Abstract
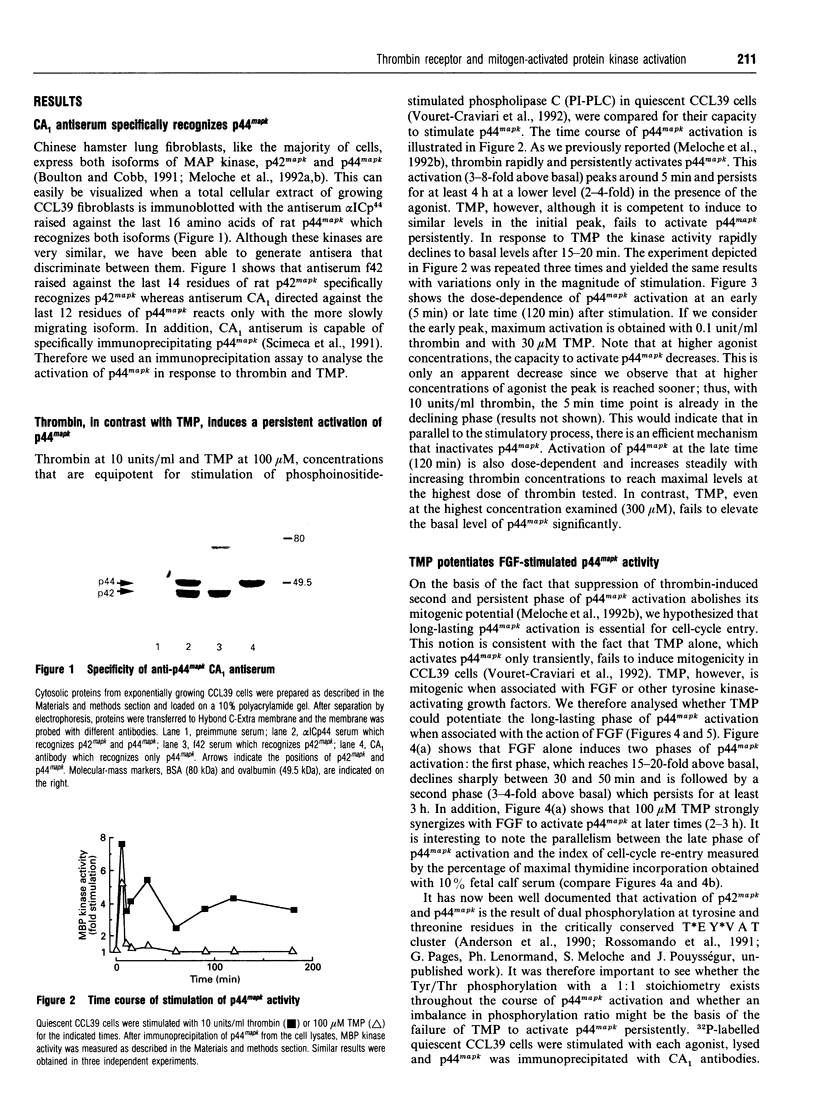
alpha-Thrombin (thrombin), a potent mitogen for CCL39 hamster lung fibroblasts, stimulates phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) and inhibits adenylate cyclase via cleavage of a specific G-protein-coupled receptor (TH-R), recently cloned from human and hamster cells. This action can be entirely mimicked by the synthetic peptide SFFLRNP, referred to here as TMP (thrombin-mimicking peptide). TMP corresponds to the first seven amino acids of the new N-terminus generated by thrombin cleavage of the hamster TH-R. Although thrombin and TMP apparently generate identical early transmembrane signals, only thrombin is mitogenic on its own. TMP needs to be associated with fibroblast growth factor (FGF), a tyrosine kinase-activating growth factor, to induce cell-cycle re-entry. Here, we have examined the early and late phase of p44 MAP kinase (p44mapk) activation in G0-arrested CCL39 cells after stimulation by thrombin, TMP, FGF or TMP+FGF. We found that: (i) both thrombin and TMP rapidly activate p44mapk in a dose-dependent manner with maximum activation at around 5 min, (ii) after the initial burst of activation, a second and long-lasting wave of activation is observed in response to thrombin (10-100 nM) but not to TMP (up to 300 microM), (iii) FGF alone (25 ng/ml), like thrombin, rapidly and persistently activates p44mapk (20-fold at 5 min and about 3-fold after 2 h), (iv) TMP added together with FGF strongly potentiates the second and sustained phase of p44mapk activation. From these results we propose that: (1) thrombin-induced mitogenesis is mediated only in part by the TH-R recently cloned and (2) activation of p44mapk, in particular the long-lasting phase that correlates with DNA synthesis, is an obligatory event for cell-cycle re-entry.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. Identification of multiple extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) with antipeptide antibodies. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):357–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Glenn K. C., Cunningham D. D. Conditions which affect initiation of animal cell division by trypsin and thrombin. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Apr;95(1):13–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenic activity of blood components. I. Thrombin and prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Robbins D. J., Boulton T. G. ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated MAP-2 kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Regulation of thrombin generation and functions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1988 Jul;14(3):234–240. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan C., Seuwen K., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Coordinate, biphasic activation of p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase and S6 kinase by growth factors in hamster fibroblasts. Evidence for thrombin-induced signals different from phosphoinositide turnover and adenylylcyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13369–13375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno M., Pouysségur J. Alpha-thrombin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of 43,000- and 41,000-Mr proteins is independent of cytoplasmic alkalinization in quiescent fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):451–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2380451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnaldo I., Pouysségur J., Paris S. Thrombin exerts a dual effect on stimulated adenylate cyclase in hamster fibroblasts, an inhibition via a GTP-binding protein and a potentiation via activation of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):711–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2530711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kosako H., Takenaka K., Moriyama K., Sakai H., Akiyama T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):973–982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., Pagès G., Pouysségur J. Functional expression and growth factor activation of an epitope-tagged p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, p44mapk. