Abstract
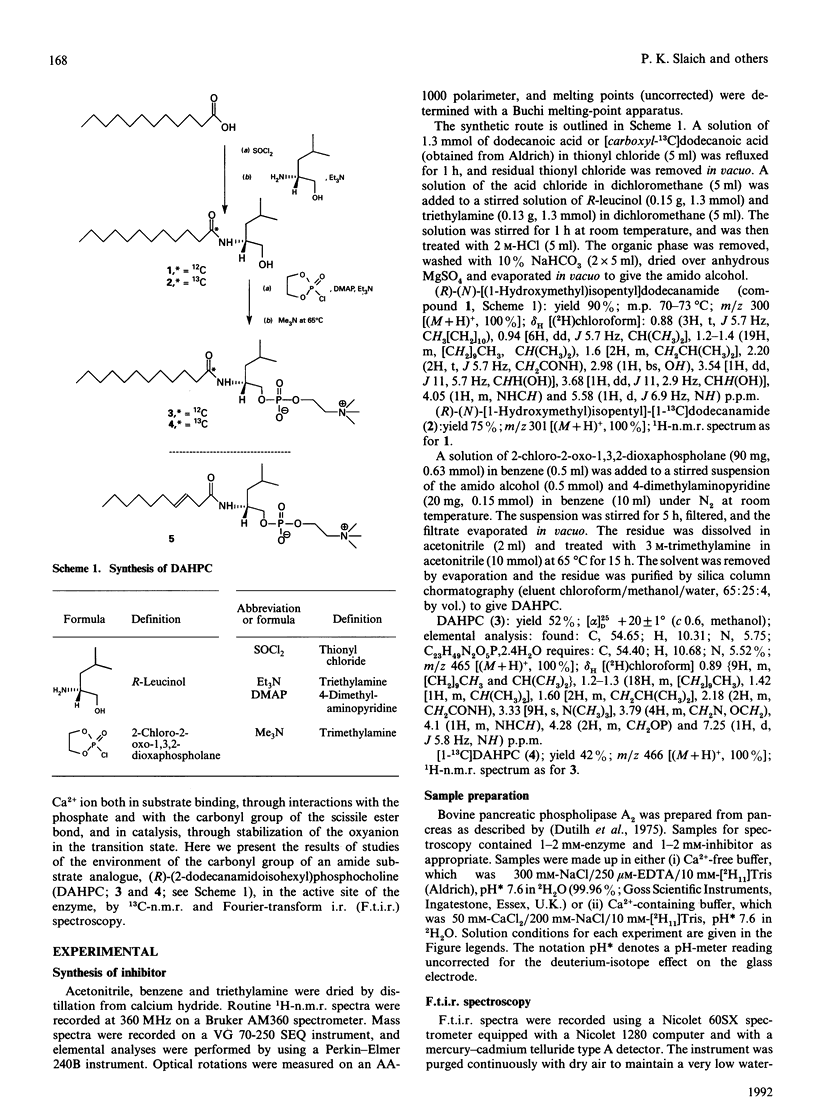
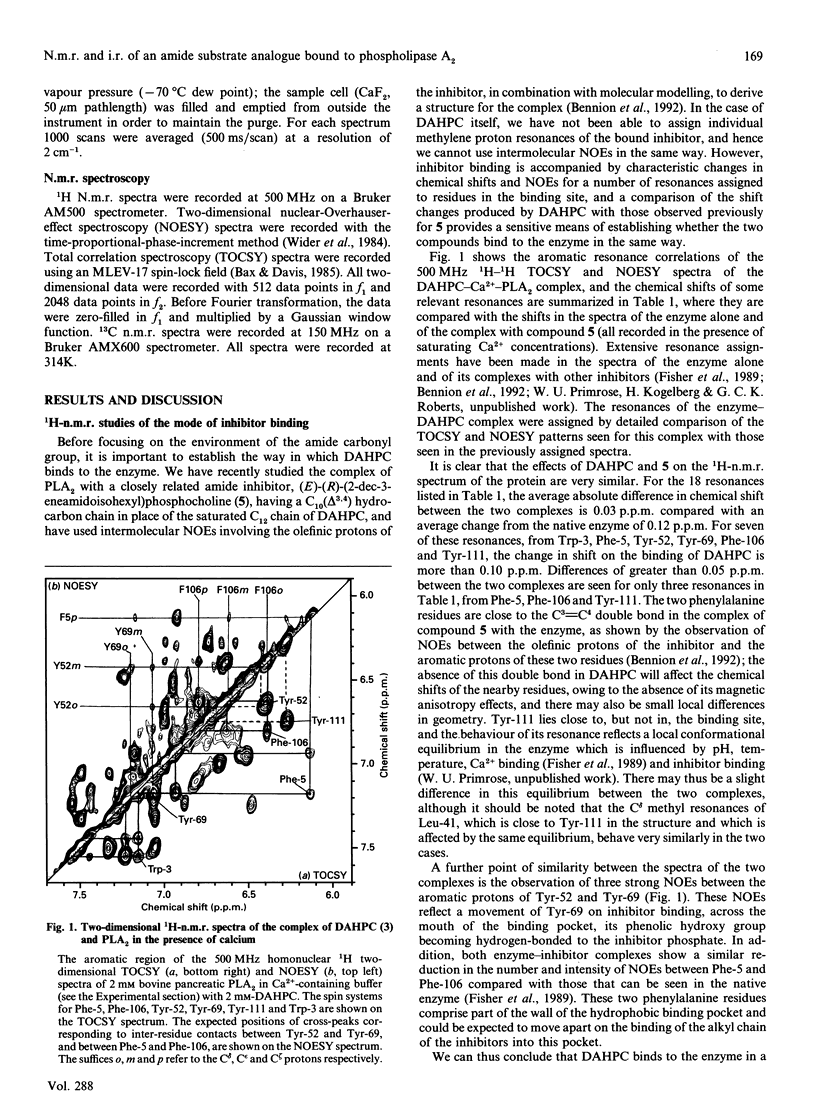
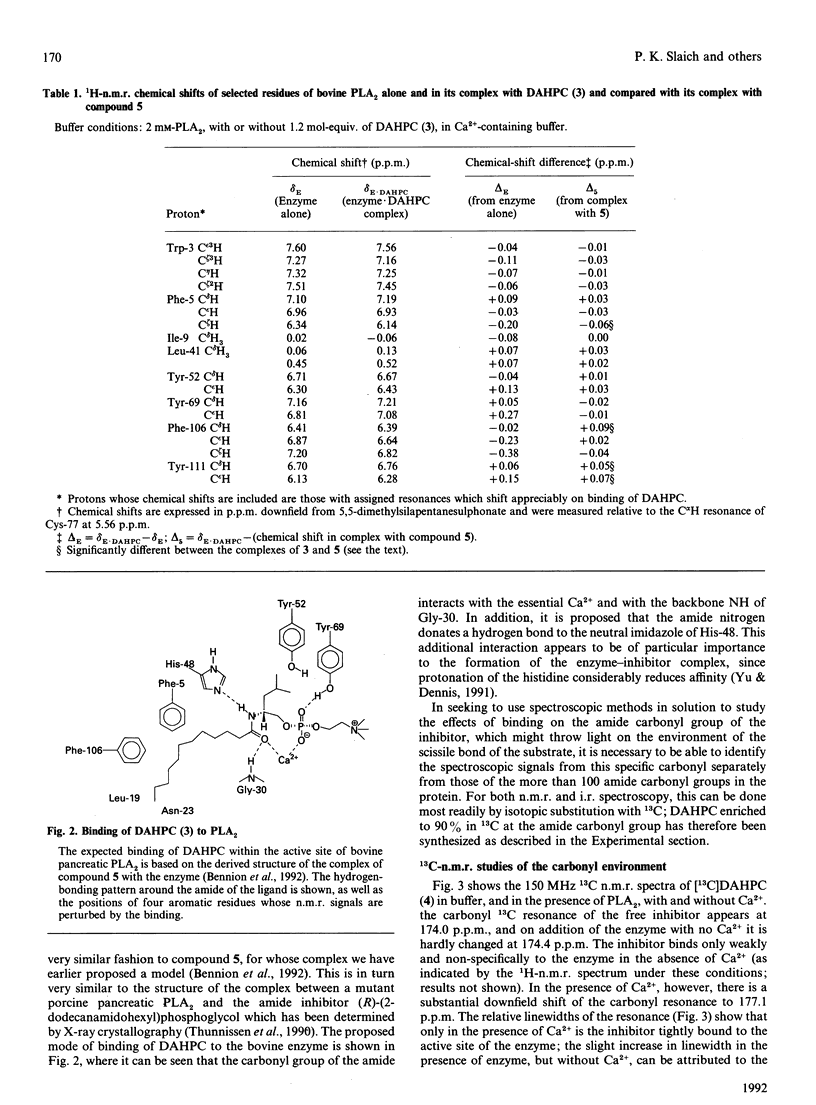
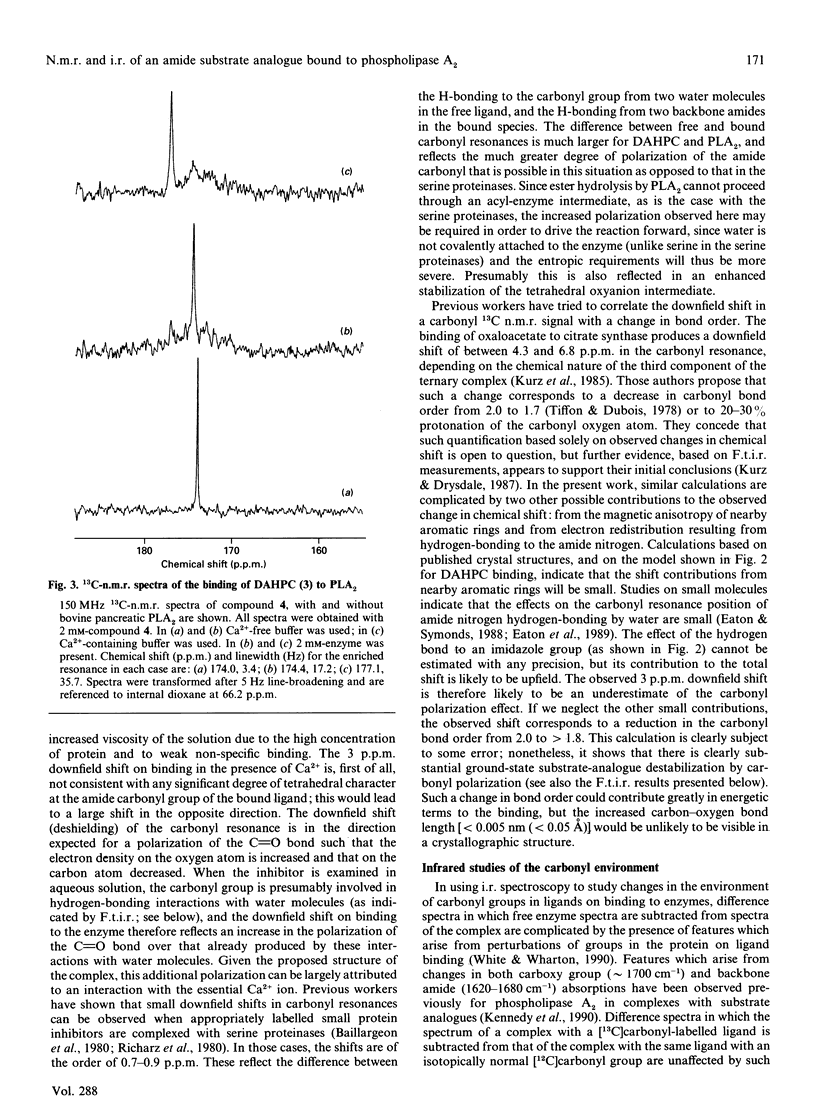
(R)-(2-dodecanamidoisohexyl)phosphocholine (DAHPC), labelled with 13C at the amide carbonyl group, has been synthesized and its binding to bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 (PLA2) studied by n.m.r. and i.r. spectroscopy. Two-dimensional 1H-n.m.r. spectra show that, in the presence of Ca2+, DAHPC binds to the active site of the enzyme in a similar manner to other phospholipid amide substrate analogues. The environment of the labelled carbonyl group has been investigated by a combination of 13C n.m.r. and difference-Fourier-transform i.r. spectroscopy. The carbonyl resonance shifts 3 p.p.m. downfield on the binding of DAHPC to PLA2. The carbonyl absorption frequency decreases by 14-18 cm-1, accompanied by a marked sharpening of the absorption band. These results indicate that the carbonyl bond undergoes significant polarization in the enzyme-ligand complex, facilitated by the enzyme-bound Ca2+ ion. This suggests that ground-state strain is likely to promote catalysis in the case of substrate binding. Simple calculations, based on the i.r. data, indicate that the carbonyl bond is weakened by 5-9 kJ.mol-1. This is the first report of observation of the amide vibration of a bound ligand against the strong background of protein amide vibrations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baillargeon M. W., Laskowski M., Jr, Neves D. E., Porubcan M. A., Santini R. E., Markely J. L. Soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz) and its complex with trypsin. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the reactive site arginine. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5703–5703. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Knowles J. R. Direct observation of substrate distortion by triosephosphate isomerase using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):472–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Knowles J. R. Polarization of substrate carbonyl groups by yeast aldolase: investigation by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):122–129. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion C., Connolly S., Gensmantel N. P., Hallam C., Jackson C. G., Primrose W. U., Roberts G. C., Robinson D. H., Slaich P. K. Design and synthesis of some substrate analogue inhibitors of phospholipase A2 and investigations by NMR and molecular modeling into the binding interactions in the enzyme-inhibitor complex. J Med Chem. 1992 Aug 7;35(16):2939–2951. doi: 10.1021/jm00094a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunie S., Bolin J., Gewirth D., Sigler P. B. The refined crystal structure of dimeric phospholipase A2 at 2.5 A. Access to a shielded catalytic center. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9742–9749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béréziat G., Etienne J., Kokkinidis M., Olivier J. L., Pernas P. New trends in mammalian non-pancreatic phospholipase A2 research. J Lipid Mediat. 1990 May-Jul;2(3-4):159–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker N., Peters A. R., Slotboom A. J., Boelens R., Kaptein R., de Haas G. Porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2: sequence-specific 1H and 15N NMR assignments and secondary structure. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 26;30(12):3135–3146. doi: 10.1021/bi00226a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra B. W., Kalk K. H., Hol W. G., Drenth J. Structure of bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at 1.7A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):97–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra B. W., Renetseder R., Kalk K. H., Hol W. G., Drenth J. Structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at 2.6 A resolution and comparison with bovine phospholipase A2. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):163–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Primrose W. U., Roberts G. C., Dekker N., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Slotboom A. J. 1H NMR studies of bovine and porcine phospholipase A2: assignment of aromatic resonances and evidence for a conformational equilibrium in solution. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5939–5946. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamer G., Argos P. Comparison of the active center geometries in phospholipase, trypsin and thermolysin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 29;669(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. F., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H., Chapman D. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic (FTIR) study of porcine and bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 and their interaction with substrate analogues and a transition-state inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 27;1040(3):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komives E. A., Chang L. C., Lolis E., Tilton R. F., Petsko G. A., Knowles J. R. Electrophilic catalysis in triosephosphate isomerase: the role of histidine-95. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 26;30(12):3011–3019. doi: 10.1021/bi00226a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz L. C., Ackerman J. J., Drysdale G. R. Evidence from 13C NMR for polarization of the carbonyl of oxaloacetate in the active site of citrate synthase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):452–457. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz L. C., Drysdale G. R. Evidence from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for polarization of the carbonyl of oxaloacetate in the active site of citrate synthase. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2623–2627. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeser R. F., Smith D. M., Turner R. A. Phospholipase activity in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and crystal-associated arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Jul-Aug;8(4):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A. Metabolism of arachidonic acid. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;522:454–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb33385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarz R., Tschesche H., Wüthrich K. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the selectively isotope-labeled reactive site peptide bond of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor in the complexes with trypsin, trypsinogen, and anhydrotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5711–5715. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S. E., Lindgren J. A., Rouzer C. A., Serhan C. N. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1171–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.2820055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Otwinowski Z., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of bee-venom phospholipase A2 in a complex with a transition-state analogue. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2274788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., White S. P., Browning J. L., Rosa J. J., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Structures of free and inhibited human secretory phospholipase A2 from inflammatory exudate. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1007–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.1948070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., White S. P., Otwinowski Z., Yuan W., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Interfacial catalysis: the mechanism of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1541–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2274785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder F. Chemical and biochemical aspects of platelet activating factor: a novel class of acetylated ether-linked