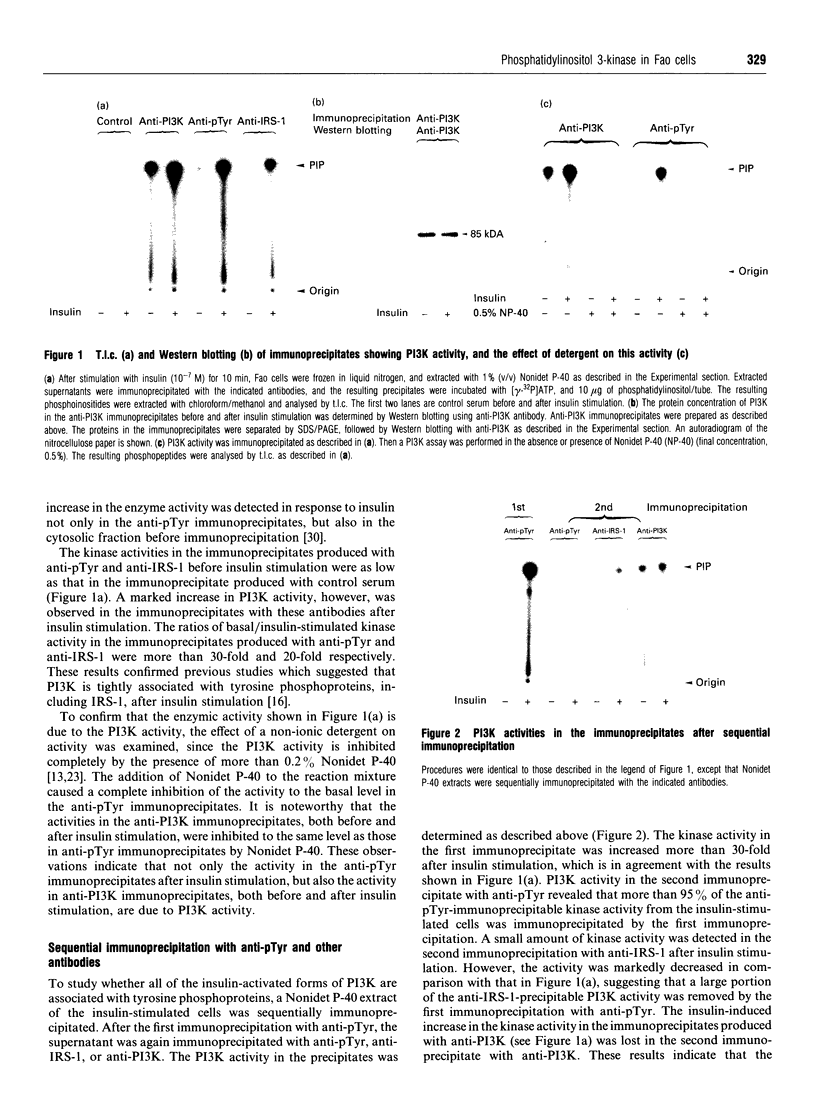
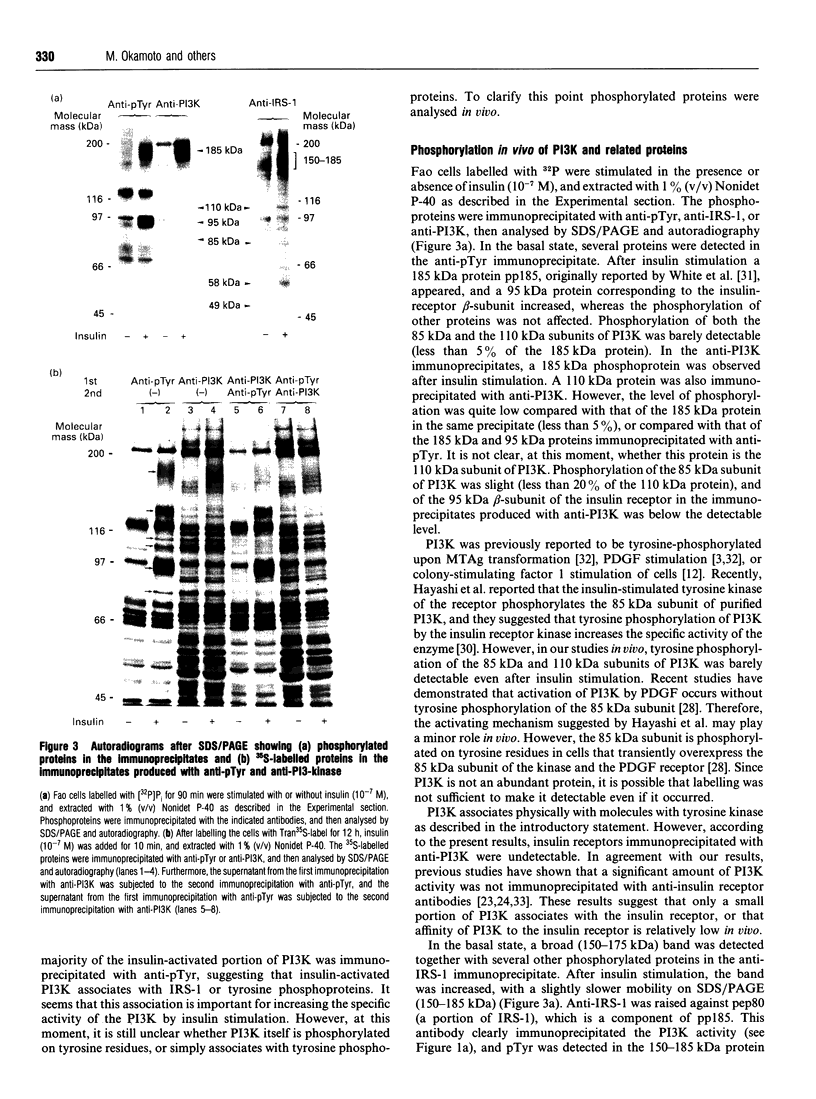
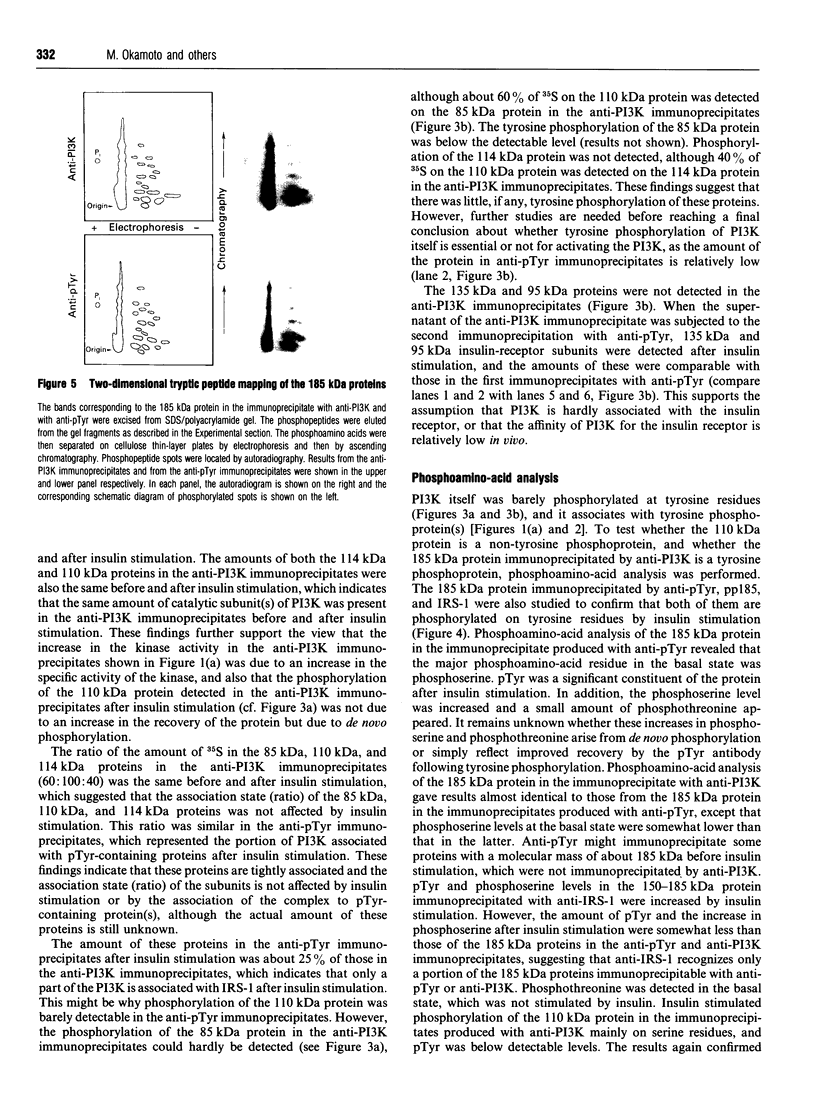
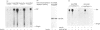Abstract
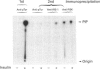
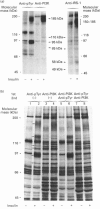
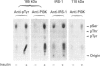
We investigated whether phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is phosphorylated and whether its specific activity is increased by insulin stimulation in vivo using Fao cells and antibodies raised against the 85 kDa subunit of PI3K, insulin-receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), and phosphotyrosine (pTyr). PI3K activity was detected in the immunoprecipitate produced with anti-PI3K at a basal state. The activity was increased 2-3-fold by insulin stimulation, although the protein concentration of kinase in the anti-PI3K immunoprecipitates was the same before and after insulin stimulation. Both anti-pTyr and anti-IRS-1 antibodies immunoprecipitated the kinase activity only after insulin stimulation. After the first immunoprecipitation with anti-pTyr, the supernatant was immunoprecipitated once more with anti-PI3K. PI3K activity in the second immunoprecipitate revealed little difference between the basal and insulin-stimulated states, suggesting that most of the insulin-activated portion of PI3K was precipitated by anti-pTyr. Both IRS-1 and the insulin-receptor beta-subunit (95 kDa) were phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by insulin stimulation and immunoprecipitated with anti-pTyr. However, phosphorylation of neither subunit of PI3K (85 kDa or 110 kDa) was detectable in the immunoprecipitate produced with anti-pTyr. The 185 kDa pTyr-containing protein was immunoprecipitated with anti-PI3K after insulin stimulation, although there was little phosphorylation of the 85 kDa protein. pTyr in the 110 kDa protein immunoprecipitated with anti-PI3K was below detectable levels. These results indicate that the specific activity of PI3K is increased by insulin stimulation without detectable tyrosine phosphorylation of PI3K itself in Fao cells. The majority of the insulin-activated portion of PI3K is associated with pTyr-containing proteins including IRS-1, which suggests that this is important for