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):63–71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., Seuwen K., Pagès G., Pouysségur J. Biphasic and synergistic activation of p44mapk (ERK1) by growth factors: correlation between late phase activation and mitogenicity. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 May;6(5):845–854. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.5.1603090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Seuwen K. Transmembrane receptors and intracellular pathways that control cell proliferation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:195–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rodriquez R., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factor requirements of Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts in serum free media: high mitogenic action of thrombin. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1981 Apr;5(4):347–357. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(81)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen U. B., Vouret-Craviari V., Jallat S., Schlesinger Y., Pagès G., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Pouysségur J., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. cDNA cloning and expression of a hamster alpha-thrombin receptor coupled to Ca2+ mobilization. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Sanghera J. S., Marsden L. A., Weber M. J., Pelech S. L., Sturgill T. W. Biochemical characterization of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases regulated by tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20270–20275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scimeca J. C., Ballotti R., Nguyen T. T., Filloux C., Van Obberghen E. Tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of an immunoaffinity-purified 44-kDa MAP kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9313–9319. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Kahan C., Hartmann T., Pouyssegur J. Strong and persistent activation of inositol lipid breakdown induces early mitogenic events but not Go to S phase progression in hamster fibroblasts. Comparison of thrombin and carbachol action in cells expressing M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22292–22299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. MAP kinase by any other name smells just as sweet. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90199-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Chambard J. C., Paris S., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. alpha-Thrombin-induced early mitogenic signalling events and G0 to S-phase transition of fibroblasts require continual external stimulation. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2927–2932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-potentiating action and binding characteristics of insulin and insulin-like growth factors in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Sep;147(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vouret-Craviari V., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Rasmussen U. B., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Pouysségur J. Synthetic alpha-thrombin receptor peptides activate G protein-coupled signaling pathways but are unable to induce mitogenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):95–102. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]