choline-phospholipids. Med Res Rev. 1985 Jan-Mar;5(1):107–140. doi: 10.1002/med.2610050105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunnissen M. M., Ab E., Kalk K. H., Drenth J., Dijkstra B. W., Kuipers O. P., Dijkman R., de Haas G. H., Verheij H. M. X-ray structure of phospholipase A2 complexed with a substrate-derived inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):689–691. doi: 10.1038/347689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonge P. J., Pusztai M., White A. J., Wharton C. W., Carey P. R. Resonance Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic studies of the acyl carbonyl group in [3-(5-methyl-2-thienyl)acryloyl]chymotrypsin: evidence for artifacts in the spectra obtained by both techniques. Biochemistry. 1991 May 14;30(19):4790–4795. doi: 10.1021/bi00233a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij H. M., Volwerk J. J., Jansen E. H., Puyk W. C., Dijkstra B. W., Drenth J., de Haas G. H. Methylation of histidine-48 in pancreatic phospholipase A2. Role of histidine and calcium ion in the catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):743–750. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzien H. U. Cytolytic and membrane-perturbing properties of lysophosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 20;559(2-3):259–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wery J. P., Schevitz R. W., Clawson D. K., Bobbitt J. L., Dow E. R., Gamboa G., Goodson T., Jr, Hermann R. B., Kramer R. M., McClure D. B. Structure of recombinant human rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid phospholipase A2 at 2.2 A resolution. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):79–82. doi: 10.1038/352079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. J., Wharton C. W. Hydrogen-bonding in enzyme catalysis. Fourier-transform infrared detection of ground-state electronic strain in acyl-chymotrypsins and analysis of the kinetic consequences. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):627–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2700627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. P., Scott D. L., Otwinowski Z., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of cobra-venom phospholipase A2 in a complex with a transition-state analogue. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1560–1563. doi: 10.1126/science.2274787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Dennis E. A. Critical role of a hydrogen bond in the interaction of phospholipase A2 with transition-state and substrate analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9325–9329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


