Abstract
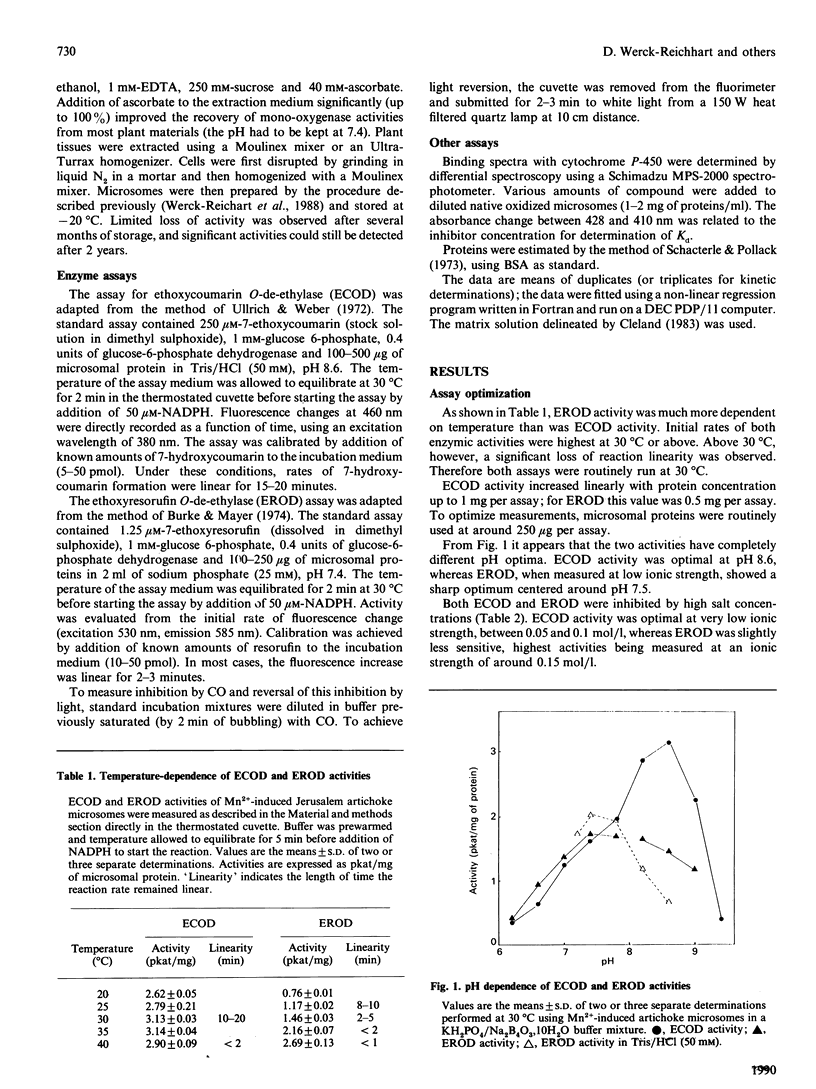
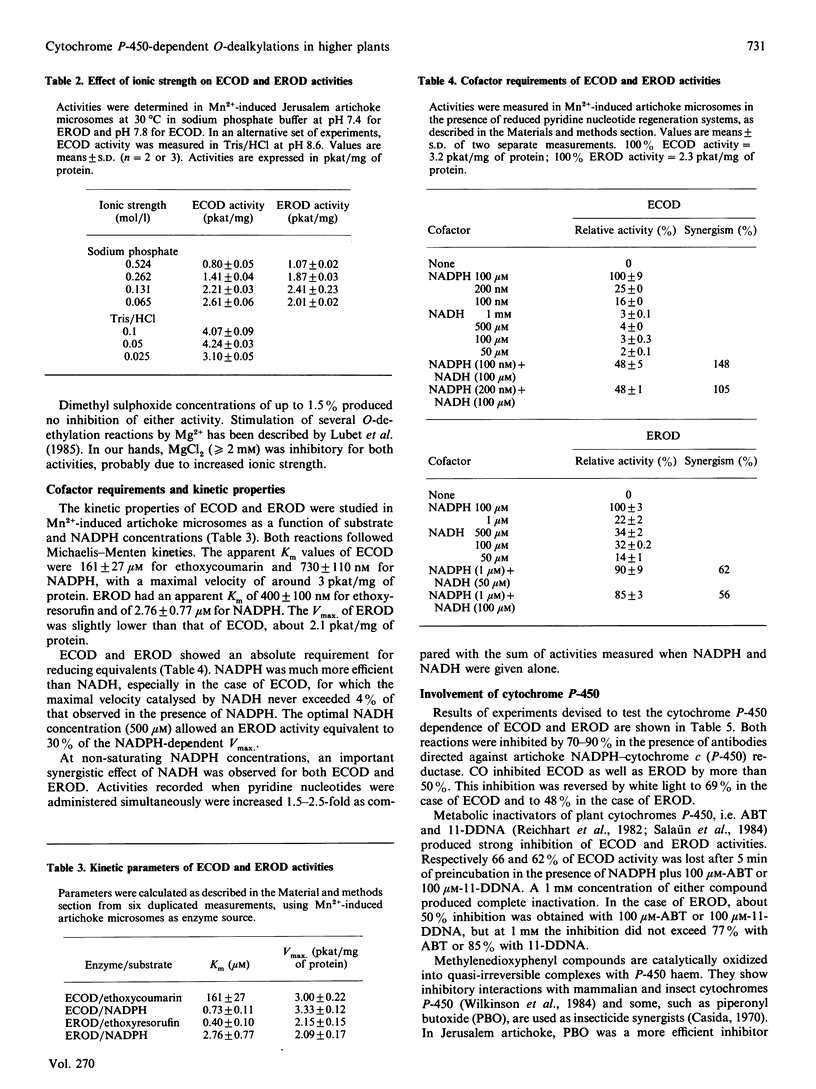
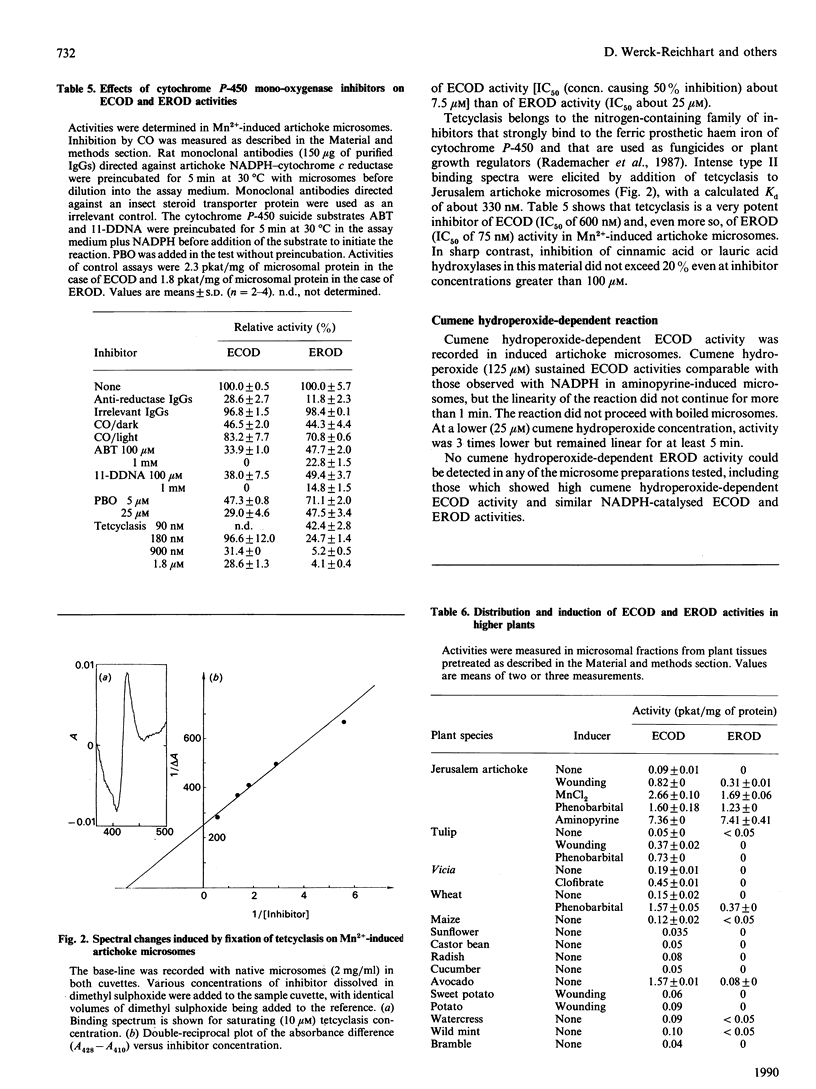
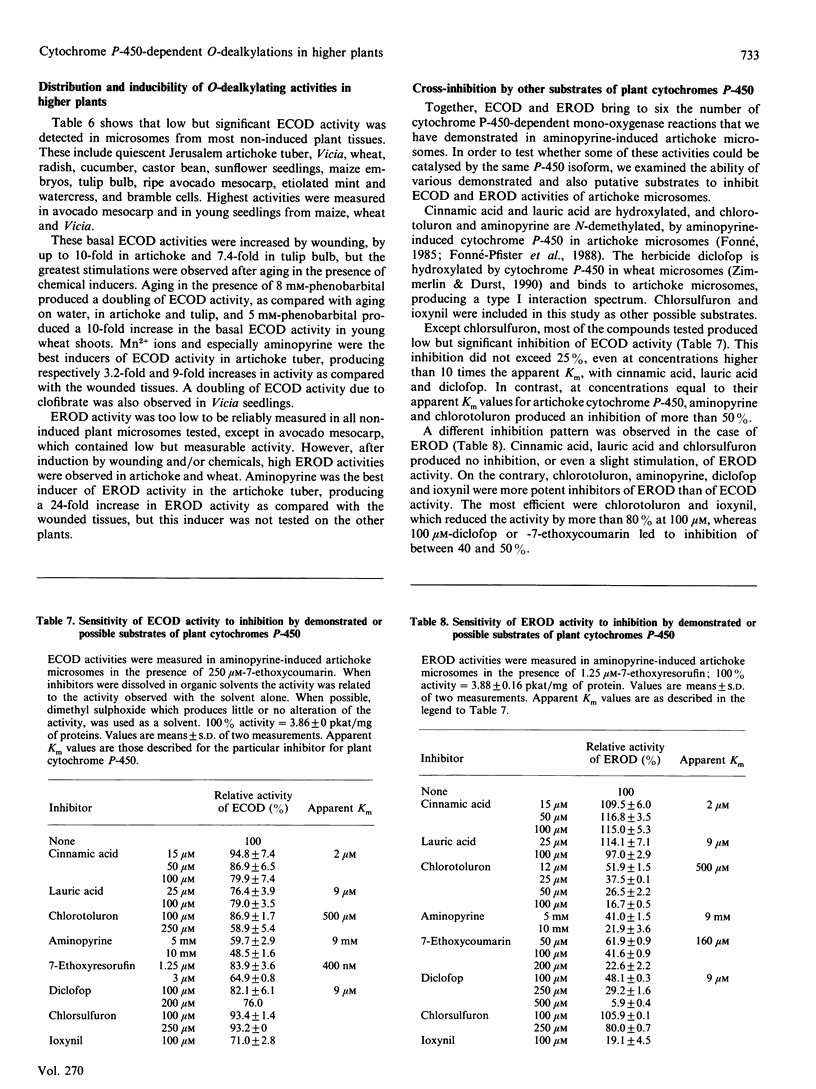
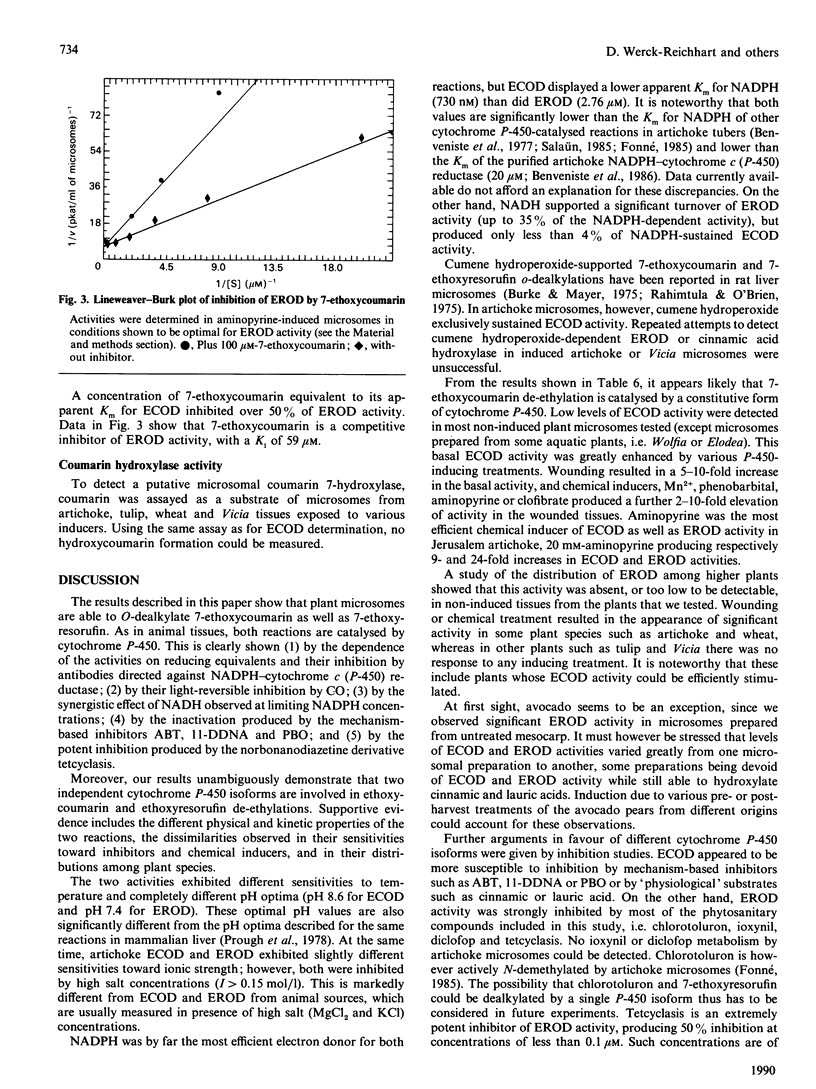
The O-dealkylating activities of 7-ethoxycoumarin O-de-ethylase (ECOD) and 7-ethoxyresorufin O-de-ethylase (EROD) have been fluorimetrically detected in microsomes prepared from manganese-induced Jerusalem artichoke tubers. Cytochrome P-450 dependence of the reactions was demonstrated by light-reversed CO inhibition, NADPH-dependence, NADH-NADPH synergism and by use of specific inhibitors: antibodies to NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase, mechanism-based inactivators and tetcyclasis. Apparent Km values of 161 microM for 7-ethoxycoumarin and 0.4 microM for 7-ethoxyresorufin were determined. O-De-ethylase activity was also detected in microsomes prepared from several other plant species, including wheat, maize, tulip, avocado and Vicia. ECOD and EROD were low or undetectable in uninduced plant tissues, and both activities were stimulated by wounding or by chemical inducers. Two distinct cytochrome P-450 isoforms are involved in ECOD and EROD activities since (1) they showed different distributions among plant species; (2) they showed contrasting inhibition and induction patterns; and (3) ECOD but not EROD activity was supported by cumene hydroperoxide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste I., Gabriac B., Durst F. Purification and characterization of the NADPH-cytochrome P-450 (cytochrome c) reductase from higher-plant microsomal fraction. