Abstract
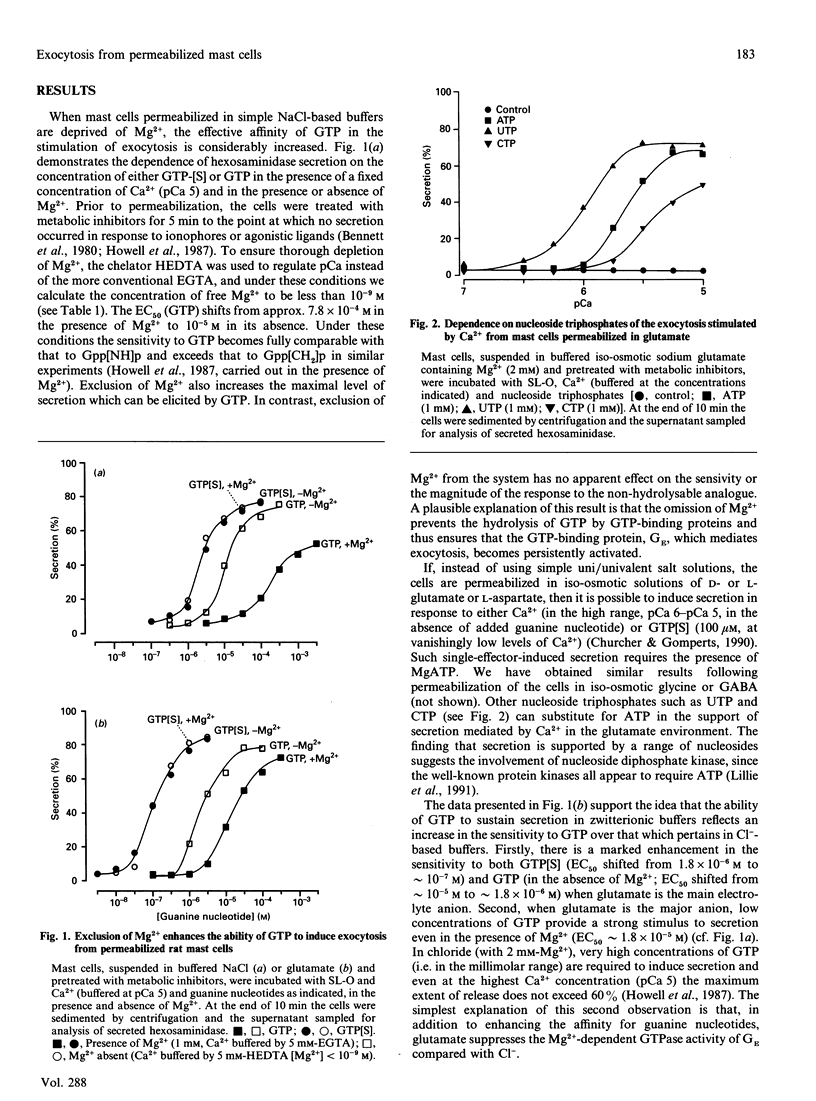
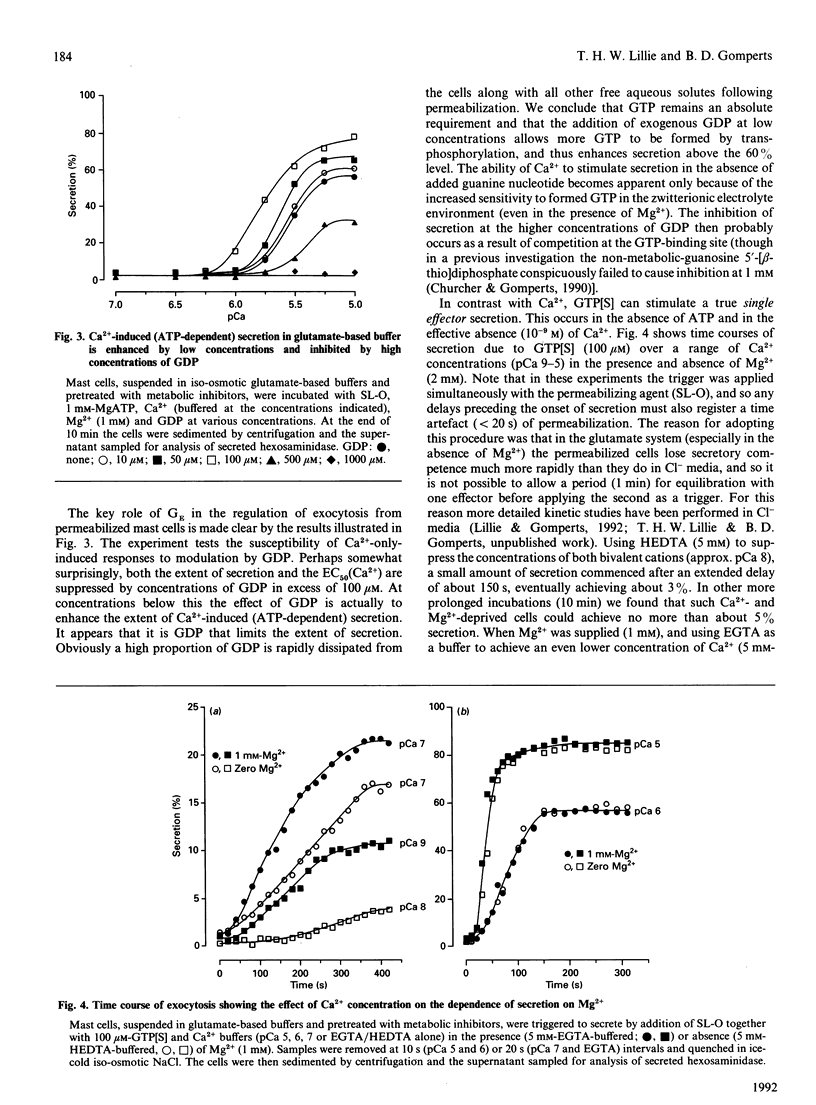
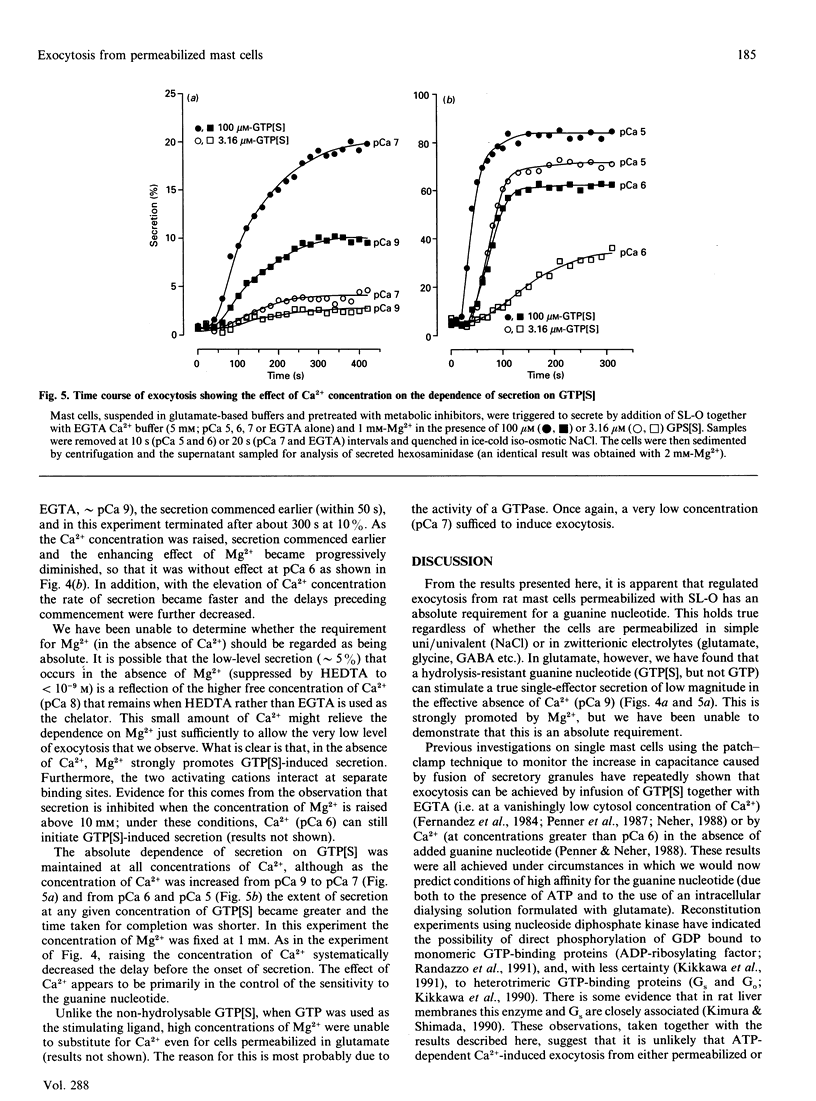
Exocytosis from metabolically depleted permeabilized rat mast cells was measured in response to provision of Ca2+ and guanine nucleotide [GTP or guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S])]. For cells permeabilized in simple salt solutions (NaCl), both of these effectors were required to induce secretion. Exclusion of Mg2+ caused an increase in both the sensitivity of the system to GTP and the extent of secretion elicited, while having no such effects on secretion induced by GTP[S]. The effect of Mg2+ depletion on the ability of GTP to stimulate secretion is probably due to the dependence on Mg2+ of the GTPase activity of GE (a postulated GTP-binding protein which mediates exocytosis). This argues that a persistent stimulus to the G-protein is required to support secretion. Affinity for both GTP[S] and GTP is enhanced when the cells are permeabilized in zwitterionic electrolytes (glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, glycine) instead of NaCl. Under these conditions, secretion occurs in response to provision of either GTP[S] [in the effective absence of Ca2+ (pCa 9)] or Ca2+ (in the absence of guanine nucleotide). Secretion induced by GTP[S] is strongly promoted by the presence of Mg2+ at concentrations in the millimolar range; this promotion by Mg2+ declines as the concentration of Ca2+ is elevated towards pCa 7. At pCa 6, Mg2+ is without effect. Ca(2+)-induced secretion requires the provision of MgATP. Since this is further enhanced by low concentrations (< 100 microM) and then inhibited by high concentrations of GDP, the essential role of ATP is likely to be in the maintenance of GTP via transphosphorylation by a nucleoside diphosphate kinase reaction. Thus, under conditions of high affinity (glutamate environment), GTP[S] alone is capable of inducing exocytosis. Ca2+ acts in concert with guanine nucleotides: it enhances the rate and extent of secretion and increases the affinity for Mg2+ and guanine nucleotides in the activation of the GTP-binding protein (GE) which regulates exocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon R. A., Salminen A., Ruohola H., Novick P., Ferro-Novick S. The GTP-binding protein Ypt1 is required for transport in vitro: the Golgi apparatus is defective in ypt1 mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Ionomycin stimulates mast cell histamine secretion by forming a lipid-soluble calcium complex. