Abstract
The S1 subunit of pertussis toxin catalyses the hydrolysis of NAD+ (NAD+ glycohydrolysis) and the NAD(+)-dependent ADP-ribosylation of guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins. Recently, the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin was shown to be photolabelled by using radiolabelled NAD+ and u.v.; the primary labelled residue was Glu-129, thereby implicating this residue in the binding of NAD+. Studies from various laboratories have shown that the N-terminal portion of the S1 subunit, which shows sequence similarity to cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin, is important to the maintenance of both glycohydrolase and transferase activity. In the present study the photolabelling technique was applied to the analysis of a series of recombinant-derived S1 molecules that possessed deletions or substitutions near the N-terminus of the S1 molecule. The results revealed a positive correlation between the extent of photolabelling with NAD+ and the magnitude of specific NAD+ glycohydrolase activity exhibited by the mutants. Enzyme kinetic analyses of the N-terminal mutants also identified a mutant with substantially reduced activity, a depressed photolabelling efficiency and a markedly increased Km for NAD+. The results support a direct role for the N-terminal region of the S1 subunit in the binding of NAD+, thereby providing a rationale for the effect of mutations in this region on enzymic activity.
Full text
PDF

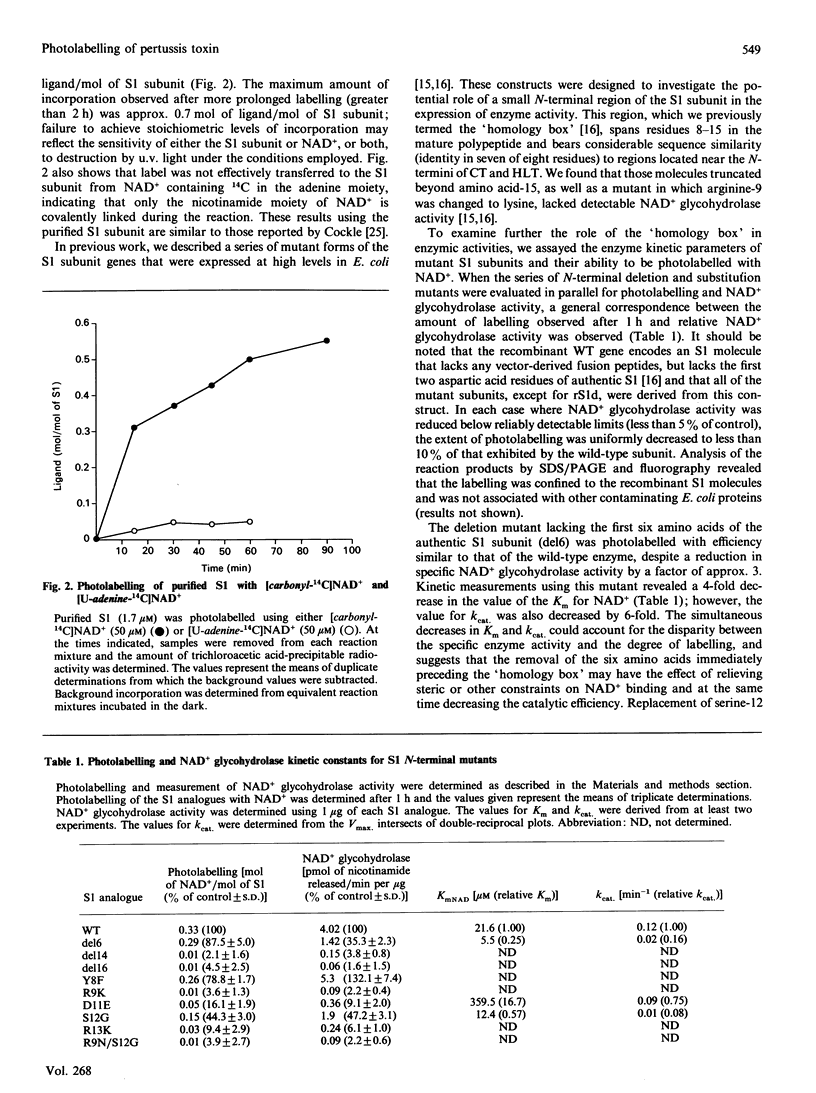


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. L., Belshe R. B., Bartram J. Differences in reactogenicity and antigenicity of acellular and standard pertussis vaccines combined with diphtheria and tetanus in infants. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):731–737. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri J. T., Cortina G. ADP-ribosyltransferase mutations in the catalytic S-1 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1934–1941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1934-1941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri J. T., Mende-Mueller L. M., Rappuoli R., Collier R. J. Photolabeling of Glu-129 of the S-1 subunit of pertussis toxin with NAD. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3549–3554. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3549-3554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri J. T., Rappuoli R., Collier R. J. Expression of the S-1 catalytic subunit of pertussis toxin in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1321–1323. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1321-1323.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N., Cieplak W., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Sato H., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin S1 mutant with reduced enzyme activity and a conserved protective epitope. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2459776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Kenimer J. G., Manclark C. R. Role of the A subunit of pertussis toxin in alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.24-28.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiau C., Petre J., Van Damme J., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J. Protein-chemical analysis of pertussis toxin reveals homology between the subunits S2 and S3, between S1 and the A chains of enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli and identifies S2 as the haptoglobin-binding subunit. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80839-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Collier R. J. Active site of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Glutamic acid 553 is photolabeled by NAD and shows functional homology with glutamic acid 148 of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8707–8711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Collier R. J. NAD binding site of diphtheria toxin: identification of a residue within the nicotinamide subsite by photochemical modification with NAD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., McCloskey J. A., Crain P. F., Oppenheimer N. J., Marschner T. M., Collier R. J. Photoaffinity labeling of diphtheria toxin fragment A with NAD: structure of the photoproduct at position 148. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Morris C. F., Chen K. K., Sato H., Keith J. M. Identification of a region in the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin that is required for enzymatic activity and that contributes to the formation of a neutralizing antigenic determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4667–4671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockle S. A. Identification of an active-site residue in subunit S1 of pertussis toxin by photocrosslinking to NAD. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80652-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. M., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: substitution of glutamic acid 553 with aspartic acid drastically reduces toxicity and enzymatic activity. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4967–4971. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4967-4971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. ADP ribosylation of the specific membrane protein of C6 cells by islet-activating protein associated with modification of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobet Y., Cieplak W., Jr, Smith S. G., Keith J. M. Effects of mutations on enzyme activity and immunoreactivity of the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3660–3662. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3660-3662.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Capiau C., Feron C. Identification of amino acid residues essential for the enzymatic activities of pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Cieplak W., Marchitto K. S., Sato H., Keith J. M. Activities of complete and truncated forms of pertussis toxin subunits S1 and S2 synthesized by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2546-2553.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Lobet Y., Feron C., Cieplak W., Keith J. M. The role of cysteine 41 in the enzymatic activities of the pertussis toxin S1 subunit as investigated by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4552–4559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Bergman R. K., Sadowski P. L. Biological activities of crystalline pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Bartoloni A., Perugini M., Rappuoli R. Expression and immunological properties of the five subunits of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):963–967. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.963-967.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Bartoloni A., Prugnola A., Silvestri S., Rappuoli R. Subunit S1 of pertussis toxin: mapping of the regions essential for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7521–7525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Covacci A., Bartoloni A., Perugini M., Nencioni L., De Magistris M. T., Villa L., Nucci D., Manetti R., Bugnoli M. Mutants of pertussis toxin suitable for vaccine development. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.2683073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Kimura M., Fukumi H. Development of a pertussis component vaccine in Japan. Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):122–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Barbieri J. T., Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin. Effect of substituting aspartic acid for glutamic acid 148 on ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10392–10394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]