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):365–373. doi: 10.1042/bj2350365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Mayer R. T. Ethoxyresorufin: direct fluorimetric assay of a microsomal O-dealkylation which is preferentially inducible by 3-methylcholanthrene. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Nov-Dec;2(6):583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Mayer R. T. Inherent specificities of purified cytochromes P-450 and P-448 toward biphenyl hydroxylation and ethoxyresorufin deethylation. Drug Metab Dispos. 1975 Jul-Aug;3(4):245–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. D., Thompson S., Elcombe C. R., Halpert J., Haaparanta T., Mayer R. T. Ethoxy-, pentoxy- and benzyloxyphenoxazones and homologues: a series of substrates to distinguish between different induced cytochromes P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 15;34(18):3337–3345. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casida J. E. Mixed-function oxidase involvement in the biochemistry of insecticide synergists. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 Sep-Oct;18(5):753–772. doi: 10.1021/jf60171a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:103–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohn D. R., Krieger R. I. N-demethylation of p-chloro-N-methylaniline catalyzed by subcellular fractions from the avocado pear (Persea americana). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elcombe C. R., Lech J. J. Induction and characterization of hemoprotein(s) P-450 and monooxygenation in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;49(3):437–450. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefcoate C. R. Measurement of substrate and inhibitor binding to microsomal cytochrome P-450 by optical-difference spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:258–279. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz A. V., Stegeman J. J., Walsh C. An aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylating hepatic cytochrome P-450 from the marine fish Stenotomus chrysops. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 15;226(2):578–592. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubet R. A., Mayer R. T., Cameron J. W., Nims R. W., Burke M. D., Wolff T., Guengerich F. P. Dealkylation of pentoxyresorufin: a rapid and sensitive assay for measuring induction of cytochrome(s) P-450 by phenobarbital and other xenobiotics in the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Apr;238(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa G. T., Harada N., Lu