Abstract
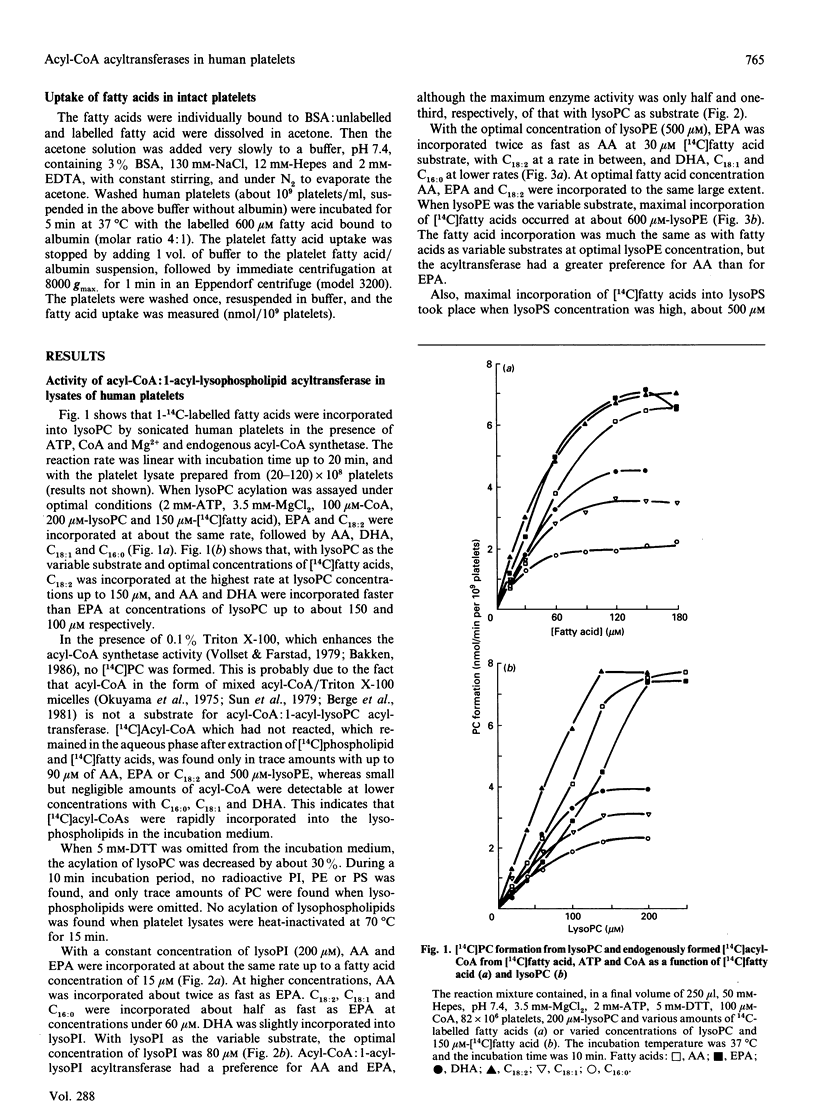
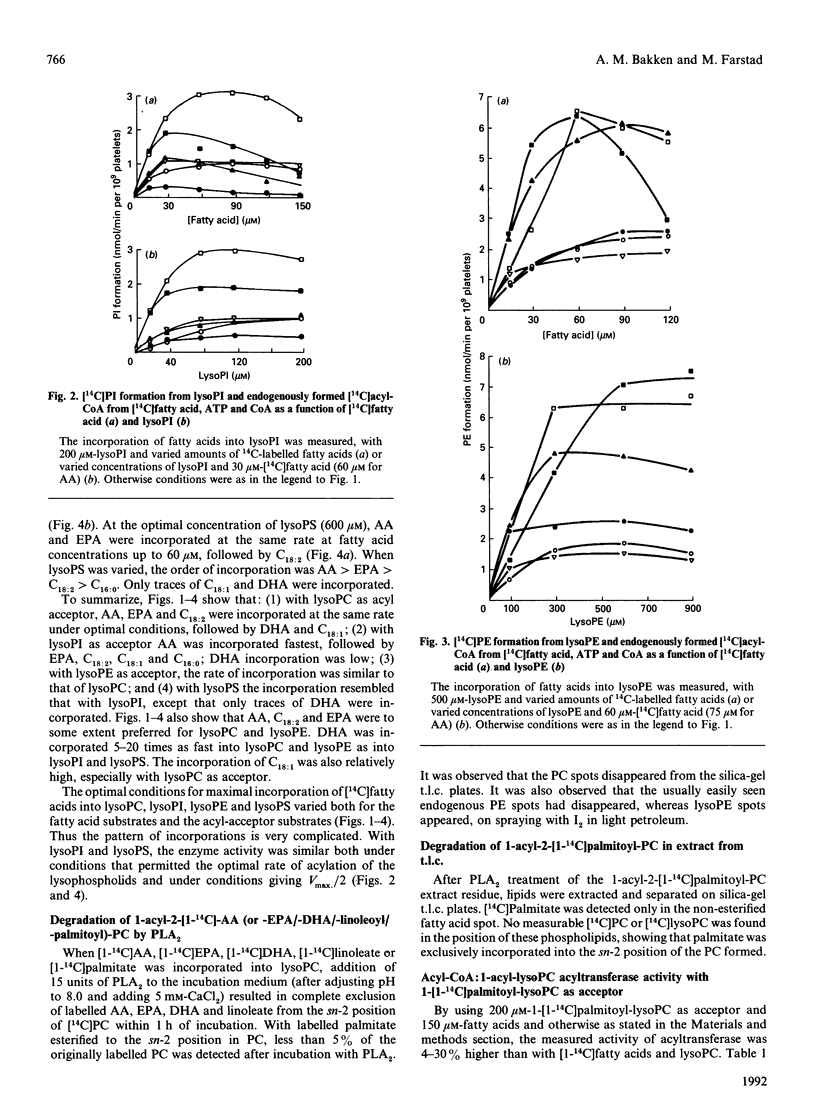
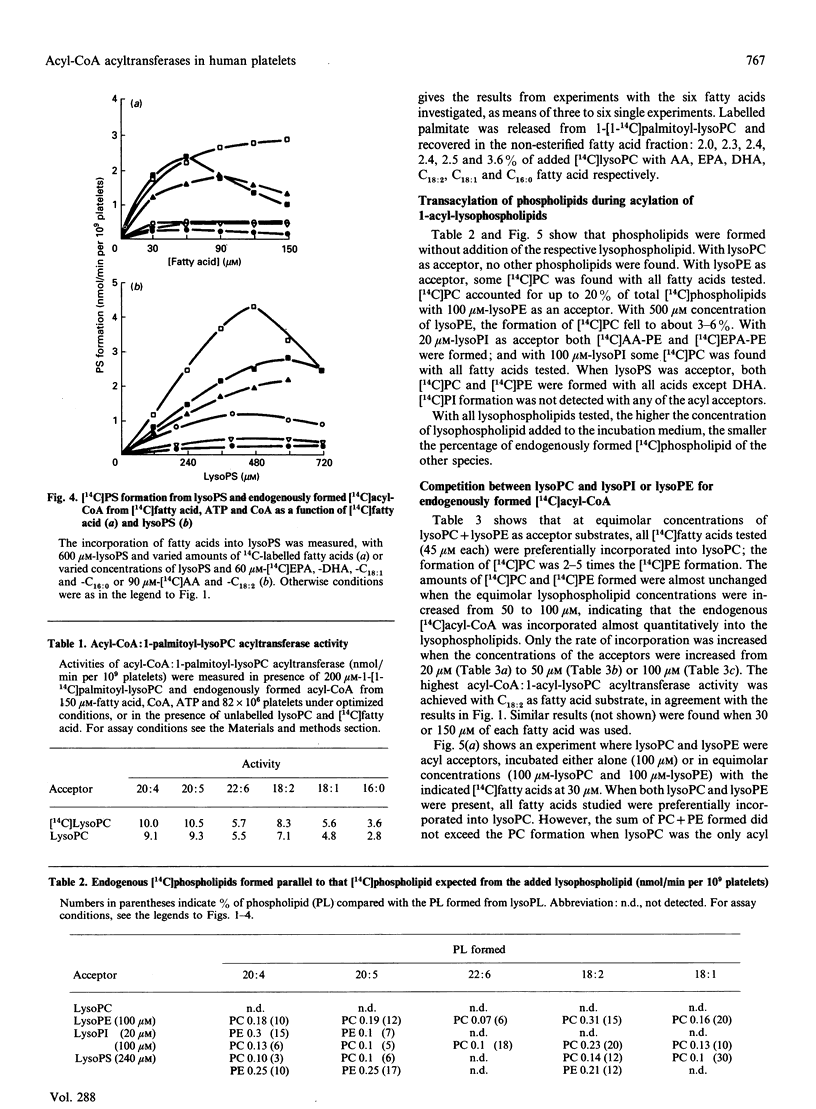
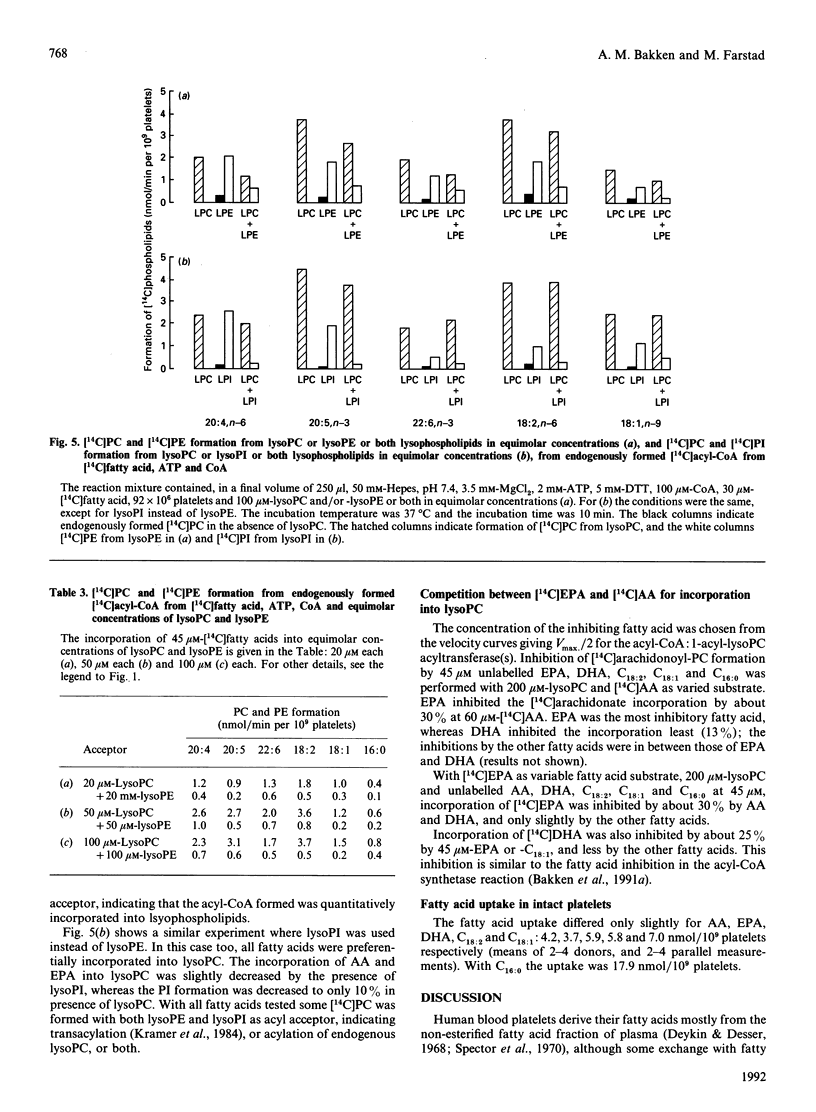
The activities of acyl-CoA:1-acyl-lysophospholipid acyltransferases (EC 2.3.1.23) have been studied in human platelet lysates by using endogenously formed [14C]acyl-CoA from [14C]fatty acid, ATP and CoA in the presence of 1-acyl-lysophosphatidyl-choline (lysoPC), -ethanolamine (lysoPE), -serine (lysoPS) or -inositol (lysoPI). Linoleic acid as fatty acid substrate had the highest affinity to acyl-CoA:1-acyl-lysophospholipid acyltransferase with lysoPC as variable substrate, followed by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and arachidonic acid (AA). The activity at optimal conditions was 7.4, 7.3 and 7.2 nmol/min per 10(9) platelets with lysoPC as substrate, with linoleic acid, AA and EPA respectively. EPA and AA were incorporated into all lyso-forms. Linoleic acid was also incorporated into lysoPE at a high rate, but less into lysoPS and lysoPI. DHA was incorporated into lysoPC and lysoPE, but only slightly into lysoPI and lysoPS. Whereas incorporation of all fatty acids tested was maximal for lysoPC and lysoPI at 200 and 80 microM respectively, maximal incorporation needed over 500 microM for lysoPE and lysoPS. The optimal concentration for [14C]fatty acid substrates was in the range 15-150 microM for all lysophospholipids. Competition experiments with equimolar concentrations of either lysoPC and lysoPI or lysoPE resulted in formation of [14C]PC almost as if lysoPI or lysoPE were not added to the assay medium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken A. M., Farstad M., Holmsen H. Fatty acids in human platelets and plasma. Fish oils decrease sensitivity toward N2 microbubbles. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Jun;70(6):2669–2672. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.6.2669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken A. M., Farstad M., Holmsen H. Identity between palmitoyl-CoA synthetase and arachidonoyl-CoA synthetase in human platelet? Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):145–152. doi: 10.1042/bj2740145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken A. M., Farstad M. Identical subcellular distribution of palmitoyl-CoA and arachidonoyl-CoA synthetase activities in human blood platelets. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):71–76. doi: 10.1042/bj2610071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge R. K., Farstad M. Hydrolysis of long-chain fatty acyl-CoA in homogenates of human blood platelets: the existence of a platelet palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;38(8):699–706. doi: 10.1080/00365517809104876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge R. K., Slinde E., Farstad M. Variations in the activity of microsomal palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase in mixed micelle solutions of palmitoyl-CoA and non-ionic detergents of the triton X series. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Ward J. W., Marcus A. J. Phospholipid metabolism in stimulated human platelets. Changes in phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid, and lysophospholipids. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):275–283. doi: 10.1172/JCI109854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D., Desser R. K. The incorporation of acetate and palmitate into lipids by human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1590–1602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Weber P. C. Prostaglandin I3 is formed in vivo in man after dietary eicosapentaenoic acid. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):165–168. doi: 10.1038/307165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Weber P. C. Thromboxane A3 (TXA3) is formed in human platelets after dietary eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5 omega 3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway J. H., Cartwright I. J., Woodcock B. E., Greaves M., Russell R. G., Preston F. E. Effects of dietary fish oil supplementation on the fatty acid composition of the human platelet membrane: demonstration of selectivity in the incorporation of eicosapentaenoic acid into membrane phospholipid pools. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):449–454. doi: 10.1042/cs0680449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grønn M., Gørbitz C., Christensen E., Levorsen A., Ose L., Hagve T. A., Christophersen B. O. Dietary n-6 fatty acids inhibit the incorporation of dietary n-3 fatty acids in thrombocyte and serum phospholipids in humans: a controlled dietetic study. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1991 May;51(3):255–263. doi: 10.3109/00365519109091612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajarine M., Lagarde M. Studies on polyenoic acid incorporation into human platelet lipid stores: interactions with linoleic and arachidonic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 27;877(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamid M. A., Kunicki T. J., Aster R. H. Lipid composition of freshly prepared and stored platelet concentrates. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):124–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J. W., Feijge M. A., Kalafusz R., Hornstra G. Influence of dietary fatty acids on membrane fluidity and activation of rat platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 8;1004(2):252–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herold P. M., Kinsella J. E. Fish oil consumption and decreased risk of cardiovascular disease: a comparison of findings from animal and human feeding trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 Apr;43(4):566–598. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.4.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Ostvold A. C., Pimentel M. A. Enzymatic properties of 5'-AMP deaminase in platelet lysates. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Jun 30;37(3):380–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Pritzker C. R., Deykin D. Coenzyme A-mediated arachidonic acid transacylation in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2403–2406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata M., Krueger C. M., Saffitz J. E. Selective uptake of [3H]arachidonic acid into the dense tubular system of human platelets. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G., Hoffman J. M., Meisel E., Bilgin S. Pancreatic islet arachidonic acid turnover and metabolism and insulin release in response to delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;35(12):2003–2008. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90733-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. Quantitative loss of individual eicosapentaenoyl-relative to arachidonoyl-containing phospholipids in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Lipid Res. 1987 Nov;28(11):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Ullman H. L., Safier L. B. Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda M., Kudo I., Naito M., Mizushima H., Inoue K. Phospholipid composition of rat megakaryocytes and its rearrangement in platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 3;1083(3):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90077-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean M. L., Silver M. J., Authi K. S., Crawford N. Formation of diacyl- and alkylacylphosphatidylcholine by the membranes of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean M. L., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Formation of lysophosphatidylcholine by human platelets in response to thrombin. Support for the phospholipase A2 pathway for the liberation of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1522–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean M. L., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Phospholipid biosynthesis in human platelets. Formation of phosphatidylcholine from 1-acyl lysophosphatidylcholine by acyl-CoA:1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11278–11283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn M. E., Loscalzo J. Role of platelets in cholesteryl ester formation by U-937 cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):62–68. doi: 10.1172/JCI113311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. J., Wilson D. B., Sprecher H., Majerus P. W. High affinity esterification of eicosanoid precursor fatty acids by platelets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):214–220. doi: 10.1172/JCI110959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordoy A., Strom E., Gjesdal K. The effect of alimentary hyperlipaemia and primary hypertriglyceridaemia on platelets in man. Scand J Haematol. 1974;12(5):329–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama H., Yamada K., Ikezawa H. Accepton concentration effect in the selectivity of acyl coenzyme A: U aclglycerylphosphorylcholine acyltransferase system in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1710–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plantavid M., Perret B. P., Chap H., Simon M. F., Douste-Blazy L. Asymmetry of arachidonic acid metabolism in the phospholipids of the human platelet membrane as studied with purified phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 22;693(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90453-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roshanai F., Sanders T. A. Influence of different supplements of N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on blood and tissue lipids in rats receiving high intakes of linoleic acid. Ann Nutr Metab. 