Abstract
In this study we have prepared peptides of the C-terminal domain of apolipoprotein CII (ApoCII) by a solid-peptide-synthesis technique and demonstrated that the C-terminal tetrapeptide, Lys-Gly-Glu-Glu, represents an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase. The tetrapeptide not only inhibits the basal activity of lipoprotein lipase, but also blocks the activation effect of native ApoCII. The lengthening of this tetrapeptide resulted in a corresponding increase in affinity for lipoprotein lipase. This suggested that amino acids other than those of the C-terminal tetrapeptide also contribute to the binding affinity of ApoCII for lipoprotein lipase. On the basis of an essential requirement of the ApoCII terminal domain for binding to lipoprotein lipase, we suggest that the initial interaction of ApoCII, mediated via the C-terminal tetrapeptide, promotes the proper alignment of ApoCII with lipoprotein lipase, followed by the weak interaction of the ApoCII activator domain with the lipoprotein lipase activator site, enhancing the lipolysis process.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balasubramaniam A., Demel R. A., Murphy R. F., Sparrow J. T., Jackson R. L. Substitution of Ser61----Gly61 in human apolipoprotein C-II does not alter its activation of lipoprotein lipase. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Mar-Apr;39(4):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. W., Maguire G. F., Hofmann T., Little J. A. Structure of apolipoprotein C-IIToronto, a nonfunctional human apolipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):270–273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A. Tissue lipoprotein lipase activity and its action in lipoprotein metabolism. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(5):525–541. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Goldberg I. J., Steiner L., Yost T. J., Paterniti J. R., Jr Plasma lipolytic activity. Relationship to postheparin lipolytic activity and evidence for metabolic regulation. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):610–615. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairwell T., Hospattankar A. V., Brewer H. B., Jr, Khan S. A. Human plasma apolipoprotein C-II: total solid-phase synthesis and chemical and biological characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4796–4800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Balasubramaniam A., Murphy R. F., Demel R. A. Interaction of synthetic peptides of apolipoprotein C-II and lipoprotein lipase at monomolecular lipid films. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen P. K., Jackson R. L., Smith L. C., Gotto A. M., Jr, Sparrow J. T. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by native and synthetic fragments of human plasma apolipoprotein C-II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4848–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
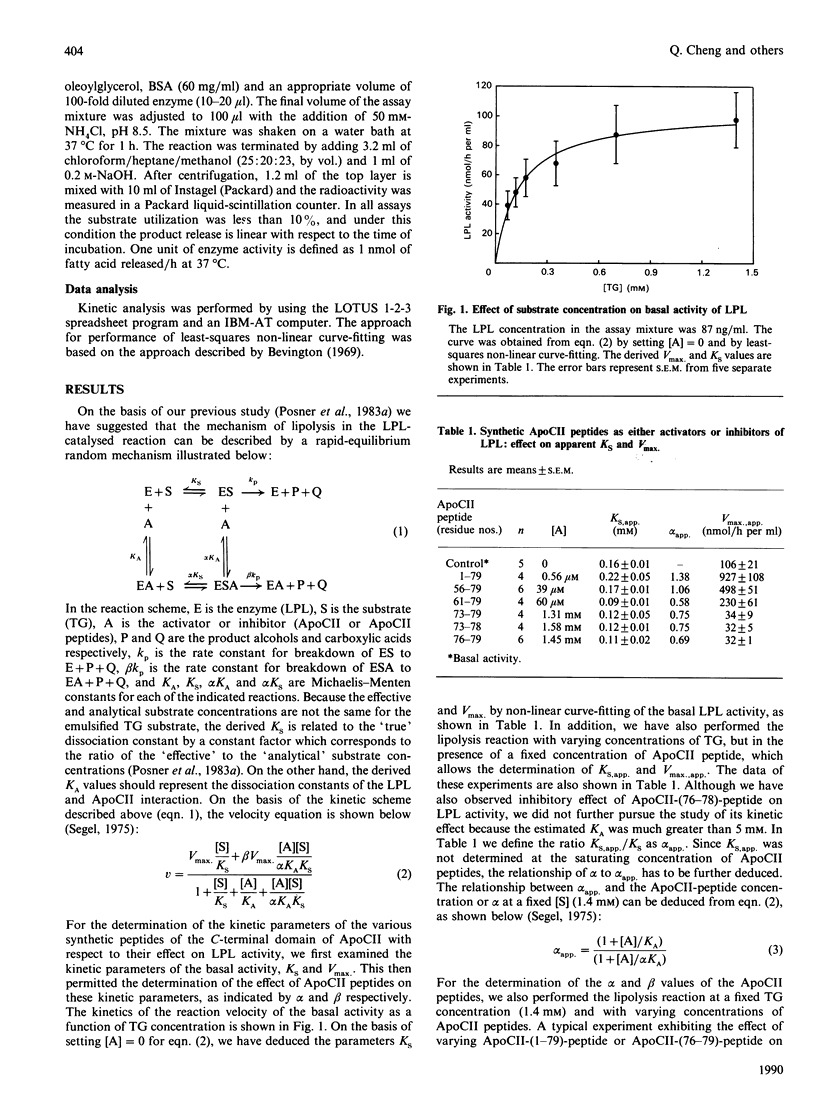
- Posner I., Wang C. S., McConathy W. J. Kinetics of bovine milk lipoprotein lipase and the mechanism of enzyme activation by apolipoprotein C-II. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4041–4047. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner I., Wang C. S., McConathy W. J. The comparative kinetics of soluble and heparin-Sepharose-immobilized bovine lipoprotein lipase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):306–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn D., Shirai K., Jackson R. L. Lipoprotein lipase: mechanism of action and role in lipoprotein metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 1983;22(1):35–78. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(83)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. C., Voyta J. C., Kinnunen P. K., Gotto A. M., Sparrow J. T. Lipoprotein Lipase Interaction with Synthetic N-Dansyl Fragments of Apolipoprotein C-II. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):174–175. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(82)84657-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


