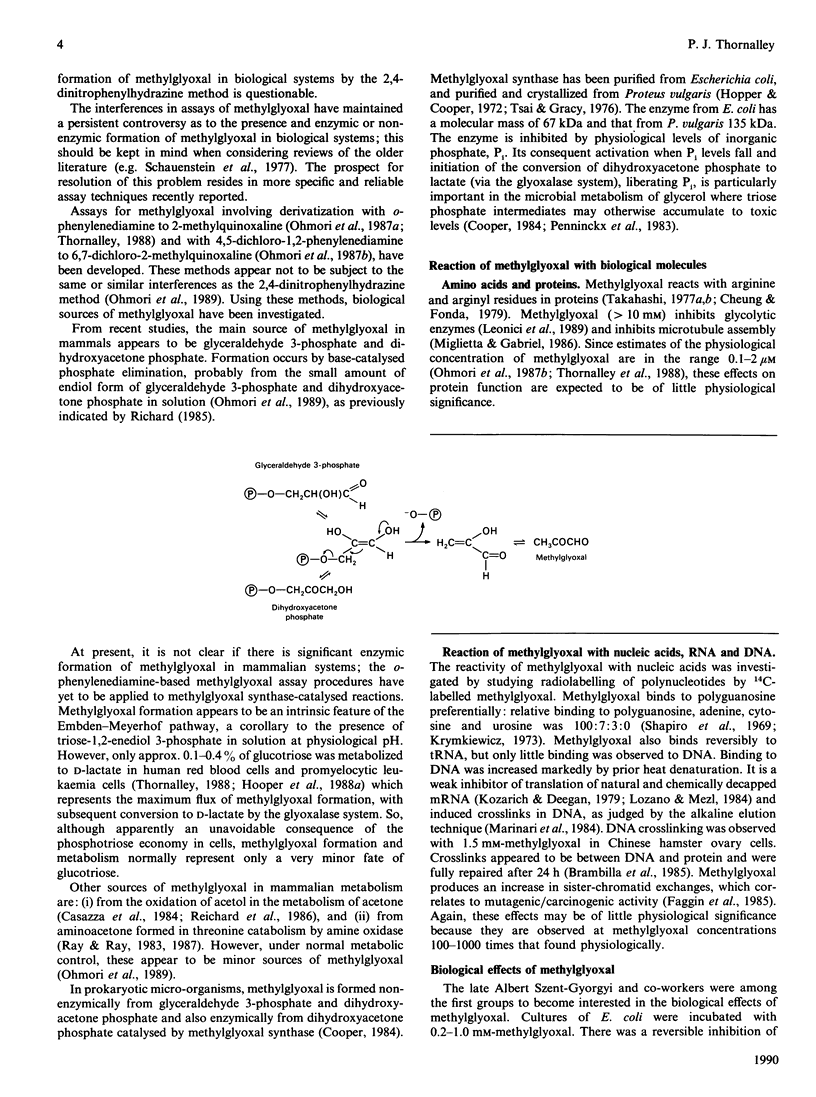
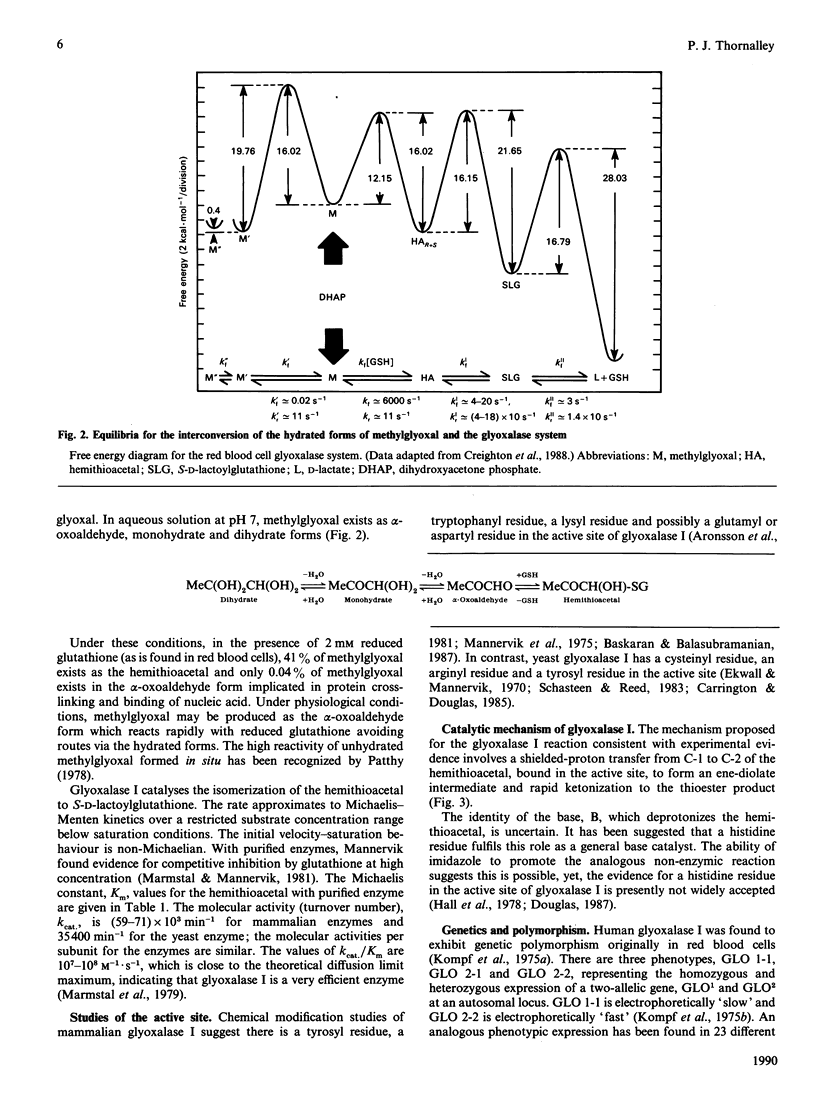
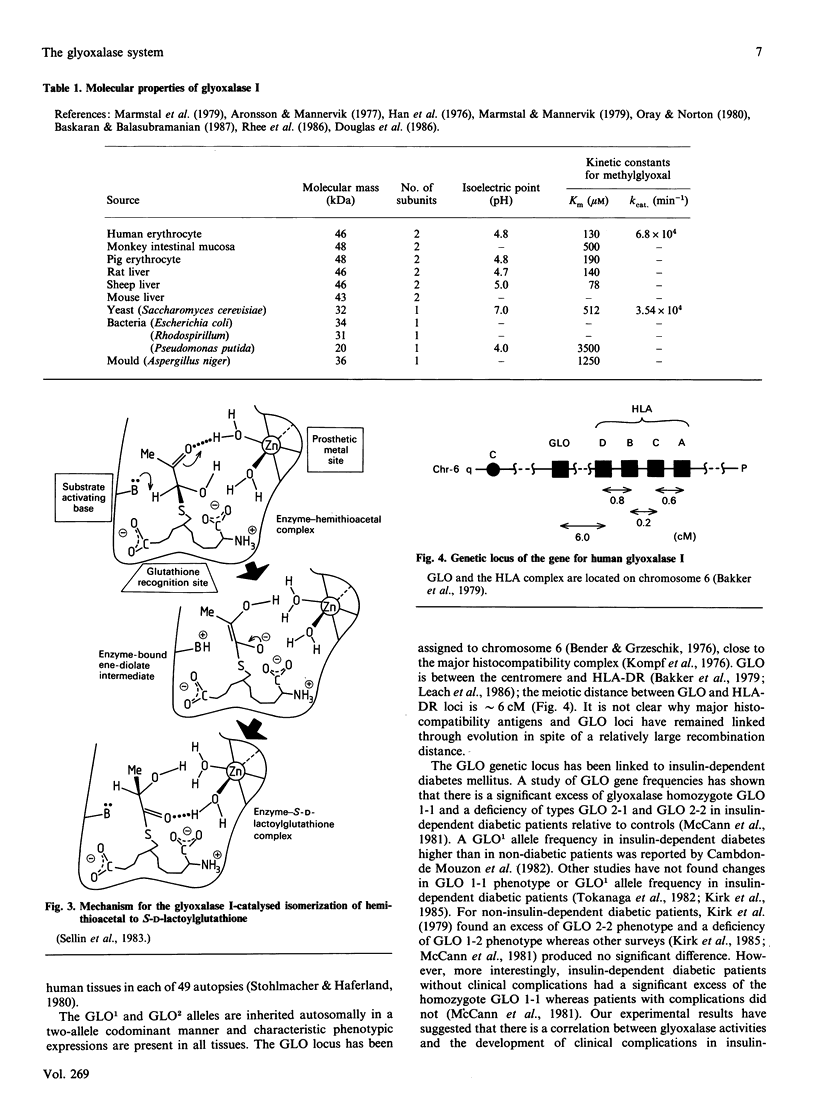
Full text
PDF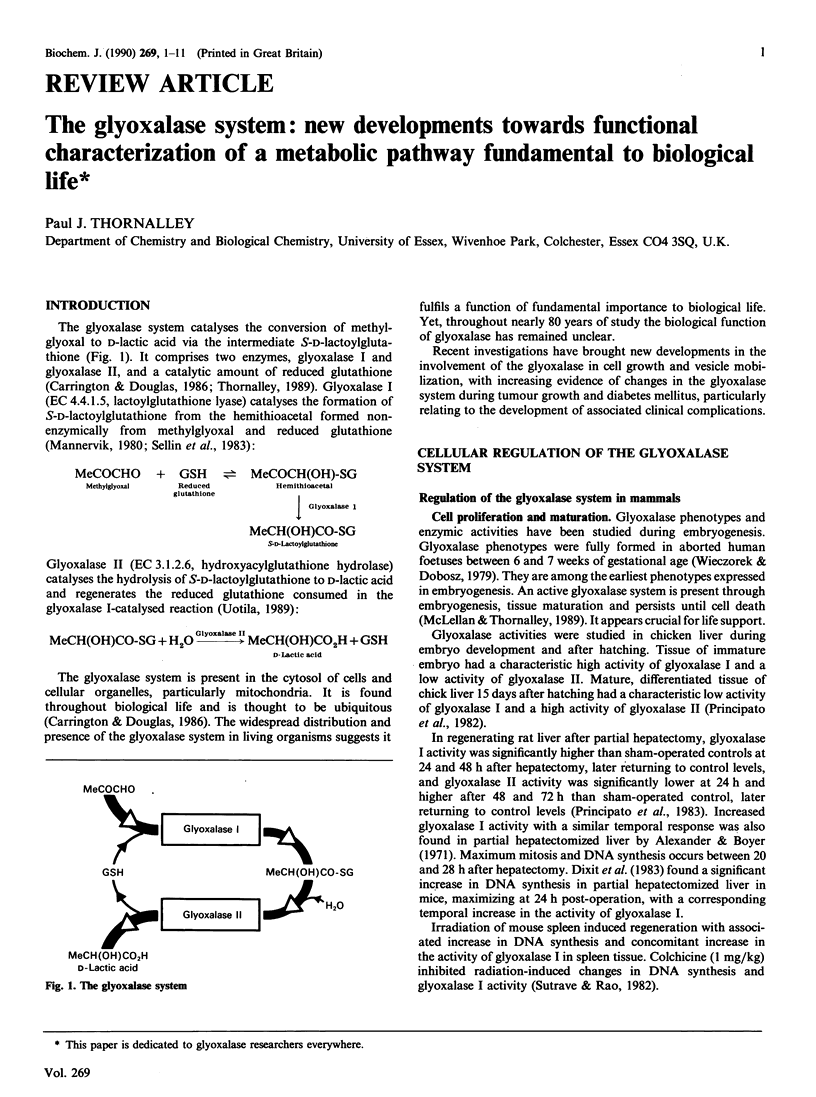






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Timari A., Douglas K. T. Inhibition by glutathione derivatives of bovine liver glyoxalase II (hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase) as a probe of the N- and S-sites for substrate binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 28;870(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander N. M., Boyer J. L. Glyoxalase activity in sham- and partially hepatectomized rats. Cancer Res. 1971 Dec;31(12):1875–1878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronsson A. C., Mannervik B. Characterization of glyoxalase I purified from pig erythrocytes by affinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):503–509. doi: 10.1042/bj1650503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronsson A. C., Sellin S., Tibbelin G., Mannervik B. Probing the active site of glyoxalase I from human erythrocytes by use of the strong reversible inhibitor S-p-bromobenzylglutathione and metal substitutions. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):67–75. doi: 10.1042/bj1970067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Pearson P. L., Meera Khan P., Schreuder G. M., Madan K. Orientation of major histocompatibility (MHC) genes relative to the centromere of human chromosome 6. Clin Genet. 1979 Feb;15(2):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. C., Vander Jagt D. L. Purification of S-2-hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (glyoxalase II) from rat erythrocytes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):472–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. C., Vander Jagt D. L. S-2-hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (glyoxalase II): active-site mapping of a nonserine thiolesterase. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):899–905. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran S., Balasubramanian K. A. Purification and active site modification studies on glyoxalase I from monkey intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 7;913(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender K., Grzeschik K. H. Assignment of the genes for human glyoxalase I to chromosome 6 and for human esterase D to chromosome 13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):93–96. doi: 10.1159/000130561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Board P. G. Genetic polymorphism of human erythrocyte glyoxalase II. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Sep;32(5):690–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla G., Sciabà L., Faggin P., Finollo R., Bassi A. M., Ferro M., Marinari U. M. Methylglyoxal-induced DNA-protein cross-links and cytotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Carcinogenesis. 1985 May;6(5):683–686. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush P. E., Norton S. J. S-(nitrocarbobenzoxy)glutathiones: potent competitive inhibitors of mammalian glyoxalase II. J Med Chem. 1985 Jun;28(6):828–830. doi: 10.1021/jm00383a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARNEGIE P. R. STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF A HOMOLOGUE OF GLUTATHIONE. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:471–478. doi: 10.1042/bj0890471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambon-de Mouzon A., Ohayon E., Hauptmann G., Sevin A., Abbal M., Sommer E., Vergnes H., Ducos J. HLA-A, B, C, DR antigens, Bf, C4 and glyoxalase I (GLO) polymorphisms in French Basques with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Tissue Antigens. 1982 May;19(5):366–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb01463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casazza J. P., Felver M. E., Veech R. L. The metabolism of acetone in rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth D. Starch-gel electrophoresis of four enzymes from human red blood cells: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, fructoaldolase, glyoxalase II and sorbitol dehydrogenase. Ann Hum Genet. 1972 Apr;35(4):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1957.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung S. T., Fonda M. L. Reaction of phenylglyoxal with arginine. The effect of buffers and pH. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):940–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91918-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy P. J. Carcinostatic activity of methylglyoxal and related substances in tumour-bearing mice. Ciba Found Symp. 1978;(67):271–300. doi: 10.1002/9780470720493.ch17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Metabolism of methylglyoxal in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:49–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton D. J., Migliorini M., Pourmotabbed T., Guha M. K. Optimization of efficiency in the glyoxalase pathway. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7376–7384. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling T. N., Blum J. J. D-lactate production by Leishmania braziliensis through the glyoxalase pathway. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Mar;28(2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Sutrave P., Rao A. R. Glyoxalase I in regenerating mouse liver exposed to carcinogens. Biochem Int. 1983 Aug;7(2):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas K. T. Mechanism of action of glutathione-dependent enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1987;59:103–167. doi: 10.1002/9780470123058.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas K. T., Seddon A. P., Nakagawa Y. Yeast glyoxalase I. Circular dichroic spectra and pH effects. Int J Biochem. 1986;18(6):549–555. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(86)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudani A. K., Srivastava L. K., Prasad R. Glyoxalase-I activity and cell cycle regulation in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):962–967. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Együd L. G., Szent-Györgyi A. Cancerostatic action of methylglyoxal. Science. 1968 Jun 7;160(3832):1140–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3832.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Együd L. G., Szent-Györgyi A. Cell division, SH, ketoaldehydes, and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):388–393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Együd L. G., Szent-Györgyi A. On the regulation of cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):203–207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekwall K., Mannervik B. Inhibition of yeast S-lactylglutathione lyase (glyoxalase I) by sulfhydryl reagents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH F. A., FREEDLANDER B. L. Carcinostatic action of polycarbonyl compounds and their derivatives. I. 