Abstract
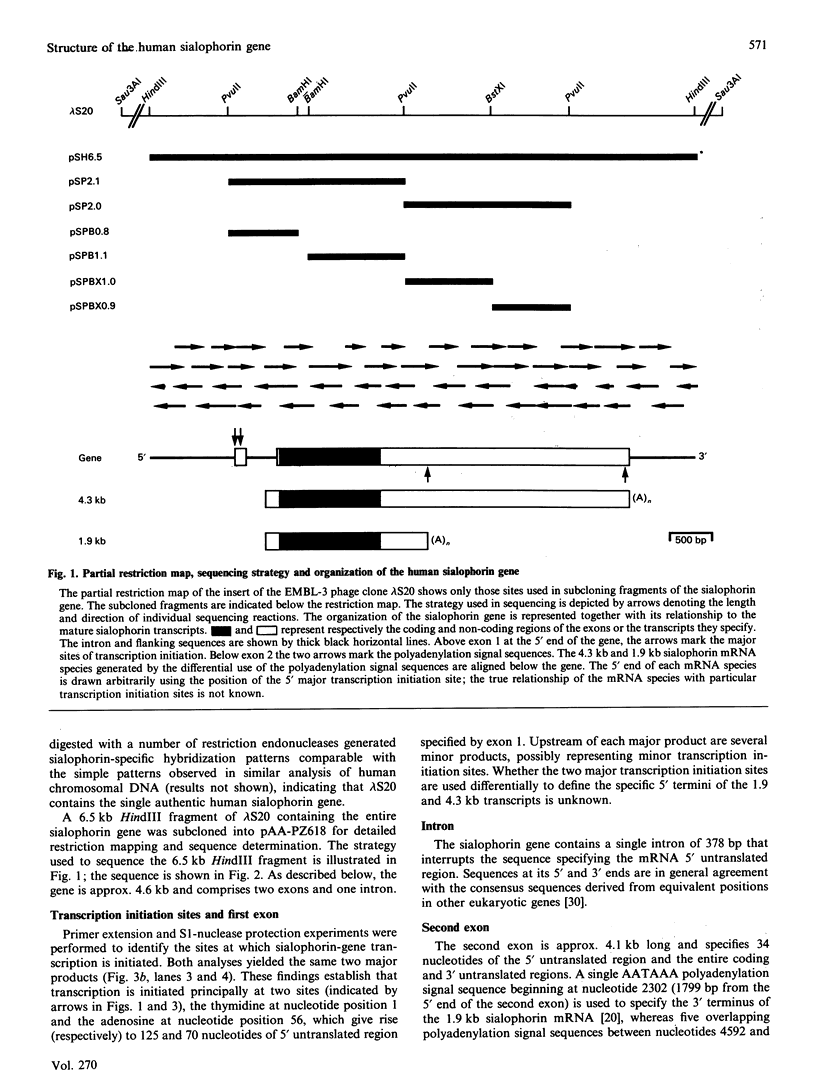
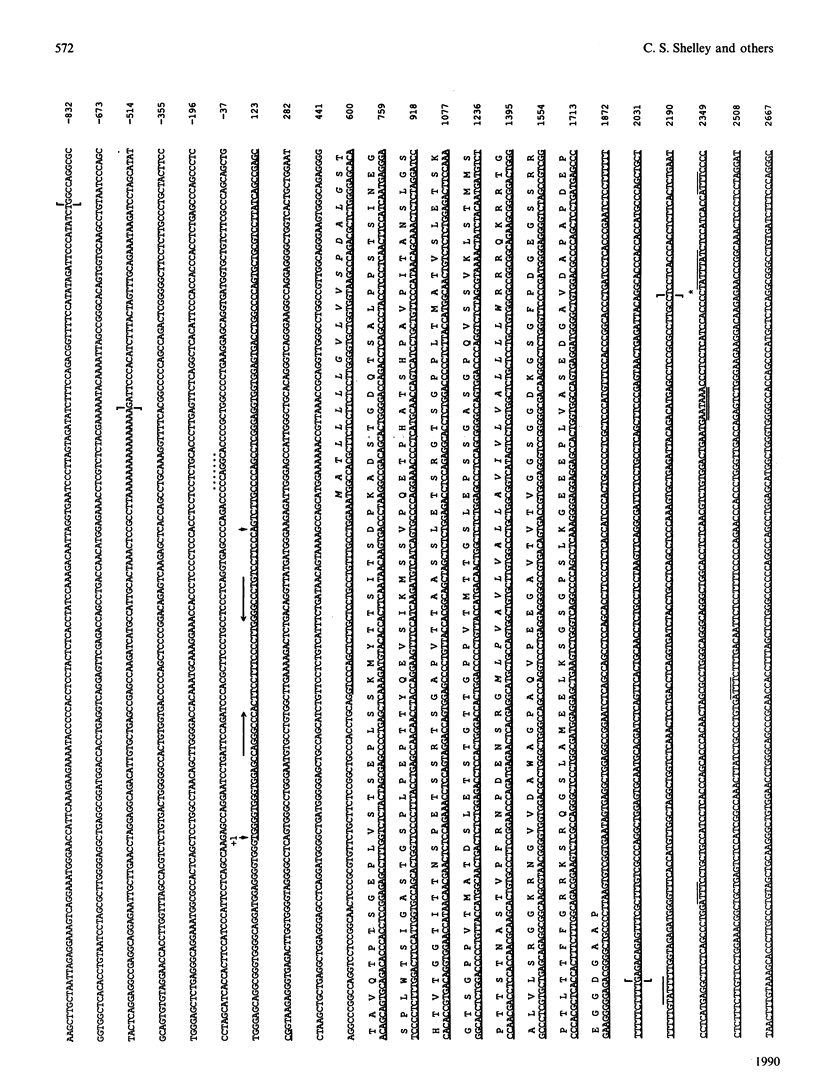
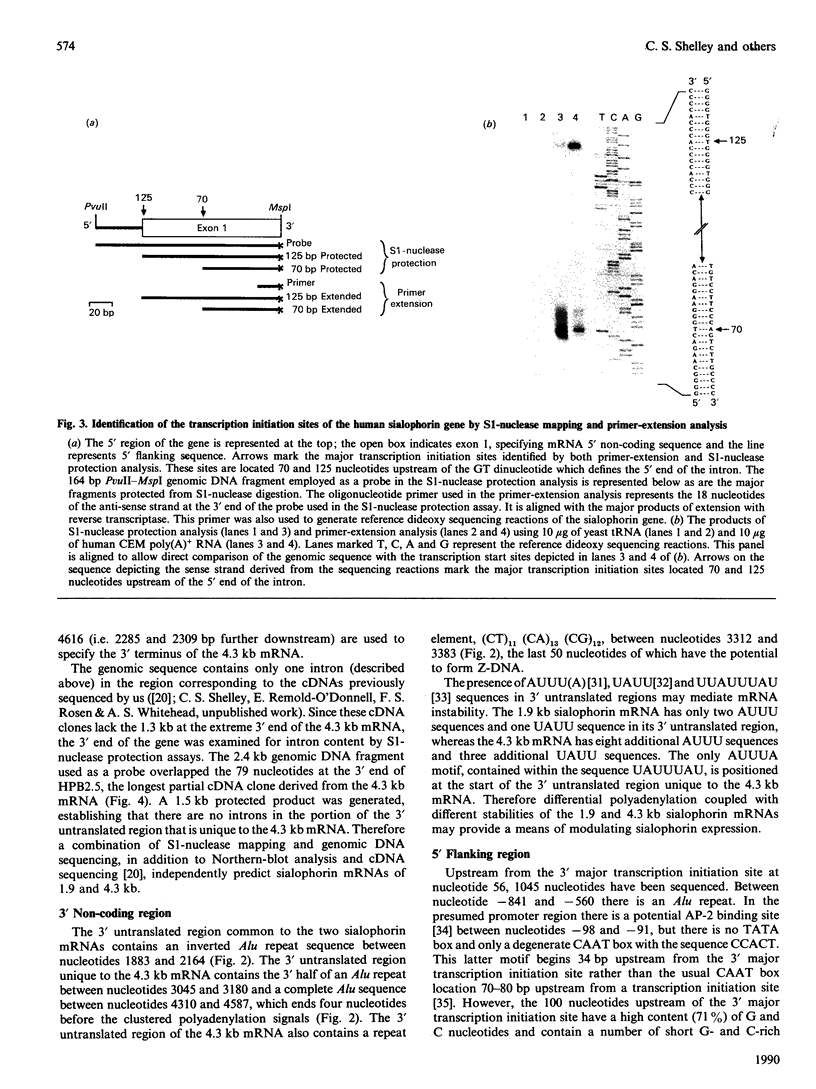
A human sialophorin (CD43) specific genomic clone was isolated, and a 6.5 kb fragment containing the 4.6 kb sialophorin gene was sequenced. The promoter region contains no TATA or CAAT boxes, but is highly enriched in G and C nucleotides and contains short repeat sequences similar to those found in the promoters of 'housekeeping' genes. S1-nuclease protection and primer-extension experiments established that the sialophorin gene has two major transcription initiation sites. There is a single intron of 378 bp that interrupts the sequence specifying the mRNA 5' untranslated region. The gene is therefore unusual in that the discrete extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular regions of the protein, including repeat sequences in the extracellular region, are not encoded by separate exons. Utilization of alternative polyadenylation signals was previously shown to generate two sialophorin mRNAs of 1.9 and 4.3 kb, which differ in the length of their 3' untranslated regions. Sequence analysis of the gene establishes that a single polyadenylation signal 2301 bp downstream of the first major transcription initiation site and five overlapping polyadenylation signals beginning a further 2290 bp downstream define the 3' termini of the 1.9 and 4.3 kb mRNA species respectively. The gene contains potential Z-DNA structures, Aly sequences, and elements that may be involved in regulating mRNA stability.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson B., Youseffi-Etemad R., Hammarström S., Perlmann P. Induction of aggregation and enhancement of proliferation and IL-2 secretion in human T cells by antibodies to CD43. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):2912–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borche L., Lozano F., Vilella R., Vives J. CD43 monoclonal antibodies recognize the large sialoglycoprotein of human leukocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1523–1526. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Barclay A. N., Sunderland C. A., Williams A. F. Identification of a glycophorin-like molecule at the cell surface of rat thymocytes. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):456–460. doi: 10.1038/289456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Fukuda M. Isolation and characterization of leukosialin, a major sialoglycoprotein on human leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12779–12786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatila T. A., Geha R. S. Phosphorylation of T cell membrane proteins by activators of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4308–4314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Clarkson