Abstract
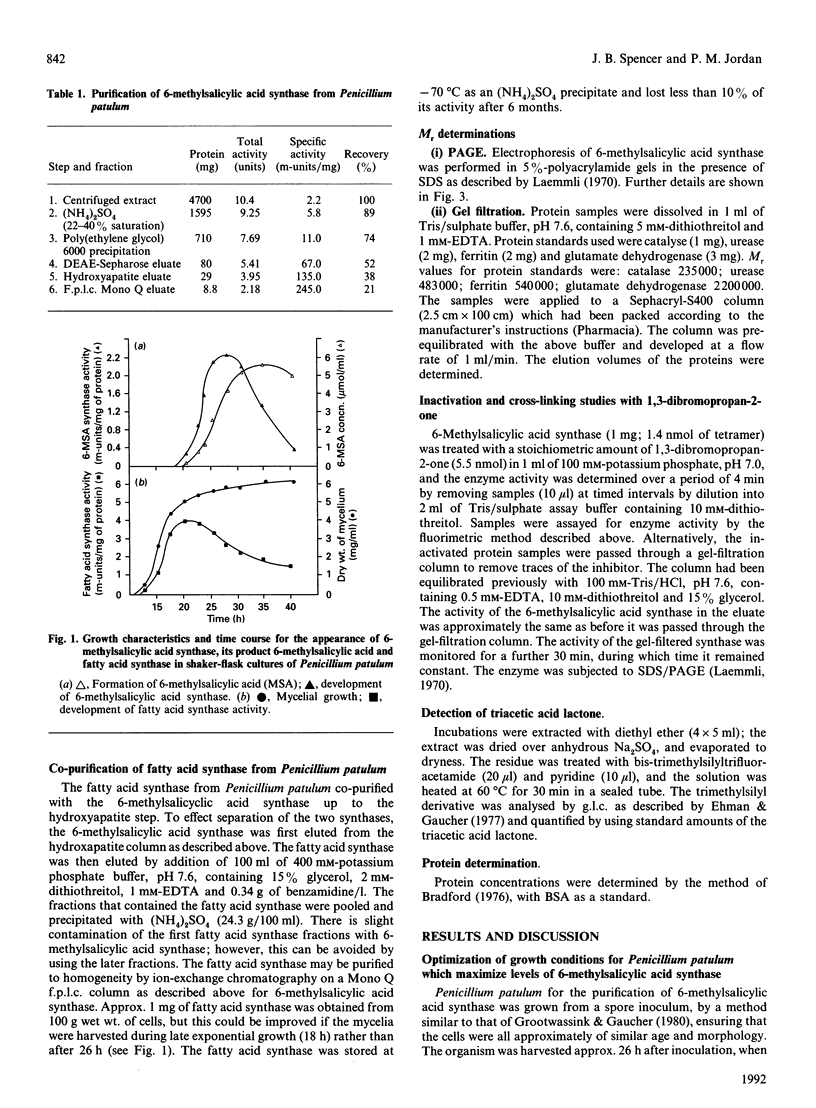
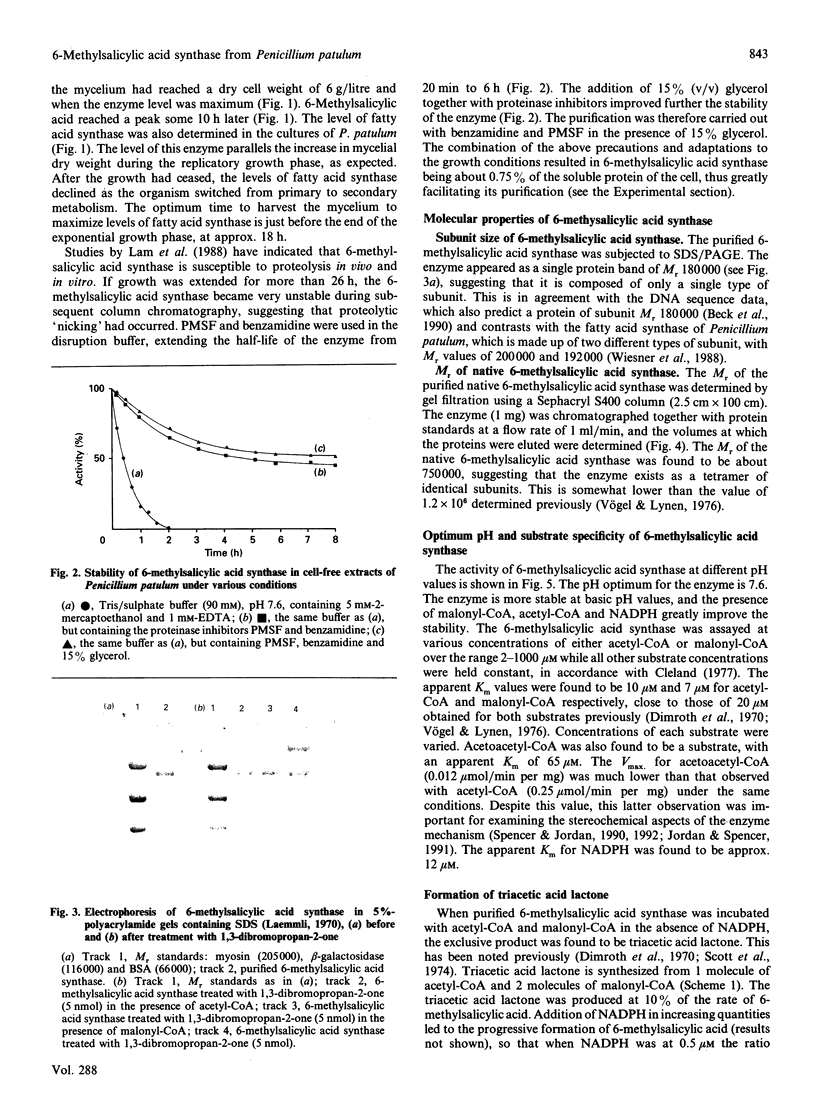
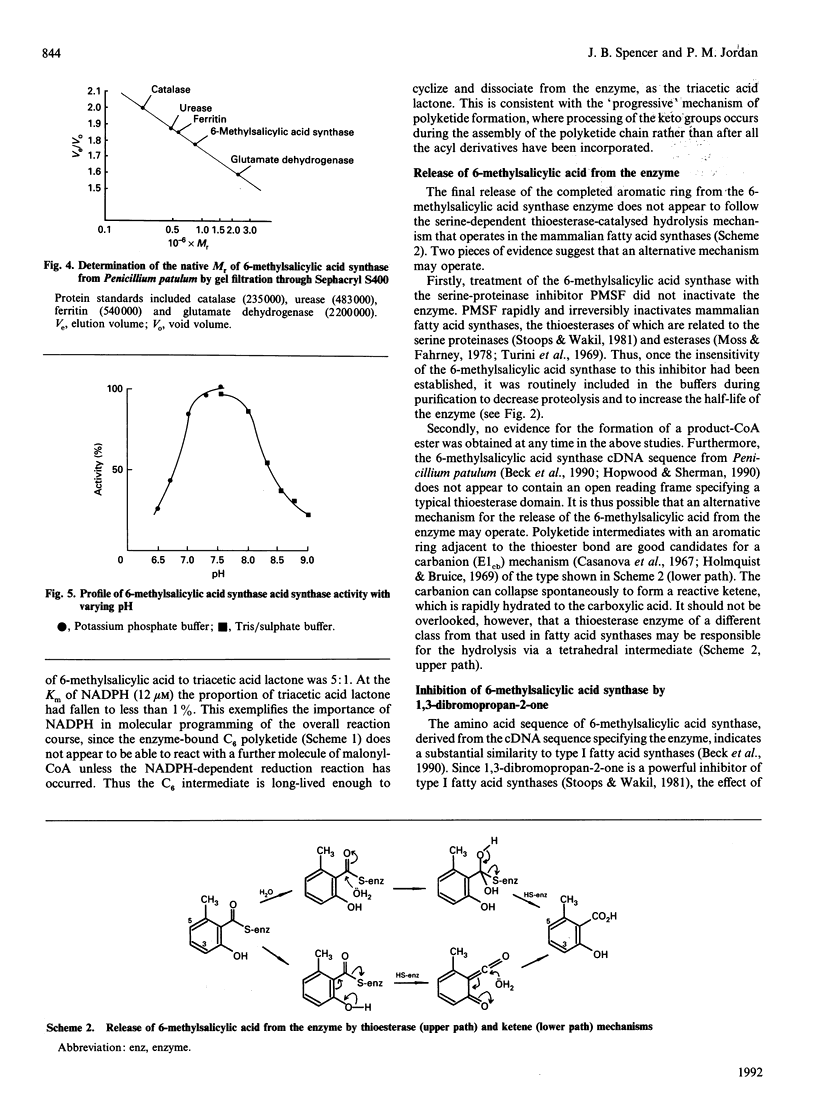
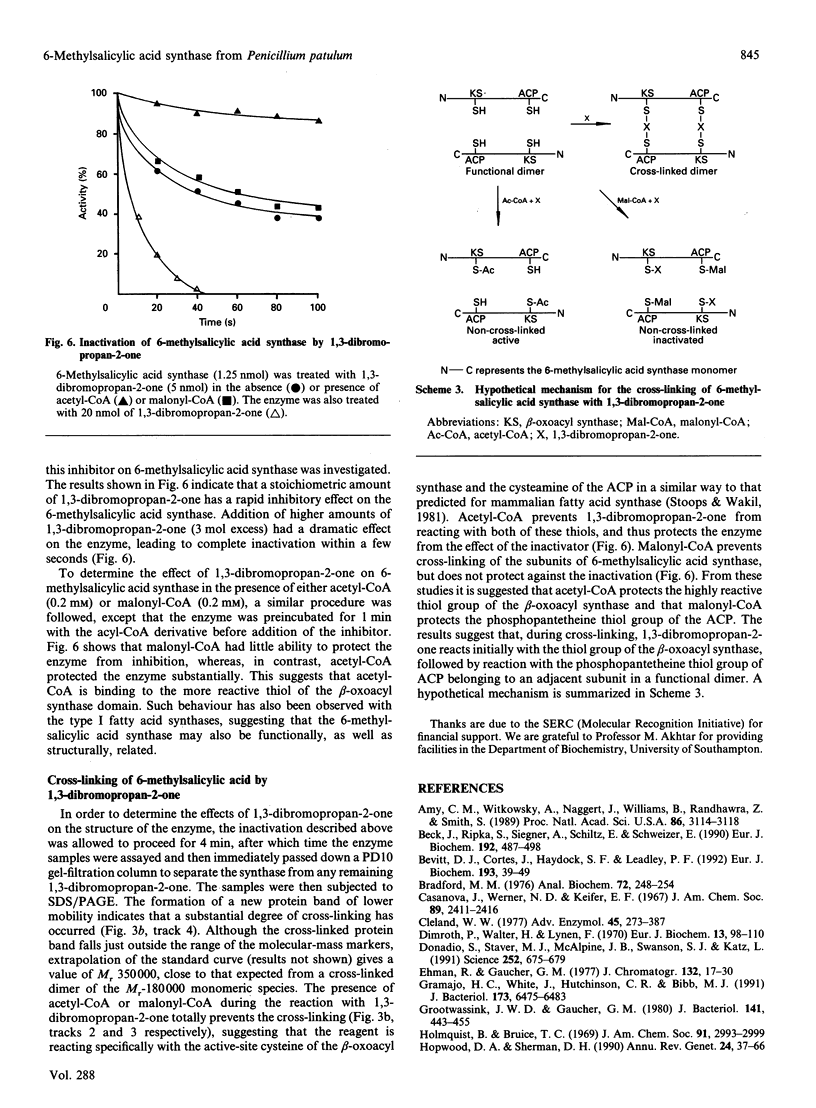
6-Methylsalicylic acid synthase has been isolated in homogeneous form from Penicillium patulum grown in liquid culture from a spore inoculum. The enzyme is highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation in vivo and in vitro, but may be stabilized during purification by incorporating proteinase inhibitors in the buffers. The enzyme exists as a homotetramer of M(r) 750,000, with a subunit M(r) of 180,000. 6-Methylsalicyclic acid synthase also accepts acetoacetyl-CoA as an alternative starter molecule to acetyl-CoA. The enzyme also catalyses the formation of small amounts of triacetic acid lactone as an oligatory by-product of the reaction. In the absence of NADPH, triacetic acid lactone is the exclusive enzymic product, being formed at 10% of the rate of 6-methylsalicylic acid. The enzyme is inactivated by 1,3-dibromopropan-2-one, leading to the formation of cross-linked dimers similar to that observed with type I fatty acid synthases. Acetyl-CoA protects the enzyme against the inactivation and inhibits dimer formation. An adaptation of the purification method for 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase may be used for the isolation of fatty acid sythase from Penicillium patulum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy C. M., Witkowski A., Naggert J., Williams B., Randhawa Z., Smith S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of cDNAs encoding the entire rat fatty acid synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3114–3118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