3-Ethoxy-2-ketobutyraldehyde and related compounds. Cancer Res. 1958 Feb;18(2):172–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggin P., Bassi A. M., Finollo R., Brambilla G. Induction of sister-chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster ovary cells by the biotic ketoaldehyde methylglyoxal. Mutat Res. 1985 Nov;144(3):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(85)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor G., Mujumdar R., Szent-Gyorgyi A. Isolation of methylglyoxal from liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4317–4319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraval H. N., McBrien D. C. The effect of methyl glyoxal on cell division and the synthesis of protein and DNA in synchronous and asynchronous cultures of Escherichia coli B/r. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):127–134. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie E. Effects of S-lactoylglutathione and inhibitors of glyoxalase I on histamine release from human leukocytes. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):135–137. doi: 10.1038/277135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie E. The tumor promoting phorbol diester, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) increases glyoxalase I and decreases glyoxalase II activity in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jan 30;98(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha M. K., Vander Jagt D. L., Creighton D. J. Diffusion-dependent rates for the hydrolysis reaction catalyzed by glyoxalase II from rat erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8818–8822. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han L. P., Davison L. M., Vander Jagt D. L. Purification and kinetic study of glyoxalase-I from rat liver, erythrocytes, brain and kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 14;445(2):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey N. K., Shows T. B. Assignment of the glyoxalase II gene (HAGH) to human chromosome 16. Hum Genet. 1981;58(4):358–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00282815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. I., Tisdale M. J., Thornalley P. J. Glyoxalase activity and cell proliferation in Burkitt's lymphoma and transformed lymphoblast cells in vitro. Cell Mol Biol. 1988;34(4):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. I., Tisdale M. J., Thornalley P. J. Glyoxalase activity during differentiation of human leukaemia cells in vitro. Leuk Res. 1987;11(12):1141–1148. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(87)90169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. I., Tisdale M. J., Thornalley P. J. Modification of the glyoxalase system in human HL60 promyelocytic leukaemia cells during differentiation to neutrophils in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 8;966(3):362–369. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins F. G., Morgan E. J. On the distribution of glyoxalase and glutathione. Biochem J. 1945;39(4):320–324. doi: 10.1042/bj0390320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Cooper R. A. The purification and properties of Escherichia coli methylglyoxal synthase. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):321–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1280321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Bong-Young C., Murata K., Kimura A. Sexual response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: alteration of enzyme activity in the glyoxalase system by mating factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92714-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENCKS W. P., CARRIUOLO J. Imidazole catalysis. II. Acyl transfer and the reactions of acetyl imidazole with water and oxygen anions. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1272–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzykowski T., Matuszewski W., Otrzonsek N., Winter R. Antineoplastic action of methylglyoxal. Neoplasma. 1970;17(1):25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzykowski T., Matuszewski W., Tarnawski R., Winter R., Herman Z. S., Sokola A. Changes of certain pharmacological and biochemical indices in acute methylglyoxal poisoning. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1975;23(4):549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzykowski T., Winter R., Matuszewski W., Piskorska D. A re-evaluation of studies on the distribution of glyoxalases in animal and tumour tissues. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(11):853–860. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzykowski T., Winter R., Matuszewski W., Szczurek Z. Glyoxalase II activity in tumours. Experientia. 1975 Jan 15;31(1):32–33. doi: 10.1007/BF01924663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan F., Cohen J. F., Wang C. T., Wilmott J. M., Hall S. S., Foxall D. L. Glyoxalase I: mechanism-based inhibitors. Drug Metab Rev. 1983;14(4):723–740. doi: 10.3109/03602538308991407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk R. L., Ranford P. R., Serjeantson S. W., Thompson A. R., Munirathnam Chetty S. M., John L., Mohan V., Ramachandran A., Snehalatha C., Viswanathan M. HLA, complement C2, C4, properdin factor B and glyoxalase types in South Indian diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1985 Mar;1(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(85)80027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk R. L., Theophilus J., Whitehouse S., Court J., Zimmet P. Genetic susceptibility to diabetes mellitus: the distribution of properdin factor B (Bf) and glyoxalase (GLO) phenotypes. Diabetes. 1979 Oct;28(10):949–951. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.10.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarich J. W., Deegan J. L. 7-Methylguanosine-dependent inhibition of globin mRNA translation by methylglyoxal. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9345–9348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krymkiewicz N. Reactions of methylglyoxal with nucleic acids. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 1;29(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kömpf J., Bissbort S. Confirmation of linkage between the loci for HL-A and glyoxalase I. Hum Genet. 1976 May 19;32(2):197–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00291503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kömpf J., Bissbort S., Gussmann S., Ritter H. Polymorphism of red cell glyoxalase I (EI: 4.4.1.5); a new genetic marker in man. Investigation of 169 mother-child combinations. Humangenetik. 1975;27(2):141–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00273329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kömpf J., Bissbort S., Ritter H. Red cell glyoxalase i (E.C.: 4.4.1.5): formal genetics and linkage relations. Humangenetik. 