A. Y. Kinetic isotope effects on cytochrome P-450-catalyzed oxidation reactions: full expression of the intrinsic isotope effect during the O-deethylation of 7-ethoxycoumarin by liver microsomes from 3-methylcholanthrene-induced hamsters. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 15;239(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90822-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa G. T., Walsh J. S., Lu A. Y. Kinetic isotope effects on cytochrome P-450-catalyzed oxidation reactions. The oxidative O-dealkylation of 7-ethoxycoumarin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3000–3004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahimtula A. D., O'Brien P. J. Hydroperoxide dependent O-dealkylation reactions catalyzed by liver microsomal cytochrome P450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichhart D., Simon A., Durst F., Mathews J. M., Ortiz de Montellano P. R. Autocatalytic inactivation of plant cytochrome P-450 enzymes: selective inactivation of cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase from Helianthus tuberosus by 1-aminobenzotriazole. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jul;216(2):522–529. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivière J. L. 7-Ethoxycoumarin dealkylase and cytochrome P-450 from grey partridge (Perdix perdix) hepatic and duodenal microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):546–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivière J. L., Grolleau G., Bach J. Hepatic biotransformation in the buzzard (Buteo buteo) and the Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix): effect of PCBs. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1985;82(2):439–443. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(85)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaun J. P., Reichhart D., Simon A., Durst F., Reich N. O., Ortiz de Montellano P. R. Autocatalytic inactivation of plant cytochrome P-450 enzymes: selective inactivation of the lauric acid in-chain hydroxylase from Helianthus tuberosus L. by unsaturated substrate analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jul;232(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich V., Weber P. The O-dealkylation of 7-ethoxycoumarin by liver microsomes. A direct fluorometric test. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1171–1177. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werck-Reichhart D., Jones O. T., Durst F. Haem synthesis during cytochrome P-450 induction in higher plants. 5-Aminolaevulinic acid synthesis through a five-carbon pathway in Helianthus tuberosus tuber tissues aged in the dark. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):473–480. doi: 10.1042/bj2490473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


