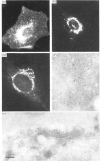
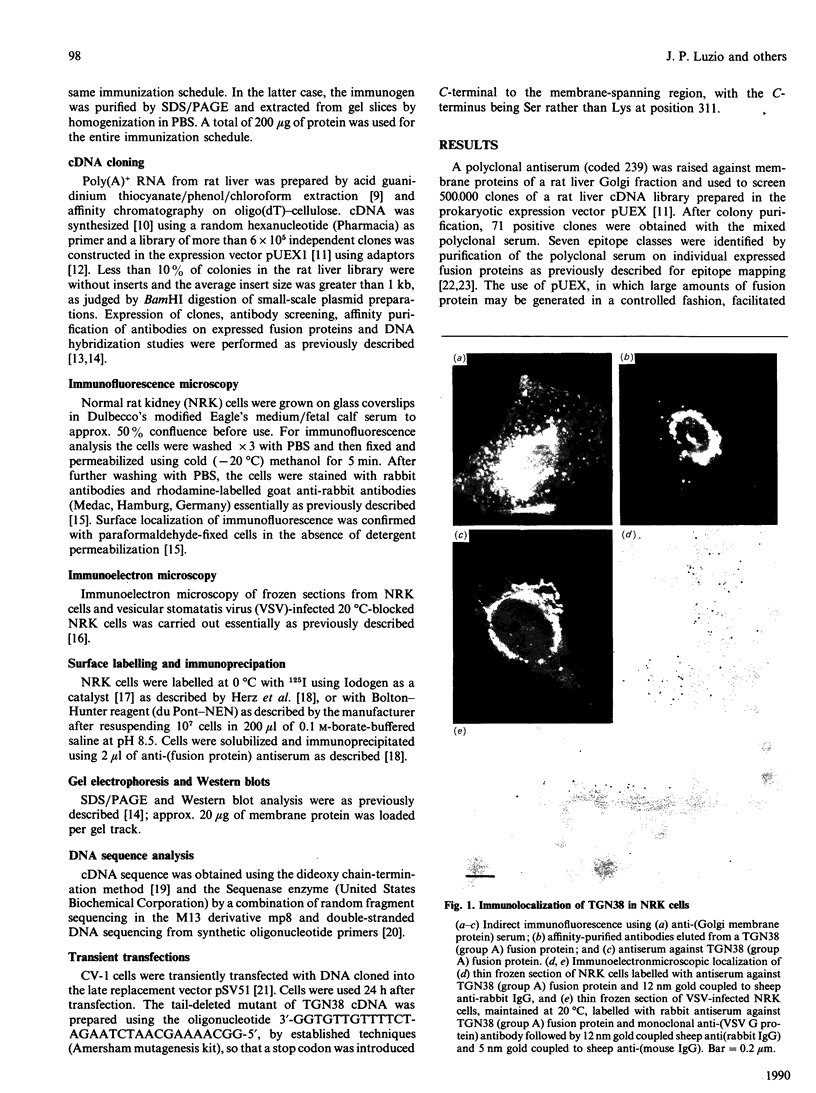
Abstract
Organelle-specific integral membrane proteins were identified by a novel strategy which gives rise to monospecific antibodies to these proteins as well as to the cDNA clones encoding them. A cDNA expression library was screened with a polyclonal antiserum raised against Triton X-114-extracted organelle proteins and clones were then grouped using antibodies affinity-purified on individual fusion proteins. The identification, molecular cloning and sequencing are described of a type 1 membrane protein (TGN38) which is located specifically in the trans-Golgi network.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banting G., Brake B., Braghetta P., Luzio J. P., Stanley K. K. Intracellular targetting signals of polymeric immunoglobulin receptors are highly conserved between species. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake B., Braghetta P., Banting G., Bressan G., Luzio J. P., Stanley K. K. A new recombinant DNA strategy for the molecular cloning of rare membrane proteins. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2670631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitfeld P. P., Casanova J. E., Simister N. E., Ross S. A., McKinnon W. C., Mostov K. E. Sorting signals. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;1(4):617–623. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90024-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressan G. M., Stanley K. K. pUEX, a bacterial expression vector related to pEX with universal host specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10056–10056. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. NPXY, a sequence often found in cytoplasmic tails, is required for coated pit-mediated internalization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3116–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. S., Cornell-Bell A. H., Chernjavsky A., Dani J. W., Smith S. J. Tubulovesicular processes emerge from trans-Golgi cisternae, extend along microtubules, and interlink adjacent trans-golgi elements into a reticulum. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90221-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., van Driel I. R., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The low density lipoprotein receptor. Identification of amino acids in cytoplasmic domain required for rapid endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4075–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJong J. L., Morgenstern R., Jörnvall H., DePierre J. W., Tu C. P. Gene expression of rat and human microsomal glutathione S-transferases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8430–8436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibrat J. F., Garnier J., Robson B. Further developments of protein secondary structure prediction using information theory. New parameters and consideration of residue pairs. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Pfeiffer S., Simons K., Matlin K. Exit of newly synthesized membrane proteins from the trans cisterna of the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):949–964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haymerle H., Herz J., Bressan G. M., Frank R., Stanley K. K. Efficient construction of cDNA libraries in plasmid expression vectors using an adaptor strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8615–8624. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Ito A., Palade G. E. Endoplasmic reticulum marker enzymes in Golgi fractions--what does this mean? J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):581–589. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell K. E., Palade G. E. Hepatic Golgi fractions resolved into membrane and content subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):822–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B. Tyrosine sulfation and the secretory pathway. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:363–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huylebroeck D., Maertens G., Verhoeyen M., Lopez C., Raeymakers A., Jou W. M., Fiers W. High-level transient expression of influenza virus proteins from a series of SV40 late and early replacement vectors. Gene. 1988 Jun 30;66(2):163–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovits J., Roth M. A single amino acid change in the cytoplasmic domain allows the influenza virus hemagglutinin to be endocytosed through coated pits. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzio J. P., Brake B., Banting G., Howell K., Bressan G., Braghetta P., Stanley K. K. Expression cloning of proteins on membrane traffic pathways. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Apr;18(2):148–149. doi: 10.1042/bst0180148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohana Rao J. K., Argos P. A conformational preference parameter to predict helices in integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Jackson M., Peterson P. A. Short cytoplasmic sequences serve as retention signals for transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Powell S. K., Quinn D. L., Moore H. P. The trans-most cisternae of the Golgi complex: a compartment for sorting of secretory and plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnholm R., Pettersson R. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of the M RNA segment of Uukuniemi virus encoding the membrane glycoproteins G1 and G2. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Burke B., Pitt T., Siddle K., Luzio J. P. Localisation of 5'-nucleotidase in a rat liver cell line using a monoclonal antibody and indirect immunofluorescent labelling. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Mar;144(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Herz J. Topological mapping of complement component C9 by recombinant DNA techniques suggests a novel mechanism for its insertion into target membranes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1951–1957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze S. A., Stanley K. K. Identification of two epitopes in the carboxyterminal 15 amino acids of the E1 glycoprotein of mouse hepatitis virus A59 by using hybrid proteins. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):928–934. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.928-934.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. A., Strominger J. L. Constitutive endocytosis of HLA class I antigens requires a specific portion of the intracytoplasmic tail that shares structural features with other endocytosed molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2688–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Hollenberg S. M., Ong E. S., Harmon J. M., Brower S. T., Cidlowski J., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Identification of human glucocorticoid receptor complementary DNA clones by epitope selection. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):740–742. doi: 10.1126/science.2581314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Barriocanal J. G., Bonifacino J. S., Sandoval I. V. Two integral membrane proteins located in the cis-middle and trans-part of the Golgi system acquire sialylated N-linked carbohydrates and display different turnovers and sensitivity to cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):215–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]