1975 Jul 23;28(3):249–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00278552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen K., Aronsson A. C., Marmstål E., Mannervik B. Immunological comparison of glyoxalase I from yeast and mammals and quantitative determination of the enzyme in human tissues by radioimmunoassay. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1985;82(4):625–638. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(85)90499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R., DeMars R., Hasstedt S., White R. Construction of a map of the short arm of human chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3909–3913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoncini G., Maresca M., Buzzi E. Inhibition of the glycolytic pathway by methylglyoxal in human platelets. Cell Biochem Funct. 1989 Jan;7(1):65–70. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290070111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozano A. M., Mezl V. A. Methylglyoxal inhibits the translation of natural and chemically decapped mRNAs. Biosci Rep. 1984 Sep;4(9):783–788. doi: 10.1007/BF01128820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Marmstål E., Ekwall K., Górna-Hall B. Inactivation of glyoxalase I from porcine erythrocytes and yeast by amino-group reagents. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinari U. M., Ferro M., Sciaba L., Finollo R., Bassi A. M., Brambilla G. DNA-damaging activity of biotic and xenobiotic aldehydes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 1984 Oct;2(4):243–248. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290020411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmstål E., Aronsson A. C., Mannervik B. Comparison of glyoxalase I purified from yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) with the enzyme from mammalian sources. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 1;183(1):23–30. doi: 10.1042/bj1830023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmstål E., Mannervik B. Purification, characterization and kinetic studies of glyoxalase I from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 9;566(2):362–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmstål E., Mannervik B. Subunit structure of glyoxalase I from yeast. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 15;85(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann V. J., Davis R. E., Welborn T. A., Constable I. J., Beale D. G. Glyoxalase phenotypes in patients with diabetes mellitus. Aust N Z J Med. 1981 Aug;11(4):380–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1981.tb03516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan A. C., Thornalley P. J. Glyoxalase activity in human red blood cells fractioned by age. Mech Ageing Dev. 1989 Apr;48(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(89)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miglietta A., Gabriel L. Methylglyoxal-tubulin interaction: studies on the aldehyde effects on hepatoma, liver and purified microtubular protein. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;51(2):245–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Kimura A. [Cloning of metabolic regulators and regulation of cell proliferation]. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1986 Sep;31(11):1010–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori S., Kawase M., Mori M., Hirota T. Simple and sensitive determination of methylglyoxal in biological samples by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. J Chromatogr. 