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):851–853. doi: 10.1038/282851a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher Y., Gomperts B. D. ATP-dependent and ATP-independent pathways of exocytosis revealed by interchanging glutamate and chloride as the major anion in permeabilized mast cells. Cell Regul. 1990 Mar;1(4):337–346. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.4.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Bennett J. P., Hide I., Kay A. B., Gomperts B. D. Mechanisms of granule enzyme secretion from permeabilized guinea pig eosinophils. Dependence on Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1905–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Neher E., Gomperts B. D. Capacitance measurements reveal stepwise fusion events in degranulating mast cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):453–455. doi: 10.1038/312453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. A small GTP-binding protein dissociates from synaptic vesicles during exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):79–81. doi: 10.1038/349079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S. Dual role for guanine nucleotides in stimulus-secretion coupling. Fed Proc. 1986 Jun;45(7):2156–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Tatham P. E. Regulated exocytotic secretion from permeabilized cells. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:178–189. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Saraste J. Small GTP-binding protein associated with Golgi cisternae. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):553–556. doi: 10.1038/345553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Potentiation by thrombin of the secretion of serotonin from permeabilized platelets equilibrated with Ca2+ buffers. Relationship to protein phosphorylation and diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):351–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2220351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of hormone-sensitive GTP-dependent regulatory proteins by chloride. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3597–3602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Essential synergy between Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides in exocytotic secretion from permeabilized rat mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):191–197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L. Hormone receptor modulates the regulatory component of adenylyl cyclase by reducing its requirement for Mg2+ and enhancing its extent of activation by guanine nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5179–5183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L. Hysteretic