Abstract
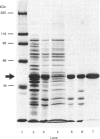
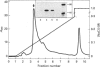
The Synechococcus phytoene desaturase has been isolated from an overexpressing strain of Escherichia coli. The plasma pPDSde135 mediated the overexpression of the full-length polypeptide directly. The recombinant protein comprised 5% of the total cellular protein and was found predominantly in the inclusion body fraction. Urea was used to solubilize the recombinant protein from the inclusion fraction and the protein was subsequently purified to homogeneity on a DEAE-cellulose column. The purification scheme yielded 4.0 mg of homogeneous desaturase protein after a 20-fold purification, recovering 40% of the original protein from a 100 ml suspension culture of E. coli. The recombinant desaturase had an apparent molecular mass of 53 kDa on SDS/PAGE and crossreacted with an antiserum raised against the expressed protein. Desaturase activity was restored upon the removal of urea. The enzyme catalysed the conversion of phytoene to zeta-carotene via phytofluene. These products of the desaturase reaction existed predominantly in a cis configuration. Lipid replenishment enhanced activity. NAD+ and NADP+ were observed to be involved, whilst FAD was an ineffective electron acceptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong G. A., Alberti M., Hearst J. E. Conserved enzymes mediate the early reactions of carotenoid biosynthesis in nonphotosynthetic and photosynthetic prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9975–9979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. A., Alberti M., Leach F., Hearst J. E. Nucleotide sequence, organization, and nature of the protein products of the carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):254–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00334364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley G. E., Schmidhauser T. J., Yanofsky C., Scolnik P. A. Carotenoid desaturases from Rhodobacter capsulatus and Neurospora crassa are structurally and functionally conserved and contain domains homologous to flavoprotein disulfide oxidoreductases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):16020–16024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley G. E., Scolnik P. A. Carotenoid biosynthesis in photosynthetic bacteria. Genetic characterization of the Rhodobacter capsulatus CrtI protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13109–13113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley G. E., Viitanen P. V., Pecker I., Chamovitz D., Hirschberg J., Scolnik P. A. Molecular cloning and expression in photosynthetic bacteria of a soybean cDNA coding for phytoene desaturase, an enzyme of the carotenoid biosynthesis pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6532–6536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamovitz D., Pecker I., Hirschberg J. The molecular basis of resistance to the herbicide norflurazon. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):967–974. doi: 10.1007/BF00016069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. D., Sandmann G. In vitro assays of three carotenogenic membrane-bound enzymes from Escherichia coli transformed with different crt genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80947-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W. Developments in carotenoid biochemistry over 40 years. The third Morton lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Oct;11(5):473–483. doi: 10.1042/bst0110473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden H., Misawa N., Chamovitz D., Pecker I., Hirschberg J., Sandmann G. Functional complementation in Escherichia coli of different phytoene desaturase genes and analysis of accumulated carotenes. Z Naturforsch C. 1991 Nov-Dec;46(11-12):1045–1051. doi: 10.1515/znc-1991-11-1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misawa N., Nakagawa M., Kobayashi K., Yamano S., Izawa Y., Nakamura K., Harashima K. Elucidation of the Erwinia uredovora carotenoid biosynthetic pathway by functional analysis of gene products expressed in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6704–6712. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6704-6712.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecker I., Chamovitz D., Linden H., Sandmann G., Hirschberg J. A single polypeptide catalyzing the conversion of phytoene to zeta-carotene is transcriptionally regulated during tomato fruit ripening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4962–4966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. C., Swietlicki E., Roth K. A., Gordon J. I. Use of fetal intestinal isografts from normal and transgenic mice to study the programming of positional information along the duodenal-to-colonic axis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15122–15133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasiak K., Rilling H. C. Purification to homogeneity and some properties of squalene synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):622–627. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Sandmann G. In vitro characterization of two different Phycomyces blakesleeanus mutants with impaired phytoene desaturation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4103–4105. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4103-4105.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]