1987 Apr 10;415(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori S., Mori M., Kawase M., Tsuboi S. Determination of methylglyoxal as 2-methylquinoxaline by high-performance liquid chromatography and its application to biological samples. J Chromatogr. 1987 Feb 20;414(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori S., Mori M., Shiraha K., Kawase M. Biosynthesis and degradation of methylglyoxal in animals. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;290:397–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oray B., Norton S. J. Purification and characterization of mouse liver glyoxalase II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 11;611(1):168–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFLEIDERER G., SANDMANN B., WIELAND T. Zur Stereospezifität der Glyoxalase II. Biochem Z. 1956;328(4):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Role of nascent alpha-ketoaldehyde in substrate-dependent oxidative inactivation of aldolase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):191–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penninckx M. J., Jaspers C. J., Legrain M. J. The glutathione-dependent glyoxalase pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6030–6036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principato G. B., Bodo M., Biagioni M. G., Rosi G., Liotti F. S. Glyoxalases and glutathione reductase activity changes in chicken liver during embryo development and after hatching. Acta Embryol Morphol Exp. 1982 Dec;3(3):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principato G. B., Locci P., Rosi G., Talesa V., Giovannini E. Activity changes of glyoxalases I-II and glutathione reductase in regenerating rat liver. Biochem Int. 1983 Feb;6(2):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principato G. B., Rosi G., Talesa V., Bocchini V., Giovannini E. Purification of S-2-hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (Glyoxalase II) from calf brain. Biochem Int. 1984 Sep;9(3):351–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principato G. B., Rosi G., Talesa V., Giovannini E., Norton S. J. A comparative study on glyoxalase II from vertebrata. Enzyme. 1987;37(3):164–168. doi: 10.1159/000469255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principato G. B., Rosi G., Talesa V., Giovannini E., Uotila L. Purification and characterization of two forms of glyoxalase II from the liver and brain of Wistar rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 25;911(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Principato G. B., Talesa V., Norton S. J., Giovannini E., Rosi G. Effects of some S-blocked glutathione derivatives on the prevalent glyoxalase II (a form) of rat liver. Enzyme. 1989;41(3):175–180. doi: 10.1159/000469073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. The mechanism of action of glyoxalase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jun;190(2):685–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES H. C., AJL S. J. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS AND METABOLISM OF HYDROXYPYRUVIC ALDEHYDE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:569–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M., Ray S. Aminoacetone oxidase from goat liver. Formation of methylglyoxal from aminoacetone. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5974–5977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S., Ray M. Formation of methylglyoxal from aminoacetone by amine oxidase from goat plasma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3461–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard G. A., Jr, Skutches C. L., Hoeldtke R. D., Owen O. E. Acetone metabolism in humans during diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 1986 Jun;35(6):668–674. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.6.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee H., Murata K., Kimura A. Molecular cloning of the Pseudomonas putida glyoxalase I gene in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee H., Murata K., Kimura A. Purification and characterization of glyoxalase I from Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 30;141(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard J. P. Reaction of triosephosphate isomerase with L-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and triose 1,2-enediol 3-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):949–953. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle V., Lorenz F. W. Nonenzymic, polyvalent anion-catalyzed formation of methylglyoxal as an explanation of its presence in physiological systems. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2718–2724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato J., Wang Y. M., van Eys J. Methylglyoxal formation in rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2046–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schasteen C. S., Reed D. J. Involvement of arginine residues in glutathione binding to yeast glyoxalase I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 26;742(2):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Cohen B. I., Shiuey S. J., Maurer H. On the reaction of guanine with glyoxal, pyruvaldehyde, and kethoxal, and the structure of the acylguanines. A new synthesis of N2-alkylguanines. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):238–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöhlmacher P., Haferland W. Glyoxalase I (GLO) in menschlichen Körpergeweben. Z Rechtsmed. 1980;85(3):165–168. doi: 10.1007/BF02116315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. The living state and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2844–2847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. Further studies on the reactions of phenylglyoxal and related reagents with proteins. J Biochem. 1977 Feb;81(2):403–414. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. The reactions of phenylglyoxal and related reagents with amino acids. J Biochem. 1977 Feb;81(2):395–402. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talesa V., Uotila L., Koivusalo M., Principato G., Giovannini E., Rosi G. Demonstration of glyoxalase II in rat liver mitochondria. Partial purification and occurrence in multiple forms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 29;955(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talesa V., Uotila L., Koivusalo M., Principato G., Giovannini E., Rosi G. Isolation of glyoxalase II from two different compartments of rat liver mitochondria. Kinetic and immunochemical characterization of the enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 13;993(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with S-acyl derivatives of glutathione. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 1;54(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80930-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R., Agius L. The biochemistry of diabetes. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):625–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2500625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J., Bellavite P. Modification of the glyoxalase system during the functional activation of human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 12;931(2):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J., Della Bianca V., Bellavite P., Rossi F. S-D-lactoylglutathione in resting and activated human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):769–774. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J., Hooper N. I., Jennings P. E., Florkowski C. M., Jones A. F., Lunec J., Barnett A. H. The human red blood cell glyoxalase system in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1989 Aug 1;7(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(89)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J. Modification of the glyoxalase system in human red blood cells by glucose in vitro. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):751–755. doi: 10.1042/bj2540751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J. Monosaccharide autoxidation in health and disease. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Dec;64:297–307. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8564297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J., Tisdale M. J. Inhibition of proliferation of human promyelocytic leukaemia HL60 cells by S-D-lactoylglutathione in vitro. Leuk Res. 1988;12(11-12):897–904. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P., Wolff S., Crabbe J., Stern A. The autoxidation of glyceraldehyde and other simple monosaccharides under physiological conditions catalysed by buffer ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 14;797(2):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Omoto K., Juji T., Itoh T. Polymorphism of BF, C2, and GLO in Japanese patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: confirmation of an increase of BF*FT. Hum Genet. 1982;62(1):86–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00295609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai P. K., Gracy R. W. Isolation and characterization of crystalline methylglyoxal synthetase from Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):364–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uotila L. Glutathione thiol esterases of human red blood cells. Fractionation by gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 24;580(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uotila L. Purification and characterization of S-2-hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (glyoxalase II) from human liver. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3944–3951. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Jagt D. L., Daub E., Krohn J. A., Han L. P. Effects of pH and thiols on the kinetics of yeast glyoxalase I. An evaluation of the random pathway mechanism. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 12;14(16):3669–3675. doi: 10.1021/bi00687a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEAVER R. H., LARDY H. A. Synthesis and some biochemical properties of phosphohydroxypyruvic aldehyde and of 3-phosphoglyceryl glutathione thiol ester. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIELAND T., PFLEIDERER G., LAU H. H. Zur Kenntnis der Glyoxalasen. Biochem Z. 1956;327(6):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek E., Dobosz T. Fenotypy układów grupowych enzymów krwi AK, ADA, 6PGD, PGM1, EsD i GLO w okresie zycia płodowego człowieka. Ginekol Pol. 1979 Jan;50(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


