Abstract
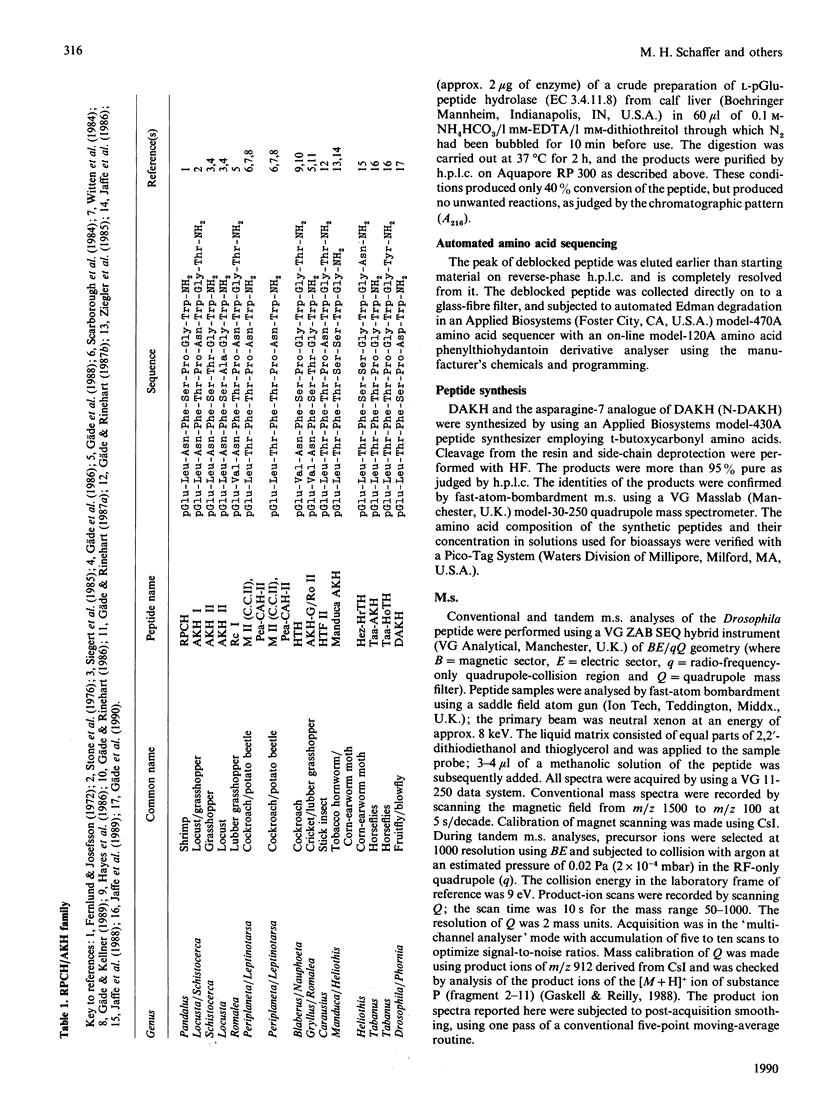
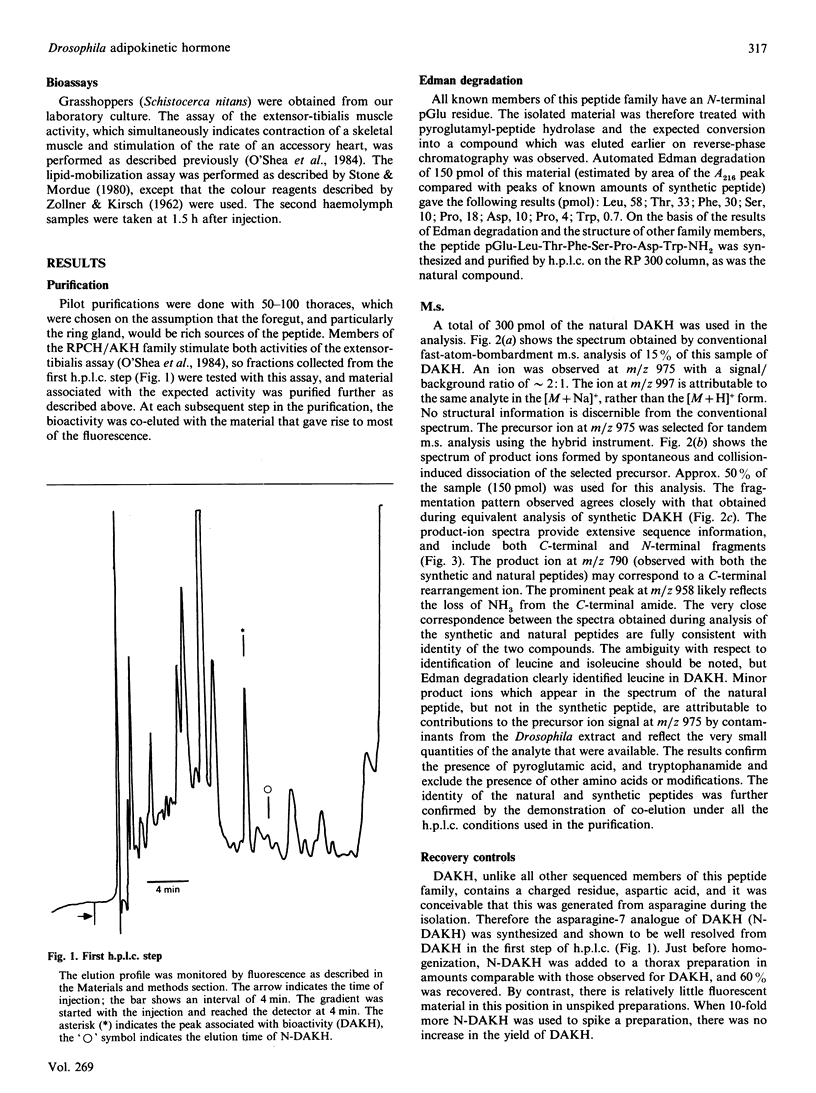
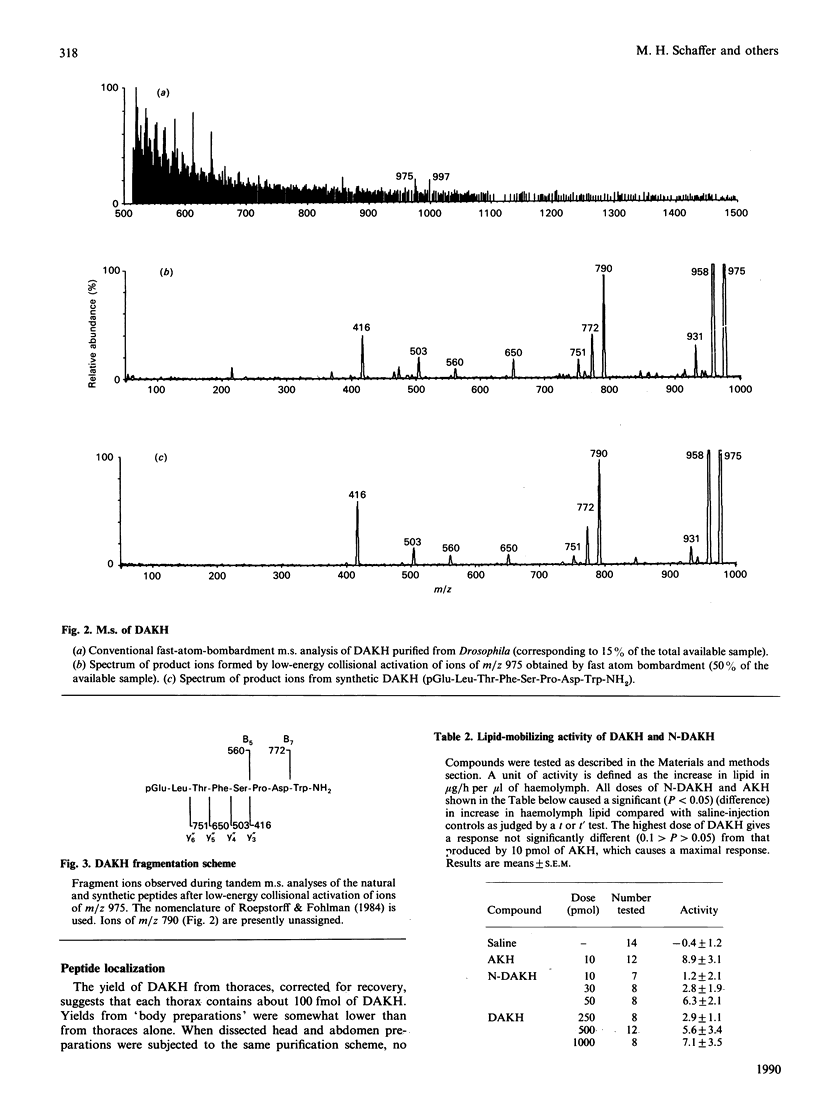
A member of the RPCH/AKH (red-pigment-concentrating hormone/adipokinetic hormone) family of arthropod neuropeptides was identified in the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster, and its structure was determined by automated Edman degradation and m.s. using fast-atom-bombardment ionization and a tandem hybrid instrument capable of high sensitivity. The sequence of this peptide, which we call 'DAKH', is pGlu-Leu-Thr-Phe-Ser-Pro-Asp-Trp-NH2 (where pGlu is pyroglutamic acid and Trp-NH2 is tryptophan carboxyamide). H.p.l.c. analyses of extracts of the three body segments revealed that more than 80% of the peptide is contained in the thorax. Although DAKH is typical of family members in its general structure and distribution in the animal, it is unique in containing a residue which is charged under physiological conditions. The evolutionary significance of this change is considered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biemann K., Scoble H. A. Characterization by tandem mass spectrometry of structural modifications in proteins. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):992–998. doi: 10.1126/science.3303336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson P. A., Ridgway N. D., Slaughter C. A., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. cDNA cloning and expression of oxysterol-binding protein, an oligomer with a potential leucine zipper. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16798–16803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson P. S., Marder E. Peptidergic modulation of a multioscillator system in the lobster. I. Activation of the cardiac sac motor pattern by the neuropeptides proctolin and red pigment-concentrating hormone. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Apr;61(4):833–844. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.4.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Josefsson L. Crustacean color-change hormone: amino acid sequence and chemical synthesis. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):173–175. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskell S. J., Reilly M. H. Hybrid tandem mass spectrometry of peptides above mass 1000. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1988 Sep;2(9):188–191. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290020907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Goldsworthy G. J., Schaffer M. H., Cook J. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr Sequence analyses of adipokinetic hormones II from corpora cardiaca of Schistocerca nitans, Schistocerca gregaria, and Locusta migratoria by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):723–730. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Hilbich C., Beyreuther K., Rinehart K. L. Sequence analyses of two neuropeptides of the AKH/RPCH-family from the lubber grasshopper, Romalea microptera. Peptides. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Kellner R. The metabolic neuropeptides of the corpus cardiacum from the potato beetle and the American cockroach are identical. Peptides. 1989 Nov-Dec;10(6):1287–1289. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Rinehart K. L., Jr Amino acid sequence of a hypertrehalosaemic neuropeptide from the corpus cardiacum of the cockroach, Nauphoeta cinerea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):774–781. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Rinehart K. L., Jr Primary structure of the hypertrehalosaemic factor II from the corpus cardiacum of the Indian stick insect, Carausius morosus, determined by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Jan;368(1):67–75. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Rinehart K. L. Primary sequence analysis by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry of a peptide with adipokinetic activity from the corpora cardiaca of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):908–914. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Wilps H., Kellner R. Isolation and structure of a novel charged member of the red-pigment-concentrating hormone-adipokinetic hormone family of peptides isolated from the corpora cardiaca of the blowfly Phormia terraenovae (Diptera). Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):309–313. doi: 10.1042/bj2690309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. K., Keeley L. L., Knight D. W. Insect hypertrehalosemic hormone: isolation and primary structure from Blaberus discoidalis cockroaches. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):674–678. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90784-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Yates J. R., 3rd, Shabanowitz J., Winston S., Hauer C. R. Protein sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6233–6237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H., Raina A. K., Riley C. T., Fraser B. A., Bird T. G., Tseng C. M., Zhang Y. S., Hayes D. K. Isolation and primary structure of a neuropeptide hormone from Heliothis zea with hypertrehalosemic and adipokinetic activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):344–350. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H., Raina A. K., Riley C. T., Fraser B. A., Holman G. M., Wagner R. M., Ridgway R. L., Hayes D. K. Isolation and primary structure of a peptide from the corpora cardiaca of Heliothis zea with adipokinetic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):622–628. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H., Raina A. K., Riley C. T., Fraser B. A., Nachman R. J., Vogel V. W., Zhang Y. S., Hayes D. K. Primary structure of two neuropeptide hormones with adipokinetic and hypotrehalosemic activity isolated from the corpora cardiaca of horse flies (Diptera). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8161–8164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. R., Snyder S. H. Neuropeptides: multiple molecular forms, metabolic pathways, and receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:773–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea M., Witten J., Schaffer M. Isolation and characterization of two myoactive neuropeptides: further evidence of an invertebrate peptide family. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):521–529. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00521.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P., Fohlman J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1984 Nov;11(11):601–601. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200111109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Jamieson G. C., Kalish F., Kramer S. J., McEnroe G. A., Miller C. A., Schooley D. A. Isolation and primary structure of two peptides with cardioacceleratory and hyperglycemic activity from the corpora cardiaca of Periplaneta americana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5575–5579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooneveld H., Tesser G. I., Veenstra J. A., Romberg-Privee H. M. Adipokinetic hormone and AKH-like peptide demonstrated in the corpora cardiaca and nervous system of Locusta migratoria by immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;230(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00216028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooneveld H., van Herp F., van Minnen J. Demonstration of substances immunologically related to the identified arthropod neuropeptides AKH/RPCH in the CNS of several invertebrate species. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 17;406(1-2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90786-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert K., Morgan P., Mordue W. Primary structures of locust adipokinetic hormones II. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Aug;366(8):723–727. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. V., Mordue W., Batley K. E., Morris H. R. Structure of locust adipokinetic hormone, a neurohormone that regulates lipid utilisation during flight. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):207–211. doi: 10.1038/263207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Sato S., Tsuchiya T., Suzuki Y., Muramatsu H., Ishihara N., Shimoda S. Identification and characterization of adipokinetic hormone (Locusta migratoria)-like immunoreactivity in the human cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):534–540. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witten J. L., Schaffer M. H., O'Shea M., Cook J. C., Hemling M. E., Rinehart K. L., Jr Structures of two cockroach neuropeptides assigned by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91560-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler R., Eckart K., Schwarz H., Keller R. Amino acid sequence of Manduca sexta adipokinetic hormone elucidated by combined fast atom bombardment (FAB)/tandem mass spectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91880-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