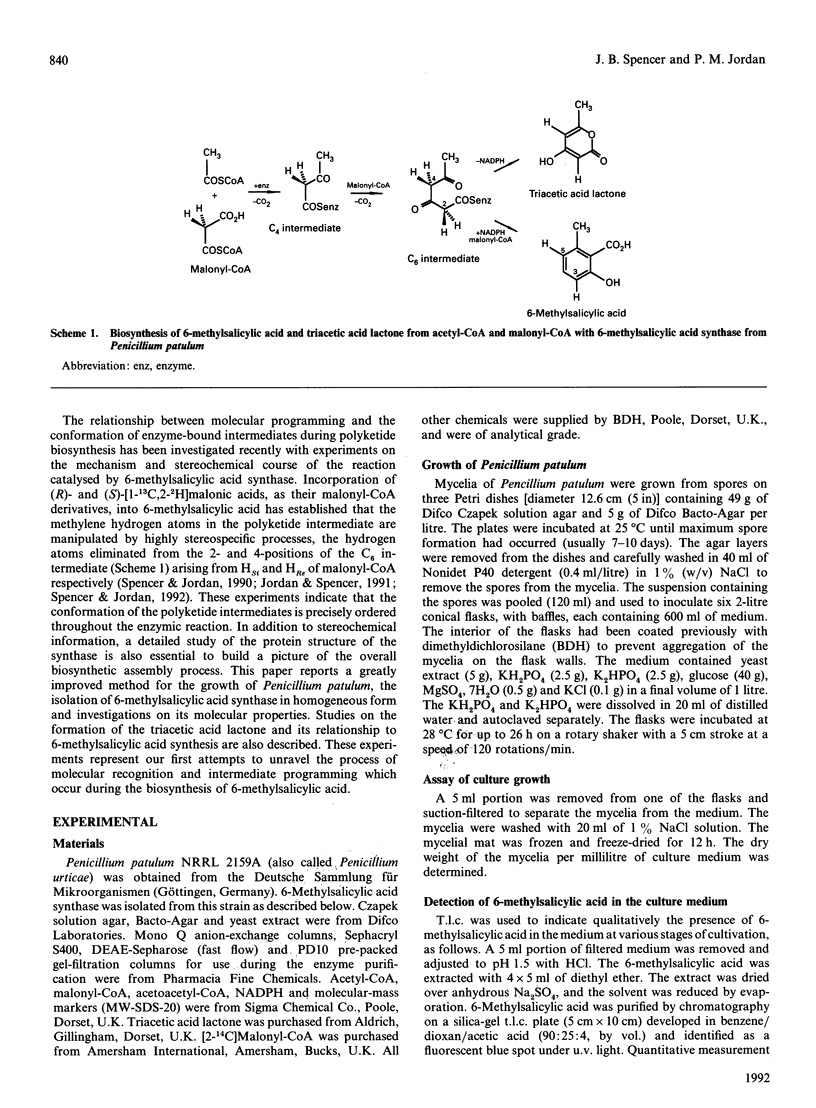
- Beck J., Ripka S., Siegner A., Schiltz E., Schweizer E. The multifunctional 6-methylsalicylic acid synthase gene of Penicillium patulum. Its gene structure relative to that of other polyketide synthases. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):487–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevitt D. J., Cortes J., Haydock S. F., Leadlay P. F. 6-Deoxyerythronolide-B synthase 2 from Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Cloning of the structural gene, sequence analysis and inferred domain structure of the multifunctional enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):39–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Determining the chemical mechanisms of enzyme-catalyzed reactions by kinetic studies. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1977;45:273–387. doi: 10.1002/9780470122907.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimroth P., Walter H., Lynen F. Biosynthese von 6-Methylsalicylsäure. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):98–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donadio S., Staver M. J., McAlpine J. B., Swanson S. J., Katz L. Modular organization of genes required for complex polyketide biosynthesis. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):675–679. doi: 10.1126/science.2024119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehman J., Gaucher G. M. Quantitation of patulin pathway metabolites using gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1977 Feb 1;132(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93766-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramajo H. C., White J., Hutchinson C. R., Bibb M. J. Overproduction and localization of components of the polyketide synthase of Streptomyces glaucescens involved in the production of the antibiotic tetracenomycin C. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6475–6483. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6475-6483.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grootwassink J. W., Gaucher G. M. De novo biosynthesis of secondary metabolism enzymes in homogeneous cultures of Penicillium urticae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):443–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.443-455.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Sherman D. H. Molecular genetics of polyketides and its comparison to fatty acid biosynthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:37–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzaler F., Hahlbrock K. Enzymic synthesis of an aromatic ring from acetate units. Partial purification and some properties of flavanone synthase from cell-suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):205–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Neway J. O., Gaucher G. M. In vitro stabilization of 6-methylsalicylic acid synthetase from Penicillium urticae. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Jan;34(1):30–37. doi: 10.1139/m88-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C. Purification and crystallization of rat liver fatty acid synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):613–619. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. E., Fahrney D. Kinetic analysis of differences in brain acetylcholinesterase from fish or mammalian sources. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(23):2693–2698. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöppner A., Kindl H. Purification and properties of a stilbene synthase from induced cell suspension cultures of peanut. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6806–6811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoops J. K., Wakil S. J. Animal fatty acid synthetase. A novel arrangement of the beta-ketoacyl synthetase sites comprising domains of the two subunits. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5128–5133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turini P., Kurooka S., Steer M., Corbascio A. N., Singer T. P. The action of phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride on human acetylcholinesterase, chymotyrpsin and trypsin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 May;167(1):98–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel G., Lynen F. 6-Methylsalicylic acid synthetase. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:520–530. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner P., Beck J., Beck K. F., Ripka S., Müller G., Lücke S., Schweizer E. Isolation and sequence analysis of the fatty acid synthetase FAS2 gene from Penicillium patulum. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):69–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]