S. G. 5'-flanking sequences that inhibit in vitro transcription of a xenopus laevis tRNA gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman R. W., Beeler D. L., Fritze L., Soff G., Rosenberg R. D. Human thrombomodulin gene is intron depleted: nucleic acid sequences of the cDNA and gene predict protein structure and suggest sites of regulatory control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6425–6429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney D., Cairns L., Remold-O'Donnell E., Peterson J., Rosen F. S., Parkman R. Morphological abnormalities in the lymphocytes of patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1329–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen N., Barclay A. N., Willis A. C., Williams A. F. The sequence of rat leukosialin (W3/13 antigen) reveals a molecule with O-linked glycosylation of one third of its extracellular amino acids. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4029–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G., Toniolo D., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., Dono R., Viglietto G., Paonessa G., D'Urso M., Persico M. G. Structural analysis of the X-linked gene encoding human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer S. J., Remold-O'Donnell E., Crimmins M. A., Bierer B. E., Rosen F. S., Burakoff S. J. Sialophorin, a surface sialoglycoprotein defective in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, is involved in human T lymphocyte proliferation. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Krystal M., Arnheim N. A member of a new repeated sequence family which is conserved throughout eucaryotic evolution is found between the human delta and beta globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5931–5947. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nong Y. H., Remold-O'Donnell E., LeBien T. W., Remold H. G. A monoclonal antibody to sialophorin (CD43) induces homotypic adhesion and activation of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):259–267. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Tesser P., Azorin F., Kwon Y. H., Möller A., Rich A. Isolation of Drosophila proteins that bind selectively to left-handed Z-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7729–7733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallant A., Eskenazi A., Mattei M. G., Fournier R. E., Carlsson S. R., Fukuda M., Frelinger J. G. Characterization of cDNAs encoding human leukosialin and localization of the leukosialin gene to chromosome 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1328–1332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Remold-O'Donnell E., Kenney D. M., Perrine S., Rosen F. S. Surface protein abnormalities in lymphocytes and platelets from patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1387–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92802-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piller F., Piller V., Fox R. I., Fukuda M. Human T-lymphocyte activation is associated with changes in O-glycan biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15146–15150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Elton T. S., Nissen M. S., Lehn D., Johnson K. R. Posttranscriptional gene regulation and specific binding of the nonhistone protein HMG-I by the 3' untranslated region of bovine interleukin 2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6531–6535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Davis A. E., 3rd, Kenney D., Bhaskar K. R., Rosen F. S. Purification and chemical composition of gpL115, the human lymphocyte surface sialoglycoprotein that is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7526–7530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Kenney D. M., Parkman R., Cairns L., Savage B., Rosen F. S. Characterization of a human lymphocyte surface sialoglycoprotein that is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1705–1723. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Kenney D., Rosen F. S. Biosynthesis of human sialophorins and analysis of the polypeptide core. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3908–3913. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Zimmerman C., Kenney D., Rosen F. S. Expression on blood cells of sialophorin, the surface glycoprotein that is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):104–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Remold-O'Donnell E., Davis A. E., 3rd, Bruns G. A., Rosen F. S., Carroll M. C., Whitehead A. S. Molecular characterization of sialophorin (CD43), the lymphocyte surface sialoglycoprotein defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L. B., Wong R. C., Remold-O'Donnell E., Vercelli D., Sancho J., Terhorst C., Rosen F., Geha R., Chatila T. Mechanism of mononuclear cell activation by an anti-CD43 (sialophorin) agonistic antibody. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4194–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Cortes M., Axelsson B., Larsson A., Berzins T., Perlmann P. Enhancement of human spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity by a monoclonal antibody against the large sialoglycoprotein (CD 43) on peripheral blood lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Jun;27(6):661–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger R. H., Kieffer N., Wicki A. N., Clemetson K. J. Structure of the human blood platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib alpha gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):389–395. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




