Abstract
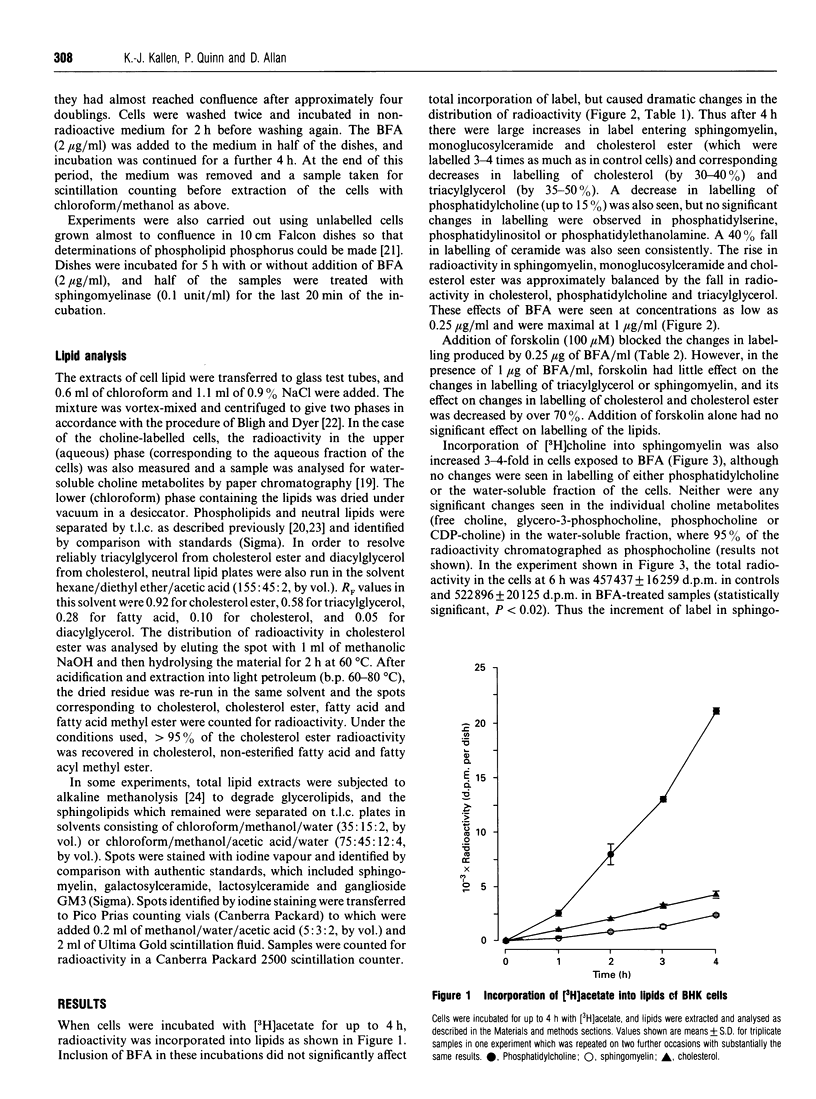
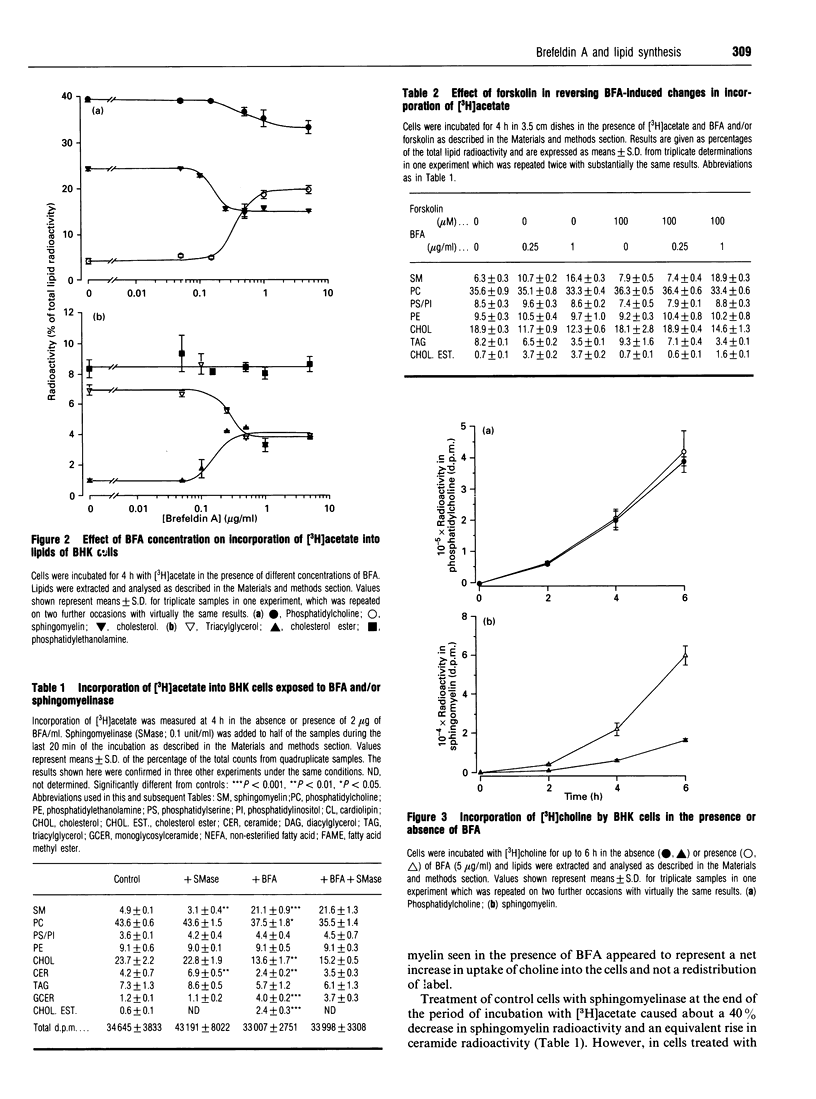
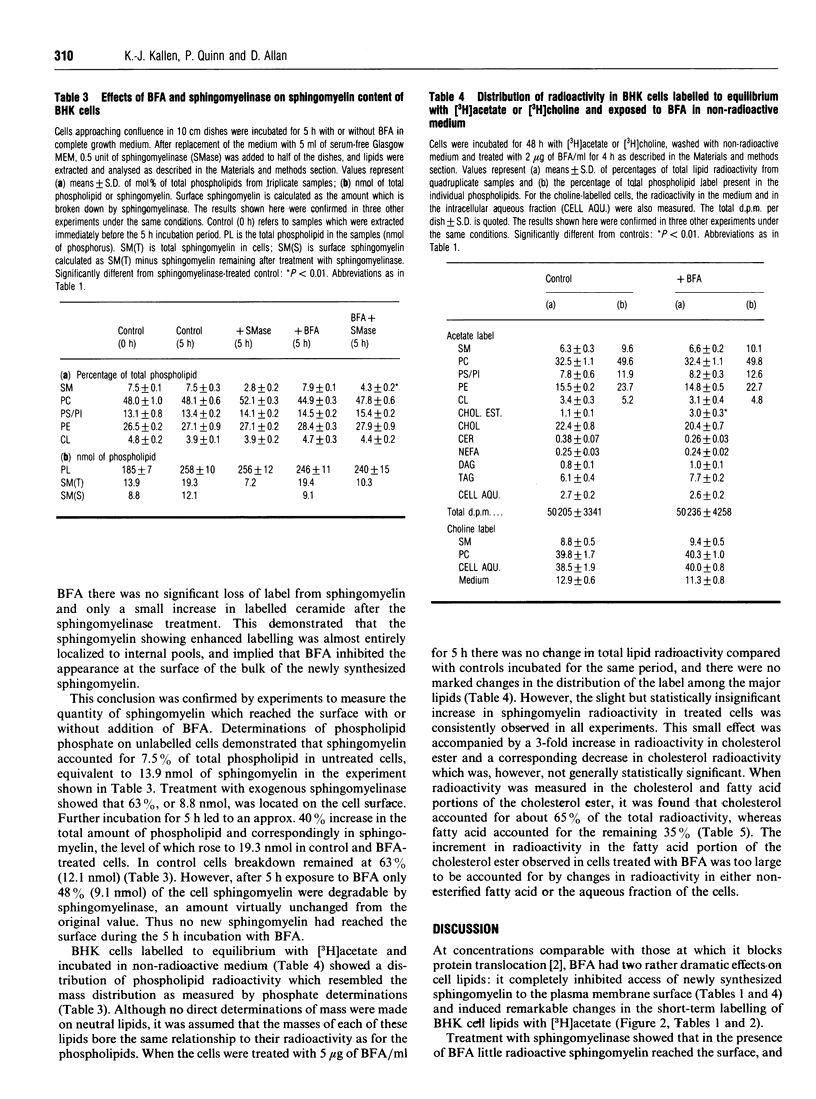
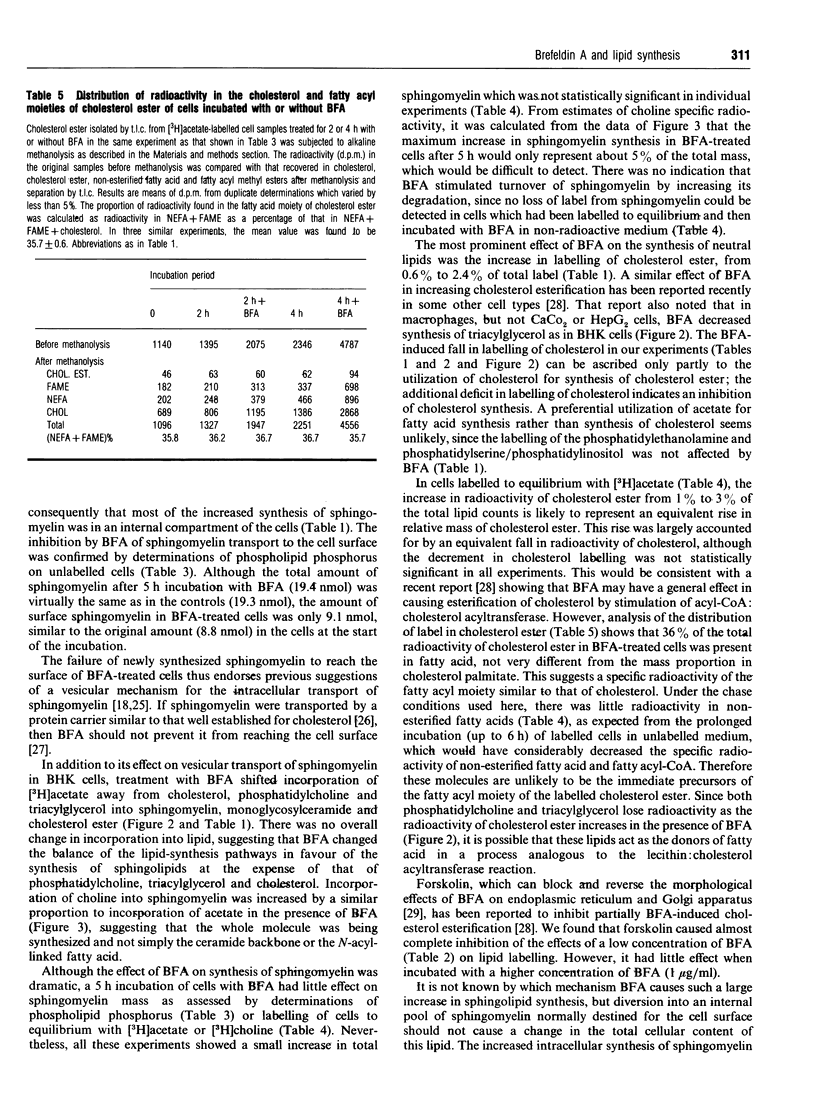
1. Addition of brefeldin A (BFA) to BHK cells incubated for 4 h with [3H]acetate led to a 3-4-fold increase in incorporation of label into sphingomyelin, monoglucosylceramide and cholesterol ester compared with untreated controls. There was a similar increase in incorporation of [3H]choline into sphingomyelin. The level of cholesterol ester increased 3-fold when BFA was added to cells labelled to equilibrium with [3H]acetate, but no statistically significant changes in the levels of other lipids were seen. 2. BFA appeared to act by diverting incorporation of acetate into sphingolipids and cholesterol ester at the expense of phosphatidylcholine (decreased by up to 15%), cholesterol (decreased by 30-40%) and triacylglycerol (decreased by 35-50%). 3. Forskolin (100 microM) prevented the changes in labelling induced by 0.25 micrograms of BFA/ml, but in the presence of 1 micrograms of BFA/ml it had no effect on sphingomyelin and triacylglycerol labelling and only partly blocked the effects of BFA on labelling of cholesterol and cholesterol ester. 4. None of the labelled sphingomyelin was degraded in BFA-treated cells which were subsequently exposed to an extracellular sphingomyelinase, showing that all the newly synthesized sphingomyelin remained inside the cells. Determinations of phospholipid phosphorus in unlabelled cells confirmed that, in the presence of BFA, no newly synthesized sphingomyelin was able to reach the cell surface, supporting the idea that sphingomyelin normally depends on vesicular transport for its passage to the plasma membrane. 5. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that cholesterol synthesis and esterification processes in BHK cells are sensitive to the plasma-membrane deficit of sphingomyelin caused by BFA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcalde J., Bonay P., Roa A., Vilaro S., Sandoval I. V. Assembly and disassembly of the Golgi complex: two processes arranged in a cis-trans direction. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):69–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Quinn P. Resynthesis of sphingomyelin from plasma-membrane phosphatidylcholine in BHK cells treated with Staphylococcus aureus sphingomyelinase. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):765–771. doi: 10.1042/bj2540765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billheimer J. T., Reinhart M. P. Intracellular trafficking of sterols. Subcell Biochem. 1990;16:301–331. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1621-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüning A., Karrenbauer A., Schnabel E., Wieland F. T. Brefeldin A-induced increase of sphingomyelin synthesis. Assay for the action of the antibiotic in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5052–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuticke B. Properties and structural basis of simple diffusion pathways in the erythrocyte membrane. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;78:1–97. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Stieger B., Hubbard A. L., Pagano R. E. Sphingomyelin synthesis in rat liver occurs predominantly at the cis and medial cisternae of the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8650–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Barenholz Y. Enzymes of complex lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):61–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. K., Rudney H. Plasma membrane sphingomyelin and the regulation of HMG-CoA reductase activity and cholesterol biosynthesis in cell cultures. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jan;32(1):125–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeckel D., Karrenbauer A., Birk R., Schmidt R. R., Wieland F. Sphingomyelin is synthesized in the cis Golgi. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80659-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeckel D., Karrenbauer A., Burger K. N., van Meer G., Wieland F. Glucosylceramide is synthesized at the cytosolic surface of various Golgi subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):259–267. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Pagano R. E. Lipid transport during mitosis. Alternative pathways for delivery of newly synthesized lipids to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5966–5973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval M., Pagano R. E. Lipid recycling between the plasma membrane and intracellular compartments: transport and metabolism of fluorescent sphingomyelin analogues in cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2169–2181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Glickman J., Donaldson J. G., Robbins J., Kreis T. E., Seamon K. B., Sheetz M. P., Klausner R. D. Forskolin inhibits and reverses the effects of brefeldin A on Golgi morphology by a cAMP-independent mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):567–577. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky N. G., Pagano R. E. Intracellular translocation of fluorescent sphingolipids in cultured fibroblasts: endogenously synthesized sphingomyelin and glucocerebroside analogues pass through the Golgi apparatus en route to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):27–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandon E. C., Ehses I., Rother J., van Echten G., Sandhoff K. Subcellular localization and membrane topology of serine palmitoyltransferase, 3-dehydrosphinganine reductase, and sphinganine N-acyltransferase in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11144–11148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Prodraza H., Fishman P. H. Effect of drugs and temperature on biosynthesis and transport of glycosphingolipids in cultured neurotumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 22;804(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E. What is the fate of diacylglycerol produced at the Golgi apparatus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jun;13(6):202–205. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Multiple targets for brefeldin A. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):449–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P., Allan D. Two separate pools of sphingomyelin in BHK cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 20;1124(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90131-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Banting G. Perturbation of the morphology of the trans-Golgi network following Brefeldin A treatment: redistribution of a TGN-specific integral membrane protein, TGN38. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):85–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Saito M., Rosenberg A. Action of monensin, a monovalent cationophore, on cultured human fibroblasts: evidence that it induces high cellular accumulation of glucosyl- and lactosylceramide (gluco- and lactocerebroside). Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1043–1046. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotte J. P., Härmälä A. S., Jansson C., Pörn M. I. Rapid turn-over of plasma membrane sphingomyelin and cholesterol in baby hamster kidney cells after exposure to sphingomyelinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Dec 14;1030(2):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotte J. P., Tenhunen J., Pörn I. Effects of sphingomyelin degradation on cholesterol mobilization and efflux to high-density lipoproteins in cultured fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 27;1025(2):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Dabach Y., Hollander G., Ben-Naim M., Stein Y. Dissimilar effects of Brefeldin A on cholesteryl ester and triacylglycerol metabolism in CaCo2 and HepG2 cells as compared to peritoneal macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 8;1125(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90151-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbani L., Simoni R. D. Cholesterol and vesicular stomatitis virus G protein take separate routes from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1919–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van 't Hof W., van Meer G. Generation of lipid polarity in intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells: sphingolipid synthesis in the Golgi complex and sorting before vesicular traffic to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):977–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Echten G., Iber H., Stotz H., Takatsuki A., Sandhoff K. Uncoupling of ganglioside biosynthesis by Brefeldin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;51(1):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G. Lipid traffic in animal cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:247–275. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Stelzer E. H., Wijnaendts-van-Resandt R. W., Simons K. Sorting of sphingolipids in epithelial (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1623–1635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