activation of PI3K by insulin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Carpenter C. L., Shoelson S. E., Piwnica-Worms H., Cantley L. C. Polyoma virus middle T antigen-pp60c-src complex associates with purified phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5408–5415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Schroeder G. G., Kahn C. R., Myers M. G., Jr, Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., White M. F. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity maps to insulin receptor regions required for endogenous substrate phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1367–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Miyake N., Kanai F., Shibasaki F., Takenawa T., Ebina Y. Phosphorylation in vitro of the 85 kDa subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and its possible activation by insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):769–775. doi: 10.1042/bj2800769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Chen K. S., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B. S., Backer J., White M. F., Cantley L. C., Ruderman N. B. Mutations in the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor impair activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;5(6):769–777. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Pallas D. C., Morgan W., Schaffhausen B., Roberts T. M. Mechanisms of transformation by polyoma virus middle T antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb;948(3):345–364. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Ruderman N. B., Chen K. S. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in isolated rat adipocytes. Activation by insulin and subcellular distribution. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3423–3428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. S., Ascoli M. Anti-phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitation of phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase activity in different cell types after exposure to epidermal growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):289–295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Kahn C. R., Maron R., White M. F. Decreased autophosphorylation of EGF receptor in insulin-deficient diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):E429–E434. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.4.E429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Karasik A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Coordinate phosphorylation of insulin-receptor kinase and its 175,000-Mr endogenous substrate in rat hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):66–72. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Karasik A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Epidermal growth factor stimulated phosphorylation of a 120-kilodalton endogenous substrate protein in rat hepatocytes. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9489–9494. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Predominance of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptors during the initial response of intact cells to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7131–7136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Steele-Perkins G., Hari J., Stover C., Pierce S., Turner J., Edman J. C., Rutter W. J. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors and responses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):537–543. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Backer J. M. Preparation and use of anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies to study structure and function of insulin receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:65–79. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01009-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa K., Pierce S., Stover C., Aggerbeck M., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Endogenous substrates of the insulin receptor: studies with cells expressing wild-type and mutant receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;293:227–238. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5949-4_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa K., Yokono K., Shii K., Ogawa W., Ando A., Hara K., Baba S., Kaburagi Y., Yamamoto-Honda R., Momomura K. In vitro association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity with the activated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):440–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]