Abstract
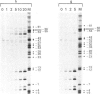
Transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli galP1 promoter does not depend on specific nucleotide sequences in the -35 region. Footprint analysis of transcriptionally competent complexes between E. coli RNA polymerase and DNA fragments carrying galP1 shows that RNA polymerase protects sequences as far upstream as -55, whereas sequences around the -35 region are exposed. In contrast, with galP1 derivatives carrying -35 region sequences resembling the consensus, RNA polymerase protects bases as far as -45, and the -35 region is fully protected. Taken together, our data suggest that the overall architecture of RNA polymerase-promoter complexes can vary according to whether or not consensus -35 region sequences are present; in the absence of these sequences, open complex formation requires distortion of the promoter DNA. However, the unwinding of promoter DNA around the transcription start is not affected by the nature of the -35 region sequence. With a galP1 derivative carrying point mutations in the spacer region that greatly reduce promoter activity, the protection of bases by RNA polymerase around the -10 sequence and transcription start site is reduced. In contrast, protection of the region upstream of -25 is unaffected by the spacer mutations, although sequences from -46 to -54 become hypersensitive to attack by potassium permanganate, indicating severe distortion or kinking of this zone. We suggest that, with this galP1 derivative, RNA polymerase is blocked in a complex that is an intermediate on the path to open complex formation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham A. H., Ponnambalam S., Chan B., Busby S. Mutations that reduce expression from the P2 promoter of the Escherichia coli galactose operon. Gene. 1986;41(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Zhang L., Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. DNA supercoiling promotes formation of a bent repression loop in lac DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Dreyfus M. Segment-specific mutagenesis of the regulatory region in the Escherichia coli galactose operon: isolation of mutations reducing the initiation of transcription and translation. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Kotlarz D., Buc H. Deletion mutagenesis of the Escherichia coli galactose operon promoter region. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Spassky A., Chan B. RNA polymerase makes important contacts upstream from base pair -49 at the Escherichia coli galactose operon P1 promoter. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B., Busby S. Recognition of nucleotide sequences at the Escherichia coli galactose operon P1 promoter by RNA polymerase. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis C. M., Molloy P. L., Both G. W., Drew H. R. Influence of the sequence-dependent flexure of DNA on transcription in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9447–9468. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Chan B., Kolb A., Fox J., Busby S. Alterations in the binding site of the cyclic AMP receptor protein at the Escherichia coli galactose operon regulatory region. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):809–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2530809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Kolb A., Busby S. Binding of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to DNA fragments containing consensus nucleotide sequences. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):649–653. doi: 10.1042/bj2610649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman P. S., Peakman T. C., Busby S. J., Quincey R. V., Cole J. A. Location and sequence of the promoter of the gene for the NADH-dependent nitrite reductase of Escherichia coli and its regulation by oxygen, the Fnr protein and nitrite. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90404-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston F., Ponnambalam S., Busby S. Binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to a promoter carrying mutations that stop transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):745–748. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilty S., Rosenberg M. Constitutive function of a positively regulated promoter reveals new sequences essential for activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6389–6395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Halloran T. V., Frantz B., Shin M. K., Ralston D. M., Wright J. G. The MerR heavy metal receptor mediates positive activation in a topologically novel transcription complex. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90990-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnambalam S., Chan B., Busby S. Functional analysis of different sequence elements in the Escherichia coli galactose operon P2 promoter. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):165–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnambalam S., Webster C., Bingham A., Busby S. Transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli galactose operon promoters in the absence of the normal -35 region sequences. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16043–16048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S., Spassky A., Rimsky S., Buc H. Conformational analysis of lac promoters using the nuclease activity of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion. Biopolymers. 1985 Jan;24(1):183–197. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S., Buc H. On the action of the cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein complex at the Escherichia coli lactose and galactose promoter regions. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Rimsky S., Buc H., Busby S. Correlation between the conformation of Escherichia coli -10 hexamer sequences and promoter strength: use of orthophenanthroline cuprous complex as a structural index. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1871–1879. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Structure and function of E. coli promoter DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(3):181–219. doi: 10.3109/10409238709101483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Healy J., Carter H. L., 3rd, Cutting S., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Mutation changing the specificity of an RNA polymerase sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]