activation of adenylyl cyclases. I. Effect of Mg ion on the rate of activation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11036–11041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R. Hysteretic activation of adenylyl cyclases. II. Mg ion regulation of the activation of the regulatory component as analyzed by reconstitution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11042–11050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Pilkis S. J., Hamet P. Liver membrane adenylate cyclase. Synergistic effects of anions on fluoride, glucagon, and guanyl nucleotide stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6599–6607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa S., Takahashi K., Takahashi K., Shimada N., Ui M., Kimura N., Katada T. Conversion of GDP into GTP by nucleoside diphosphate kinase on the GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21536–21540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Shimada N. Evidence for complex formation between GTP binding protein(Gs) and membrane-associated nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91680-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. The phorbol ester TPA increases the affinity of exocytosis for calcium in 'leaky' adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmann W. R., Jr, Jackson R. C. Calcium- and guanine-nucleotide-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized rat mast cells. Modulation by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):365–373. doi: 10.1042/bj2650365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie T. H., Gomperts B. D. Nucleotides and divalent cations as effectors and modulators of exocytosis in permeabilized rat mast cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Apr 29;336(1276):25–34. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie T. H., Whalley T. D., Gomperts B. D. Modulation of the exocytotic reaction of permeabilised rat mast cells by ATP, other nucleotides and Mg2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 24;1094(3):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90097-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt D. L., Gruber H. E., Walker L. L. Ribavirin inhibits mast cell mediator release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jan;240(1):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Moore H. P. Reconstitution of constitutive secretion using semi-intact cells: regulation by GTP but not calcium. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):39–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. The influence of intracellular calcium concentration on degranulation of dialysed mast cells from rat peritoneum. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:193–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P. J., Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Nair J., Potenza M. Regulation of vesicular traffic by a GTP-binding protein on the cytoplasmic surface of secretory vesicles in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):637–647. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsse O., Lindau M., Cromwell O., Kay A. B., Gomperts B. D. Intracellular application of guanosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) induces exocytotic granule fusion in guinea pig eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):775–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E. Secretory responses of rat peritoneal mast cells to high intracellular calcium. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Pusch M., Neher E. Washout phenomena in dialyzed mast cells allow discrimination of different steps in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biosci Rep. 1987 Apr;7(4):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF01121453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Northup J. K., Kahn R. A. Activation of a small GTP-binding protein by nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1658935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter S. M., Valenzuela D., Kennedy T. E., Neer E. J., Fishman M. C. G0 is a major growth cone protein subject to regulation by GAP-43. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):836–841. doi: 10.1038/344836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Guanine nucleotides stimulate polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytotic secretion from HL60 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2500375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M., Christophe J. The monovalent anions chloride and azide as potent activators of NaF- and p(NH)ppG-stimulation of pancreatic adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 15;86(2):230–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Goud B., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J. Mutational analysis of SEC4 suggests a cyclical mechanism for the regulation of vesicular traffic. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1685–1693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Natsumeda Y., Weber G. Action of the active metabolites of tiazofurin and ribavirin on purified IMP dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2193–2196. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