1985;29(3):189–196. doi: 10.1159/000176962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P., Thompson R. H., Laychock S. G. Characterization of phospholipase A2 and acyltransferase activities in purified zymogen granule membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 6;1045(3):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90127-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellner P. A., Phillips A. R. Phospholipid synthesis by chick retinal microsomes: fatty acid preference and effect of fatty acid binding protein. Lipids. 1991 Jan;26(1):62–67. doi: 10.1007/BF02544026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Hoak J. C., Warner E. D., Fry G. L. Utilization of long-chain free fatty acids by human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Aug;49(8):1489–1496. doi: 10.1172/JCI106366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun G. Y., Corbin D. R., Wise R. W., MacQuarrie R. Effects of lipid intermediates, lyso-glycerophospholipids and detergents on arachidonate transfer to 1-acyl-glycerophospholipids by brain synaptosomes. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(6):557–563. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun G. Y., MacQuarrie R. A. Deacylation-reacylation of arachidonoyl groups in cerebral phospholipids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;559:37–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollset S. E., Farstad M. A study of assay conditions for palmitoyl-CoA synthetase and carnitine palmitoyltransferase in homogenates of human blood platelets. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 Feb;39(1):15–21. doi: 10.3109/00365517909104934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver B. J., Holub B. J. The relative incorporation of arachidonic and eicosapentaenoic acids into human platelet phospholipids. Lipids. 1985 Nov;20(11):773–777. doi: 10.1007/BF02534401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. Discovery of an arachidonoyl coenzyme A synthetase in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3510–3515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


