Abstract
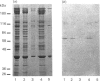
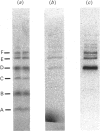
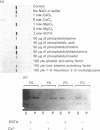
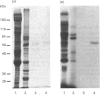
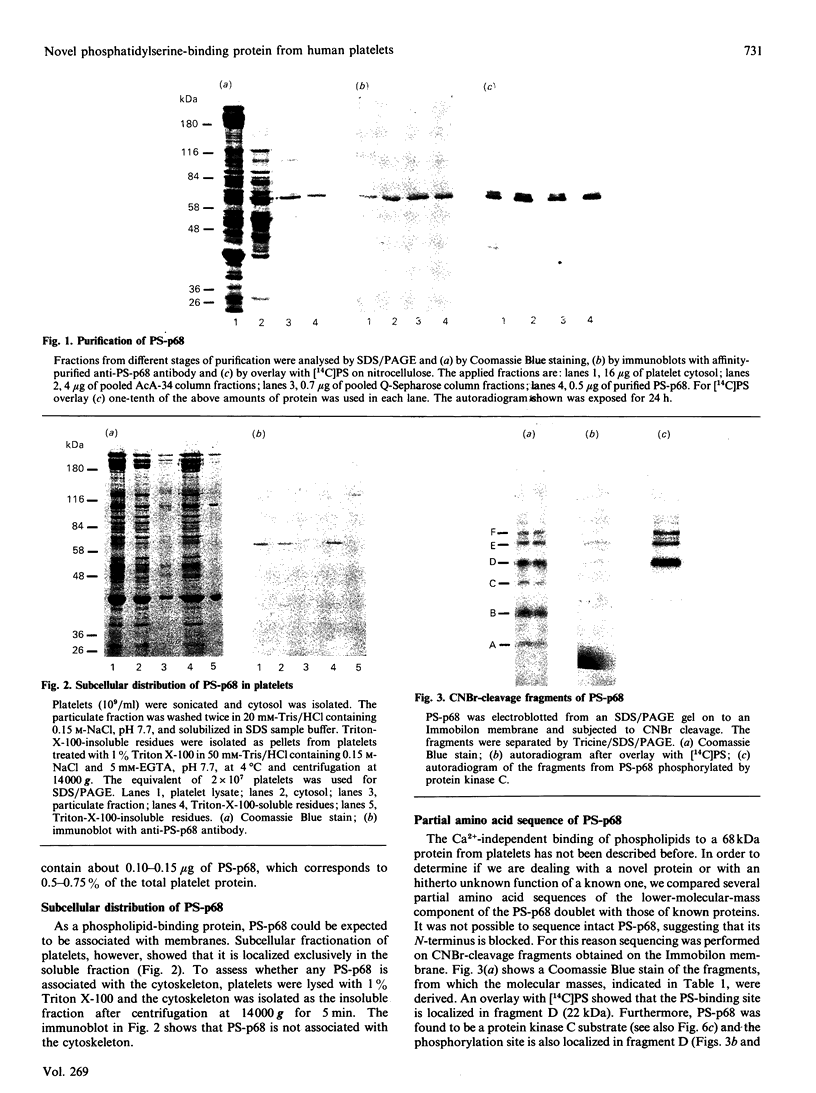
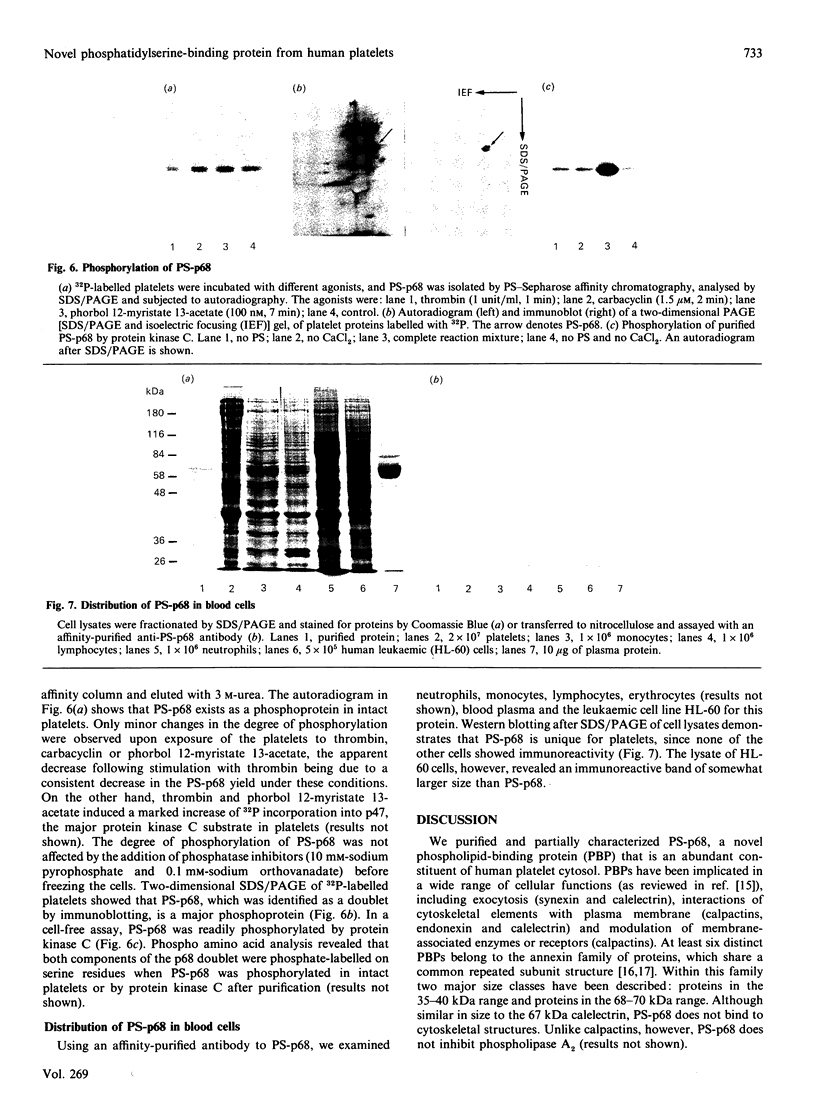
We describe the isolation, lipid-binding properties and partial amino acid sequence of PS-p68, a novel 68 kDa phosphatidylserine-binding protein from human platelets. PS-p68 is an abundant constituent of platelets, accounting for 0.5-0.75% of total cell protein. It was purified from platelet cytosol by affinity chromatography. Amino acid sequence analysis yielded no similarity to identified proteins. In contrast with most known phospholipid-binding proteins, PS-p68 does not bind Ca2+ and does not require Ca2+ for its binding of phosphatidylserine. Phosphatidylserine binding to PS-p68 was inhibited by phosphatidic acid and by alkylphospholipids. PS-p68 was isolated as a major phosphoprotein from 32P-labelled platelets and was found to function as a protein kinase C substrate in vitro. However, treatment of intact platelets with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, thrombin or carbacyclin did not increase PS-p68 phosphorylation. Platelets appear to be the only blood cells containing PS-p68, which was not detected in neutrophils, monocytes and lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clemetson K. J., Bienz D., Zahno M. L., Lüscher E. F. Distribution of platelet glycoproteins and phosphoproteins in hydrophobic and hydrophilic phases in Triton X-114 phase partition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 19;778(3):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Moss S. E., Crumpton M. J. Diversity in the lipocortin/calpactin family. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. P., Bühler F. R. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity during the reversible shape change in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):649–657. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Fitch J. M., Jones J. M., Schlaepfer D. D. Two lipocortin-like proteins, endonexin II and anchorin CII, may be alternate splices of the same gene. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):48–50. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B. Ca2+-dependent phospholipid- (and membrane-) binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6645–6653. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers P., Ernst J. D., Düzgünes N., Hong K. L., Fedor J., Goldstein I. M., Papahadjopoulos D. Synexin-like proteins from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Identification and characterization of granule-aggregating and membrane-fusing activities. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7850–7858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. S., Moore P. B. 67 k calcimedin (67 kDa) is distinct from p67 calelectrin and lymphocyte 68 kDa Ca2+-binding protein. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2510171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. G., Crimmins D. L., McCourt D. W., Tarrand J. J., Eyerman M. C., Nahm M. H. A simple in situ cyanogen bromide cleavage method to obtain internal amino acid sequence of proteins electroblotted to polyvinyldifluoride membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1353–1359. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tous G. I., Fausnaugh J. L., Akinyosoye O., Lackland H., Winter-Cash P., Vitorica F. J., Stein S. Amino acid analysis on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 15;179(1):50–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. J., McDougall J., Wittmann-Liebold B. Extended N-terminal sequencing of proteins of archaebacterial ribosomes blotted from two-dimensional gels onto glass fiber and poly(vinylidene difluoride) membrane. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6867–6876. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Baggiolini M. Identification of phosphatidylserine-binding proteins in human white blood cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):723–728. doi: 10.1042/bj2690723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Sahyoun N. Protein kinase C and phosphatidylserine bind to Mr 110,000/115,000 polypeptides enriched in cytoskeletal and postsynaptic density preparations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13327–13332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen S. W., Chui A. H., Wilson K. J., Yuan P. M. Microanalysis of SDS-PAGE electroblotted proteins. Biotechniques. 1989 Jan;7(1):74–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]