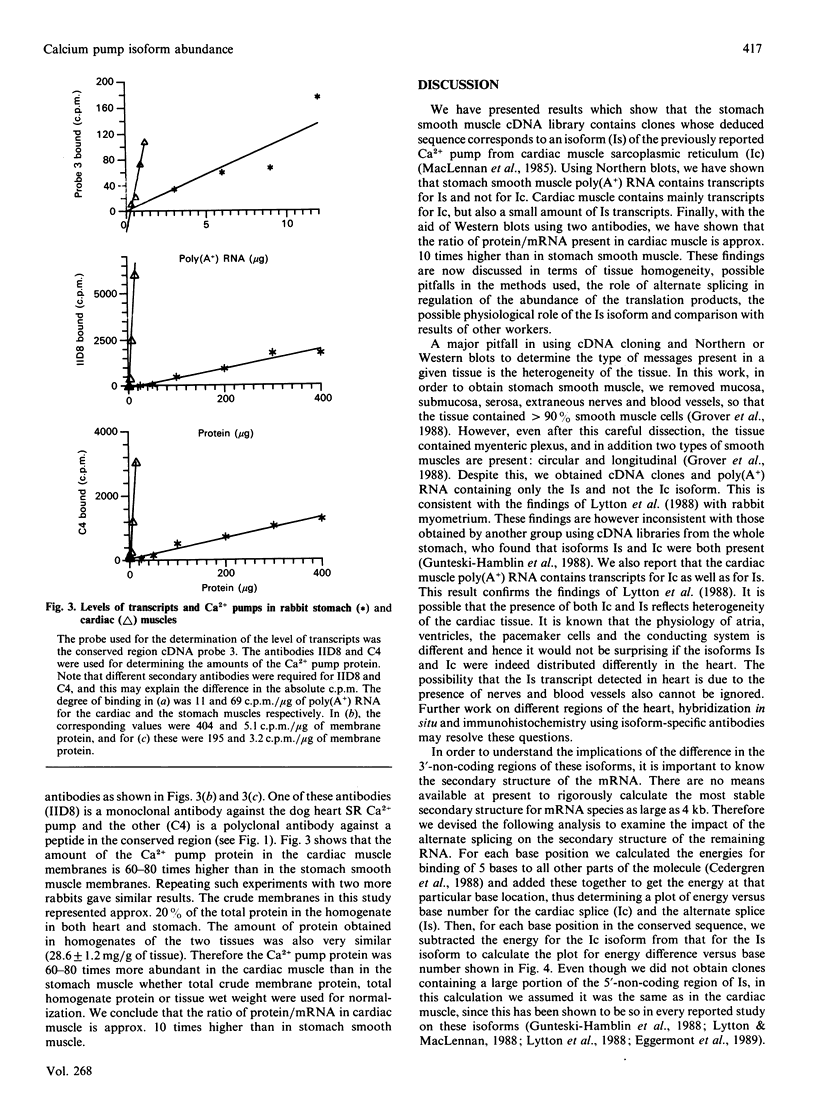
Rabbit stomach smooth muscle contains mRNA for an internal Ca2+ pump identical in sequence to that reported for rabbit uterus [Lytton, Zarain-Herzberg, Periasamy & MacLennan (198) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 7059-7065]. This is an alternatively spliced form (Is) of the cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump (Ic). The splicing results in replacement of the last 4 amino acids (Ala-Ile-Leu-Glu) present in Ic by 49 amino acids and by a different 3'-non-coding region. Using cDNA probes against the conserved and the alternatively spliced regions, we determined that poly(A+) RNA isolated from rabbit stomach smooth muscle did not contain any transcripts for Ic. The poly(A+) RNA from cardiac muscle contained transcripts mostly for Ic, but also some for Is. The abundance of the Ca2(+)-pump transcripts as measured by the binding of a cDNA probe against the conserved region to poly(A+) RNA was 6-8 times higher in cardiac than in smooth muscle. The amount of the corresponding pump protein, measured using two antibodies, was 60-80 times higher in cardiac membranes than in smooth muscle membranes. Thus the protein-to-transcript level was approx. 10-fold higher in the cardiac muscle. We conclude that the regulation of the abundance of this protein occurs at steps leading to the formation of the mature mRNA for the two splices, which may differ in their translation efficiency.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedergren R., Gautheret D., Lapalme G., Major F. A secondary and tertiary structure editor for nucleic acids. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):143–146. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermont J. A., Wuytack F., De Jaegere S., Nelles L., Casteels R. Evidence for two isoforms of the endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+ pump in pig smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):757–761. doi: 10.1042/bj2600757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A. K. Ca-pumps in smooth muscle: one in plasma membrane and another in endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Calcium. 1985 Jun;6(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A. K. Monoclonal antibody against an epitope on the cytoplasmic aspect of the plasma membrane calcium pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19510–19512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A. K., Samson S. E. Effect of superoxide radical on Ca2+ pumps of coronary artery. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C297–C303. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A. K., Samson S. E. Pig coronary artery smooth muscle: substrate and pH dependence of the two calcium pumps. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C529–C534. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunteski-Hamblin A. M., Greeb J., Shull G. E. A novel Ca2+ pump expressed in brain, kidney, and stomach is encoded by an alternative transcript of the slow-twitch muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase gene. Identification of cDNAs encoding Ca2+ and other cation-transporting ATPases using an oligonucleotide probe derived from the ATP-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15032–15040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruys V., Wathelet M., Poupart P., Contreras R., Fiers W., Content J., Huez G. The 3' untranslated region of the human interferon-beta mRNA has an inhibitory effect on translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNAs from human kidney coding for two alternatively spliced products of the cardiac Ca2+-ATPase gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15024–15031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Zarain-Herzberg A., Periasamy M., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of the mammalian smooth muscle sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7059–7065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. The calcium pump of the surface membrane and of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:473–485. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Greeb J. Molecular cloning of two isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca2+-transporting ATPase from rat brain. Structural and functional domains exhibit similarity to Na+,K+- and other cation transport ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8646–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Rickles R. J., Vassalli J. D. Antisense RNA directed against the 3' noncoding region prevents dormant mRNA activation in mouse oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):680–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2456615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Filoteo A. G., Stanford D. R., Wieben E. D., Penniston J. T., Strehler E. E., Fischer R., Heim R., Vogel G., Mathews S. Complete primary structure of a human plasma membrane Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14152–14159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Morel N., Godfraind T. Differentiation of Ca2+ pumps linked to plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum in the microsomal fraction from intestinal smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 21;649(3):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L., De Schutter G., Casteels R. Demonstration of the phosphorylated intermediates of the Ca2+-transport ATPase in a microsomal fraction and in a (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase purified from smooth muscle by means of calmodulin affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Raeymaekers L., Verbist J., De Smedt H., Casteels R. Evidence for the presence in smooth muscle of two types of Ca2+-transport ATPase. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):445–451. doi: 10.1042/bj2240445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Bastie D., Wisnewsky C., Schwartz K., Lompré A. M. (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-dependent ATPase mRNA from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum differs from that in cardiac and fast skeletal muscles. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]